
panda
code powering the comma.ai panda
Stars: 1558
Panda is a car interface tool that speaks CAN and CAN FD, running on STM32F413 and STM32H725. It provides safety modes and controls_allowed feature for message handling. The tool ensures code rigor through CI regression tests, including static code analysis, MISRA C:2012 violations check, unit tests, and hardware-in-the-loop tests. The software interface supports Python library, C++ library, and socketcan in kernel. Panda is licensed under the MIT license.
README:
panda speaks CAN and CAN FD, and it runs on STM32F413 and STM32H725.
.
├── board # Code that runs on the STM32
├── drivers # Drivers (not needed for use with Python)
├── python # Python userspace library for interfacing with the panda
├── tests # Tests and helper programs for panda
When a panda powers up, by default it's in SAFETY_SILENT mode. While in SAFETY_SILENT mode, the CAN buses are forced to be silent. In order to send messages, you have to select a safety mode. Some of safety modes (for example SAFETY_ALLOUTPUT) are disabled in release firmwares. In order to use them, compile and flash your own build.
Safety modes optionally support controls_allowed, which allows or blocks a subset of messages based on a customizable state in the board.
The panda firmware is written for its use in conjunction with openpilot. The panda firmware, through its safety model, provides and enforces the
openpilot safety. Due to its critical function, it's important that the application code rigor within the board folder is held to high standards.
These are the CI regression tests we have in place:
- A generic static code analysis is performed by cppcheck.
- In addition, cppcheck has a specific addon to check for MISRA C:2012 violations. See current coverage.
- Compiler options are relatively strict: the flags
-Wall -Wextra -Wstrict-prototypes -Werrorare enforced. - The safety logic is tested and verified by unit tests for each supported car variant. to ensure that the behavior remains unchanged.
- A hardware-in-the-loop test verifies panda's functionalities on all active panda variants, including:
- additional safety model checks
- compiling and flashing the bootstub and app code
- receiving, sending, and forwarding CAN messages on all buses
- CAN loopback and latency tests through USB and SPI
The above tests are themselves tested by:
- a mutation test on the MISRA coverage
- 100% line coverage enforced on the safety unit tests
In addition, we run the ruff linter and mypy on panda's Python library.
Setup dependencies:
# Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install dfu-util gcc-arm-none-eabi python3-pip libffi-dev git clang-17
# macOS
brew install --cask gcc-arm-embedded
brew install python3 dfu-util gcc@13Clone panda repository and install:
git clone https://github.com/commaai/panda.git
cd panda
# install dependencies
pip install -e .[dev]
# install panda
python setup.py installSee the Panda class for how to interact with the panda.
For example, to receive CAN messages:
>>> from panda import Panda
>>> panda = Panda()
>>> panda.can_recv()And to send one on bus 0:
>>> panda.set_safety_mode(Panda.SAFETY_ALLOUTPUT)
>>> panda.can_send(0x1aa, b'message', 0)Note that you may have to setup udev rules for Linux, such as
sudo tee /etc/udev/rules.d/11-panda.rules <<EOF
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="3801", ATTRS{idProduct}=="ddcc", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="3801", ATTRS{idProduct}=="ddee", MODE="0666"
EOF
sudo udevadm control --reload-rules && sudo udevadm triggerThe panda jungle uses different udev rules. See the repo for instructions.
As a universal car interface, it should support every reasonable software interface.
panda software is released under the MIT license unless otherwise specified.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for panda
Similar Open Source Tools

panda
Panda is a car interface tool that speaks CAN and CAN FD, running on STM32F413 and STM32H725. It provides safety modes and controls_allowed feature for message handling. The tool ensures code rigor through CI regression tests, including static code analysis, MISRA C:2012 violations check, unit tests, and hardware-in-the-loop tests. The software interface supports Python library, C++ library, and socketcan in kernel. Panda is licensed under the MIT license.
torchchat
torchchat is a codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. It allows running LLMs using Python in various environments such as desktop, server, iOS, and Android. The tool supports running models via PyTorch, chatting, generating text, running chat in the browser, and running models on desktop/server without Python. It also provides features like AOT Inductor for faster execution, running in C++ using the runner, and deploying and running on iOS and Android. The tool supports popular hardware and OS including Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS, with various data types and execution modes available.
OSWorld
OSWorld is a benchmarking tool designed to evaluate multimodal agents for open-ended tasks in real computer environments. It provides a platform for running experiments, setting up virtual machines, and interacting with the environment using Python scripts. Users can install the tool on their desktop or server, manage dependencies with Conda, and run benchmark tasks. The tool supports actions like executing commands, checking for specific results, and evaluating agent performance. OSWorld aims to facilitate research in AI by providing a standardized environment for testing and comparing different agent baselines.
SWELancer-Benchmark
SWE-Lancer is a benchmark repository containing datasets and code for the paper 'SWE-Lancer: Can Frontier LLMs Earn $1 Million from Real-World Freelance Software Engineering?'. It provides instructions for package management, building Docker images, configuring environment variables, and running evaluations. Users can use this tool to assess the performance of language models in real-world freelance software engineering tasks.
gpustack
GPUStack is an open-source GPU cluster manager designed for running large language models (LLMs). It supports a wide variety of hardware, scales with GPU inventory, offers lightweight Python package with minimal dependencies, provides OpenAI-compatible APIs, simplifies user and API key management, enables GPU metrics monitoring, and facilitates token usage and rate metrics tracking. The tool is suitable for managing GPU clusters efficiently and effectively.
LlamaEdge
The LlamaEdge project makes it easy to run LLM inference apps and create OpenAI-compatible API services for the Llama2 series of LLMs locally. It provides a Rust+Wasm stack for fast, portable, and secure LLM inference on heterogeneous edge devices. The project includes source code for text generation, chatbot, and API server applications, supporting all LLMs based on the llama2 framework in the GGUF format. LlamaEdge is committed to continuously testing and validating new open-source models and offers a list of supported models with download links and startup commands. It is cross-platform, supporting various OSes, CPUs, and GPUs, and provides troubleshooting tips for common errors.
bittensor
Bittensor is an internet-scale neural network that incentivizes computers to provide access to machine learning models in a decentralized and censorship-resistant manner. It operates through a token-based mechanism where miners host, train, and procure machine learning systems to fulfill verification problems defined by validators. The network rewards miners and validators for their contributions, ensuring continuous improvement in knowledge output. Bittensor allows anyone to participate, extract value, and govern the network without centralized control. It supports tasks such as generating text, audio, images, and extracting numerical representations.
CoML
CoML (formerly MLCopilot) is an interactive coding assistant for data scientists and machine learning developers, empowered on large language models. It offers an out-of-the-box interactive natural language programming interface for data mining and machine learning tasks, integration with Jupyter lab and Jupyter notebook, and a built-in large knowledge base of machine learning to enhance the ability to solve complex tasks. The tool is designed to assist users in coding tasks related to data analysis and machine learning using natural language commands within Jupyter environments.
Sanmill
Sanmill is a free, powerful UCI-like N men's morris program with CUI, Flutter GUI and Qt GUI. Nine men's morris is a strategy board game for two players dating at least to the Roman Empire. The game is also known as nine-man morris , mill , mills , the mill game , merels , merrills , merelles , marelles , morelles , and ninepenny marl in English.
simply
Simply is a minimal and scalable research codebase in JAX, designed for rapid iteration on frontier research in LLM and other autoregressive models. It is quick to fork and hack for fast iteration, with minimal abstractions and dependencies for a simple and self-contained codebase. Users can easily implement new architectures, optimizers, training losses, etc., in a few hours. Simply allows users to get started with hacking quickly, providing example commands for local testing and running on Google Cloud TPUs. The main dependencies include Jax for model and training, Orbax for checkpoint management, and Grain for data pipeline. Users can install dependencies, set up model checkpoints and datasets, and cite the tool if found helpful.
LARS
LARS is an application that enables users to run Large Language Models (LLMs) locally on their devices, upload their own documents, and engage in conversations where the LLM grounds its responses with the uploaded content. The application focuses on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to increase accuracy and reduce AI-generated inaccuracies. LARS provides advanced citations, supports various file formats, allows follow-up questions, provides full chat history, and offers customization options for LLM settings. Users can force enable or disable RAG, change system prompts, and tweak advanced LLM settings. The application also supports GPU-accelerated inferencing, multiple embedding models, and text extraction methods. LARS is open-source and aims to be the ultimate RAG-centric LLM application.
testzeus-hercules
Hercules is the world’s first open-source testing agent designed to handle the toughest testing tasks for modern web applications. It turns simple Gherkin steps into fully automated end-to-end tests, making testing simple, reliable, and efficient. Hercules adapts to various platforms like Salesforce and is suitable for CI/CD pipelines. It aims to democratize and disrupt test automation, making top-tier testing accessible to everyone. The tool is transparent, reliable, and community-driven, empowering teams to deliver better software. Hercules offers multiple ways to get started, including using PyPI package, Docker, or building and running from source code. It supports various AI models, provides detailed installation and usage instructions, and integrates with Nuclei for security testing and WCAG for accessibility testing. The tool is production-ready, open core, and open source, with plans for enhanced LLM support, advanced tooling, improved DOM distillation, community contributions, extensive documentation, and a bounty program.
uwazi
Uwazi is a flexible database application designed for capturing and organizing collections of information, with a focus on document management. It is developed and supported by HURIDOCS, benefiting human rights organizations globally. The tool requires NodeJs, ElasticSearch, ICU Analysis Plugin, MongoDB, Yarn, and pdftotext for installation. It offers production and development installation guides, including Docker setup. Uwazi supports hot reloading, unit and integration testing with JEST, and end-to-end testing with Nightmare or Puppeteer. The system requirements include RAM, CPU, and disk space recommendations for on-premises and development usage.
RepoAgent
RepoAgent is an LLM-powered framework designed for repository-level code documentation generation. It automates the process of detecting changes in Git repositories, analyzing code structure through AST, identifying inter-object relationships, replacing Markdown content, and executing multi-threaded operations. The tool aims to assist developers in understanding and maintaining codebases by providing comprehensive documentation, ultimately improving efficiency and saving time.

unitycatalog
Unity Catalog is an open and interoperable catalog for data and AI, supporting multi-format tables, unstructured data, and AI assets. It offers plugin support for extensibility and interoperates with Delta Sharing protocol. The catalog is fully open with OpenAPI spec and OSS implementation, providing unified governance for data and AI with asset-level access control enforced through REST APIs.
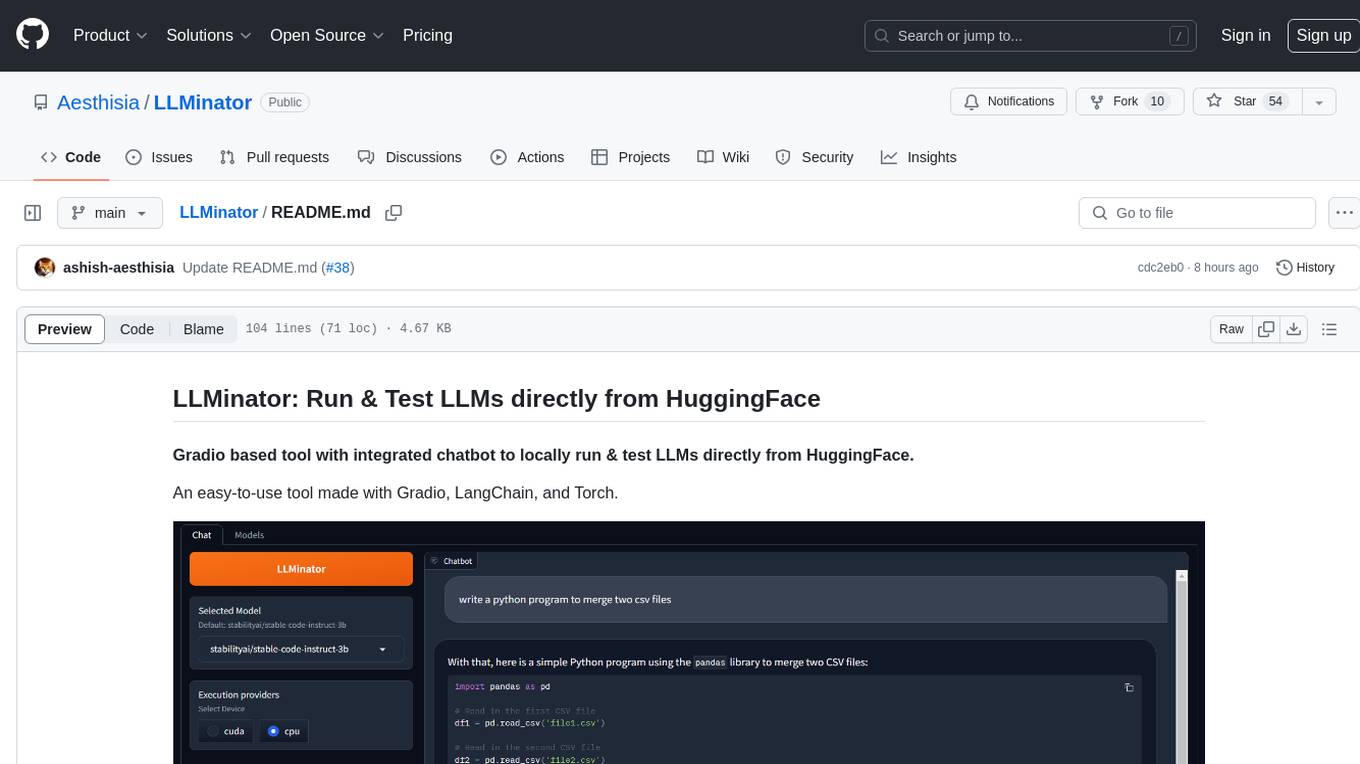
LLMinator
LLMinator is a Gradio-based tool with an integrated chatbot designed to locally run and test Language Model Models (LLMs) directly from HuggingFace. It provides an easy-to-use interface made with Gradio, LangChain, and Torch, offering features such as context-aware streaming chatbot, inbuilt code syntax highlighting, loading any LLM repo from HuggingFace, support for both CPU and CUDA modes, enabling LLM inference with llama.cpp, and model conversion capabilities.
For similar tasks

panda
Panda is a car interface tool that speaks CAN and CAN FD, running on STM32F413 and STM32H725. It provides safety modes and controls_allowed feature for message handling. The tool ensures code rigor through CI regression tests, including static code analysis, MISRA C:2012 violations check, unit tests, and hardware-in-the-loop tests. The software interface supports Python library, C++ library, and socketcan in kernel. Panda is licensed under the MIT license.
For similar jobs
AeonLabs-AI-Volvo-MKII-Open-Hardware
This open hardware project aims to extend the life of Volvo P2 platform vehicles by updating them to current EU safety and emission standards. It involves designing and prototyping OEM hardware electronics that can replace existing electronics in these vehicles, using the existing wiring and without requiring reverse engineering or modifications. The project focuses on serviceability, maintenance, repairability, and personal ownership safety, and explores the advantages of using open solutions compared to conventional hardware electronics solutions.

panda
Panda is a car interface tool that speaks CAN and CAN FD, running on STM32F413 and STM32H725. It provides safety modes and controls_allowed feature for message handling. The tool ensures code rigor through CI regression tests, including static code analysis, MISRA C:2012 violations check, unit tests, and hardware-in-the-loop tests. The software interface supports Python library, C++ library, and socketcan in kernel. Panda is licensed under the MIT license.

Lecture_AI_in_Automotive_Technology
This Github repository contains practice session materials for the TUM course on Artificial Intelligence in Automotive Technology. It includes coding examples used in the lectures to teach the foundations of AI in automotive technology. The repository aims to provide hands-on experience and practical knowledge in applying AI concepts to the automotive industry.
CoDrivingLLM
CoDrivingLLM is a machine learning model for predicting driving behavior based on sensor data collected from vehicles. It utilizes a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network to analyze patterns in the data and make predictions about future driving actions. The model is trained on a large dataset of driving scenarios and can be used to improve driver assistance systems, enhance road safety, and optimize vehicle performance. CoDrivingLLM is designed to be easily integrated into existing automotive systems and can provide real-time feedback to drivers to help them make safer and more efficient driving decisions.

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.