
rhesis
Open-source platform & SDK for testing LLM and agentic apps. Define expected behavior, generate and run test scenarios, and review failures collaboratively.
Stars: 277
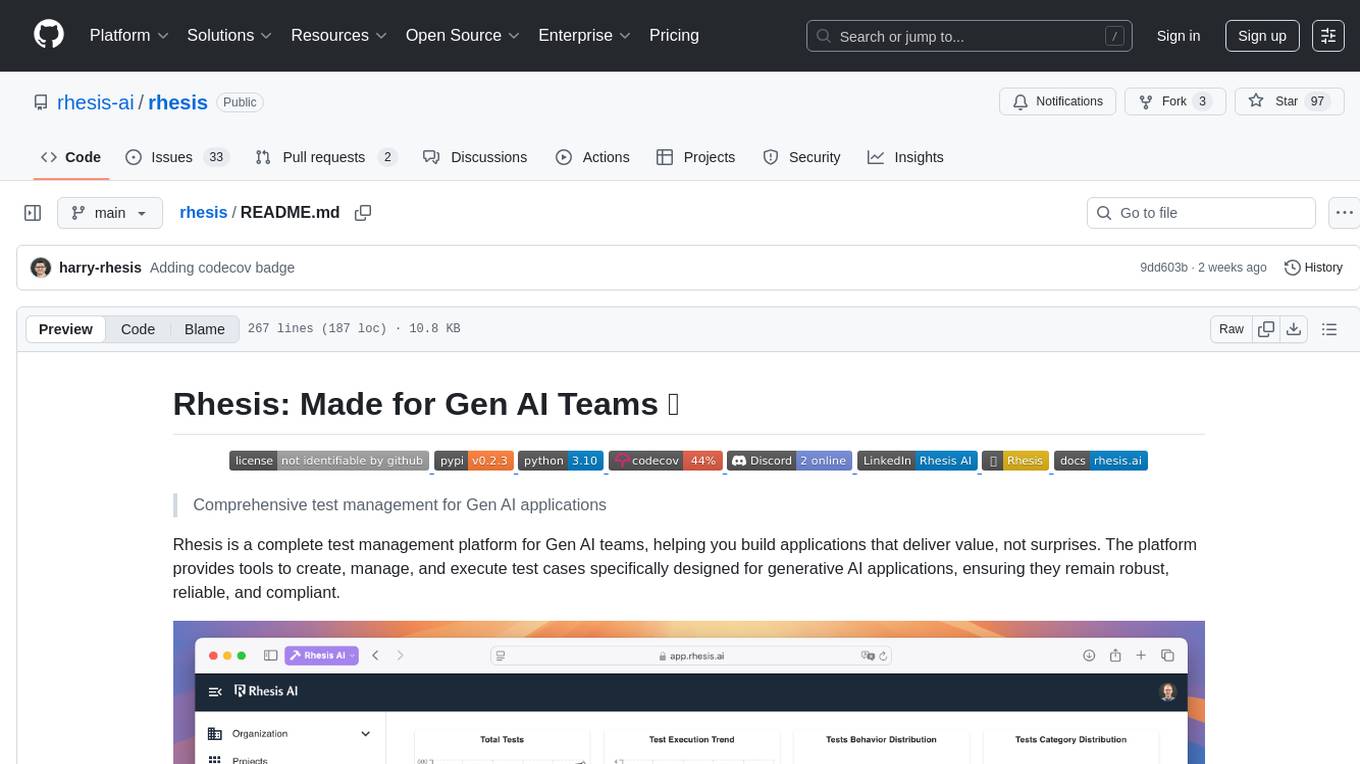
Rhesis is a comprehensive test management platform designed for Gen AI teams, offering tools to create, manage, and execute test cases for generative AI applications. It ensures the robustness, reliability, and compliance of AI systems through features like test set management, automated test generation, edge case discovery, compliance validation, integration capabilities, and performance tracking. The platform is open source, emphasizing community-driven development, transparency, extensible architecture, and democratizing AI safety. It includes components such as backend services, frontend applications, SDK for developers, worker services, chatbot applications, and Polyphemus for uncensored LLM service. Rhesis enables users to address challenges unique to testing generative AI applications, such as non-deterministic outputs, hallucinations, edge cases, ethical concerns, and compliance requirements.
README:
Website · Docs · Discord · Changelog
Generate tests from requirements, simulate conversation flows, detect adversarial behaviors, evaluate with 60+ metrics, and trace failures with OpenTelemetry. Engineers and domain experts, working together.
AI-Powered Synthesis - Describe requirements in plain language. Rhesis generates hundreds of test scenarios including edge cases and adversarial prompts.
Knowledge-Aware - Connect context sources via file upload or MCP (Notion, GitHub, Jira, Confluence) for better test generation.
Single-turn for Q&A validation. Conversation simulation for dialogue flows.
Penelope Agent simulates realistic conversations to test context retention, role adherence, and dialogue coherence across extended interactions.
Polyphemus Agent proactively finds vulnerabilities:
- Jailbreak attempts and prompt injection
- PII leakage and data extraction
- Harmful content generation
- Role violation and instruction bypassing
Garak Integration - Built-in support for garak, the LLM vulnerability scanner, for comprehensive security testing.
| Framework | Example Metrics |
|---|---|
| RAGAS | Context relevance, faithfulness, answer accuracy |
| DeepEval | Bias, toxicity, PII leakage, role violation, turn relevancy, knowledge retention |
| Garak | Jailbreak detection, prompt injection, XSS, malware generation, data leakage |
| Custom | NumericJudge, CategoricalJudge for domain-specific evaluation |
All metrics include LLM-as-Judge reasoning explanations.
Monitor your LLM applications with OpenTelemetry-based tracing:
from rhesis.sdk.decorators import observe
@observe.llm(model="gpt-4")
def generate_response(prompt: str) -> str:
# Your LLM call here
return responseTrack LLM calls, latency, token usage, and link traces to test results for debugging.
Use any LLM provider for test generation and evaluation:
Cloud: OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, Mistral, Cohere, Groq, Together AI
Local/Self-hosted: Ollama, vLLM, LiteLLM
See Model Configuration Docs for setup instructions.
Platform for teams. SDK for developers.
Use the collaborative platform for team-based testing: product managers define requirements, domain experts review results, engineers integrate via CI/CD. Or integrate directly with the Python SDK for code-first workflows.
Six integrated phases from project setup to team collaboration:
| Phase | What You Do |
|---|---|
| 1. Projects | Configure your AI application, upload & connect context sources (files, docs), set up SDK connectors |
| 2. Requirements | Define expected behaviors (what your app should and shouldn't do), cover all relevant aspects from product, marketing, customer support, legal and compliance teams |
| 3. Metrics | Select from 60+ pre-built metrics or create custom LLM-as-Judge evaluations to assess whether your requirements are met |
| 4. Tests | Generate single-turn and conversation simulation test scenarios. Organize in test sets and understand your test coverage |
| 5. Execution | Run tests via UI, SDK, or API; integrate into CI/CD pipelines; collect traces during execution |
| 6. Collaboration | Review results with your team through comments, tasks, workflows, and side-by-side comparisons |
| Instead of... | Rhesis gives you... |
|---|---|
| Manual testing | AI-generated test cases based on your context, hundreds in minutes |
| Traditional test frameworks | Non-deterministic output handling built-in |
| LLM observability tools | Pre-production validation, not post-production monitoring |
| Red-teaming services | Continuous, self-service adversarial testing, not one-time audits |
| Use Case | What Rhesis Tests |
|---|---|
| Conversational AI | Conversation simulation, role adherence, knowledge retention |
| RAG Systems | Context relevance, faithfulness, hallucination detection |
| NL-to-SQL / NL-to-Code | Query accuracy, syntax validation, edge case handling |
| Agentic Systems | Tool selection, goal achievement, multi-agent coordination |
Test your Python functions directly with the @endpoint decorator:
from rhesis.sdk.decorators import endpoint
@endpoint(name="my-chatbot")
def chat(message: str) -> str:
# Your LLM logic here
return responseFeatures: Zero configuration, automatic parameter binding, auto-reconnection, environment management (dev/staging/production).
Generate tests programmatically:
from rhesis.sdk.synthesizers import PromptSynthesizer
synthesizer = PromptSynthesizer(
prompt="Generate tests for a medical chatbot that must never provide diagnosis"
)
test_set = synthesizer.generate(num_tests=10)| Option | Best For | Setup Time |
|---|---|---|
| Rhesis Cloud | Teams wanting managed deployment | Instant |
| Docker | Local development and testing | 5 minutes |
| Kubernetes | Production self-hosting | See docs |
Option 1: Cloud (fastest) - app.rhesis.ai - Managed service, just connect your app
Option 2: Self-host with Docker
git clone https://github.com/rhesis-ai/rhesis.git && cd rhesis && ./rh startAccess: Frontend at localhost:3000, API at localhost:8080/docs
Commands: ./rh logs · ./rh stop · ./rh restart · ./rh delete
Note: This setup enables auto-login for local testing. For production, see Self-hosting Documentation.
Option 3: Python SDK
pip install rhesis-sdkConnect Rhesis to your LLM stack:
| Integration | Languages | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Rhesis SDK | Python, JS/TS | Native SDK with decorators for endpoints and observability. Full control over test execution and tracing. |
| OpenAI | Python | Drop-in replacement for OpenAI SDK. Automatic instrumentation with zero code changes. |
| Anthropic | Python | Native support for Claude models with automatic tracing. |
| LangChain | Python | Add Rhesis callback handler to your LangChain app for automatic tracing and test execution. |
| LangGraph | Python | Built-in integration for LangGraph agent workflows with full observability. |
| AutoGen | Python | Automatic instrumentation for Microsoft AutoGen multi-agent conversations. |
| LiteLLM | Python | Unified interface for 100+ LLMs (OpenAI, Azure, Anthropic, Cohere, Ollama, vLLM, HuggingFace, Replicate). |
| Google Gemini | Python | Native integration for Google's Gemini models. |
| Ollama | Python | Local LLM deployment with Ollama integration. |
| OpenRouter | Python | Access to multiple LLM providers through OpenRouter. |
| Vertex AI | Python | Google Cloud Vertex AI model support. |
| HuggingFace | Python | Direct integration with HuggingFace models. |
| REST API | Any | Direct API access for custom integrations. OpenAPI spec available. |
See Integration Docs for setup instructions.
MIT licensed. No plans to relicense core features. Enterprise version will live in ee/ folders and remain separate.
We built Rhesis because existing LLM testing tools didn't meet our needs. If you face the same challenges, contributions are welcome.
See CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines.
Ways to contribute: Fix bugs or add features · Contribute test sets for common failure modes · Improve documentation · Help others in Discord or GitHub discussions
- Documentation - Guides and API reference
- Discord - Community support
- GitHub Issues - Bug reports and feature requests
We take data security seriously. See our Privacy Policy for details.
Telemetry: Rhesis collects basic, anonymized usage statistics to improve the product. No sensitive data is collected or shared with third parties.
-
Self-hosted: Opt out by setting
OTEL_RHESIS_TELEMETRY_ENABLED=false - Cloud: Telemetry enabled as part of Terms & Conditions
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for rhesis
Similar Open Source Tools

rhesis
Rhesis is a comprehensive test management platform designed for Gen AI teams, offering tools to create, manage, and execute test cases for generative AI applications. It ensures the robustness, reliability, and compliance of AI systems through features like test set management, automated test generation, edge case discovery, compliance validation, integration capabilities, and performance tracking. The platform is open source, emphasizing community-driven development, transparency, extensible architecture, and democratizing AI safety. It includes components such as backend services, frontend applications, SDK for developers, worker services, chatbot applications, and Polyphemus for uncensored LLM service. Rhesis enables users to address challenges unique to testing generative AI applications, such as non-deterministic outputs, hallucinations, edge cases, ethical concerns, and compliance requirements.
netdata
Netdata is an open-source, real-time infrastructure monitoring platform that provides instant insights, zero configuration deployment, ML-powered anomaly detection, efficient monitoring with minimal resource usage, and secure & distributed data storage. It offers real-time, per-second updates and clear insights at a glance. Netdata's origin story involves addressing the limitations of existing monitoring tools and led to a fundamental shift in infrastructure monitoring. It is recognized as the most energy-efficient tool for monitoring Docker-based systems according to a study by the University of Amsterdam.

motia
Motia is an AI agent framework designed for software engineers to create, test, and deploy production-ready AI agents quickly. It provides a code-first approach, allowing developers to write agent logic in familiar languages and visualize execution in real-time. With Motia, developers can focus on business logic rather than infrastructure, offering zero infrastructure headaches, multi-language support, composable steps, built-in observability, instant APIs, and full control over AI logic. Ideal for building sophisticated agents and intelligent automations, Motia's event-driven architecture and modular steps enable the creation of GenAI-powered workflows, decision-making systems, and data processing pipelines.
awesome-slash
Automate the entire development workflow beyond coding. awesome-slash provides production-ready skills, agents, and commands for managing tasks, branches, reviews, CI, and deployments. It automates the entire workflow, including task exploration, planning, implementation, review, and shipping. The tool includes 11 plugins, 40 agents, 26 skills, and 26k lines of lib code, with 3,357 tests and support for 3 platforms. It works with Claude Code, OpenCode, and Codex CLI, offering specialized capabilities through skills and agents.
Evaluator
NeMo Evaluator SDK is an open-source platform for robust, reproducible, and scalable evaluation of Large Language Models. It enables running hundreds of benchmarks across popular evaluation harnesses against any OpenAI-compatible model API. The platform ensures auditable and trustworthy results by executing evaluations in open-source Docker containers. NeMo Evaluator SDK is built on four core principles: Reproducibility by Default, Scale Anywhere, State-of-the-Art Benchmarking, and Extensible and Customizable.
runtime
Exosphere is a lightweight runtime designed to make AI agents resilient to failure and enable infinite scaling across distributed compute. It provides a powerful foundation for building and orchestrating AI applications with features such as lightweight runtime, inbuilt failure handling, infinite parallel agents, dynamic execution graphs, native state persistence, and observability. Whether you're working on data pipelines, AI agents, or complex workflow orchestrations, Exosphere offers the infrastructure backbone to make your AI applications production-ready and scalable.
axonhub
AxonHub is an all-in-one AI development platform that serves as an AI gateway allowing users to switch between model providers without changing any code. It provides features like vendor lock-in prevention, integration simplification, observability enhancement, and cost control. Users can access any model using any SDK with zero code changes. The platform offers full request tracing, enterprise RBAC, smart load balancing, and real-time cost tracking. AxonHub supports multiple databases, provides a unified API gateway, and offers flexible model management and API key creation for authentication. It also integrates with various AI coding tools and SDKs for seamless usage.
sktime
sktime is a Python library for time series analysis that provides a unified interface for various time series learning tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, annotation, and forecasting. It offers time series algorithms and tools compatible with scikit-learn for building, tuning, and validating time series models. sktime aims to enhance the interoperability and usability of the time series analysis ecosystem by empowering users to apply algorithms across different tasks and providing interfaces to related libraries like scikit-learn, statsmodels, tsfresh, PyOD, and fbprophet.
bumblecore
BumbleCore is a hands-on large language model training framework that allows complete control over every training detail. It provides manual training loop, customizable model architecture, and support for mainstream open-source models. The framework follows core principles of transparency, flexibility, and efficiency. BumbleCore is suitable for deep learning researchers, algorithm engineers, learners, and enterprise teams looking for customization and control over model training processes.
auto-dev
AutoDev Xiuper is an AI-native, multi-agent development platform built on Kotlin Multiplatform. It covers all seven phases of the software development lifecycle and runs on 8+ platforms. The platform provides a unified architecture for writing code once and running it anywhere, with specialized agents for each phase of development. It supports various devices including IntelliJ IDEA, VS Code, CLI, Web, Desktop, Android, iOS, and Server. The platform also offers features like Multi-LLM support, DevIns language for workflow automation, MCP Protocol for extensible tool ecosystem, and code intelligence for multiple programming languages.

deepfabric
DeepFabric is a CLI tool and SDK designed for researchers and developers to generate high-quality synthetic datasets at scale using large language models. It leverages a graph and tree-based architecture to create diverse and domain-specific datasets while minimizing redundancy. The tool supports generating Chain of Thought datasets for step-by-step reasoning tasks and offers multi-provider support for using different language models. DeepFabric also allows for automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub and uses YAML configuration files for flexibility in dataset generation.
monoscope
Monoscope is an open-source monitoring and observability platform that uses artificial intelligence to understand and monitor systems automatically. It allows users to ingest and explore logs, traces, and metrics in S3 buckets, query in natural language via LLMs, and create AI agents to detect anomalies. Key capabilities include universal data ingestion, AI-powered understanding, natural language interface, cost-effective storage, and zero configuration. Monoscope is designed to reduce alert fatigue, catch issues before they impact users, and provide visibility across complex systems.

llm4ad
LLM4AD is an open-source Python-based platform leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Algorithm Design (AD). It provides unified interfaces for methods, tasks, and LLMs, along with features like evaluation acceleration, secure evaluation, logs, GUI support, and more. The platform was originally developed for optimization tasks but is versatile enough to be used in other areas such as machine learning, science discovery, game theory, and engineering design. It offers various search methods and algorithm design tasks across different domains. LLM4AD supports remote LLM API, local HuggingFace LLM deployment, and custom LLM interfaces. The project is licensed under the MIT License and welcomes contributions, collaborations, and issue reports.
camel
CAMEL is an open-source library designed for the study of autonomous and communicative agents. We believe that studying these agents on a large scale offers valuable insights into their behaviors, capabilities, and potential risks. To facilitate research in this field, we implement and support various types of agents, tasks, prompts, models, and simulated environments.
pai-opencode
PAI-OpenCode is a complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode, an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant. It brings modular capabilities, dynamic multi-agent orchestration, session history, and lifecycle automation to personalize AI assistants for users. With support for 75+ AI providers, PAI-OpenCode offers dynamic per-task model routing, full PAI infrastructure, real-time session sharing, and multiple client options. The tool optimizes cost and quality with a 3-tier model strategy and a 3-tier research system, allowing users to switch presets for different routing strategies. PAI-OpenCode's architecture preserves PAI's design while adapting to OpenCode, documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs).
eko
Eko is a lightweight and flexible command-line tool for managing environment variables in your projects. It allows you to easily set, get, and delete environment variables for different environments, making it simple to manage configurations across development, staging, and production environments. With Eko, you can streamline your workflow and ensure consistency in your application settings without the need for complex setup or configuration files.
For similar tasks

rhesis
Rhesis is a comprehensive test management platform designed for Gen AI teams, offering tools to create, manage, and execute test cases for generative AI applications. It ensures the robustness, reliability, and compliance of AI systems through features like test set management, automated test generation, edge case discovery, compliance validation, integration capabilities, and performance tracking. The platform is open source, emphasizing community-driven development, transparency, extensible architecture, and democratizing AI safety. It includes components such as backend services, frontend applications, SDK for developers, worker services, chatbot applications, and Polyphemus for uncensored LLM service. Rhesis enables users to address challenges unique to testing generative AI applications, such as non-deterministic outputs, hallucinations, edge cases, ethical concerns, and compliance requirements.

EvoMaster
EvoMaster is an open-source AI-driven tool that automatically generates system-level test cases for web/enterprise applications. It uses Evolutionary Algorithm and Dynamic Program Analysis to evolve test cases, maximizing code coverage and fault detection. It supports REST, GraphQL, and RPC APIs, with whitebox testing for JVM-compiled APIs. The tool generates JUnit tests in Java or Kotlin, focusing on fault detection, self-contained tests, SQL handling, and authentication. Known limitations include manual driver creation for whitebox testing and longer execution times for better results. EvoMaster has been funded by ERC and RCN grants.
repopack
Repopack is a powerful tool that packs your entire repository into a single, AI-friendly file. It optimizes your codebase for AI comprehension, is simple to use with customizable options, and respects Gitignore files for security. The tool generates a packed file with clear separators and AI-oriented explanations, making it ideal for use with Generative AI tools like Claude or ChatGPT. Repopack offers command line options, configuration settings, and multiple methods for setting ignore patterns to exclude specific files or directories during the packing process. It includes features like comment removal for supported file types and a security check using Secretlint to detect sensitive information in files.
EvoMaster
EvoMaster is an open-source AI-driven tool that automatically generates system-level test cases for web/enterprise applications. It uses an Evolutionary Algorithm and Dynamic Program Analysis to evolve test cases, maximizing code coverage and fault detection. The tool supports REST, GraphQL, and RPC APIs, with whitebox testing for JVM-compiled languages. It generates JUnit tests, detects faults, handles SQL databases, and supports authentication. EvoMaster has been funded by the European Research Council and the Research Council of Norway.
ianvs
Ianvs is a distributed synergy AI benchmarking project incubated in KubeEdge SIG AI. It aims to test the performance of distributed synergy AI solutions following recognized standards, providing end-to-end benchmark toolkits, test environment management tools, test case control tools, and benchmark presentation tools. It also collaborates with other organizations to establish comprehensive benchmarks and related applications. The architecture includes critical components like Test Environment Manager, Test Case Controller, Generation Assistant, Simulation Controller, and Story Manager. Ianvs documentation covers quick start, guides, dataset descriptions, algorithms, user interfaces, stories, and roadmap.
NotHotDog
NotHotDog is an open-source platform for testing, evaluating, and simulating AI agents. It offers a robust framework for generating test cases, running conversational scenarios, and analyzing agent performance.
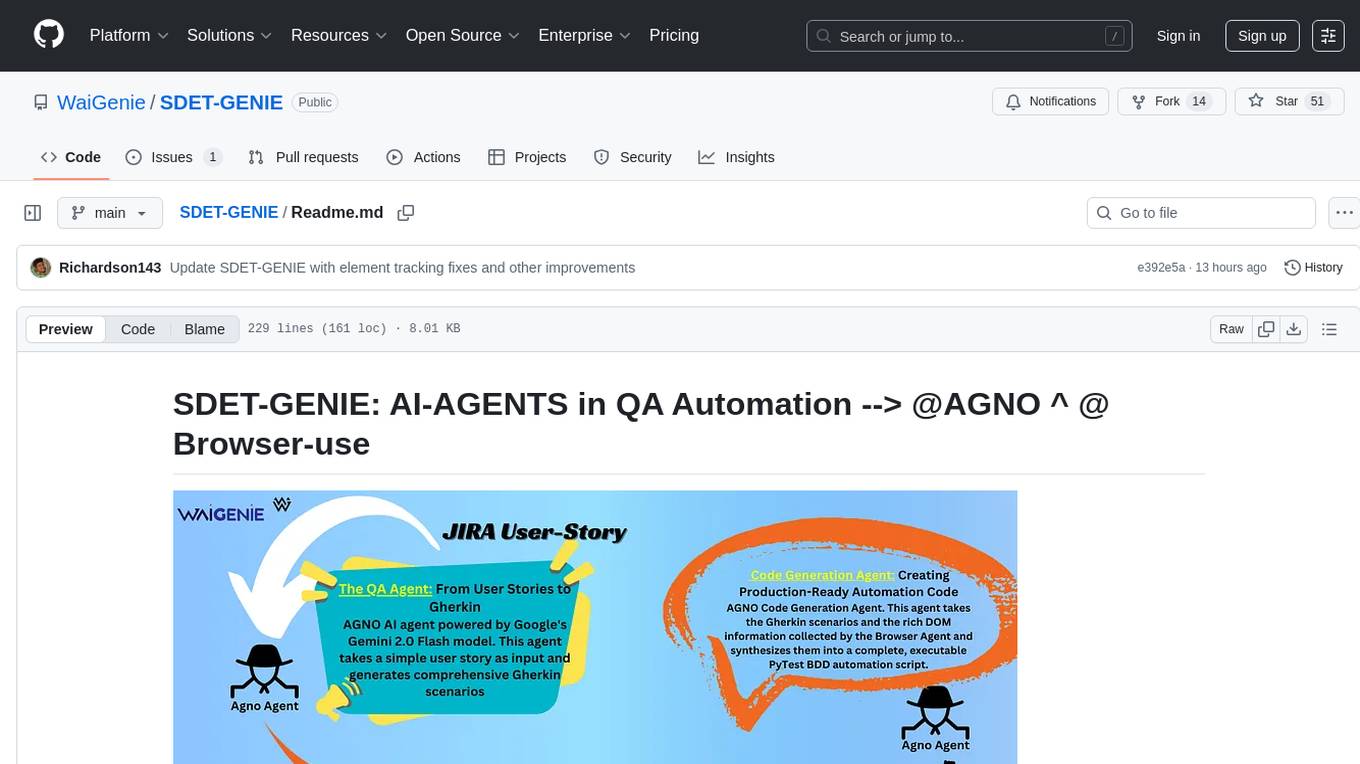
SDET-GENIE
SDET-GENIE is a cutting-edge, AI-powered Quality Assurance (QA) automation framework that revolutionizes the software testing process. Leveraging a suite of specialized AI agents, SDET-GENIE transforms rough user stories into comprehensive, executable test automation code through a seamless end-to-end process. The framework integrates five powerful AI agents working in sequence: User Story Enhancement Agent, Manual Test Case Agent, Gherkin Scenario Agent, Browser Agent, and Code Generation Agent. It supports multiple testing frameworks and provides advanced browser automation capabilities with AI features.

auto-dev
AutoDev Xiuper is an AI-native, multi-agent development platform built on Kotlin Multiplatform. It covers all seven phases of the software development lifecycle and runs on 8+ platforms. The platform provides a unified architecture for writing code once and running it anywhere, with specialized agents for each phase of development. It supports various devices including IntelliJ IDEA, VS Code, CLI, Web, Desktop, Android, iOS, and Server. The platform also offers features like Multi-LLM support, DevIns language for workflow automation, MCP Protocol for extensible tool ecosystem, and code intelligence for multiple programming languages.
For similar jobs

rhesis
Rhesis is a comprehensive test management platform designed for Gen AI teams, offering tools to create, manage, and execute test cases for generative AI applications. It ensures the robustness, reliability, and compliance of AI systems through features like test set management, automated test generation, edge case discovery, compliance validation, integration capabilities, and performance tracking. The platform is open source, emphasizing community-driven development, transparency, extensible architecture, and democratizing AI safety. It includes components such as backend services, frontend applications, SDK for developers, worker services, chatbot applications, and Polyphemus for uncensored LLM service. Rhesis enables users to address challenges unique to testing generative AI applications, such as non-deterministic outputs, hallucinations, edge cases, ethical concerns, and compliance requirements.
arthur-engine
The Arthur Engine is a comprehensive tool for monitoring and governing AI/ML workloads. It provides evaluation and benchmarking of machine learning models, guardrails enforcement, and extensibility for fitting into various application architectures. With support for a wide range of evaluation metrics and customizable features, the tool aims to improve model understanding, optimize generative AI outputs, and prevent data-security and compliance risks. Key features include real-time guardrails, model performance monitoring, feature importance visualization, error breakdowns, and support for custom metrics and models integration.

dingo
Dingo is a data quality evaluation tool that automatically detects data quality issues in datasets. It provides built-in rules and model evaluation methods, supports text and multimodal datasets, and offers local CLI and SDK usage. Dingo is designed for easy integration into evaluation platforms like OpenCompass.
LitServe
LitServe is a high-throughput serving engine designed for deploying AI models at scale. It generates an API endpoint for models, handles batching, streaming, and autoscaling across CPU/GPUs. LitServe is built for enterprise scale with a focus on minimal, hackable code-base without bloat. It supports various model types like LLMs, vision, time-series, and works with frameworks like PyTorch, JAX, Tensorflow, and more. The tool allows users to focus on model performance rather than serving boilerplate, providing full control and flexibility.
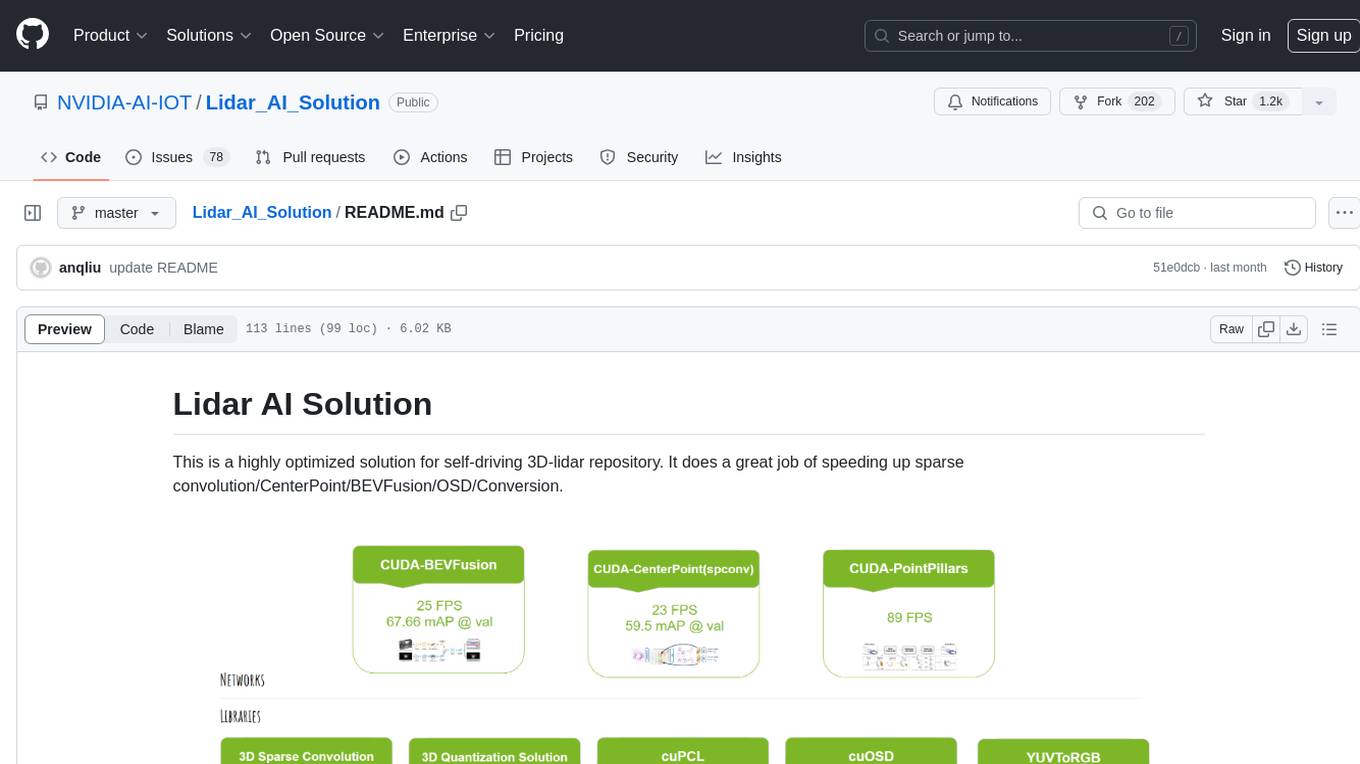
Lidar_AI_Solution
Lidar AI Solution is a highly optimized repository for self-driving 3D lidar, providing solutions for sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, OSD, and Conversion. It includes CUDA and TensorRT implementations for various tasks such as 3D sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, PointPillars, V2XFusion, cuOSD, cuPCL, and YUV to RGB conversion. The repository offers easy-to-use solutions, high accuracy, low memory usage, and quantization options for different tasks related to self-driving technology.
generative-ai-sagemaker-cdk-demo
This repository showcases how to deploy generative AI models from Amazon SageMaker JumpStart using the AWS CDK. Generative AI is a type of AI that can create new content and ideas, such as conversations, stories, images, videos, and music. The repository provides a detailed guide on deploying image and text generative AI models, utilizing pre-trained models from SageMaker JumpStart. The web application is built on Streamlit and hosted on Amazon ECS with Fargate. It interacts with the SageMaker model endpoints through Lambda functions and Amazon API Gateway. The repository also includes instructions on setting up the AWS CDK application, deploying the stacks, using the models, and viewing the deployed resources on the AWS Management Console.
cake
cake is a pure Rust implementation of the llama3 LLM distributed inference based on Candle. The project aims to enable running large models on consumer hardware clusters of iOS, macOS, Linux, and Windows devices by sharding transformer blocks. It allows running inferences on models that wouldn't fit in a single device's GPU memory by batching contiguous transformer blocks on the same worker to minimize latency. The tool provides a way to optimize memory and disk space by splitting the model into smaller bundles for workers, ensuring they only have the necessary data. cake supports various OS, architectures, and accelerations, with different statuses for each configuration.
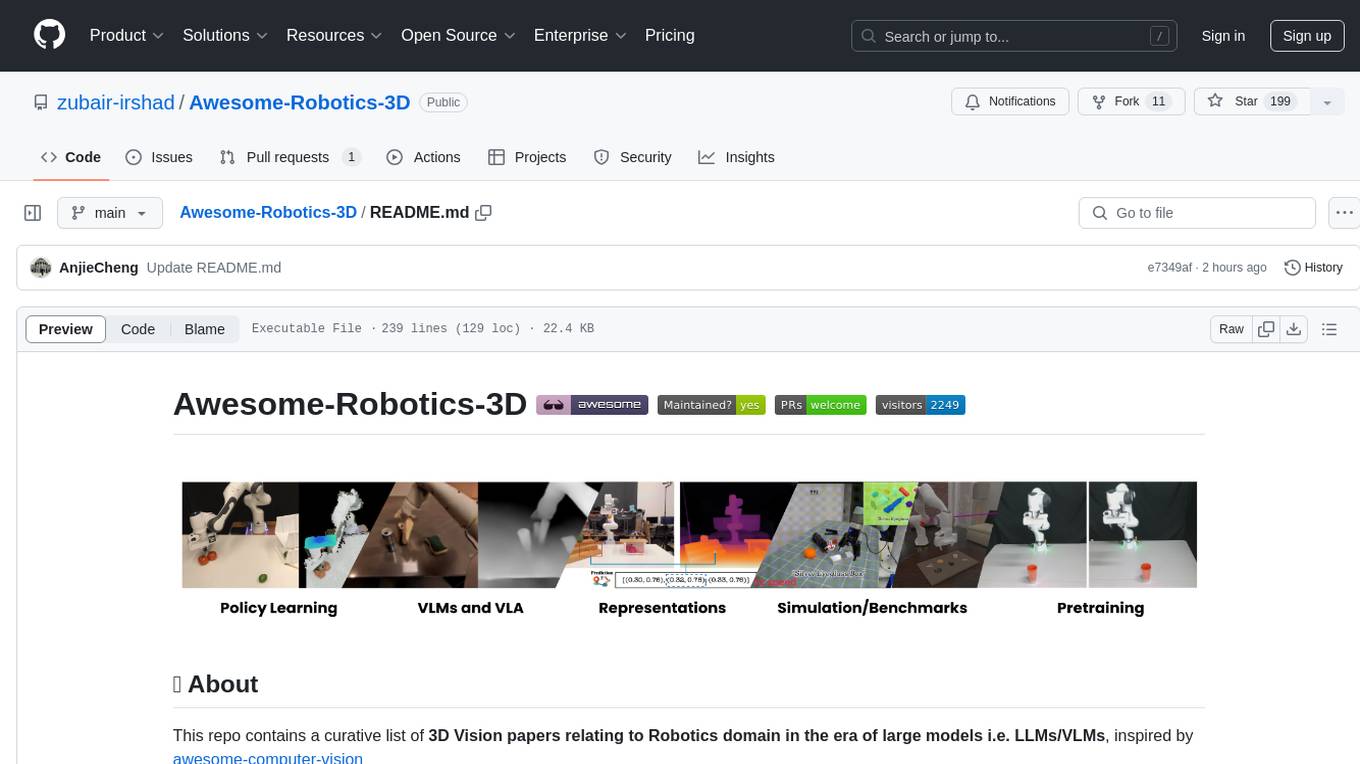
Awesome-Robotics-3D
Awesome-Robotics-3D is a curated list of 3D Vision papers related to Robotics domain, focusing on large models like LLMs/VLMs. It includes papers on Policy Learning, Pretraining, VLM and LLM, Representations, and Simulations, Datasets, and Benchmarks. The repository is maintained by Zubair Irshad and welcomes contributions and suggestions for adding papers. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of Robotics and Computer Vision.








