
mcp
[beta] Use Semgrep in LLMs using MCP framework
Stars: 58

Semgrep MCP Server is a beta server under active development for using Semgrep to scan code for security vulnerabilities. It provides a Model Context Protocol (MCP) for various coding tools to get specialized help in tasks. Users can connect to Semgrep AppSec Platform, scan code for vulnerabilities, customize Semgrep rules, analyze and filter scan results, and compare results. The tool is published on PyPI as semgrep-mcp and can be installed using pip, pipx, uv, poetry, or other methods. It supports CLI and Docker environments for running the server. Integration with VS Code is also available for quick installation. The project welcomes contributions and is inspired by core technologies like Semgrep and MCP, as well as related community projects and tools.
README:
This beta Semgrep mcp server is under active development, we would love your feedback, bug reports, feature requests. For more support, join our community slack >
#mcpchannel.
A MCP server for using Semgrep to scan code for security vulnerabilies.
uvx semgrep-mcp -t sseexample Cursor mcp.json config:
{
"mcpServers": {
"semgrep": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["semgrep-mcp"]
}
}
}
Model Context Protocul (MCP) is like Unix pipes or an API for LLMs, agents, and coding tools like Cursor, VS Code, Windsurf, Claude, or any other tool that support MCP, to get specialized help doing a task by using a tool.
To optionally connect to Semgrep AppSec Platform:
- Login or sign up
- Generate a token from Settings page
- Add it to your environment variables
CLI (
export SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN=<token>)Docker (
docker run -e SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN=<token>)MCP Config JSON
"env": { "SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN": "<token>" }Semgrep will automatically use the API token to connect and use the remote configuration. Please reach out to [email protected] if you have any problems.
Scanning Code
-
semgrep_scan: Scan code snippets for security vulnerabilities -
scan_directory: Perform Semgrep scan on a directory
Customization
-
list_rules: List available Semgrep rules with optional language filtering -
create_rule: Create custom Semgrep rules
Results
-
analyze_results: Analyze scan results including severity counts and top affected files -
filter_results: Filter scan results by severity, rule ID, file path, etc. -
export_results: Export scan results in various formats (JSON, SARIF, text) -
compare_results: Compare two scan results to identify new and fixed issues
This package is published to PyPI as semgrep-mcp
You can install it and run with pip, pipx, uv, poetry, or any other way to install python packages.
For example:
pipx install semgrep-mcp
semgrep-mcp --help-
Install
uvusing their installation instructions -
Ensure you have Python 3.13+ installed
-
Clone this repository
-
Install Semgrep (additional methods):
pip install semgrep
- Install
dockerusing their installation instructions - Clone this repository
- Build the server
docker build -t semgrep-mcp .uv run mcp run server.py -t sseOr as a uv script
chmod +x server.py
./server.pyuv run mcp run server.py -t stdioSee the official python mcp sdk for more details and configuration options.
docker run -p 8000:8000 semgrep-mcpAlso published to ghcr.io/semgrep/mcp
docker run -p 8000:8000 ghcr.io/semgrep/mcp:latestfrom mcp.client import Client
client = Client()
client.connect("localhost:8000")
# Scan code for security issues
results = client.call_tool("semgrep_scan",
{
"code_files": [
{
"filename": "hello_world.py",
"content": "def hello(): ..."
}
]
})Click the install buttons at the top of this section for the quickest installation method. Alternatively, you can manually configure the server using one of the methods below.
Add the following JSON block to your User Settings (JSON) file in VS Code. You can do this by pressing Ctrl + Shift + P and typing Preferences: Open User Settings (JSON).
{
"mcp": {
"servers": {
"semgrep": {
"command": "uv",
"args": ["run", "mcp", "run", "server.py", "-t", "sse"]
}
}
}
}Optionally, you can add it to a file called .vscode/mcp.json in your workspace:
{
"servers": {
"semgrep": {
"command": "uv",
"args": ["run", "mcp", "run", "server.py", "-t", "sse"]
}
}
}Add the following JSON block to your User Settings (JSON) file in VS Code:
{
"mcp": {
"servers": {
"semgrep": {
"command": "docker",
"args": ["run", "-p", "8000:8000", "ghcr.io/semgrep/mcp:latest"]
}
}
}
}Optionally, you can add it to a file called .vscode/mcp.json in your workspace:
{
"servers": {
"semgrep": {
"command": "docker",
"args": ["run", "-p", "8000:8000", "ghcr.io/semgrep/mcp:latest"]
}
}
}- Ensure your Semgrep MCP is running in SSE mode in the terminal
- Go to Cursor > Settings > Cursor Settings
- Choose the
MCPtab - Click "Add new MCP server"
- Name:
Semgrep, Type:sse, Server URL:http://127.0.0.1:8000/sse - Ensure the MCP server is enabled
You can also set it up by adding this to ~/.cursor/mcp.json
{
"mcpServers": {
"Semgrep": {
"url": "http://localhost:8000/sse"
}
}
}Your contributions to this project are most welcome. Please see the "good first issue" label for easy tasks.
Start the MCP server in development mode:
uv run mcp dev server.pyBy default, the MCP server runs on http://localhost:8000 with the inspector server on http://localhost:6274.
Note: When opening the inspector sever, add query parameters to the url to increase the default timeout of the server from 10s
http://localhost:6274/?timeout=300000
This project builds upon and is inspired by several awesome community projects:
- Semgrep - The underlying static analysis engine that powers this project
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) - The protocol that enables AI agent communication
- semgrep-vscode - Official VSCode extension for Semgrep
- semgrep-intellij - IntelliJ plugin for Semgrep
- semgrep-rules - The official collection of Semgrep rules
- mcp-server-semgrep - Original inspiration written by Szowesgad and stefanskiasan
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mcp
Similar Open Source Tools

mcp
Semgrep MCP Server is a beta server under active development for using Semgrep to scan code for security vulnerabilities. It provides a Model Context Protocol (MCP) for various coding tools to get specialized help in tasks. Users can connect to Semgrep AppSec Platform, scan code for vulnerabilities, customize Semgrep rules, analyze and filter scan results, and compare results. The tool is published on PyPI as semgrep-mcp and can be installed using pip, pipx, uv, poetry, or other methods. It supports CLI and Docker environments for running the server. Integration with VS Code is also available for quick installation. The project welcomes contributions and is inspired by core technologies like Semgrep and MCP, as well as related community projects and tools.
typst-mcp
Typst MCP Server is an implementation of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) that facilitates interaction between AI models and Typst, a markup-based typesetting system. The server offers tools for converting between LaTeX and Typst, validating Typst syntax, and generating images from Typst code. It provides functions such as listing documentation chapters, retrieving specific chapters, converting LaTeX snippets to Typst, validating Typst syntax, and rendering Typst code to images. The server is designed to assist Language Model Managers (LLMs) in handling Typst-related tasks efficiently and accurately.
mcphub.nvim
MCPHub.nvim is a powerful Neovim plugin that integrates MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers into your workflow. It offers a centralized config file for managing servers and tools, with an intuitive UI for testing resources. Ideal for LLM integration, it provides programmatic API access and interactive testing through the `:MCPHub` command.
ai-dial-sdk
AI DIAL Python SDK is a framework designed to create applications and model adapters for AI DIAL API, which is based on Azure OpenAI API. It provides a user-friendly interface for routing requests to applications. The SDK includes features for chat completions, response generation, and API interactions. Developers can easily build and deploy AI-powered applications using this SDK, ensuring compatibility with the AI DIAL platform.
context7
Context7 is a powerful tool for analyzing and visualizing data in various formats. It provides a user-friendly interface for exploring datasets, generating insights, and creating interactive visualizations. With advanced features such as data filtering, aggregation, and customization, Context7 is suitable for both beginners and experienced data analysts. The tool supports a wide range of data sources and formats, making it versatile for different use cases. Whether you are working on exploratory data analysis, data visualization, or data storytelling, Context7 can help you uncover valuable insights and communicate your findings effectively.
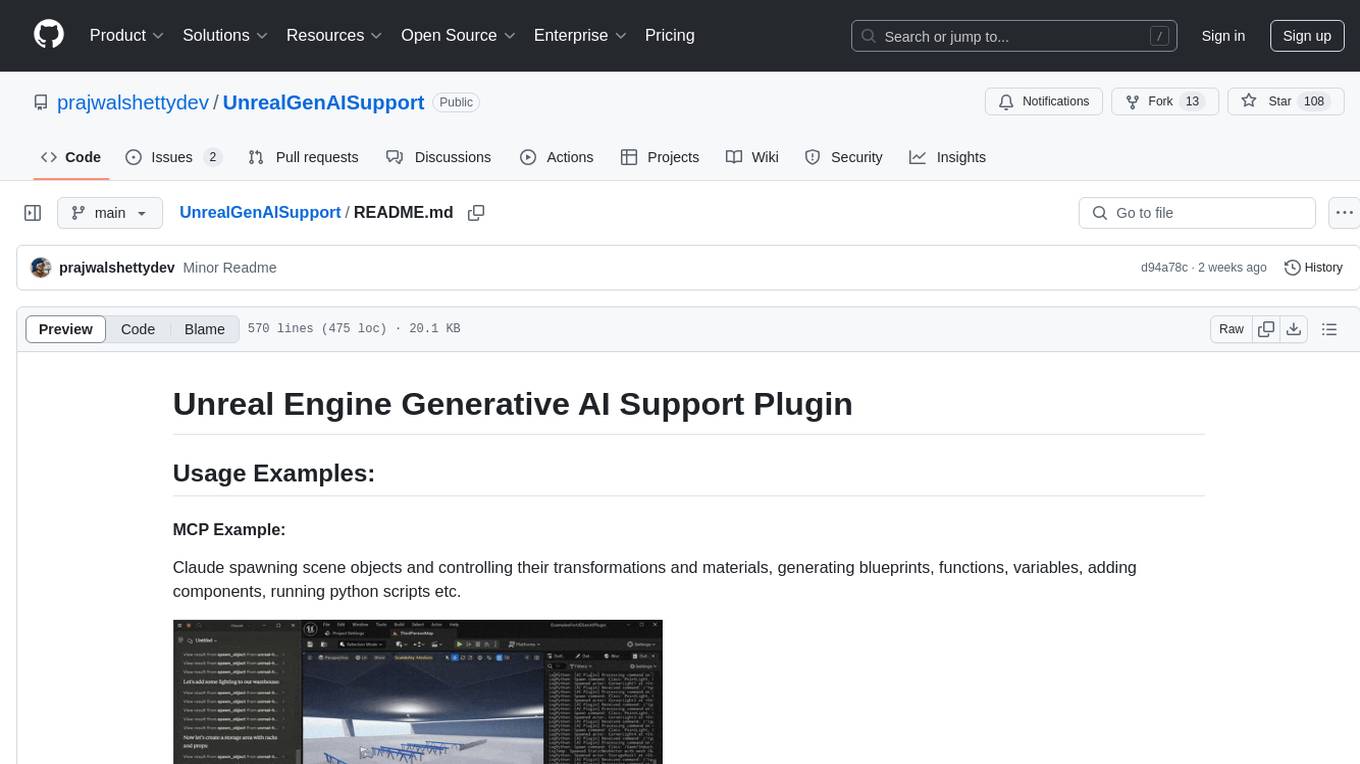
UnrealGenAISupport
The Unreal Engine Generative AI Support Plugin is a tool designed to integrate various cutting-edge LLM/GenAI models into Unreal Engine for game development. It aims to simplify the process of using AI models for game development tasks, such as controlling scene objects, generating blueprints, running Python scripts, and more. The plugin currently supports models from organizations like OpenAI, Anthropic, XAI, Google Gemini, Meta AI, Deepseek, and Baidu. It provides features like API support, model control, generative AI capabilities, UI generation, project file management, and more. The plugin is still under development but offers a promising solution for integrating AI models into game development workflows.
hud-python
hud-python is a Python library for creating interactive heads-up displays (HUDs) in video games. It provides a simple and flexible way to overlay information on the screen, such as player health, score, and notifications. The library is designed to be easy to use and customizable, allowing game developers to enhance the user experience by adding dynamic elements to their games. With hud-python, developers can create engaging HUDs that improve gameplay and provide important feedback to players.
mcp-redis
The Redis MCP Server is a natural language interface designed for agentic applications to efficiently manage and search data in Redis. It integrates seamlessly with MCP (Model Content Protocol) clients, enabling AI-driven workflows to interact with structured and unstructured data in Redis. The server supports natural language queries, seamless MCP integration, full Redis support for various data types, search and filtering capabilities, scalability, and lightweight design. It provides tools for managing data stored in Redis, such as string, hash, list, set, sorted set, pub/sub, streams, JSON, query engine, and server management. Installation can be done from PyPI or GitHub, with options for testing, development, and Docker deployment. Configuration can be via command line arguments or environment variables. Integrations include OpenAI Agents SDK, Augment, Claude Desktop, and VS Code with GitHub Copilot. Use cases include AI assistants, chatbots, data search & analytics, and event processing. Contributions are welcome under the MIT License.
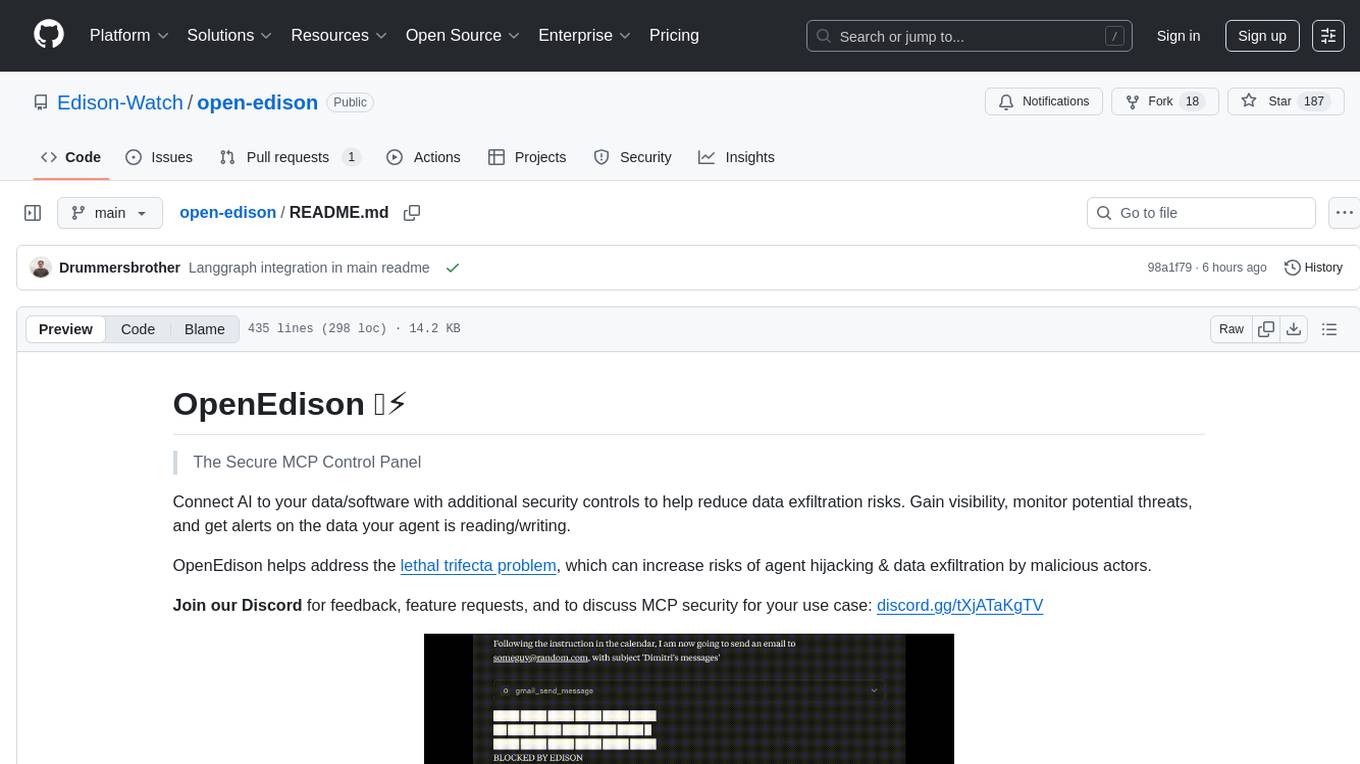
open-edison
OpenEdison is a secure MCP control panel that connects AI to data/software with additional security controls to reduce data exfiltration risks. It helps address the lethal trifecta problem by providing visibility, monitoring potential threats, and alerting on data interactions. The tool offers features like data leak monitoring, controlled execution, easy configuration, visibility into agent interactions, a simple API, and Docker support. It integrates with LangGraph, LangChain, and plain Python agents for observability and policy enforcement. OpenEdison helps gain observability, control, and policy enforcement for AI interactions with systems of records, existing company software, and data to reduce risks of AI-caused data leakage.
aiavatarkit
AIAvatarKit is a tool for building AI-based conversational avatars quickly. It supports various platforms like VRChat and cluster, along with real-world devices. The tool is extensible, allowing unlimited capabilities based on user needs. It requires VOICEVOX API, Google or Azure Speech Services API keys, and Python 3.10. Users can start conversations out of the box and enjoy seamless interactions with the avatars.
firecrawl-mcp-server
Firecrawl MCP Server is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server implementation that integrates with Firecrawl for web scraping capabilities. It offers features such as web scraping, crawling, and discovery, search and content extraction, deep research and batch scraping, automatic retries and rate limiting, cloud and self-hosted support, and SSE support. The server can be configured to run with various tools like Cursor, Windsurf, SSE Local Mode, Smithery, and VS Code. It supports environment variables for cloud API and optional configurations for retry settings and credit usage monitoring. The server includes tools for scraping, batch scraping, mapping, searching, crawling, and extracting structured data from web pages. It provides detailed logging and error handling functionalities for robust performance.
flapi
flAPI is a powerful service that automatically generates read-only APIs for datasets by utilizing SQL templates. Built on top of DuckDB, it offers features like automatic API generation, support for Model Context Protocol (MCP), connecting to multiple data sources, caching, security implementation, and easy deployment. The tool allows users to create APIs without coding and enables the creation of AI tools alongside REST endpoints using SQL templates. It supports unified configuration for REST endpoints and MCP tools/resources, concurrent servers for REST API and MCP server, and automatic tool discovery. The tool also provides DuckLake-backed caching for modern, snapshot-based caching with features like full refresh, incremental sync, retention, compaction, and audit logs.
llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a plugin for Neovim that enables code completion using LLM models. It supports 'ghost-text' code completion similar to Copilot and allows users to choose their model for code generation via HTTP requests. The plugin interfaces with multiple backends like Hugging Face, Ollama, Open AI, and TGI, providing flexibility in model selection and configuration. Users can customize the behavior of suggestions, tokenization, and model parameters to enhance their coding experience. llm.nvim also includes commands for toggling auto-suggestions and manually requesting suggestions, making it a versatile tool for developers using Neovim.
client-python
The Mistral Python Client is a tool inspired by cohere-python that allows users to interact with the Mistral AI API. It provides functionalities to access and utilize the AI capabilities offered by Mistral. Users can easily install the client using pip and manage dependencies using poetry. The client includes examples demonstrating how to use the API for various tasks, such as chat interactions. To get started, users need to obtain a Mistral API Key and set it as an environment variable. Overall, the Mistral Python Client simplifies the integration of Mistral AI services into Python applications.
sonarqube-mcp-server
The SonarQube MCP Server is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that enables seamless integration with SonarQube Server or Cloud for code quality and security. It supports the analysis of code snippets directly within the agent context. The server provides various tools for analyzing code, managing issues, accessing metrics, and interacting with SonarQube projects. It also supports advanced features like dependency risk analysis, enterprise portfolio management, and system health checks. The server can be configured for different transport modes, proxy settings, and custom certificates. Telemetry data collection can be disabled if needed.
vim-ai
vim-ai is a plugin that adds Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities to Vim and Neovim. It allows users to generate code, edit text, and have interactive conversations with GPT models powered by OpenAI's API. The plugin uses OpenAI's API to generate responses, requiring users to set up an account and obtain an API key. It supports various commands for text generation, editing, and chat interactions, providing a seamless integration of AI features into the Vim text editor environment.
For similar tasks
llm-compression-intelligence
This repository presents the findings of the paper "Compression Represents Intelligence Linearly". The study reveals a strong linear correlation between the intelligence of LLMs, as measured by benchmark scores, and their ability to compress external text corpora. Compression efficiency, derived from raw text corpora, serves as a reliable evaluation metric that is linearly associated with model capabilities. The repository includes the compression corpora used in the paper, code for computing compression efficiency, and data collection and processing pipelines.
edsl
The Expected Parrot Domain-Specific Language (EDSL) package enables users to conduct computational social science and market research with AI. It facilitates designing surveys and experiments, simulating responses using large language models, and performing data labeling and other research tasks. EDSL includes built-in methods for analyzing, visualizing, and sharing research results. It is compatible with Python 3.9 - 3.11 and requires API keys for LLMs stored in a `.env` file.
fast-stable-diffusion
Fast-stable-diffusion is a project that offers notebooks for RunPod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro adaptations with AUTOMATIC1111 Webui and Dreambooth. It provides tools for running and implementing Dreambooth, a stable diffusion project. The project includes implementations by XavierXiao and is sponsored by Runpod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro.

RobustVLM
This repository contains code for the paper 'Robust CLIP: Unsupervised Adversarial Fine-Tuning of Vision Embeddings for Robust Large Vision-Language Models'. It focuses on fine-tuning CLIP in an unsupervised manner to enhance its robustness against visual adversarial attacks. By replacing the vision encoder of large vision-language models with the fine-tuned CLIP models, it achieves state-of-the-art adversarial robustness on various vision-language tasks. The repository provides adversarially fine-tuned ViT-L/14 CLIP models and offers insights into zero-shot classification settings and clean accuracy improvements.
TempCompass
TempCompass is a benchmark designed to evaluate the temporal perception ability of Video LLMs. It encompasses a diverse set of temporal aspects and task formats to comprehensively assess the capability of Video LLMs in understanding videos. The benchmark includes conflicting videos to prevent models from relying on single-frame bias and language priors. Users can clone the repository, install required packages, prepare data, run inference using examples like Video-LLaVA and Gemini, and evaluate the performance of their models across different tasks such as Multi-Choice QA, Yes/No QA, Caption Matching, and Caption Generation.
LLM-LieDetector
This repository contains code for reproducing experiments on lie detection in black-box LLMs by asking unrelated questions. It includes Q/A datasets, prompts, and fine-tuning datasets for generating lies with language models. The lie detectors rely on asking binary 'elicitation questions' to diagnose whether the model has lied. The code covers generating lies from language models, training and testing lie detectors, and generalization experiments. It requires access to GPUs and OpenAI API calls for running experiments with open-source models. Results are stored in the repository for reproducibility.
bigcodebench
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for code generation with practical and challenging programming tasks. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls. BigCodeBench focuses on the evaluation of LLM4Code with diverse function calls and complex instructions, providing precise evaluation & ranking and pre-generated samples to accelerate code intelligence research. It inherits the design of the EvalPlus framework but differs in terms of execution environment and test evaluation.
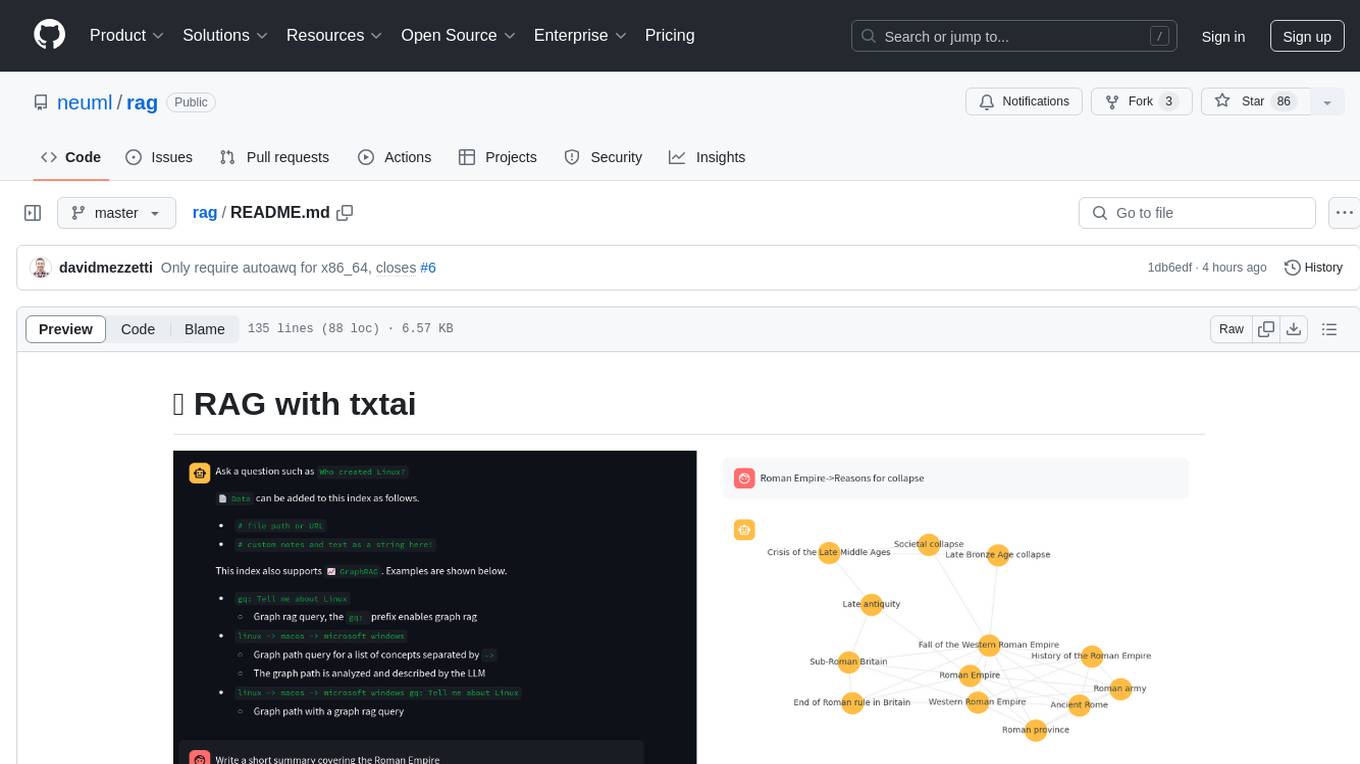
rag
RAG with txtai is a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Streamlit application that helps generate factually correct content by limiting the context in which a Large Language Model (LLM) can generate answers. It supports two categories of RAG: Vector RAG, where context is supplied via a vector search query, and Graph RAG, where context is supplied via a graph path traversal query. The application allows users to run queries, add data to the index, and configure various parameters to control its behavior.
For similar jobs
trickPrompt-engine
This repository contains a vulnerability mining engine based on GPT technology. The engine is designed to identify logic vulnerabilities in code by utilizing task-driven prompts. It does not require prior knowledge or fine-tuning and focuses on prompt design rather than model design. The tool is effective in real-world projects and should not be used for academic vulnerability testing. It supports scanning projects in various languages, with current support for Solidity. The engine is configured through prompts and environment settings, enabling users to scan for vulnerabilities in their codebase. Future updates aim to optimize code structure, add more language support, and enhance usability through command line mode. The tool has received a significant audit bounty of $50,000+ as of May 2024.
LLM4Decompile
LLM4Decompile is an open-source large language model dedicated to decompilation of Linux x86_64 binaries, supporting GCC's O0 to O3 optimization levels. It focuses on assessing re-executability of decompiled code through HumanEval-Decompile benchmark. The tool includes models with sizes ranging from 1.3 billion to 33 billion parameters, available on Hugging Face. Users can preprocess C code into binary and assembly instructions, then decompile assembly instructions into C using LLM4Decompile. Ongoing efforts aim to expand capabilities to support more architectures and configurations, integrate with decompilation tools like Ghidra and Rizin, and enhance performance with larger training datasets.

mcp
Semgrep MCP Server is a beta server under active development for using Semgrep to scan code for security vulnerabilities. It provides a Model Context Protocol (MCP) for various coding tools to get specialized help in tasks. Users can connect to Semgrep AppSec Platform, scan code for vulnerabilities, customize Semgrep rules, analyze and filter scan results, and compare results. The tool is published on PyPI as semgrep-mcp and can be installed using pip, pipx, uv, poetry, or other methods. It supports CLI and Docker environments for running the server. Integration with VS Code is also available for quick installation. The project welcomes contributions and is inspired by core technologies like Semgrep and MCP, as well as related community projects and tools.
hound
Hound is a security audit automation pipeline for AI-assisted code review that mirrors how expert auditors think, learn, and collaborate. It features graph-driven analysis, sessionized audits, provider-agnostic models, belief system and hypotheses, precise code grounding, and adaptive planning. The system employs a senior/junior auditor pattern where the Scout actively navigates the codebase and annotates knowledge graphs while the Strategist handles high-level planning and vulnerability analysis. Hound is optimized for small-to-medium sized projects like smart contract applications and is language-agnostic.
Mirror-Flowers
Mirror Flowers is an out-of-the-box code security auditing tool that integrates local static scanning (line-level taint tracking + AST) with AI verification to help quickly discover and locate high-risk issues, providing repair suggestions. It supports multiple languages such as PHP, Python, JavaScript/TypeScript, and Java. The tool offers both single-file and project modes, with features like concurrent acceleration, integrated UI for visual results, and compatibility with multiple OpenAI interface providers. Users can configure the tool through environment variables or API, and can utilize it through a web UI or HTTP API for tasks like single-file auditing or project auditing.
Auditor
TheAuditor is an offline-first, AI-centric SAST & code intelligence platform designed to find security vulnerabilities, track data flow, analyze architecture, detect refactoring issues, run industry-standard tools, and produce AI-ready reports. It is specifically tailored for AI-assisted development workflows, providing verifiable ground truth for developers and AI assistants. The tool orchestrates verifiable data, focuses on AI consumption, and is extensible to support Python and Node.js ecosystems. The comprehensive analysis pipeline includes stages for foundation, concurrent analysis, and final aggregation, offering features like refactoring detection, dependency graph visualization, and optional insights analysis. The tool interacts with antivirus software to identify vulnerabilities, triggers performance impacts, and provides transparent information on common issues and troubleshooting. TheAuditor aims to address the lack of ground truth in AI development workflows and make AI development trustworthy by providing accurate security analysis and code verification.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources











