dingo
Dingo: A Comprehensive Data Quality Evaluation Tool
Stars: 109

Dingo is a data quality evaluation tool that automatically detects data quality issues in datasets. It provides built-in rules and model evaluation methods, supports text and multimodal datasets, and offers local CLI and SDK usage. Dingo is designed for easy integration into evaluation platforms like OpenCompass.
README:
- 2024/12/27: Project Initialization
Dingo is a data quality evaluation tool that helps you automatically detect data quality issues in your datasets. Dingo provides a variety of built-in rules and model evaluation methods, and also supports custom evaluation methods. Dingo supports commonly used text datasets and multimodal datasets, including pre-training datasets, fine-tuning datasets, and evaluation datasets. In addition, Dingo supports multiple usage methods, including local CLI and SDK, making it easy to integrate into various evaluation platforms, such as OpenCompass.
pip install dingo-pythonfrom dingo.io import InputArgs
from dingo.exec import Executor
# Evaluate a plaintext file
input_data = {
"eval_group": "sft", # Rule set for SFT data
"input_path": "data.txt", # Path to local text file
"dataset": "local",
"data_format": "plaintext", # Format: plaintext
"save_data": True # Save evaluation results
}
input_args = InputArgs(**input_data)
executor = Executor.exec_map["local"](input_args)
result = executor.execute()
print(result)from dingo.io import InputArgs
from dingo.exec import Executor
# Evaluate a dataset from Hugging Face
input_data = {
"eval_group": "sft", # Rule set for SFT data
"input_path": "tatsu-lab/alpaca", # Dataset from Hugging Face
"data_format": "plaintext", # Format: plaintext
"save_data": True # Save evaluation results
}
input_args = InputArgs(**input_data)
executor = Executor.exec_map["local"](input_args)
result = executor.execute()
print(result)from dingo.io import InputArgs
from dingo.exec import Executor
# Evaluate a JSON file
input_data = {
"eval_group": "default", # Default rule set
"input_path": "data.json", # Path to local JSON file
"dataset": "local",
"data_format": "json", # Format: json
"column_content": "text", # Column containing the text to evaluate
"save_data": True # Save evaluation results
}
input_args = InputArgs(**input_data)
executor = Executor.exec_map["local"](input_args)
result = executor.execute()
print(result)from dingo.io import InputArgs
from dingo.exec import Executor
# Evaluate using GPT model
input_data = {
"input_path": "data.jsonl", # Path to local JSONL file
"dataset": "local",
"data_format": "jsonl",
"column_content": "content",
"custom_config": {
"prompt_list": ["PromptRepeat"], # Prompt to use
"llm_config": {
"detect_text_quality": {
"model": "gpt-4o",
"key": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"api_url": "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions"
}
}
}
}
input_args = InputArgs(**input_data)
executor = Executor.exec_map["local"](input_args)
result = executor.execute()
print(result)python -m dingo.run.cli --input_path data.txt --dataset local -e sft --data_format plaintext --save_data Truepython -m dingo.run.cli --input_path data.json --dataset local -e openai --data_format json --column_content text --custom_config config_gpt.json --save_data TrueExample config_gpt.json:
{
"llm_config": {
"openai": {
"model": "gpt-4o",
"key": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"api_url": "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions"
}
}
}After evaluation (with save_data=True), a frontend page will be automatically generated. To manually start the frontend:
python -m dingo.run.vsl --input output_directoryWhere output_directory contains the evaluation results with a summary.json file.
Try Dingo on our online demo: (Hugging Face)🤗
Dingo classifies data quality issues into 7 dimensions of Quality Metrics. Each dimension can be evaluated using both rule-based methods and LLM-based prompts:
| Quality Metric | Description | Rule Examples | LLM Prompt Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMPLETENESS | Checks if data is incomplete or missing |
RuleColonEnd, RuleContentNull
|
Evaluates if text abruptly ends with a colon or ellipsis, has mismatched parentheses, or missing critical components |
| EFFECTIVENESS | Checks if data is meaningful and properly formatted |
RuleAbnormalChar, RuleHtmlEntity, RuleSpecialCharacter
|
Detects garbled text, words stuck together without spaces, and text lacking proper punctuation |
| FLUENCY | Checks if text is grammatically correct and reads naturally |
RuleAbnormalNumber, RuleNoPunc, RuleWordStuck
|
Identifies excessively long words, text fragments without punctuation, or content with chaotic reading order |
| RELEVANCE | Detects irrelevant content within the data |
RuleHeadWord variants for different languages |
Examines for irrelevant information like citation details, headers/footers, entity markers, HTML tags |
| SECURITY | Identifies sensitive information or value conflicts |
RuleIDCard, RuleUnsafeWords
|
Checks for personal information, and content related to gambling, pornography, political issues |
| SIMILARITY | Detects repetitive or highly similar content | RuleDocRepeat |
Evaluates text for consecutive repeated content or multiple occurrences of special characters |
| UNDERSTANDABILITY | Assesses how easily data can be interpreted | RuleCapitalWords |
Ensures LaTeX formulas and Markdown are correctly formatted, with proper segmentation and line breaks |
Dingo provides several LLM-based assessment methods defined by prompts in the dingo/model/prompt directory. These prompts are registered using the prompt_register decorator and can be combined with LLM models for quality evaluation:
| Prompt Type | Metric | Description |
|---|---|---|
TEXT_QUALITY_V2, TEXT_QUALITY_V3
|
Various quality dimensions | Comprehensive text quality evaluation covering effectiveness, relevance, completeness, understandability, similarity, fluency, and security |
QUALITY_BAD_EFFECTIVENESS |
Effectiveness | Detects garbled text and anti-crawling content |
QUALITY_BAD_SIMILARITY |
Similarity | Identifies text repetition issues |
WORD_STICK |
Fluency | Checks for words stuck together without proper spacing |
CODE_LIST_ISSUE |
Completeness | Evaluates code blocks and list formatting issues |
UNREAD_ISSUE |
Effectiveness | Detects unreadable characters due to encoding issues |
| Prompt Type | Metric | Description |
|---|---|---|
QUALITY_HONEST |
Honesty | Evaluates if responses provide accurate information without fabrication or deception |
QUALITY_HELPFUL |
Helpfulness | Assesses if responses address questions directly and follow instructions appropriately |
QUALITY_HARMLESS |
Harmlessness | Checks if responses avoid harmful content, discriminatory language, and dangerous assistance |
| Prompt Type | Metric | Description |
|---|---|---|
TEXT_QUALITY_KAOTI |
Exam question quality | Specialized assessment for evaluating the quality of exam questions, focusing on formula rendering, table formatting, paragraph structure, and answer formatting |
Html_Abstract |
HTML extraction quality | Compares different methods of extracting Markdown from HTML, evaluating completeness, formatting accuracy, and semantic coherence |
| Prompt Type | Metric | Description |
|---|---|---|
CLASSIFY_TOPIC |
Topic Categorization | Classifies text into categories like language processing, writing, code, mathematics, role-play, or knowledge Q&A |
CLASSIFY_QR |
Image Classification | Identifies images as CAPTCHA, QR code, or normal images |
| Prompt Type | Metric | Description |
|---|---|---|
IMAGE_RELEVANCE |
Image Relevance | Evaluates if an image matches reference image in terms of face count, feature details, and visual elements |
To use these assessment prompts in your evaluations, specify them in your configuration:
input_data = {
# Other parameters...
"custom_config": {
"prompt_list": ["QUALITY_BAD_SIMILARITY"], # Specific prompt to use
"llm_config": {
"detect_text_quality": { # LLM model to use
"model": "gpt-4o",
"key": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"api_url": "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions"
}
}
}
}You can customize these prompts to focus on specific quality dimensions or to adapt to particular domain requirements. When combined with appropriate LLM models, these prompts enable comprehensive evaluation of data quality across multiple dimensions.
Dingo provides pre-configured rule groups for different types of datasets:
| Group | Use Case | Example Rules |
|---|---|---|
default |
General text quality |
RuleColonEnd, RuleContentNull, RuleDocRepeat, etc. |
sft |
Fine-tuning datasets | Rules from default plus RuleLineStartWithBulletpoint
|
pretrain |
Pre-training datasets | Comprehensive set of 20+ rules including RuleAlphaWords, RuleCapitalWords, etc. |
To use a specific rule group:
input_data = {
"eval_group": "sft", # Use "default", "sft", or "pretrain"
# other parameters...
}- Data Sources: Local files, Hugging Face datasets, S3 storage
- Data Types: Pre-training, fine-tuning, and evaluation datasets
- Data Modalities: Text and image
- Built-in Rules: 20+ general heuristic evaluation rules
- LLM Integration: OpenAI, Kimi, and local models (e.g., Llama3)
- Custom Rules: Easily extend with your own rules and models
- Security Evaluation: Perspective API integration
- Interfaces: CLI and SDK options
- Integration: Easy integration with other platforms
- Execution Engines: Local and Spark
- Quality Metrics: 7-dimensional quality assessment
- Traceability: Detailed reports for anomaly tracking
If the built-in rules don't meet your requirements, you can create custom ones:
from dingo.model import Model
from dingo.model.rule.base import BaseRule
from dingo.config.config import DynamicRuleConfig
from dingo.io import MetaData
from dingo.model.modelres import ModelRes
@Model.rule_register('QUALITY_BAD_RELEVANCE', ['default'])
class MyCustomRule(BaseRule):
"""Check for custom pattern in text"""
dynamic_config = DynamicRuleConfig(pattern=r'your_pattern_here')
@classmethod
def eval(cls, input_data: MetaData) -> ModelRes:
res = ModelRes()
# Your rule implementation here
return resfrom dingo.model import Model
from dingo.model.llm.base_openai import BaseOpenAI
@Model.llm_register('my_custom_model')
class MyCustomModel(BaseOpenAI):
# Custom implementation here
passSee more examples in:
from dingo.io import InputArgs
from dingo.exec import Executor
input_args = InputArgs(**input_data)
executor = Executor.exec_map["local"](input_args)
result = executor.execute()
# Get results
summary = executor.get_summary() # Overall evaluation summary
bad_data = executor.get_bad_info_list() # List of problematic data
good_data = executor.get_good_info_list() # List of high-quality datafrom dingo.io import InputArgs
from dingo.exec import Executor
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Initialize Spark
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("Dingo").getOrCreate()
spark_rdd = spark.sparkContext.parallelize([...]) # Your data as MetaData objects
input_args = InputArgs(eval_group="default", save_data=True)
executor = Executor.exec_map["spark"](input_args, spark_session=spark, spark_rdd=spark_rdd)
result = executor.execute()After evaluation, Dingo generates:
-
Summary Report (
summary.json): Overall metrics and scores - Detailed Reports: Specific issues for each rule violation
Example summary:
{
"task_id": "d6c922ec-981c-11ef-b723-7c10c9512fac",
"task_name": "dingo",
"eval_group": "default",
"input_path": "test/data/test_local_jsonl.jsonl",
"output_path": "outputs/d6c921ac-981c-11ef-b723-7c10c9512fac",
"create_time": "20241101_144510",
"score": 50.0,
"num_good": 1,
"num_bad": 1,
"total": 2,
"type_ratio": {
"QUALITY_BAD_COMPLETENESS": 0.5,
"QUALITY_BAD_RELEVANCE": 0.5
},
"name_ratio": {
"QUALITY_BAD_COMPLETENESS-RuleColonEnd": 0.5,
"QUALITY_BAD_RELEVANCE-RuleSpecialCharacter": 0.5
}
}- [ ] Richer graphic and text evaluation indicators
- [ ] Audio and video data modality evaluation
- [ ] Small model evaluation (fasttext, Qurating)
- [ ] Data diversity evaluation
The current built-in detection rules and model methods focus on common data quality problems. For specialized evaluation needs, we recommend customizing detection rules.
We appreciate all the contributors for their efforts to improve and enhance Dingo. Please refer to the Contribution Guide for guidance on contributing to the project.
This project uses the Apache 2.0 Open Source License.
If you find this project useful, please consider citing our tool:
@misc{dingo,
title={Dingo: A Comprehensive Data Quality Evaluation Tool for Large Models},
author={Dingo Contributors},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/DataEval/dingo}},
year={2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for dingo
Similar Open Source Tools

dingo
Dingo is a data quality evaluation tool that automatically detects data quality issues in datasets. It provides built-in rules and model evaluation methods, supports text and multimodal datasets, and offers local CLI and SDK usage. Dingo is designed for easy integration into evaluation platforms like OpenCompass.
sgr-deep-research
This repository contains a deep learning research project focused on natural language processing tasks. It includes implementations of various state-of-the-art models and algorithms for text classification, sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, and more. The project aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and developers interested in exploring deep learning techniques for NLP applications.
LightRAG
LightRAG is a repository hosting the code for LightRAG, a system that supports seamless integration of custom knowledge graphs, Oracle Database 23ai, Neo4J for storage, and multiple file types. It includes features like entity deletion, batch insert, incremental insert, and graph visualization. LightRAG provides an API server implementation for RESTful API access to RAG operations, allowing users to interact with it through HTTP requests. The repository also includes evaluation scripts, code for reproducing results, and a comprehensive code structure.
UHGEval
UHGEval is a comprehensive framework designed for evaluating the hallucination phenomena. It includes UHGEval, a framework for evaluating hallucination, XinhuaHallucinations dataset, and UHGEval-dataset pipeline for creating XinhuaHallucinations. The framework offers flexibility and extensibility for evaluating common hallucination tasks, supporting various models and datasets. Researchers can use the open-source pipeline to create customized datasets. Supported tasks include QA, dialogue, summarization, and multi-choice tasks.
FDAbench
FDABench is a benchmark tool designed for evaluating data agents' reasoning ability over heterogeneous data in analytical scenarios. It offers 2,007 tasks across various data sources, domains, difficulty levels, and task types. The tool provides ready-to-use data agent implementations, a DAG-based evaluation system, and a framework for agent-expert collaboration in dataset generation. Key features include data agent implementations, comprehensive evaluation metrics, multi-database support, different task types, extensible framework for custom agent integration, and cost tracking. Users can set up the environment using Python 3.10+ on Linux, macOS, or Windows. FDABench can be installed with a one-command setup or manually. The tool supports API configuration for LLM access and offers quick start guides for database download, dataset loading, and running examples. It also includes features like dataset generation using the PUDDING framework, custom agent integration, evaluation metrics like accuracy and rubric score, and a directory structure for easy navigation.
CrackSQL
CrackSQL is a powerful SQL dialect translation tool that integrates rule-based strategies with large language models (LLMs) for high accuracy. It enables seamless conversion between dialects (e.g., PostgreSQL → MySQL) with flexible access through Python API, command line, and web interface. The tool supports extensive dialect compatibility, precision & advanced processing, and versatile access & integration. It offers three modes for dialect translation and demonstrates high translation accuracy over collected benchmarks. Users can deploy CrackSQL using PyPI package installation or source code installation methods. The tool can be extended to support additional syntax, new dialects, and improve translation efficiency. The project is actively maintained and welcomes contributions from the community.
augustus
Augustus is a Go-based LLM vulnerability scanner designed for security professionals to test large language models against a wide range of adversarial attacks. It integrates with 28 LLM providers, covers 210+ adversarial attacks including prompt injection, jailbreaks, encoding exploits, and data extraction, and produces actionable vulnerability reports. The tool is built for production security testing with features like concurrent scanning, rate limiting, retry logic, and timeout handling out of the box.
dspy.rb
DSPy.rb is a Ruby framework for building reliable LLM applications using composable, type-safe modules. It enables developers to define typed signatures and compose them into pipelines, offering a more structured approach compared to traditional prompting. The framework embraces Ruby conventions and adds innovations like CodeAct agents and enhanced production instrumentation, resulting in scalable LLM applications that are robust and efficient. DSPy.rb is actively developed, with a focus on stability and real-world feedback through the 0.x series before reaching a stable v1.0 API.
Neosgenesis
Neogenesis System is an advanced AI decision-making framework that enables agents to 'think about how to think'. It implements a metacognitive approach with real-time learning, tool integration, and multi-LLM support, allowing AI to make expert-level decisions in complex environments. Key features include metacognitive intelligence, tool-enhanced decisions, real-time learning, aha-moment breakthroughs, experience accumulation, and multi-LLM support.
mcp-omnisearch
mcp-omnisearch is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that acts as a unified gateway to multiple search providers and AI tools. It integrates Tavily, Perplexity, Kagi, Jina AI, Brave, Exa AI, and Firecrawl to offer a wide range of search, AI response, content processing, and enhancement features through a single interface. The server provides powerful search capabilities, AI response generation, content extraction, summarization, web scraping, structured data extraction, and more. It is designed to work flexibly with the API keys available, enabling users to activate only the providers they have keys for and easily add more as needed.
paperbanana
PaperBanana is an automated academic illustration tool designed for AI scientists. It implements an agentic framework for generating publication-quality academic diagrams and statistical plots from text descriptions. The tool utilizes a two-phase multi-agent pipeline with iterative refinement, Gemini-based VLM planning, and image generation. It offers a CLI, Python API, and MCP server for IDE integration, along with Claude Code skills for generating diagrams, plots, and evaluating diagrams. PaperBanana is not affiliated with or endorsed by the original authors or Google Research, and it may differ from the original system described in the paper.
LocalAGI
LocalAGI is a powerful, self-hostable AI Agent platform that allows you to design AI automations without writing code. It provides a complete drop-in replacement for OpenAI's Responses APIs with advanced agentic capabilities. With LocalAGI, you can create customizable AI assistants, automations, chat bots, and agents that run 100% locally, without the need for cloud services or API keys. The platform offers features like no-code agents, web-based interface, advanced agent teaming, connectors for various platforms, comprehensive REST API, short & long-term memory capabilities, planning & reasoning, periodic tasks scheduling, memory management, multimodal support, extensible custom actions, fully customizable models, observability, and more.
factorio-learning-environment
Factorio Learning Environment is an open source framework designed for developing and evaluating LLM agents in the game of Factorio. It provides two settings: Lab-play with structured tasks and Open-play for building large factories. Results show limitations in spatial reasoning and automation strategies. Agents interact with the environment through code synthesis, observation, action, and feedback. Tools are provided for game actions and state representation. Agents operate in episodes with observation, planning, and action execution. Tasks specify agent goals and are implemented in JSON files. The project structure includes directories for agents, environment, cluster, data, docs, eval, and more. A database is used for checkpointing agent steps. Benchmarks show performance metrics for different configurations.
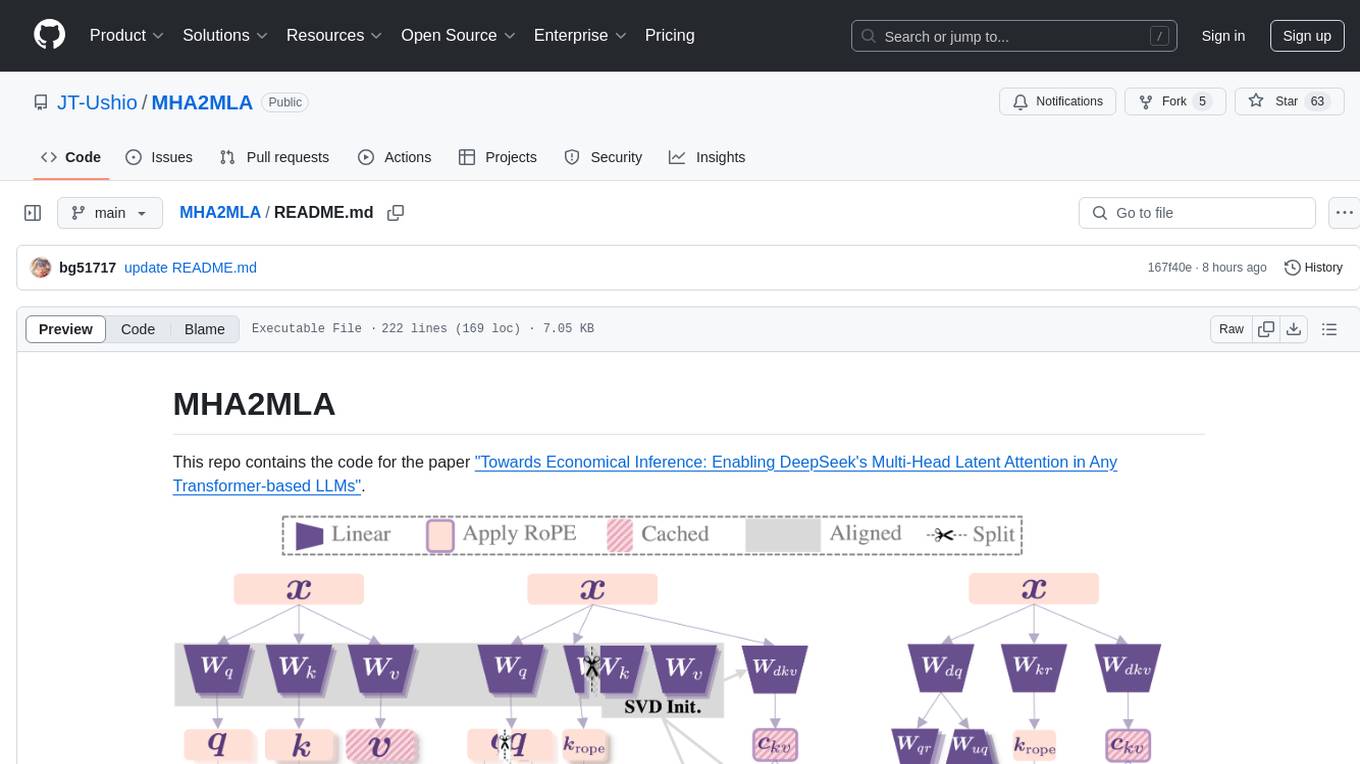
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
mcp-documentation-server
The mcp-documentation-server is a lightweight server application designed to serve documentation files for projects. It provides a simple and efficient way to host and access project documentation, making it easy for team members and stakeholders to find and reference important information. The server supports various file formats, such as markdown and HTML, and allows for easy navigation through the documentation. With mcp-documentation-server, teams can streamline their documentation process and ensure that project information is easily accessible to all involved parties.
quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
For similar tasks

dingo
Dingo is a data quality evaluation tool that automatically detects data quality issues in datasets. It provides built-in rules and model evaluation methods, supports text and multimodal datasets, and offers local CLI and SDK usage. Dingo is designed for easy integration into evaluation platforms like OpenCompass.
For similar jobs

dingo
Dingo is a data quality evaluation tool that automatically detects data quality issues in datasets. It provides built-in rules and model evaluation methods, supports text and multimodal datasets, and offers local CLI and SDK usage. Dingo is designed for easy integration into evaluation platforms like OpenCompass.
rhesis
Rhesis is a comprehensive test management platform designed for Gen AI teams, offering tools to create, manage, and execute test cases for generative AI applications. It ensures the robustness, reliability, and compliance of AI systems through features like test set management, automated test generation, edge case discovery, compliance validation, integration capabilities, and performance tracking. The platform is open source, emphasizing community-driven development, transparency, extensible architecture, and democratizing AI safety. It includes components such as backend services, frontend applications, SDK for developers, worker services, chatbot applications, and Polyphemus for uncensored LLM service. Rhesis enables users to address challenges unique to testing generative AI applications, such as non-deterministic outputs, hallucinations, edge cases, ethical concerns, and compliance requirements.

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.












