
LLMVoX
LLMVoX: Autoregressive Streaming Text-to-Speech Model for Any LLM
Stars: 167
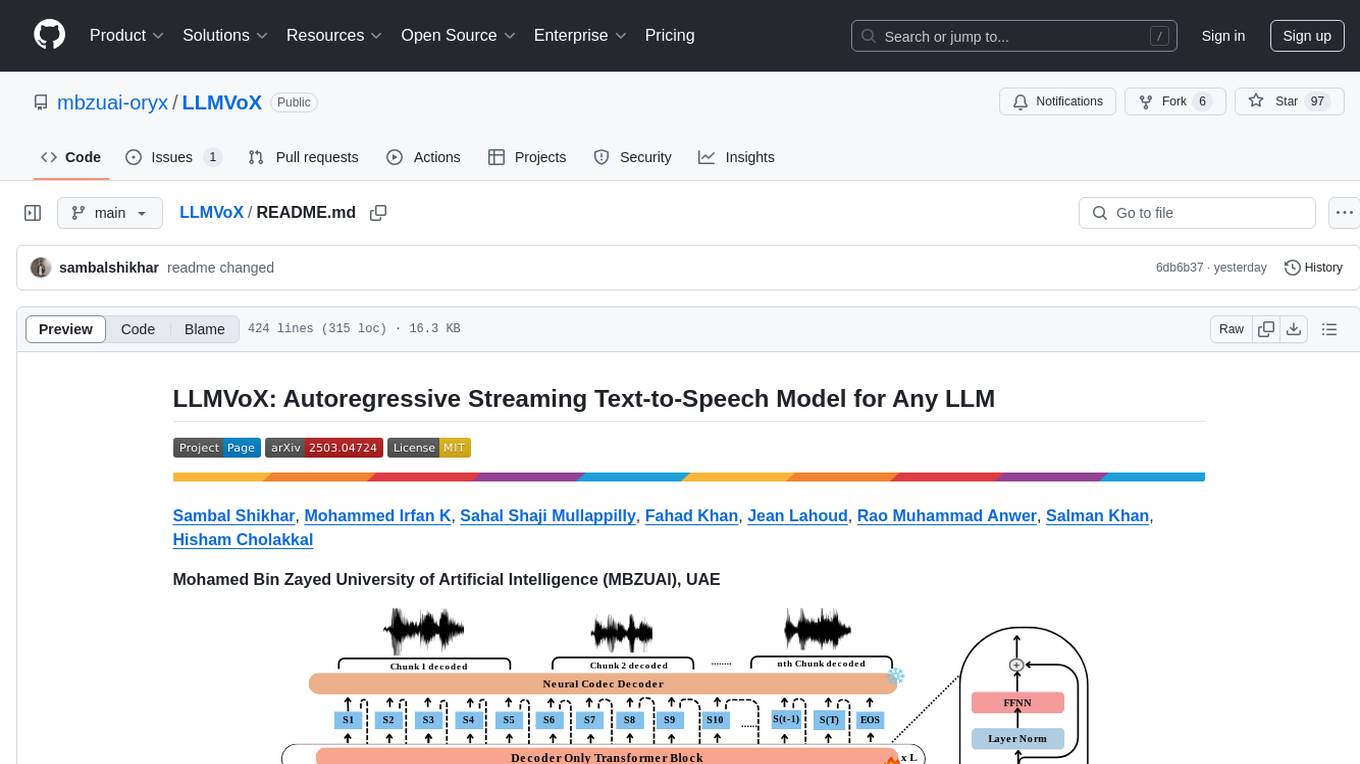
LLMVoX is a lightweight 30M-parameter, LLM-agnostic, autoregressive streaming Text-to-Speech (TTS) system designed to convert text outputs from Large Language Models into high-fidelity streaming speech with low latency. It achieves significantly lower Word Error Rate compared to speech-enabled LLMs while operating at comparable latency and speech quality. Key features include being lightweight & fast with only 30M parameters, LLM-agnostic for easy integration with existing models, multi-queue streaming for continuous speech generation, and multilingual support for easy adaptation to new languages.
README:
Sambal Shikhar, Mohammed Irfan K, Sahal Shaji Mullappilly, Fahad Khan, Jean Lahoud, Rao Muhammad Anwer, Salman Khan, Hisham Cholakkal
Mohamed Bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (MBZUAI), UAE
LLMVoX is a lightweight 30M-parameter, LLM-agnostic, autoregressive streaming Text-to-Speech (TTS) system designed to convert text outputs from Large Language Models into high-fidelity streaming speech with low latency. Our approach achieves significantly lower Word Error Rate compared to speech-enabled LLMs while operating at comparable latency and speech quality.
Key features:
- 🚀 Lightweight & Fast: Only 30M parameters, delivering speech with end-to-end latency as low as 300ms
- 🔌 LLM-Agnostic: Just plug with any existing LLM and Vision-Language Models without requiring fine-tuning or architectural modifications.
- 🌊 Multi-Queue Streaming: Enables continuous, low-latency speech generation and infinite-length dialogues
- 🌐 Multilingual Support: Easily adaptable to new languages with only dataset adaptation
# System requirements
# - CUDA 11.7 or higher
# - Flash Attention 2.0+ compatible GPU (Ampere architecture or newer)
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/LLMVoX.git
cd LLMVoX
# Create and activate a conda environment
conda create -n llmvox python=3.9
conda activate llmvox
# Install PyTorch with CUDA 11.8 support
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
# Install Flash Attention
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
# Install remaining dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Add path to wavtokenizer to avoid importing errors
export PYTHONPATH=./WavTokenizer/:$PYTHONPATH
# Download checkpoints (if not already in the repository)
mkdir -p CHECKPOINTS
# Download wavtokenizer_large_speech_320_24k.ckpt and ckpt_english_tiny.pt
# and place them in the CHECKPOINTS directoryDownload the necessary model checkpoints from Hugging Face:
🤗 Hugging Face Repository: MBZUAI/LLMVoX
LLMVoX requires a few base paths to be set correctly in the inference configuration file at configs/inference_config.py:
-
wavtokenizer_model_path: Path to the pretrained WavTokenizer model checkpoint -
llmvox_checkpoint_path: Path to the trained LLMVoX model checkpoint
LLMVoX supports voice-based conversations through its streaming server. Here's how to configure and use the voice chat functionality:
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct"LLMVoX uses a multi-queue approach with two TTS model replicas. You can specify which GPUs to use:
# Run TTS models on separate GPUs
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --tts_device_1 1 --tts_device_2 2
# Or run both on the same GPU (if memory allows)
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --tts_device_1 0 --tts_device_2 0
# Specify GPU for LLM separately
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --llm_device "cuda:0" --tts_device_1 1 --tts_device_2 2Control the balance between latency and quality:
# Lower latency setup (faster initial response but potentially lower quality)
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --initial_dump_size_1 5 --initial_dump_size_2 40 --max_dump_size 320
# Higher quality setup (slightly higher latency but better speech)
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --initial_dump_size_1 20 --initial_dump_size_2 320 --max_dump_size 2560
# Default balanced setup
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --initial_dump_size_1 10 --initial_dump_size_2 160 --max_dump_size 1280-
initial_dump_size_1: Number of speech tokens for the first chunk (smaller = faster first response) -
initial_dump_size_2: Initial chunk size for the second TTS model (can be larger as it runs while first chunk plays) -
max_dump_size: Maximum chunk size that the system will scale up to (larger = better quality)
Different LLMs use different end-of-sequence tokens:
# For LLaMA models
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --eos_token "<|eot_id|>" --llm_max_tokens 1000
# For Mistral models
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2" --eos_token "<|im_end|>" --llm_temperature 0.7
# For other models (check your model's documentation)
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "your-model-name" --eos_token "<|end|>"LLMVoX uses Whisper for converting speech to text:
# Use a larger Whisper model for better transcription
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --asr_model "medium" --asr_device "cuda:3"
# Use a smaller model for faster processing
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --asr_model "tiny" --asr_device "cuda:0"Control the LLM's response style:
# For concise responses
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --system_prompt "You are a friendly voicebot that answers questions in a concise way and do not use abbreviation. Keep responses brief."
# For more detailed explanations
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --system_prompt "You are a helpful AI assistant that provides detailed, thorough explanations. Avoid abbreviations when speaking."Here's a complete example with all key parameters configured:
python streaming_server.py \
--chat_type voice \
--llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" \
--llm_device "cuda:0" \
--tts_device_1 1 \
--tts_device_2 2 \
--asr_model "small" \
--asr_device "cuda:3" \
--initial_dump_size_1 10 \
--initial_dump_size_2 160 \
--max_dump_size 1280 \
--max_audio_length 8000 \
--eos_token "<|eot_id|>" \
--system_prompt "You are a friendly voicebot that answers questions concisely without abbreviations."When you run voice chat:
- The ASR model transcribes your speech input
- The LLM generates a response text stream
- Two LLMVoX instances alternate processing text chunks at sentence boundaries
- Initial chunks are smaller for faster response, while later chunks are larger for better quality
- Audio is played in real-time while the rest of the response is still being generated
This multi-queue architecture enables both low latency (as fast as 300ms) and high-quality speech output.
# Basic text chat with LLaMA 3.1 8B
python streaming_server.py --chat_type text --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --llm_device "cuda:0"
# Customize LLM generation parameters
python streaming_server.py --chat_type text --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --llm_temperature 0.5 --llm_top_p 0.9 --llm_top_k 30# Using Qwen 2.5 VL as the vision-language model
python streaming_server.py --chat_type visual_speech --llm_checkpoint "Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct" --llm_device "cuda:0" --asr_model "small" --eos_token "<|im_end|>"# Using Phi-4-multimodal-instruct which has multimodal input with speech , images and text
python streaming_server.py --chat_type multimodal --llm_checkpoint "microsoft/Phi-4-multimodal-instruct" --llm_device "cuda:0" --sytem_prompt ""Answer the question in short responses." --eos_token "<|end|>"
# Using LLaVA
python streaming_server.py --chat_type multimodal --llm_checkpoint "llava-hf/llava-1.5-7b-hf" --llm_device "cuda:0"Once the streaming server starts , the following is the client side API reference.
| Endpoint | Purpose | Required Parameters |
|---|---|---|
/tts |
Text-to-speech |
text: String to convert |
/voicechat |
Voice conversations |
audio_base64: Encoded speechsource_language: Input language for Whisper ASRtarget_language: Output language for Whisper ASR |
/multimodalchat |
Voice + multiple images |
audio_base64: Encoded speechimage_list: Array of base64 images |
/vlmschat |
Voice + single image |
audio_base64: Encoded speechimage_base64: Single imagesource_language: Input language for Whisper ASRtarget_language: Output language for Whisper ASR |
# Text-to-Speech
api_call("tts", {"text": "Hello world"})
# Voice Chat
api_call("voicechat", {
"audio_base64": audio_data,
"source_language": "English",
"target_language": "English"
})
# Multimodal Chat (voice + images) for models like Phi-4-multimodal-instruct
api_call("multimodalchat", {
"audio_base64": audio_data,
"image_list": [image_base64]
})
# Visual Language Model (voice + image)
api_call("vlmschat", {
"audio_base64": audio_data,
"image_base64": image_base64,
"source_language": "English",
"target_language": "English"
})import threading
import queue
import requests
import torch
import torchaudio
import numpy as np
from pyaudio import PyAudio, paFloat32
import time
def tts(text, SERVER_IP,PORT,audio_outpath='output_audio.wav'):
server_ip = SERVER_IP
endpoint = f'http://{server_ip}:PORT/tts'
# Audio playback parameters
sample_rate = 24000
channels = 1
chunk_size = 10000
frames_per_buffer = 10000 # Must match the server's chunk size if possible
audio_queue = queue.Queue() # Buffer for audio playback
audio_chunks = [] # Buffer to store audio for saving
start=time.time()
def stream_audio():
"""Streams audio from the server and enqueues it for playback and saving."""
try:
with requests.post(endpoint, json={"text": text}, stream=True) as stream:
stream.raise_for_status() # Raise an error for bad status codes
for chunk in stream.iter_content(chunk_size=None):
if chunk:
try:
# Enqueue the chunk for playback
print(f"Got chunk at {time.time()-start}")
audio_queue.put(chunk, timeout=1)
# Store the chunk for saving
audio_chunks.append(chunk)
except queue.Full:
print("Audio queue is full. Dropping chunk.")
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"RequestException: {e}")
finally:
# Signal the end of streaming
audio_queue.put(None)
def play_audio():
"""Plays audio chunks from the queue using PyAudio."""
p = PyAudio()
try:
player = p.open(format=paFloat32,
channels=channels,
rate=sample_rate,
output=True,)
while True:
chunk = audio_queue.get()
if chunk is None:
print("End of streaming.")
break # End of streaming
if not chunk:
print("Received an empty chunk. Skipping.")
continue # Skip empty chunks
try:
print("Playing chunk")
player.write(chunk)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error during playback: {e}")
break
finally:
player.stop_stream()
player.close()
p.terminate()
# Start streaming and playback in separate threads
stream_thread = threading.Thread(target=stream_audio, daemon=True)
play_thread = threading.Thread(target=play_audio, daemon=True)
stream_thread.start()
play_thread.start()
# Wait for both threads to finish
stream_thread.join()
play_thread.join()
# After streaming is complete, process and save the audio
if audio_chunks:
print("Saving audio to file...")
# Concatenate all audio kjb jb into a single bytes object
audio_bytes = b''.join(audio_chunks)
# Convert bytes to a NumPy array of float32
audio_np = np.frombuffer(audio_bytes, dtype=np.float32)
# Optional: Normalize if necessary
# Uncomment the following lines if you need to normalize the audio
# max_val = np.max(np.abs(audio_np))
# if max_val > 1.0:
# audio_np = audio_np / max_val
# Reshape the array to (channels, samples)
if channels > 1:
audio_np = audio_np.reshape(-1, channels).T # Transpose to (channels, samples)
else:
audio_np = audio_np.reshape(1, -1) # (1, samples)
# Convert float32 to int16 for 'PCM_S' encoding
# Ensure the float32 data is in the range [-1.0, 1.0]
audio_np = np.clip(audio_np, -1.0, 1.0)
audio_int16 = (audio_np * 32767).astype(np.int16)
# Convert NumPy array to PyTorch tensor
audio_tensor = torch.from_numpy(audio_int16)
# Save the audio using torchaudio with specified settings
try:
torchaudio.save(
audio_outpath,
audio_tensor,
sample_rate=sample_rate,
encoding='PCM_S',
bits_per_sample=16,
format='wav'
)
print(f"Audio successfully saved to {audio_outpath}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error saving audio: {e}")
else:
print("No audio chunks received. Nothing to save.")
if __name__ == '__main__':
text="hello how are you?"
tts(text,SERVER_IP,PORT,audio_outpath="output.wav")You can easily create text-streamer for your custom model and integrate it with LLMVoX in streaming_server.py , refer to inference folder to see the streamer template for LLMs ,VLMs and Multimodal LLMs.
This local demo UI is built using PyQt5.
#Run a streaming server
python streaming_server.py --chat_type voice --llm_checkpoint "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --eos_token "<|eot_id|>" --llm_max_tokens 1000 --api_port PORT
#Run local demo UI
python run_ui.py --ip STREAMING_SERVER_IP --port PORT
- Voice Chat
- Text Chat
- Visual Speech
- Dataset: VoiceAssistant-400K
- Format: JSON file with entries mapping text to audio files:
[
{
"speech_folder": "/path/to/audio/files",
"speech_file": "audio1.wav",
"answer_text": "Text transcript",
"id": "unique_id_1"
}
]The training configuration is in configs/train_config.py:
-
Model Architecture:
-
n_layer: Number of transformer layers (default: 4) -
n_head: Number of attention heads (default: 8) -
n_embd: Embedding dimension (default: 768) -
block_size: Context length (default: 8192)
-
-
Training Settings:
-
gradient_accumulation_steps: Accumulate gradients before updating (default: 4) -
batch_size: Batch size per GPU (default: 2) -
learning_rate: Peak learning rate (default: 3e-4) -
max_iters: Maximum iterations (default: 2600000)
-
-
Paths:
-
data_path: Path to dataset JSON -
speech_data_folder: Path to audio files -
out_dir: Output directory for checkpoints -
encoder_model_path: Path to ByT5 model for multilingual grapheme-to-phoneme conversion from CharsiuG2P that provides phoneme embeddings for words
-
python train.py \
--n_layer=4 \
--n_head=8 \
--n_embd=768 \
--block_size=8192 \
--dropout=0.0 \
--bias=False \
--data_path="/path/to/dataset.json" \
--speech_data_folder="/path/to/audio_files" \
--encoder_model_path="charsiu/g2p_multilingual_byT5_tiny_16_layers_100" \
--tokenizer_path="google/byt5-small" \
--wav_config_path="WavTokenizer/configs/wavtokenizer_smalldata_frame75_3s_nq1_code4096_dim512_kmeans200_attn.yaml" \
--wav_model_path="/path/to/wavtokenizer_large_speech_320_24k.ckpt" \
--out_dir="my_llmvox_model" \
--batch_size=2 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps=4 \
--learning_rate=3e-4 \
--weight_decay=1e-1 \
--warmup_iters=50000 \
--lr_decay_iters=2600000 \
--min_lr=3e-6 \
--eval_interval=1000 \
--compile=True \
--wandb_log=True \
--wandb_project="speech_stream" \
--wandb_run_name="llmvox_training_run"This comprehensive command shows all configurable parameters for training a LLMVoX model. Adjust values based on your hardware capabilities and specific requirements.
#Single GPU
python train.py --batch_size=8 --learning_rate=5e-5 --n_layer=6
#Distributed Training
torchrun --standalone --nproc_per_node=4 train.py --batch_size=16If you find our work useful, please consider citing:
@article{shikhar2025llmvox,
title={LLMVoX: Autoregressive Streaming Text-to-Speech Model for Any LLM},
author={Shikhar, Sambal and Kurpath, Mohammed Irfan and Mullappilly, Sahal Shaji and Lahoud, Jean and Khan, Fahad and Anwer, Rao Muhammad and Khan, Salman and Cholakkal, Hisham},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.04724},
year={2025}
}LLMVoX is released under the CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 License. For more details, please refer to the LICENSE file included in this repository.
We thank the reviewers and colleagues who provided valuable feedback on this work. We also acknowledge the open-source contributions that made this project possible:
- Andrej Karpathy's NanoGPT - Training code for LLMVoX is based on this repository
- WavTokenizer - For audio tokenization
- Whisper - Used for ASR in our pipeline
- Neural G2P - For the multilingual phoneme embeddings
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLMVoX
Similar Open Source Tools

LLMVoX
LLMVoX is a lightweight 30M-parameter, LLM-agnostic, autoregressive streaming Text-to-Speech (TTS) system designed to convert text outputs from Large Language Models into high-fidelity streaming speech with low latency. It achieves significantly lower Word Error Rate compared to speech-enabled LLMs while operating at comparable latency and speech quality. Key features include being lightweight & fast with only 30M parameters, LLM-agnostic for easy integration with existing models, multi-queue streaming for continuous speech generation, and multilingual support for easy adaptation to new languages.
aiavatarkit
AIAvatarKit is a tool for building AI-based conversational avatars quickly. It supports various platforms like VRChat and cluster, along with real-world devices. The tool is extensible, allowing unlimited capabilities based on user needs. It requires VOICEVOX API, Google or Azure Speech Services API keys, and Python 3.10. Users can start conversations out of the box and enjoy seamless interactions with the avatars.
pocketgroq
PocketGroq is a tool that provides advanced functionalities for text generation, web scraping, web search, and AI response evaluation. It includes features like an Autonomous Agent for answering questions, web crawling and scraping capabilities, enhanced web search functionality, and flexible integration with Ollama server. Users can customize the agent's behavior, evaluate responses using AI, and utilize various methods for text generation, conversation management, and Chain of Thought reasoning. The tool offers comprehensive methods for different tasks, such as initializing RAG, error handling, and tool management. PocketGroq is designed to enhance development processes and enable the creation of AI-powered applications with ease.
mlx-vlm
MLX-VLM is a package designed for running Vision LLMs on Mac systems using MLX. It provides a convenient way to install and utilize the package for processing large language models related to vision tasks. The tool simplifies the process of running LLMs on Mac computers, offering a seamless experience for users interested in leveraging MLX for vision-related projects.
alexandria-audiobook
Alexandria Audiobook Generator is a tool that transforms any book or novel into a fully-voiced audiobook using AI-powered script annotation and text-to-speech. It features a built-in Qwen3-TTS engine with batch processing and a browser-based editor for fine-tuning every line before final export. The tool offers AI-powered pipeline for automatic script annotation, smart chunking, and context preservation. It also provides voice generation capabilities with built-in TTS engine, multi-language support, custom voices, voice cloning, and LoRA voice training. The web UI editor allows users to edit, preview, and export the audiobook. Export options include combined audiobook, individual voicelines, and Audacity export for DAW editing.
quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
openvino.genai
The GenAI repository contains pipelines that implement image and text generation tasks. The implementation uses OpenVINO capabilities to optimize the pipelines. Each sample covers a family of models and suggests certain modifications to adapt the code to specific needs. It includes the following pipelines: 1. Benchmarking script for large language models 2. Text generation C++ samples that support most popular models like LLaMA 2 3. Stable Diffuison (with LoRA) C++ image generation pipeline 4. Latent Consistency Model (with LoRA) C++ image generation pipeline
candle-vllm
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.

clarifai-python
The Clarifai Python SDK offers a comprehensive set of tools to integrate Clarifai's AI platform to leverage computer vision capabilities like classification , detection ,segementation and natural language capabilities like classification , summarisation , generation , Q&A ,etc into your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can leverage cutting-edge artificial intelligence to unlock valuable insights from visual and textual content.
UnrealGenAISupport
The Unreal Engine Generative AI Support Plugin is a tool designed to integrate various cutting-edge LLM/GenAI models into Unreal Engine for game development. It aims to simplify the process of using AI models for game development tasks, such as controlling scene objects, generating blueprints, running Python scripts, and more. The plugin currently supports models from organizations like OpenAI, Anthropic, XAI, Google Gemini, Meta AI, Deepseek, and Baidu. It provides features like API support, model control, generative AI capabilities, UI generation, project file management, and more. The plugin is still under development but offers a promising solution for integrating AI models into game development workflows.
llm-sandbox
LLM Sandbox is a lightweight and portable sandbox environment designed to securely execute large language model (LLM) generated code in a safe and isolated manner using Docker containers. It provides an easy-to-use interface for setting up, managing, and executing code in a controlled Docker environment, simplifying the process of running code generated by LLMs. The tool supports multiple programming languages, offers flexibility with predefined Docker images or custom Dockerfiles, and allows scalability with support for Kubernetes and remote Docker hosts.
instructor
Instructor is a tool that provides structured outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs) in a reliable manner. It simplifies the process of extracting structured data by utilizing Pydantic for validation, type safety, and IDE support. With Instructor, users can define models and easily obtain structured data without the need for complex JSON parsing, error handling, or retries. The tool supports automatic retries, streaming support, and extraction of nested objects, making it production-ready for various AI applications. Trusted by a large community of developers and companies, Instructor is used by teams at OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, AWS, and YC startups.
LightRAG
LightRAG is a repository hosting the code for LightRAG, a system that supports seamless integration of custom knowledge graphs, Oracle Database 23ai, Neo4J for storage, and multiple file types. It includes features like entity deletion, batch insert, incremental insert, and graph visualization. LightRAG provides an API server implementation for RESTful API access to RAG operations, allowing users to interact with it through HTTP requests. The repository also includes evaluation scripts, code for reproducing results, and a comprehensive code structure.

acte
Acte is a framework designed to build GUI-like tools for AI Agents. It aims to address the issues of cognitive load and freedom degrees when interacting with multiple APIs in complex scenarios. By providing a graphical user interface (GUI) for Agents, Acte helps reduce cognitive load and constraints interaction, similar to how humans interact with computers through GUIs. The tool offers APIs for starting new sessions, executing actions, and displaying screens, accessible via HTTP requests or the SessionManager class.
Groq2API
Groq2API is a REST API wrapper around the Groq2 model, a large language model trained by Google. The API allows you to send text prompts to the model and receive generated text responses. The API is easy to use and can be integrated into a variety of applications.
mcp-documentation-server
The mcp-documentation-server is a lightweight server application designed to serve documentation files for projects. It provides a simple and efficient way to host and access project documentation, making it easy for team members and stakeholders to find and reference important information. The server supports various file formats, such as markdown and HTML, and allows for easy navigation through the documentation. With mcp-documentation-server, teams can streamline their documentation process and ensure that project information is easily accessible to all involved parties.
For similar tasks
SirChatalot
A Telegram bot that proves you don't need a body to have a personality. It can use various text and image generation APIs to generate responses to user messages. For text generation, the bot can use: * OpenAI's ChatGPT API (or other compatible API). Vision capabilities can be used with GPT-4 models. Function calling can be used with Function calling. * Anthropic's Claude API. Vision capabilities can be used with Claude 3 models. Function calling can be used with tool use. * YandexGPT API Bot can also generate images with: * OpenAI's DALL-E * Stability AI * Yandex ART This bot can also be used to generate responses to voice messages. Bot will convert the voice message to text and will then generate a response. Speech recognition can be done using the OpenAI's Whisper model. To use this feature, you need to install the ffmpeg library. This bot is also support working with files, see Files section for more details. If function calling is enabled, bot can generate images and search the web (limited).
Chat-With-RTX-python-api
This repository contains a Python API for Chat With RTX, which allows users to interact with RTX models for natural language processing. The API provides functionality to send messages and receive responses from various LLM models. It also includes information on the speed of different models supported by Chat With RTX. The repository has a history of updates, including the removal of a feature and the addition of a new model for speech-to-text conversion. The repository is licensed under CC0.

LLMVoX
LLMVoX is a lightweight 30M-parameter, LLM-agnostic, autoregressive streaming Text-to-Speech (TTS) system designed to convert text outputs from Large Language Models into high-fidelity streaming speech with low latency. It achieves significantly lower Word Error Rate compared to speech-enabled LLMs while operating at comparable latency and speech quality. Key features include being lightweight & fast with only 30M parameters, LLM-agnostic for easy integration with existing models, multi-queue streaming for continuous speech generation, and multilingual support for easy adaptation to new languages.
omniai
OmniAI provides a unified Ruby API for integrating with multiple AI providers, streamlining AI development by offering a consistent interface for features such as chat, text-to-speech, speech-to-text, and embeddings. It ensures seamless interoperability across platforms and effortless switching between providers, making integrations more flexible and reliable.
autonomous-intelligence
Tau is an autonomous robot project inspired by Pi.AI, designed for continual conversation with a single context. It features speech-based interaction, memory management, and integration with vision services. The project aims to create a local AI companion with personality, suitable for experimentation and development. Key components include long and immediate memory, speech-to-text and text-to-speech capabilities, and integration with Nvidia Jetson and Hailo vision services. Tau is open-source and encourages community contributions and experimentation.
whispering-ui
Whispering Tiger UI is a Native-UI tool designed to control the Whispering Tiger application, a free and Open-Source tool that can listen/watch to audio streams or in-game images on your machine and provide transcription or translation to a web browser using Websockets or over OSC. It features a Native-UI for Windows, easy access to all Whispering Tiger features including transcription, translation, text-to-speech, and in-game image recognition. The tool supports loopback audio device, configuration saving/loading, plugin support for additional features, and auto-update functionality. Users can create profiles, configure audio devices, select A.I. devices for speech-to-text, and install/manage plugins for extended functionality.
llama_index
LlamaIndex is a data framework for building LLM applications. It provides tools for ingesting, structuring, and querying data, as well as integrating with LLMs and other tools. LlamaIndex is designed to be easy to use for both beginner and advanced users, and it provides a comprehensive set of features for building LLM applications.
kor
Kor is a prototype tool designed to help users extract structured data from text using Language Models (LLMs). It generates prompts, sends them to specified LLMs, and parses the output. The tool works with the parsing approach and is integrated with the LangChain framework. Kor is compatible with pydantic v2 and v1, and schema is typed checked using pydantic. It is primarily used for extracting information from text based on provided reference examples and schema documentation. Kor is designed to work with all good-enough LLMs regardless of their support for function/tool calling or JSON modes.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.




