
visualwebarena
VisualWebArena is a benchmark for multimodal agents.
Stars: 157
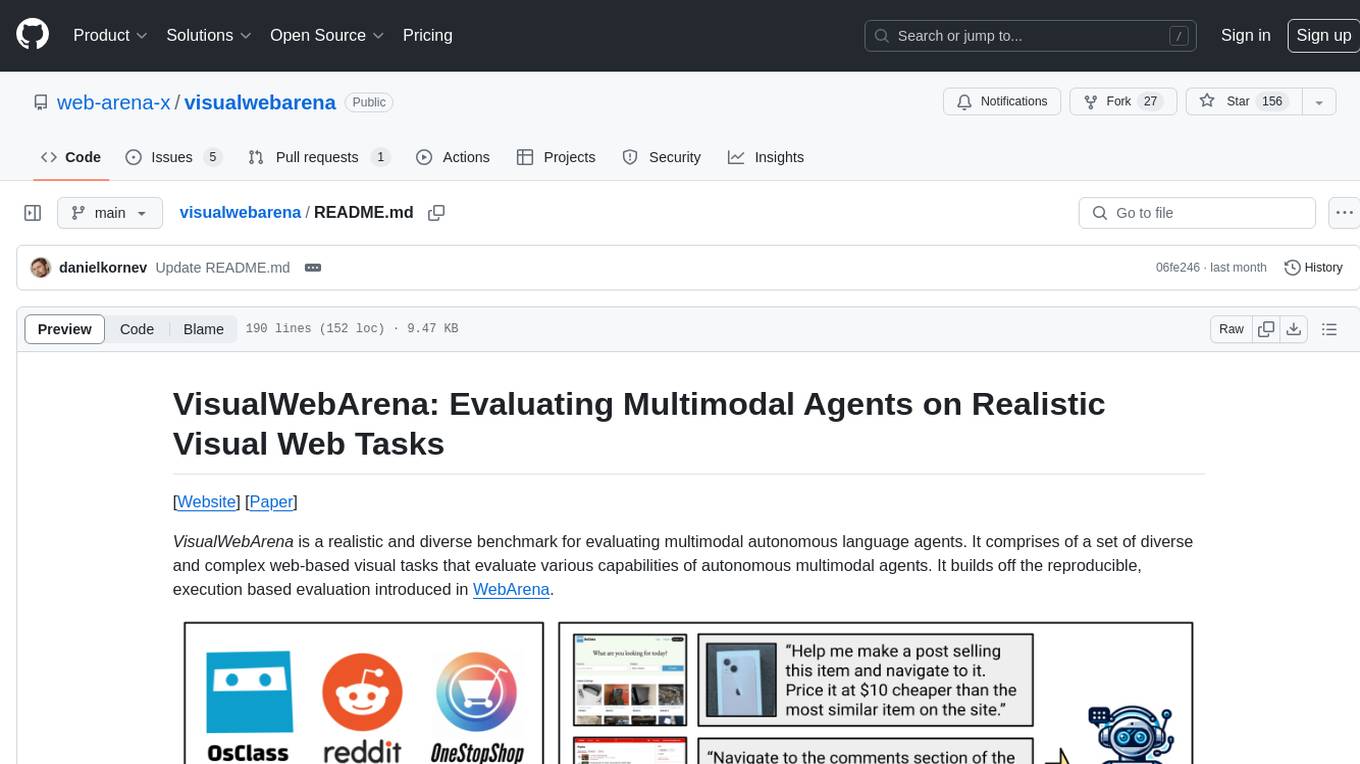
VisualWebArena is a benchmark for evaluating multimodal autonomous language agents through diverse and complex web-based visual tasks. It builds on the reproducible evaluation introduced in WebArena. The repository provides scripts for end-to-end training, demos to run multimodal agents on webpages, and tools for setting up environments for evaluation. It includes trajectories of the GPT-4V + SoM agent on VWA tasks, along with human evaluations on 233 tasks. The environment supports OpenAI models and Gemini models for evaluation.
README:
VisualWebArena is a realistic and diverse benchmark for evaluating multimodal autonomous language agents. It comprises of a set of diverse and complex web-based visual tasks that evaluate various capabilities of autonomous multimodal agents. It builds off the reproducible, execution based evaluation introduced in WebArena.
- [x] Add human trajectories.
- [x] Add GPT-4V + SoM trajectories from our paper.
- [x] Add scripts for end-to-end training and reset of environments.
- [x] Add demo to run multimodal agents on any arbitrary webpage.
- [03/8/2024]: Added the agent trajectories of our GPT-4V + SoM agent on the full set of 910 VWA tasks.
- [02/14/2024]: Added a demo script for running the GPT-4V + SoM agent on any task on an arbitrary website.
- [01/25/2024]: GitHub repo released with tasks and scripts for setting up the VWA environments.
# Python 3.10 (or 3.11, but not 3.12 cause 3.12 deprecated distutils needed here)
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
playwright install
pip install -e .You can also run the unit tests to ensure that VisualWebArena is installed correctly:
pytest -x
-
Setup the standalone environments. Please check out this page for details.
-
Configurate the urls for each website. First, export the
DATASETto bevisualwebarena:
export DATASET=visualwebarenaThen, set the URL for the websites
export CLASSIFIEDS="<your_classifieds_domain>:9980"
export CLASSIFIEDS_RESET_TOKEN="4b61655535e7ed388f0d40a93600254c" # Default reset token for classifieds site, change if you edited its docker-compose.yml
export SHOPPING="<your_shopping_site_domain>:7770"
export REDDIT="<your_reddit_domain>:9999"
export WIKIPEDIA="<your_wikipedia_domain>:8888"
export HOMEPAGE="<your_homepage_domain>:4399"In addition, if you want to run on the original WebArena tasks, make sure to also set up the CMS, GitLab, and map environments, and then set their respective environment variables:
export SHOPPING_ADMIN="<your_e_commerce_cms_domain>:7780/admin"
export GITLAB="<your_gitlab_domain>:8023"
export MAP="<your_map_domain>:3000"- Generate config files for each test example:
python scripts/generate_test_data.pyYou will see *.json files generated in the config_files folder. Each file contains the configuration for one test example.
- Obtain and save the auto-login cookies for all websites:
bash prepare.sh
- Set up API keys.
If using OpenAI models, set a valid OpenAI API key (starting with sk-) as the environment variable:
export OPENAI_API_KEY=your_key
If using Gemini, first install the gcloud CLI. Configure the API key by authenticating with Google Cloud:
gcloud auth login
gcloud config set project <your_project_name>
- Launch the evaluation. For example, to reproduce our GPT-3.5 captioning baseline:
python run.py \
--instruction_path agent/prompts/jsons/p_cot_id_actree_3s.json \
--test_start_idx 0 \
--test_end_idx 1 \
--result_dir <your_result_dir> \
--test_config_base_dir=config_files/vwa/test_classifieds \
--model gpt-3.5-turbo-1106 \
--observation_type accessibility_tree_with_captionerThis script will run the first Classifieds example with the GPT-3.5 caption-augmented agent. The trajectory will be saved in <your_result_dir>/0.html. Note that the baselines that include a captioning model run on GPU by default (e.g., BLIP-2-T5XL as the captioning model will take up approximately 12GB of GPU VRAM).
To run the GPT-4V + SoM agent we proposed in our paper, you can run evaluation with the following flags:
python run.py \
--instruction_path agent/prompts/jsons/p_som_cot_id_actree_3s.json \
--test_start_idx 0 \
--test_end_idx 1 \
--result_dir <your_result_dir> \
--test_config_base_dir=config_files/vwa/test_classifieds \
--model gpt-4-vision-preview \
--action_set_tag som --observation_type image_somTo run Gemini models, you can change the provider, model, and the max_obs_length (as Gemini uses characters instead of tokens for inputs):
python run.py \
--instruction_path agent/prompts/jsons/p_som_cot_id_actree_3s.json \
--test_start_idx 0 \
--test_end_idx 1 \
--max_steps 1 \
--result_dir <your_result_dir> \
--test_config_base_dir=config_files/vwa/test_classifieds \
--provider google --model gemini --mode completion --max_obs_length 15360 \
--action_set_tag som --observation_type image_somIf you'd like to reproduce the results from our paper, we have also provided scripts in scripts/ to run the full evaluation pipeline on each of the VWA environments. For example, to reproduce the results from the Classifieds environment, you can run:
bash scripts/run_classifieds_som.shTo facilitate analysis and evals, we have also released the trajectories of the GPT-4V + SoM agent on the full set of 910 VWA tasks here. It consists of .html files that record the agent's observations and output at each step of the trajectory.
We have also prepared a demo for you to run the agents on your own task on an arbitrary webpage. An example is shown above where the agent is tasked to find the best Thai restaurant in Pittsburgh.
After following the setup instructions above and setting the OpenAI API key (the other environment variables for website URLs aren't really used, so you should be able to set them to some dummy variable), you can run the GPT-4V + SoM agent with the following command:
python run_demo.py \
--instruction_path agent/prompts/jsons/p_som_cot_id_actree_3s.json \
--start_url "https://www.amazon.com" \
--image "https://media.npr.org/assets/img/2023/01/14/this-is-fine_wide-0077dc0607062e15b476fb7f3bd99c5f340af356-s1400-c100.jpg" \
--intent "Help me navigate to a shirt that has this on it." \
--result_dir demo_test_amazon \
--model gpt-4-vision-preview \
--action_set_tag som --observation_type image_som \
--renderThis tasks the agent to find a shirt that looks like the provided image (the "This is fine" dog) from Amazon. Have fun!
We collected human trajectories on 233 tasks (one from each template type) and the Playwright recording files are provided here. These are the same tasks reported in our paper (with a human success rate of ~89%). You can view the HTML pages, actions, etc., by running playwright show-trace <example_id>.zip. The example_id follows the same structure as the examples from the corresponding site in config_files/.
If you find our environment or our models useful, please consider citing VisualWebArena as well as WebArena:
@article{koh2024visualwebarena,
title={VisualWebArena: Evaluating Multimodal Agents on Realistic Visual Web Tasks},
author={Koh, Jing Yu and Lo, Robert and Jang, Lawrence and Duvvur, Vikram and Lim, Ming Chong and Huang, Po-Yu and Neubig, Graham and Zhou, Shuyan and Salakhutdinov, Ruslan and Fried, Daniel},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.13649},
year={2024}
}
@article{zhou2024webarena,
title={WebArena: A Realistic Web Environment for Building Autonomous Agents},
author={Zhou, Shuyan and Xu, Frank F and Zhu, Hao and Zhou, Xuhui and Lo, Robert and Sridhar, Abishek and Cheng, Xianyi and Bisk, Yonatan and Fried, Daniel and Alon, Uri and others},
journal={ICLR},
year={2024}
}
Our code is heavily based off the WebArena codebase.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for visualwebarena
Similar Open Source Tools

visualwebarena
VisualWebArena is a benchmark for evaluating multimodal autonomous language agents through diverse and complex web-based visual tasks. It builds on the reproducible evaluation introduced in WebArena. The repository provides scripts for end-to-end training, demos to run multimodal agents on webpages, and tools for setting up environments for evaluation. It includes trajectories of the GPT-4V + SoM agent on VWA tasks, along with human evaluations on 233 tasks. The environment supports OpenAI models and Gemini models for evaluation.
WindowsAgentArena
Windows Agent Arena (WAA) is a scalable Windows AI agent platform designed for testing and benchmarking multi-modal, desktop AI agents. It provides researchers and developers with a reproducible and realistic Windows OS environment for AI research, enabling testing of agentic AI workflows across various tasks. WAA supports deploying agents at scale using Azure ML cloud infrastructure, allowing parallel running of multiple agents and delivering quick benchmark results for hundreds of tasks in minutes.
OSWorld
OSWorld is a benchmarking tool designed to evaluate multimodal agents for open-ended tasks in real computer environments. It provides a platform for running experiments, setting up virtual machines, and interacting with the environment using Python scripts. Users can install the tool on their desktop or server, manage dependencies with Conda, and run benchmark tasks. The tool supports actions like executing commands, checking for specific results, and evaluating agent performance. OSWorld aims to facilitate research in AI by providing a standardized environment for testing and comparing different agent baselines.
debug-gym
debug-gym is a text-based interactive debugging framework designed for debugging Python programs. It provides an environment where agents can interact with code repositories, use various tools like pdb and grep to investigate and fix bugs, and propose code patches. The framework supports different LLM backends such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Anthropic. Users can customize tools, manage environment states, and run agents to debug code effectively. debug-gym is modular, extensible, and suitable for interactive debugging tasks in a text-based environment.
comfyui_LLM_party
COMFYUI LLM PARTY is a node library designed for LLM workflow development in ComfyUI, an extremely minimalist UI interface primarily used for AI drawing and SD model-based workflows. The project aims to provide a complete set of nodes for constructing LLM workflows, enabling users to easily integrate them into existing SD workflows. It features various functionalities such as API integration, local large model integration, RAG support, code interpreters, online queries, conditional statements, looping links for large models, persona mask attachment, and tool invocations for weather lookup, time lookup, knowledge base, code execution, web search, and single-page search. Users can rapidly develop web applications using API + Streamlit and utilize LLM as a tool node. Additionally, the project includes an omnipotent interpreter node that allows the large model to perform any task, with recommendations to use the 'show_text' node for display output.
bia-bob
BIA `bob` is a Jupyter-based assistant for interacting with data using large language models to generate Python code. It can utilize OpenAI's chatGPT, Google's Gemini, Helmholtz' blablador, and Ollama. Users need respective accounts to access these services. Bob can assist in code generation, bug fixing, code documentation, GPU-acceleration, and offers a no-code custom Jupyter Kernel. It provides example notebooks for various tasks like bio-image analysis, model selection, and bug fixing. Installation is recommended via conda/mamba environment. Custom endpoints like blablador and ollama can be used. Google Cloud AI API integration is also supported. The tool is extensible for Python libraries to enhance Bob's functionality.
vscode-pddl
The vscode-pddl extension provides comprehensive support for Planning Domain Description Language (PDDL) in Visual Studio Code. It enables users to model planning domains, validate them, industrialize planning solutions, and run planners. The extension offers features like syntax highlighting, auto-completion, plan visualization, plan validation, plan happenings evaluation, search debugging, and integration with Planning.Domains. Users can create PDDL files, run planners, visualize plans, and debug search algorithms efficiently within VS Code.
CoML
CoML (formerly MLCopilot) is an interactive coding assistant for data scientists and machine learning developers, empowered on large language models. It offers an out-of-the-box interactive natural language programming interface for data mining and machine learning tasks, integration with Jupyter lab and Jupyter notebook, and a built-in large knowledge base of machine learning to enhance the ability to solve complex tasks. The tool is designed to assist users in coding tasks related to data analysis and machine learning using natural language commands within Jupyter environments.
neuron-ai
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents, providing tools for the entire agentic application development lifecycle. It allows integration of AI entities in existing PHP applications with a powerful and flexible architecture. Neuron offers tutorials and educational content to help users get started using AI Agents in their projects. The framework supports various LLM providers, tools, and toolkits, enabling users to create fully functional agents for tasks like data analysis, chatbots, and structured output. Neuron also facilitates monitoring and debugging of AI applications, ensuring control over agent behavior and decision-making processes.
warc-gpt
WARC-GPT is an experimental retrieval augmented generation pipeline for web archive collections. It allows users to interact with WARC files, extract text, generate text embeddings, visualize embeddings, and interact with a web UI and API. The tool is highly customizable, supporting various LLMs, providers, and embedding models. Users can configure the application using environment variables, ingest WARC files, start the server, and interact with the web UI and API to search for content and generate text completions. WARC-GPT is designed for exploration and experimentation in exploring web archives using AI.
ray-llm
RayLLM (formerly known as Aviary) is an LLM serving solution that makes it easy to deploy and manage a variety of open source LLMs, built on Ray Serve. It provides an extensive suite of pre-configured open source LLMs, with defaults that work out of the box. RayLLM supports Transformer models hosted on Hugging Face Hub or present on local disk. It simplifies the deployment of multiple LLMs, the addition of new LLMs, and offers unique autoscaling support, including scale-to-zero. RayLLM fully supports multi-GPU & multi-node model deployments and offers high performance features like continuous batching, quantization and streaming. It provides a REST API that is similar to OpenAI's to make it easy to migrate and cross test them. RayLLM supports multiple LLM backends out of the box, including vLLM and TensorRT-LLM.
neuron-ai
Neuron AI is a PHP framework that provides an Agent class for creating fully functional agents to perform tasks like analyzing text for SEO optimization. The framework manages advanced mechanisms such as memory, tools, and function calls. Users can extend the Agent class to create custom agents and interact with them to get responses based on the underlying LLM. Neuron AI aims to simplify the development of AI-powered applications by offering a structured framework with documentation and guidelines for contributions under the MIT license.

fasttrackml
FastTrackML is an experiment tracking server focused on speed and scalability, fully compatible with MLFlow. It provides a user-friendly interface to track and visualize your machine learning experiments, making it easy to compare different models and identify the best performing ones. FastTrackML is open source and can be easily installed and run with pip or Docker. It is also compatible with the MLFlow Python package, making it easy to integrate with your existing MLFlow workflows.
safety-tooling
This repository, safety-tooling, is designed to be shared across various AI Safety projects. It provides an LLM API with a common interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google models. The aim is to facilitate collaboration among AI Safety researchers, especially those with limited software engineering backgrounds, by offering a platform for contributing to a larger codebase. The repo can be used as a git submodule for easy collaboration and updates. It also supports pip installation for convenience. The repository includes features for installation, secrets management, linting, formatting, Redis configuration, testing, dependency management, inference, finetuning, API usage tracking, and various utilities for data processing and experimentation.

BALROG
BALROG is a benchmark tool designed to evaluate agentic Long-Longitudinal Memory (LLM) and Vision-Language Memory (VLM) capabilities using reinforcement learning environments. It provides a comprehensive assessment of agentic abilities, supports both language and vision-language models, integrates with popular AI APIs, and allows for easy integration of custom agents, new environments, and models.
gpustack
GPUStack is an open-source GPU cluster manager designed for running large language models (LLMs). It supports a wide variety of hardware, scales with GPU inventory, offers lightweight Python package with minimal dependencies, provides OpenAI-compatible APIs, simplifies user and API key management, enables GPU metrics monitoring, and facilitates token usage and rate metrics tracking. The tool is suitable for managing GPU clusters efficiently and effectively.
For similar tasks

visualwebarena
VisualWebArena is a benchmark for evaluating multimodal autonomous language agents through diverse and complex web-based visual tasks. It builds on the reproducible evaluation introduced in WebArena. The repository provides scripts for end-to-end training, demos to run multimodal agents on webpages, and tools for setting up environments for evaluation. It includes trajectories of the GPT-4V + SoM agent on VWA tasks, along with human evaluations on 233 tasks. The environment supports OpenAI models and Gemini models for evaluation.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.


