
atropos
Atropos is a Language Model Reinforcement Learning Environments framework for collecting and evaluating LLM trajectories through diverse environments
Stars: 700
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.
README:
In Greek mythology, Atropos was the eldest of the three Fates. While her sisters spun and measured the threads of mortal lives, Atropos alone held the shears that would cut these threads, determining the final destiny of each soul. Just as Atropos guided souls to their ultimate fate, this system guides language models toward their optimal potential through reinforcement learning.
Atropos is an environment microservice framework for async RL with LLMs.
Atropos encompasses both environments, which are set up as services, and a trajectory API for the environments to send data to and for the trainer to pull batches from.
Here is a diagram of how Atropos' components can interact with a trainer & inference server to complete the RL loop (trainer & inference engine not included with the atropos package)
Atropos is a robust, scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with LLMs.
The goal: provide a flexible, scalable, and standardized platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse, interactive settings.
The framework supports collecting, distributing and evaluating LLM trajectories through diverse environments including:
| Environment Type | Examples | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 📚 Dataset environments | GSM8K, MMLU, Custom HF Datasets | Evaluate and improve LLM performance on static data |
| 🎮 Online environments | Blackjack, Taxi, Text-based games | Train LLMs through interactive game-based learning |
| 🤖 RLAIF and RLHF | LLM Judge/Reward Models | Fine-tune LLMs using human feedback and alignment |
| 🔄 Multi-Turn RL | deepresearch, internal tool calling | Train LLMs on complex multi-step interactions |
| 💻 Code Execution | MBPP, HumanEval (via coding_server.py) |
Train LLMs to generate and execute code |
| 🖼️ Multimodal | OCR VQA, Clevr (via multimodal_dpo/) |
Train LLMs on tasks involving vision and language |
We have been able to achieve significant improvements on specific domains or tasks with Atropos - Below are some of the results.
Tool Calling Environment Results:
| Berkeley Function Calling Benchmark Type | Base Model | With Atropos RL | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel Tasks | 10% | 46% | 4.6x ⬆️ |
| Simple Tasks | 21% | 51.75% | 2.5x ⬆️ |
Model Artifact: https://huggingface.co/NousResearch/DeepHermes-ToolCalling-Specialist-Atropos
Environment Used: https://github.com/NousResearch/Atropos/blob/main/environments/tool_calling_server.py
Financial Fundamentals Prediction Environment Results:
| Metric | Initial Accuracy | With Atropos RL | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Directional Prediction Eval Accuracy | 20% | 50% | 2.5x 📈 |
Model Artifact: https://huggingface.co/NousResearch/DeepHermes-Financial-Fundamentals-Prediction-Specialist-Atropos
Environment Used: https://github.com/NousResearch/Atropos/blob/main/environments/fundamental_prediction_environment.py
Using the RLAIF Environment to change the personality of the model, we have produced several artifacts of interesting and weird personalities.
DeepHermes Egregore v1 and v2 8B:
https://huggingface.co/NousResearch/DeepHermes-Egregore-v1-RLAIF-8b-Atropos https://huggingface.co/NousResearch/DeepHermes-Egregore-v2-RLAIF-8b-Atropos
DeepHermes Ascension Maze 8B:
https://huggingface.co/NousResearch/DeepHermes-AscensionMaze-RLAIF-8b-Atropos
Environment Used: https://github.com/NousResearch/atropos/blob/main/environments/rlaif_server.py
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
📁 atroposlib/
|
Core library containing base classes and utilities |
🎮 environments/
|
Collection of ready-to-use RL environments. Community contributions are typically placed in the environments/community/ subdirectory. |
📚 example_trainer/
|
Example training scripts and configurations |
Key Documents:
- Base Environment Class - Documentation for creating custom environments
- Environments Overview and Contribution Guide - Documentation for existing environments and how to contribute new ones.
- Full Environment Config Options - Documentation for creating custom environments
- Example Trainer - Getting started with training
- Slurm Guide - Guide for using Atropos with Slurm for distributed inference
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) - Answers to common questions for new users
- Contributing Guide - Guidelines for contributors
- License - MIT license details
Get your Python 3.10 (or later) environment ready, then simply pip install:
pip install atroposlibIf you're looking to get into developing the repo or using the environments:
pip install -e . # for using
pip install -e .[dev] # for development
pip install -e .[examples] # for running examples
pip install -e .[all] # for everythingImportant: If you're committing to the repository, please install the pre-commit hooks:
pre-commit install-
Create Your First Environment
- Review our Base Class Documentation to understand the core concepts
- Check out existing environments in the
environments/directory for examples
-
Run an Example Environment
You should edit the config_init section of the environment file you want (For example, in GSM8K Environment) to point to a running VLLM or SGLang inference server as well as any other configuration changes you'd like to make, such as the group size, then:
# Start the API server
run-apiIn a separate terminal, start the GSM8K environment microservice
python environments/gsm8k_server.py serve --openai.model_name Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct --slurm false
# alternatively
# python environments/gsm8k_server.py serve --config environments/configs/example.yaml
# python environments/gsm8k_server.py serve --config environments/configs/example.yaml --env.group_size 8 # cli args override corresponding config settings- Grabbing Rollouts
If you want to just start getting rollouts, and not use a trainer, see the debug section for help getting started with the available tools, we recommend starting with process or view-run
-
Training Your Model
- Follow our training example guide for detailed instructions
- Monitor progress through our built-in logging and reporting system:
- Completion lengths
- Evaluation accuracies
- Full rollouts and scores
You can use multiple environments at once, just point them all to the same server.
Environments come with detailed logging and reporting support, runs track completion lengths, eval accuracies, full rollouts and scores, and more:
Axolotl is a powerful tool for fine-tuning a wide range of AI models, supporting techniques like LoRA and QLoRA through simple YAML configurations.
The Atropos plugin for Axolotl seamlessly integrates Atropos' RL environments into Axolotl's training pipelines. This allows you to leverage Atropos for reinforcement learning while utilizing Axolotl's extensive features for model fine-tuning.
To use, follow the readme on the plugin repository.
Atropos repo contains an example trainer that should primarily be used as a reference example to show how a trainer and inference provider can be integrated with Atropos to complete the RL Training Loop.
To use the example trainer, see this page: training example guide
The trajectory-handler provides several debugging tools to help environment developers test and understand their environments locally without requiring the full distributed infrastructure.
- Flexible Model Provider Support: Atropos natively supports any model provider that adheres to the OpenAI API standard. Simply provide the provider's base URL and your API key, and Atropos can integrate with their models seamlessly for testing or running environments locally.
After launching the API and your selected environments (e.g. run-api & python environments/gsm8k_server.py serve), you are then able to view them to get a quick look, or try to prepare some datasets for some offline training:
-
View Run (
view-run): Launch a Gradio UI to inspect batches of rollouts generated by your environment runs. This is useful for visually debugging the interactions and data flow. -
Offline Data Generation: Use
atropos-sft-genandatropos-dpo-gento collect rollouts from environments and convert them into formats suitable for Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) or Direct Preference Optimization (DPO).
For developers looking to inspect and debug a single environment without the overhead of the run-api server or a full training loop, Atropos environments offer a process subcommand. This mode performs inference-only rollouts, meaning it runs your model within the environment to generate interactions, but does not perform any model training or updates.
The process subcommand executes the environment's full data pipeline:
- Generation: Produces model responses based on inputs from the environment.
- Parsing: Processes these raw model outputs into a structured format.
- Scoring: Applies the environment's reward logic to evaluate the quality of the generated responses.
Outputs and Visualization:
When you specify a path to save the generated data using the --env.data_path_to_save_groups your_output_file.jsonl argument (or a similar argument defined by the specific environment, check with --help), the process command provides several benefits:
-
JSONL Output: Saves all generated rollout groups, including prompts, responses, and scores, to the specified
.jsonlfile. This data can be useful for detailed offline analysis and debugging. -
Static HTML Visualization: Automatically generates a corresponding
.htmlfile (e.g.,your_output_file.html) that provides a user-friendly, browser-based view of the rollouts contained in the JSONL file. This is excellent for quickly understanding model behavior and identifying issues. -
WandB Logging: If Weights & Biases (
use_wandb=True) is enabled in your environment's configuration, theprocesssubcommand will also log the run data, metrics, and generated rollouts to your WandB dashboard, allowing for persistent tracking and comparison even for these inference-only runs.
Example Usage:
To run the process subcommand for an environment like gsm8k_server.py and save the outputs:
python environments/gsm8k_server.py process --env.data_path_to_save_groups gsm8k_rollouts.jsonlThis will create gsm8k_rollouts.jsonl and gsm8k_rollouts.html.
Customization:
You can customize the inference endpoint and other parameters for the process subcommand. For example, to use a different model or API endpoint:
python environments/gsm8k_server.py process \
--env.data_path_to_save_groups gsm8k_rollouts.jsonl \
--env.my_custom_field "value" \
--openai.base_url https://your-custom-api-url/v1 \
--openai.api_key YOUR_API_KEY \
--openai.model_name your_model_identifierYou can add custom fields to the env namespace by returning a custom subclass of BaseEnvConfig in config_init [example].
Always refer to the specific environment script's help for all available options:
python environments/your_environment_script.py process --helpFor running evaluation on environments, Atropos provides an evaluate subcommand that calls the environment's evaluate method:
python gsm8k_server.py evaluate \
--openai.base_url https://openrouter.ai/api/v1 \
--openai.api_key $OPENROUTER_API_KEY \
--openai.model_name qwen/qwen3-14bRun the below in separate terminals:
run-apipython gsm8k_server.py serve --slurm False # or an env of your choiceatropos-sft-gen path/to/output.jsonl --tokenizer Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct # or whichever tokenizer you have in your env configRejection sampling can be controlled via --save-top-n-per-group, --allow-negative-scores, and --minimum-score-diff-max-min. See atropos-sft-gen -h for more detailed usage info.
If you would like to use OpenAI models, please edit your config_init to something like the following:
@classmethod
def config_init(cls) -> Tuple[BaseEnvConfig, List[APIServerConfig]]:
env_config = BaseEnvConfig(
tokenizer_name="Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct",
group_size=8,
use_wandb=True,
rollout_server_url="http://localhost:8000",
total_steps=1000,
batch_size=12,
steps_per_eval=100,
max_token_length=2048,
wandb_name="gsm8k",
)
server_configs = [
APIServerConfig(
model_name="gpt-4.1-nano",
base_url=None,
api_key=os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
num_requests_for_eval=256,
),
]
return env_config, server_configsFor DPO, replace atropos-sft-gen with atropos-dpo-gen and check atropos-dpo-gen -h for data filtering and saving options.
If you have found the library helpful in your work, you can cite this repository as:
@misc{atropos,
title = {Atropos: An Async First Environment Rollout Controller},
author = {Mahan, Dakota and Jin, Roger and Teknium and Sands, Shannon and Yatsenko, Artem and Suphavadeeprasit, Jai and Malhotra, Karan and Guang, Chen and Li, Joe},
howpublished = {\url{https://www.github.com/NousResearch/Atropos}},
year = {2025},
month = apr,
note = {Version 0.3.0},
}Atropos is built by the open-source AI community, and relies on our amazing contributors! Please see our contributing guide for more details on our code formatting, testing, etc. Please follow the Code of Conduct.
Atropos is uses the MIT license, see the LICENSE file here for more information
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for atropos
Similar Open Source Tools

atropos
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.
humanoid-gym
Humanoid-Gym is a reinforcement learning framework designed for training locomotion skills for humanoid robots, focusing on zero-shot transfer from simulation to real-world environments. It integrates a sim-to-sim framework from Isaac Gym to Mujoco for verifying trained policies in different physical simulations. The codebase is verified with RobotEra's XBot-S and XBot-L humanoid robots. It offers comprehensive training guidelines, step-by-step configuration instructions, and execution scripts for easy deployment. The sim2sim support allows transferring trained policies to accurate simulated environments. The upcoming features include Denoising World Model Learning and Dexterous Hand Manipulation. Installation and usage guides are provided along with examples for training PPO policies and sim-to-sim transformations. The code structure includes environment and configuration files, with instructions on adding new environments. Troubleshooting tips are provided for common issues, along with a citation and acknowledgment section.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
BentoML
BentoML is an open-source model serving library for building performant and scalable AI applications with Python. It comes with everything you need for serving optimization, model packaging, and production deployment.
lmql
LMQL is a programming language designed for large language models (LLMs) that offers a unique way of integrating traditional programming with LLM interaction. It allows users to write programs that combine algorithmic logic with LLM calls, enabling model reasoning capabilities within the context of the program. LMQL provides features such as Python syntax integration, rich control-flow options, advanced decoding techniques, powerful constraints via logit masking, runtime optimization, sync and async API support, multi-model compatibility, and extensive applications like JSON decoding and interactive chat interfaces. The tool also offers library integration, flexible tooling, and output streaming options for easy model output handling.

guidellm
GuideLLM is a platform for evaluating and optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs). By simulating real-world inference workloads, GuideLLM enables users to assess the performance, resource requirements, and cost implications of deploying LLMs on various hardware configurations. This approach ensures efficient, scalable, and cost-effective LLM inference serving while maintaining high service quality. The tool provides features for performance evaluation, resource optimization, cost estimation, and scalability testing.
labo
LABO is a time series forecasting and analysis framework that integrates pre-trained and fine-tuned LLMs with multi-domain agent-based systems. It allows users to create and tune agents easily for various scenarios, such as stock market trend prediction and web public opinion analysis. LABO requires a specific runtime environment setup, including system requirements, Python environment, dependency installations, and configurations. Users can fine-tune their own models using LABO's Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for computational efficiency and continuous model updates. Additionally, LABO provides a Python library for building model training pipelines and customizing agents for specific tasks.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.

helix-db
HelixDB is a database designed specifically for AI applications, providing a single platform to manage all components needed for AI applications. It supports graph + vector data model and also KV, documents, and relational data. Key features include built-in tools for MCP, embeddings, knowledge graphs, RAG, security, logical isolation, and ultra-low latency. Users can interact with HelixDB using the Helix CLI tool and SDKs in TypeScript and Python. The roadmap includes features like organizational auth, server code improvements, 3rd party integrations, educational content, and binary quantisation for better performance. Long term projects involve developing in-house tools for knowledge graph ingestion, graph-vector storage engine, and network protocol & serdes libraries.
metta
Metta AI is an open-source research project focusing on the emergence of cooperation and alignment in multi-agent AI systems. It explores the impact of social dynamics like kinship and mate selection on learning and cooperative behaviors of AI agents. The project introduces a reward-sharing mechanism mimicking familial bonds and mate selection to observe the evolution of complex social behaviors among AI agents. Metta aims to contribute to the discussion on safe and beneficial AGI by creating an environment where AI agents can develop general intelligence through continuous learning and adaptation.
codellm-devkit
Codellm-devkit (CLDK) is a Python library that serves as a multilingual program analysis framework bridging traditional static analysis tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for code (CodeLLMs). It simplifies the process of analyzing codebases across multiple programming languages, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights and facilitating LLM-based code analysis. The library provides a unified interface for integrating outputs from various analysis tools and preparing them for effective use by CodeLLMs. Codellm-devkit aims to enable the development and experimentation of robust analysis pipelines that combine traditional program analysis tools and CodeLLMs, reducing friction in multi-language code analysis and ensuring compatibility across different tools and LLM platforms. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with popular analysis tools like WALA, Tree-sitter, LLVM, and CodeQL, acting as a crucial intermediary layer for efficient communication between these tools and CodeLLMs. The project is continuously evolving to include new tools and frameworks, maintaining its versatility for code analysis and LLM integration.
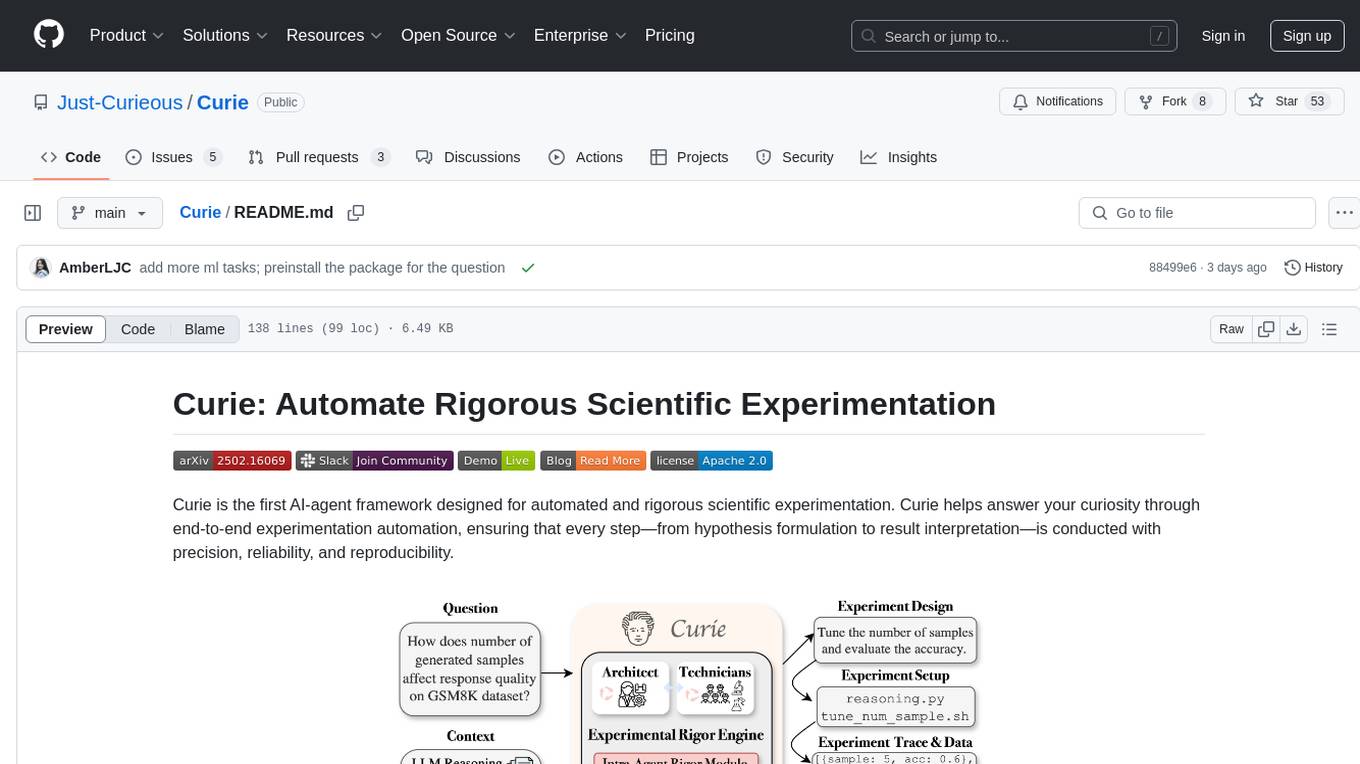
Curie
Curie is an AI-agent framework designed for automated and rigorous scientific experimentation. It automates end-to-end workflow management, ensures methodical procedure, reliability, and interpretability, and supports ML research, system analysis, and scientific discovery. It provides a benchmark with questions from 4 Computer Science domains. Users can customize experiment agents and adapt to their own tasks by configuring base_config.json. Curie is suitable for hyperparameter tuning, algorithm behavior analysis, system performance benchmarking, and automating computational simulations.
AgentBench
AgentBench is a benchmark designed to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) as autonomous agents in various environments. It includes 8 distinct environments such as Operating System, Database, Knowledge Graph, Digital Card Game, and Lateral Thinking Puzzles. The tool provides a comprehensive evaluation of LLMs' ability to operate as agents by offering Dev and Test sets for each environment. Users can quickly start using the tool by following the provided steps, configuring the agent, starting task servers, and assigning tasks. AgentBench aims to bridge the gap between LLMs' proficiency as agents and their practical usability.
habitat-lab
Habitat-Lab is a modular high-level library for end-to-end development in embodied AI. It is designed to train agents to perform a wide variety of embodied AI tasks in indoor environments, as well as develop agents that can interact with humans in performing these tasks.
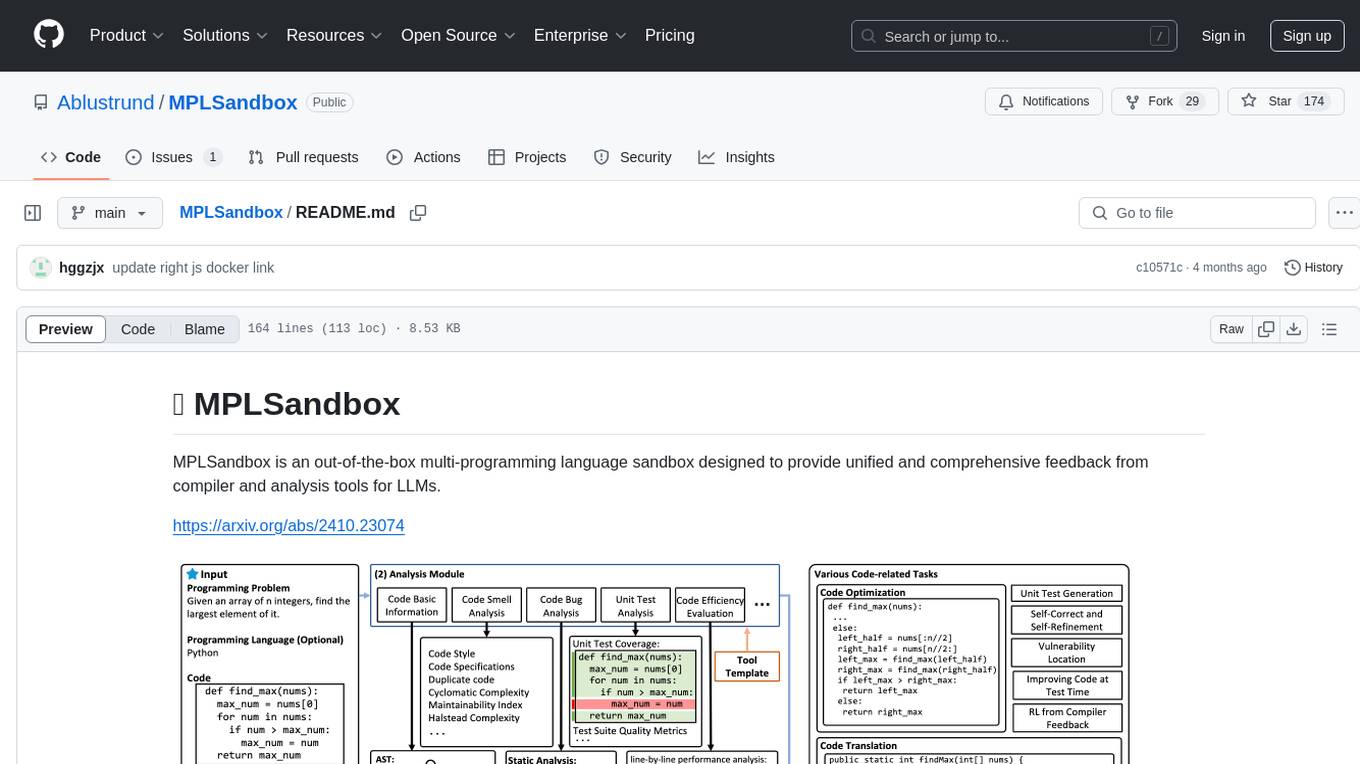
MPLSandbox
MPLSandbox is an out-of-the-box multi-programming language sandbox designed to provide unified and comprehensive feedback from compiler and analysis tools for LLMs. It simplifies code analysis for researchers and can be seamlessly integrated into LLM training and application processes to enhance performance in a range of code-related tasks. The sandbox environment ensures safe code execution, the code analysis module offers comprehensive analysis reports, and the information integration module combines compilation feedback and analysis results for complex code-related tasks.
For similar tasks

atropos
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.
litgpt
LitGPT is a command-line tool designed to easily finetune, pretrain, evaluate, and deploy 20+ LLMs **on your own data**. It features highly-optimized training recipes for the world's most powerful open-source large-language-models (LLMs).
llm.c
LLM training in simple, pure C/CUDA. There is no need for 245MB of PyTorch or 107MB of cPython. For example, training GPT-2 (CPU, fp32) is ~1,000 lines of clean code in a single file. It compiles and runs instantly, and exactly matches the PyTorch reference implementation. I chose GPT-2 as the first working example because it is the grand-daddy of LLMs, the first time the modern stack was put together.
torchtune
Torchtune is a PyTorch-native library for easily authoring, fine-tuning, and experimenting with LLMs. It provides native-PyTorch implementations of popular LLMs using composable and modular building blocks, easy-to-use and hackable training recipes for popular fine-tuning techniques, YAML configs for easily configuring training, evaluation, quantization, or inference recipes, and built-in support for many popular dataset formats and prompt templates to help you quickly get started with training.
llm-engine
Scale's LLM Engine is an open-source Python library, CLI, and Helm chart that provides everything you need to serve and fine-tune foundation models, whether you use Scale's hosted infrastructure or do it in your own cloud infrastructure using Kubernetes.
LLaMA-Factory
LLaMA Factory is a unified framework for fine-tuning 100+ large language models (LLMs) with various methods, including pre-training, supervised fine-tuning, reward modeling, PPO, DPO and ORPO. It features integrated algorithms like GaLore, BAdam, DoRA, LongLoRA, LLaMA Pro, LoRA+, LoftQ and Agent tuning, as well as practical tricks like FlashAttention-2, Unsloth, RoPE scaling, NEFTune and rsLoRA. LLaMA Factory provides experiment monitors like LlamaBoard, TensorBoard, Wandb, MLflow, etc., and supports faster inference with OpenAI-style API, Gradio UI and CLI with vLLM worker. Compared to ChatGLM's P-Tuning, LLaMA Factory's LoRA tuning offers up to 3.7 times faster training speed with a better Rouge score on the advertising text generation task. By leveraging 4-bit quantization technique, LLaMA Factory's QLoRA further improves the efficiency regarding the GPU memory.
Pai-Megatron-Patch
Pai-Megatron-Patch is a deep learning training toolkit built for developers to train and predict LLMs & VLMs by using Megatron framework easily. With the continuous development of LLMs, the model structure and scale are rapidly evolving. Although these models can be conveniently manufactured using Transformers or DeepSpeed training framework, the training efficiency is comparably low. This phenomenon becomes even severer when the model scale exceeds 10 billion. The primary objective of Pai-Megatron-Patch is to effectively utilize the computational power of GPUs for LLM. This tool allows convenient training of commonly used LLM with all the accelerating techniques provided by Megatron-LM.
LLM-PowerHouse-A-Curated-Guide-for-Large-Language-Models-with-Custom-Training-and-Inferencing
LLM-PowerHouse is a comprehensive and curated guide designed to empower developers, researchers, and enthusiasts to harness the true capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and build intelligent applications that push the boundaries of natural language understanding. This GitHub repository provides in-depth articles, codebase mastery, LLM PlayLab, and resources for cost analysis and network visualization. It covers various aspects of LLMs, including NLP, models, training, evaluation metrics, open LLMs, and more. The repository also includes a collection of code examples and tutorials to help users build and deploy LLM-based applications.
For similar jobs
LitServe
LitServe is a high-throughput serving engine designed for deploying AI models at scale. It generates an API endpoint for models, handles batching, streaming, and autoscaling across CPU/GPUs. LitServe is built for enterprise scale with a focus on minimal, hackable code-base without bloat. It supports various model types like LLMs, vision, time-series, and works with frameworks like PyTorch, JAX, Tensorflow, and more. The tool allows users to focus on model performance rather than serving boilerplate, providing full control and flexibility.
Lidar_AI_Solution
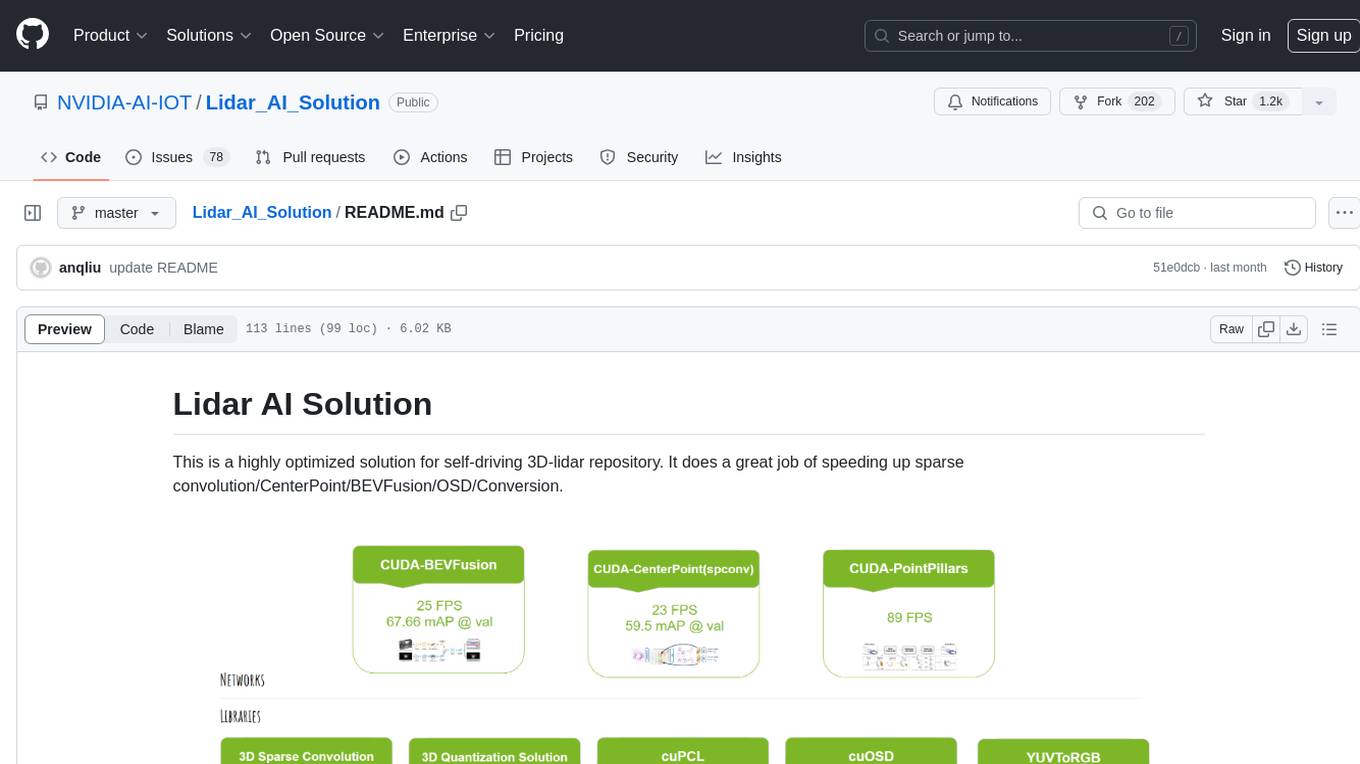
Lidar AI Solution is a highly optimized repository for self-driving 3D lidar, providing solutions for sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, OSD, and Conversion. It includes CUDA and TensorRT implementations for various tasks such as 3D sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, PointPillars, V2XFusion, cuOSD, cuPCL, and YUV to RGB conversion. The repository offers easy-to-use solutions, high accuracy, low memory usage, and quantization options for different tasks related to self-driving technology.
generative-ai-sagemaker-cdk-demo
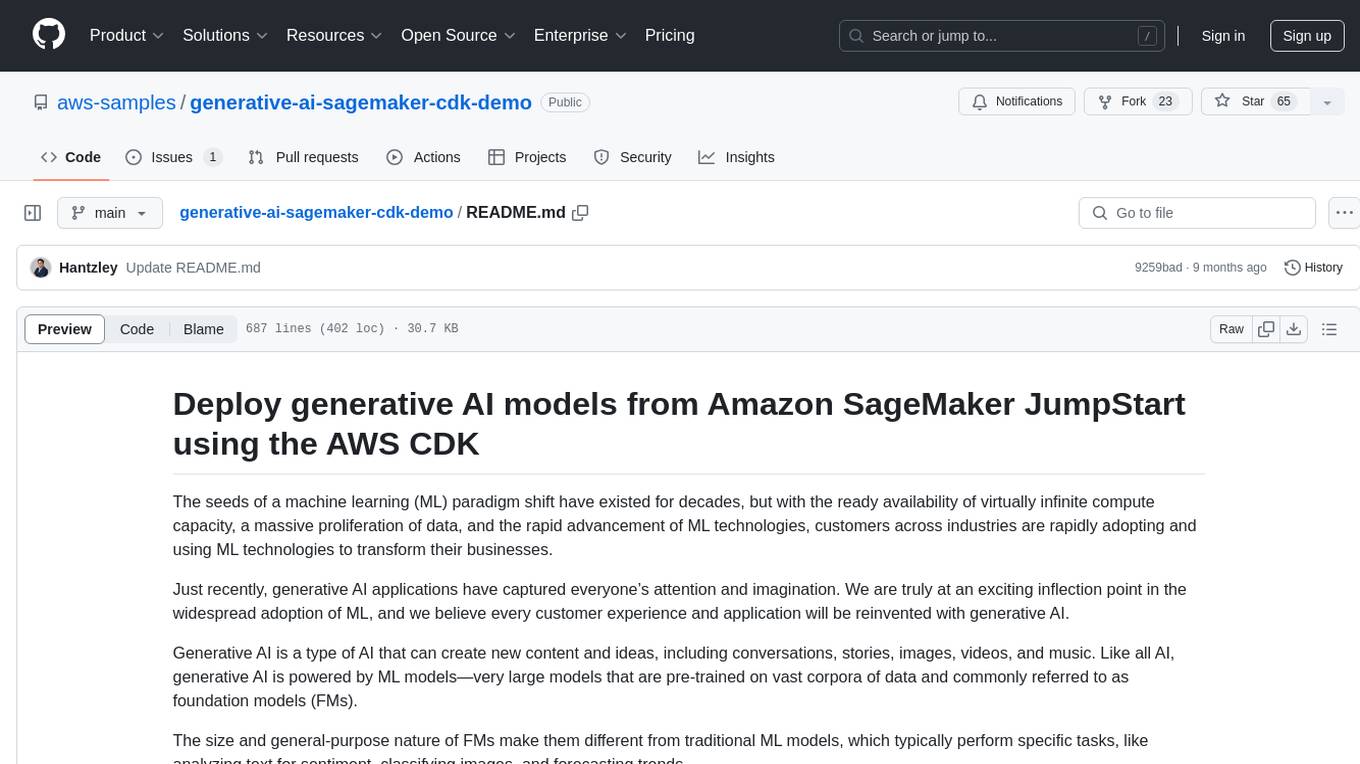
This repository showcases how to deploy generative AI models from Amazon SageMaker JumpStart using the AWS CDK. Generative AI is a type of AI that can create new content and ideas, such as conversations, stories, images, videos, and music. The repository provides a detailed guide on deploying image and text generative AI models, utilizing pre-trained models from SageMaker JumpStart. The web application is built on Streamlit and hosted on Amazon ECS with Fargate. It interacts with the SageMaker model endpoints through Lambda functions and Amazon API Gateway. The repository also includes instructions on setting up the AWS CDK application, deploying the stacks, using the models, and viewing the deployed resources on the AWS Management Console.
cake
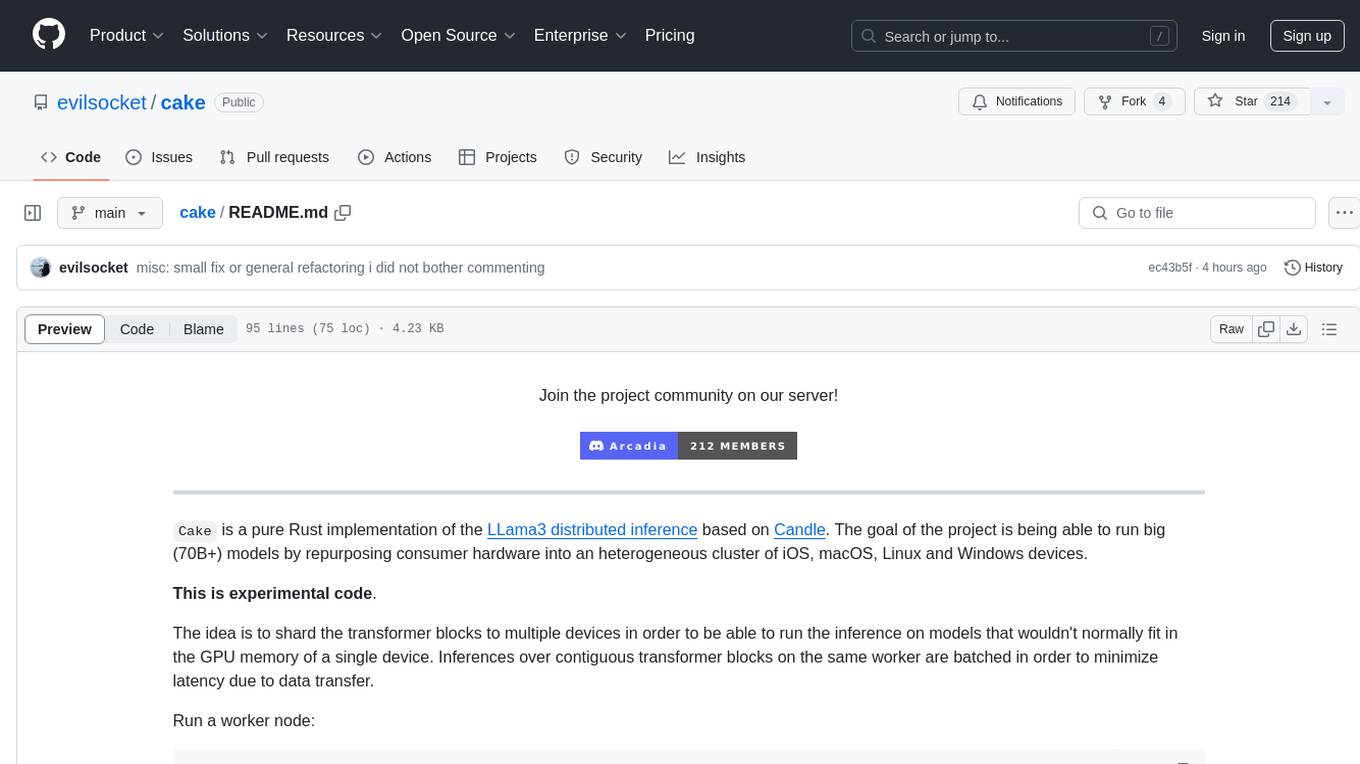
cake is a pure Rust implementation of the llama3 LLM distributed inference based on Candle. The project aims to enable running large models on consumer hardware clusters of iOS, macOS, Linux, and Windows devices by sharding transformer blocks. It allows running inferences on models that wouldn't fit in a single device's GPU memory by batching contiguous transformer blocks on the same worker to minimize latency. The tool provides a way to optimize memory and disk space by splitting the model into smaller bundles for workers, ensuring they only have the necessary data. cake supports various OS, architectures, and accelerations, with different statuses for each configuration.
Awesome-Robotics-3D
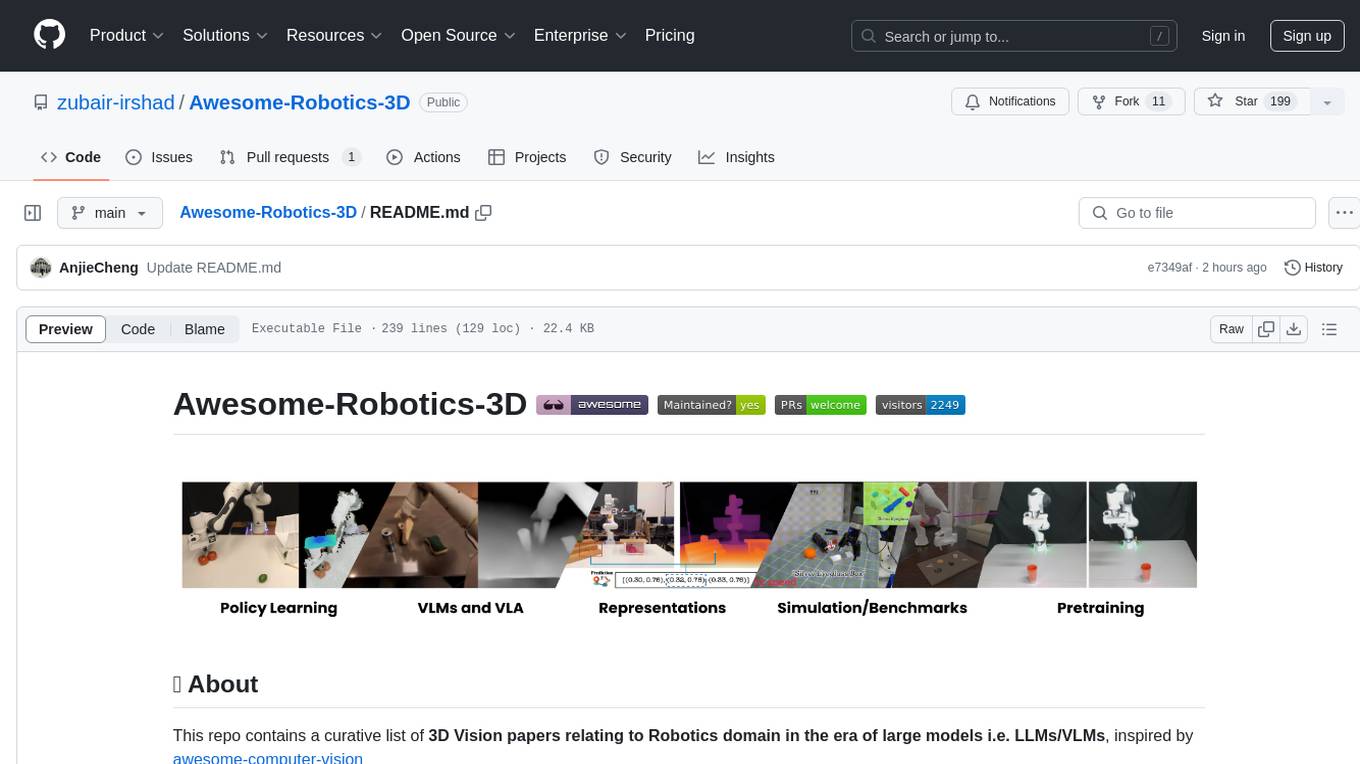
Awesome-Robotics-3D is a curated list of 3D Vision papers related to Robotics domain, focusing on large models like LLMs/VLMs. It includes papers on Policy Learning, Pretraining, VLM and LLM, Representations, and Simulations, Datasets, and Benchmarks. The repository is maintained by Zubair Irshad and welcomes contributions and suggestions for adding papers. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of Robotics and Computer Vision.
tensorzero
TensorZero is an open-source platform that helps LLM applications graduate from API wrappers into defensible AI products. It enables a data & learning flywheel for LLMs by unifying inference, observability, optimization, and experimentation. The platform includes a high-performance model gateway, structured schema-based inference, observability, experimentation, and data warehouse for analytics. TensorZero Recipes optimize prompts and models, and the platform supports experimentation features and GitOps orchestration for deployment.
vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
rhesis
Rhesis is a comprehensive test management platform designed for Gen AI teams, offering tools to create, manage, and execute test cases for generative AI applications. It ensures the robustness, reliability, and compliance of AI systems through features like test set management, automated test generation, edge case discovery, compliance validation, integration capabilities, and performance tracking. The platform is open source, emphasizing community-driven development, transparency, extensible architecture, and democratizing AI safety. It includes components such as backend services, frontend applications, SDK for developers, worker services, chatbot applications, and Polyphemus for uncensored LLM service. Rhesis enables users to address challenges unique to testing generative AI applications, such as non-deterministic outputs, hallucinations, edge cases, ethical concerns, and compliance requirements.



