
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
Awesome papers involving LLMs in Social Science.
Stars: 388
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science is a repository that compiles papers evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) from a social science perspective. It includes papers on evaluating, aligning, and simulating LLMs, as well as enhancing tools in social science research. The repository categorizes papers based on their focus on attitudes, opinions, values, personality, morality, and more. It aims to contribute to discussions on the potential and challenges of using LLMs in social science research.
README:
Below we compile awesome papers that
- evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) from a perspective of Social Science.
- align LLMs from a perspective of Social Science.
- employ LLMs to facilitate research, address issues, and enhance tools in Social Science.
- contribute surveys, perspectives, and datasets on the above topics.
The above taxonomies are by no means orthogonal. For example, evaluations require simulations. We categorize these papers based on our understanding of their focus. This collection has a special focus on Psychology and intrinsic values.
Welcome to contribute and discuss!
🤩 Papers marked with a ⭐️ are contributed by the maintainers of this repository. If you find them useful, we would greatly appreciate it if you could give the repository a star or cite our paper.
-
- 3.1. ❤️ Value
- 3.2. 🩷 Personality
- 3.3. 🔞 Morality
- 3.4. 🎤 Opinion
- 3.5. 💚 General Preference
- 3.6. 🧠 Ability
- 3.7.
⚠️ Risk
- On the Trustworthiness of Generative Foundation Models: Guideline, Assessment, and Perspective, 2025.02, [paper].
- The Road to Artificial SuperIntelligence: A Comprehensive Survey of Superalignment, 2024.12, [paper].
- Large Language Model Safety: A Holistic Survey, 2024.12, [paper].
- Political-LLM: Large Language Models in Political Science, 2024.12, [paper], [website].
- LLMs-as-Judges: A Comprehensive Survey on LLM-based Evaluation Methods, 2024.12, [paper].
- From Individual to Society: A Survey on Social Simulation Driven by Large Language Model-based Agents, 2024.12, [paper], [repo].
- A Survey on Human-Centric LLMs, 2024.11, [paper].
- Survey of Cultural Awareness in Language Models: Text and Beyond, 2024.11, [paper].
- How developments in natural language processing help us in understanding human behaviour, 2024.10 Nature Human Behavior, [paper].
- How large language models can reshape collective intelligence, 2024.09, Nature Human Behavior, [paper].
- Automated Mining of Structured Knowledge from Text in the Era of Large Language Models, 2024.08, KDD 2024, [paper].
- Affective Computing in the Era of Large Language Models: A Survey from the NLP Perspective, 2024.07, [paper].
- Perils and opportunities in using large language models in psychological research, 2024.07, [paper].
- The Potential and Challenges of Evaluating Attitudes, Opinions, and Values in Large Language Models, 2024.06, [paper].
- Can Generative AI improve social science?, 2024.05, PNAS, [paper].
- Foundational Challenges in Assuring Alignment and Safety of Large Language Models, 2024.04, [paper].
- Large Language Model based Multi-Agents: A Survey of Progress and Challenges, 2024.01, [paper], [repo].
- The Rise and Potential of Large Language Model Based Agents: A Survey, 2023, [paper], [repo].
- A Survey on Large Language Model based Autonomous Agents, 2023, [paper], [repo].
- AI Alignment: A Comprehensive Survey, 2023.11, [paper], [website].
- Aligning Large Language Models with Human: A Survey, 2023, [paper], [repo].
- Large Language Model Alignment: A Survey, 2023, [paper].
- Large Language Models Empowered Agent-based Modeling and Simulation: A Survey and Perspectives, 2023.12, Nature humanities and social sciences communications, [paper].
- A Survey on Evaluation of Large Language Models, 2023.07, [paper], [repo].
- From Instructions to Intrinsic Human Values -- A Survey of Alignment Goals for Big Models, 2023.08, [paper], [repo].
- The PRISM Alignment Dataset: What Participatory, Representative and Individualised Human Feedback Reveals About the Subjective and Multicultural Alignment of Large Language Models, NeurIPS 2024 D&B Track best paper, [paper].
- ⭐️ ValueBench: Towards Comprehensively Evaluating Value Orientations and Understanding of Large Language Models, ACL 2024, [paper], [code].
- Automating Dataset Updates Towards Reliable and Timely Evaluation of Large Language Models, NeurIPS 2024, [paper].
- https://github.com/CLUEbenchmark/CLUEDatasetSearch
- HATEDAY: Insights from a Global Hate Speech Dataset Representative of a Day on Twitter, 2024.11, [paper].
- https://lit.eecs.umich.edu/downloads.html
- COMPO: Community Preferences for Language Model Personalization, 2024.10, [paper].
- Cultural Commonsense Knowledge for Intercultural Dialogues, CIKM 2024, [paper], [dataset].
- ⭐️ Generative Psycho-Lexical Approach for Constructing Value Systems in Large Language Models, 2025.02, [paper].
- ⭐️ Measuring Human and AI Values Based on Generative Psychometrics with Large Language Models, AAAI 2025, [paper], [code].
- ⭐️ ValueBench: Towards Comprehensively Evaluating Value Orientations and Understanding of Large Language Models, ACL 2024, [paper], [code].
- Value Compass Leaderboard: A Platform for Fundamental and Validated Evaluation of LLMs Values, 2025.01, [paper].
- Causal Graph Guided Steering of LLM Values via Prompts and Sparse Autoencoders, 2025.01, [paper].
- NORMAD: A Framework for Measuring the Cultural Adaptability of Large Language Models, 2024.10, [paper].
- ValueCompass: A Framework of Fundamental Values for Human-AI Alignment, 2024.09, [paper].
- LOCALVALUEBENCH: A Collaboratively Built and Extensible Benchmark for Evaluating Localized Value Alignment and Ethical Safety in Large Language Models, 2024.08, [paper].
- Stick to your role! Stability of personal values expressed in large language models, 2024.08, [paper].
- Raising the Bar: Investigating the Values of Large Language Models via Generative Evolving Testing, 2024.07, [paper].
- Do LLMs have Consistent Values?, 2024.07, [paper].
- CLAVE: An Adaptive Framework for Evaluating Values of LLM Generated Responses, 2024.07, [paper].
- Are Large Language Models Consistent over Value-laden Questions?, 2024.07, [paper].
- Beyond Human Norms: Unveiling Unique Values of Large Language Models through Interdisciplinary Approaches, 2024.04, [paper].
- Heterogeneous Value Evaluation for Large Language Models, 2023.03, [paper], [code].
- Measuring Value Understanding in Language Models through Discriminator-Critique Gap, 2023.10, [paper].
- Value FULCRA: Mapping Large Language Models to the Multidimensional Spectrum of Basic Human Values, 2023.11, [paper].
- Value Kaleidoscope: Engaging AI with Pluralistic Human Values, Rights, and Duties, AAAI24, [paper], [code].
- High-Dimension Human Value Representation in Large Language Models, 2024.04, [paper], [code].
-
Evaluating the ability of large language models to emulate personality, 2025.01, Nature Scientific Reports, [paper].
-
Evaluating the efficacy of LLMs to emulate realistic human personalities, AAAI 2024, [paper].
-
Quantifying ai psychology: A psychometrics benchmark for large language models, 2024.07, [paper].
-
Incharacter: Evaluating personality fidelity in role-playing agents through psychological interviews, ACL 2024, [paper], [code]
-
[MBTI] Open Models, Closed Minds? On Agents Capabilities in Mimicking Human Personalities through Open Large Language Models, 2024.01, [paper]
-
Who is ChatGPT? Benchmarking LLMs' Psychological Portrayal Using PsychoBench, ICLR 2024, [paper], [code]
-
[BFI] AI Psychometrics: Assessing the Psychological Profiles of Large Language Models Through Psychometric Inventories, Journal, 2024.01, [paper]
-
Does Role-Playing Chatbots Capture the Character Personalities? Assessing Personality Traits for Role-Playing Chatbots, 2023.10, [paper]
-
[MBTI] Do LLMs Possess a Personality? Making the MBTI Test an Amazing Evaluation for Large Language Models, 2023.07, [paper]
-
[MBTI] Can ChatGPT Assess Human Personalities? A General Evaluation Framework, 2023.03, EMNLP 2023, [paper], [code].
-
[BFI] Personality Traits in Large Language Models, 2023.07, [paper]
-
[BFI] Revisiting the Reliability of Psychological Scales on Large Language Models, 2023.05, [paper]
-
[BFI] Systematic Evaluation of GPT-3 for Zero-Shot Personality Estimation, ACL 2023 workshop, [paper]
-
[BFI] Have Large Language Models Developed a Personality?: Applicability of Self-Assessment Tests in Measuring Personality in LLMs, 2023.05, [paper]
-
[BFI] Evaluating and Inducing Personality in Pre-trained Language Models, NeurIPS 2023 (spotlight), [paper]
-
[BFI] Identifying and Manipulating the Personality Traits of Language Models, 2022,12, [paper]
-
Who is GPT-3? An Exploration of Personality, Values and Demographics, 2022.09, [paper]
-
Does GPT-3 Demonstrate Psychopathy? Evaluating Large Language Models from a Psychological Perspective, 2022.12, [paper]
- Revealing the Pragmatic Dilemma for Moral Reasoning Acquisition in Language Models, 2025.02, [paper].
- Normative Evaluation of Large Language Models with Everyday Moral Dilemmas, 2025.02, [paper].
- Investigating machine moral judgement through the Delphi experiment, Nature Machine Intelligence, 2025.01, [paper].
- Moral Foundations of Large Language Models, 2023.10, [paper].
- Exploring the psychology of GPT-4's Moral and Legal Reasoning, 2023.08, [paper].
- Probing the Moral Development of Large Language Models through Defining Issues Test
- Moral Mimicry: Large Language Models Produce Moral Rationalizations Tailored to Political Identity, 2023.06, [paper]
- Evaluating the Moral Beliefs Encoded in LLMs, 2023.07, [paper]
- Large language models that replace human participants can harmfully misportray and flatten identity groups, Nature Machine Intelligence, 2025, [paper].
- Questioning the Survey Responses of Large Language Models, NeurIPS 2024 Oral, [paper].
- Political Compass or Spinning Arrow? Towards More Meaningful Evaluations for Values and Opinions in Large Language Models, ACL 2024, paper.
- More human than human: measuring ChatGPT political bias, 2023, [paper].
- Towards Measuring the Representation of Subjective Global Opinions in Language Models, 2023.07, [paper], [website].
- Diverging Preferences: When do Annotators Disagree and do Models Know?, 2024.10, [paper].
- AgentSense: Benchmarking Social Intelligence of Language Agents through Interactive Scenarios, NAACL 2025, [paper].
- Cheating Automatic LLM Benchmarks: Null Models Achieve High Win Rates, NeurIPS 2024, [paper].
- Replication for Language Models: Problems, Principles, and Best Practice for Political Science, 2024.10, [paper].
- Can Language Models Reason about Individualistic Human Values and Preferences?, 2024.10, [paper].
- Language Models in Sociological Research: An Application to Classifying Large Administrative Data and Measuring Religiosity, 2021, [paper].
- Can Large Language Models Transform Computational Social Science?, 2023, [paper], [code].
- SOTOPIA: Interactive Evaluation for Social Intelligence in Language Agents, 2023, [paper], [code].
- Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View, 2023, [paper], [code].
- Playing repeated games with Large Language Models, 2023.05, [paper].
- Machine Psychology: Investigating Emergent Capabilities and Behavior in Large Language Models Using Psychological Methods, 2023, [paper].
- Using cognitive psychology to understand GPT-3, 2023.02, PNAS, [paper].
- Large language models as a substitute for human experts in annotating political text, 2024.02, [paper].
-
From Lived Experience to Insight: Unpacking the Psychological Risks of Using AI Conversational Agents, 2024.12, [paper].
-
AIR-Bench 2024: A Safety Benchmark Based on Risk Categories from Regulations and Policies, 2024.07, [paper].
- ⭐️ Generative Psycho-Lexical Approach for Constructing Value Systems in Large Language Models, 2025.02, [paper].
- ⭐️ Measuring Human and AI Values Based on Generative Psychometrics with Large Language Models, AAAI 2025, [paper], [code].
- STAMPsy: Towards SpatioTemporal-Aware Mixed-Type Dialogues for Psychological Counseling, AAAI 2025, [paper].
- ValueScope: Unveiling Implicit Norms and Values via Return Potential Model of Social Interactions, 2024.10, [paper].
- AI can help humans find common ground in democratic deliberation, 2024.10, Science, [paper].
- PsyDI: Towards a Personalized and Progressively In-depth Chatbot for Psychological Measurements, 2024, [paper], [code].
- ChatFive: Enhancing User Experience in Likert Scale Personality Test through Interactive Conversation with LLM Agents, CUI 2024, [paper]
- LLM Agents for Psychology: A Study on Gamified Assessments, 2024.02, [paper].
- Generative Social Choice, 2023.09, [paper]
- ⭐️ Generative Psycho-Lexical Approach for Constructing Value Systems in Large Language Models, 2025.02, [paper].
- Position: We Need An Adaptive Interpretation of Helpful, Honest, and Harmless Principles, 2025.02, [paper].
- Scopes of Alignment, 2025.01, AAAI 2025 workshop, [paper]
- Aligning Large Language Models with Human Opinions through Persona Selection and Value-Belief-Norm Reasoning, 2024.11, [paper].
- SafetyAnalyst: Interpretable, transparent, and steerable LLM safety moderation, 2024.10, [paper].
- Moral Alignment for LLM Agents, 2024.10, [paper].
- ProgressGym: Alignment with a Millennium of Moral Progress, NeurIPS 2024 D&B Track Spotlight, [paper], [code].
- Strong and weak alignment of large language models with human values, 2024.08, Nature Scientific Reports, [paper].
- STELA: a community-centred approach to norm elicitation for AI alignment, 2024.03, Nature Scientific Reports, [paper].
- A Roadmap to Pluralistic Alignment, ICML 2024, [paper], [code].
- [Value] What are human values, and how do we align AI to them?, 2024.04, [paper].
- Agent Alignment in Evolving Social Norms, 2024.01, [paper].
- [Norm] Align on the Fly: Adapting Chatbot Behavior to Established Norms, 2023.12, [paper], [code].
- [MBTI] Machine Mindset: An MBTI Exploration of Large Language Models, 2023.12, [paper], [code].
- Training Socially Aligned Language Models in Simulated Human Society, 2023, [paper], [code].
- Fine-tuning language models to find agreement among humans with diverse preferences, 2022, [paper].
- ValueNet: A New Dataset for Human Value Driven Dialogue System, AAAI 2022, [paper], [dataset].
- Towards Pluralistic Value Alignment: Aggregating Value Systems through ℓp-Regression, AAMAS 2022 workshop, [paper].
- [Benchmark] Benchmarking Distributional Alignment of Large Language Models, 2024.11, [paper].
- Legal Theory for Pluralistic Alignment, 2024.10, [paper].
- Navigating the Cultural Kaleidoscope: A Hitchhiker’s Guide to Sensitivity in Large Language Models, 2024.10, [paper], [code and data].
- PAD: Personalized Alignment at Decoding-Time, 2024.10, [paper].
- Policy Prototyping for LLMs: Pluralistic Alignment via Interactive and Collaborative Policymaking, 2024.09, [paper].
- Modular Pluralism: Pluralistic Alignment via Multi-LLM Collaboration, 2024.06, [paper].
- Self-Pluralising Culture Alignment for Large Language Models, 2024.10, [paper].
- Cultural Palette: Pluralising Culture Alignment via Multi-agent Palette, 2024.12, [paper].
- AgentSociety: Large-Scale Simulation of LLM-Driven Generative Agents Advances Understanding of Human Behaviors and Society, 2025.02, [paper], [code].
- Political Actor Agent: Simulating Legislative System for Roll Call Votes Prediction with Large Language Models, AAAI 2025, [paper].
- TrendSim: Simulating Trending Topics in Social Media Under Poisoning Attacks with LLM-based Multi-agent System, 2024.12, [paper].
- Can Large Language Model Agents Simulate Human Trust Behavior?, NeurIPS 2024, [paper].
- OASIS: Open Agents Social Interaction Simulations on One Million Agents, 2024.11, [paper], [code].
- Generative Agent Simulations of 1,000 People, 2024.11, [paper].
- Social Science Meets LLMs: How Reliable Are Large Language Models in Social Simulations?, 2024.11, [paper].
- Multi-expert Prompting Improves Reliability, Safety, and Usefulness of Large Language Models, EMNLP 2024, [paper].
- Simulating Opinion Dynamics with Networks of LLM-based Agents, NAACL Findings 2024, [paper] [code]
- Beyond demographics: Aligning role-playing llm-based agents using human belief networks, EMNLP Findings 2024, [paper]
- The Wisdom of Partisan Crowds: Comparing Collective Intelligence in Humans and LLM-based Agents, CogSci 2024, [paper]
- Large Language Models can Achieve Social Balance, 2024.10, [paper].
- On the limits of agency in agent-based models, 2024.09, [paper], [code].
- United in Diversity? Contextual Biases in LLM-Based Predictions of the 2024 European Parliament Elections, 2024.09, [paper].
- Out of One, Many: Using Language Models to Simulate Human Samples, 2022, [paper].
- Social Simulacra: Creating Populated Prototypes for Social Computing Systems, 2022, [paper].
- Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior, 2023, [paper], [code].
- Using Large Language Models to Simulate Multiple Humans and Replicate Human Subject Studies, 2023, [paper], [code].
- Large Language Models as Simulated Economic Agents: What Can We Learn from Homo Silicus?, 2023 [paper], [code].
- $S^3$: Social-network Simulation System with Large Language Model-Empowered Agents, 2023, [paper].
- Rethinking the Buyer’s Inspection Paradox in Information Markets with Language Agents, 2023, [paper].
- SocioDojo: Building Lifelong Analytical Agents with Real-world Text and Time Series, 2023, [paper].
- Humanoid Agents: Platform for Simulating Human-like Generative Agents, 2023, [paper], [code].
- When Large Language Model based Agent Meets User Behavior Analysis: A Novel User Simulation Paradigm, 2023, [paper], [code].
- Large Language Model-Empowered Agents for Simulating Macroeconomic Activities, 2023, [paper].
- Generative Agent-Based Modeling: Unveiling Social System Dynamics through Coupling Mechanistic Models with Generative Artificial Intelligence, 2023, [paper].
- Using Imperfect Surrogates for Downstream Inference: Design-based Supervised Learning for Social Science Applications of Large Language Models, 2023.06, NeurIPS 2023, [paper].
- Epidemic Modeling with Generative Agents, 2023.07, [paper], [code].
- Emergent analogical reasoning in large language models, 2023.08, nature human behavior, [paper].
- MetaAgents: Simulating Interactions of Human Behaviors for LLM-based Task-oriented Coordination via Collaborative Generative Agents, 2023.10, [paper].
- War and Peace (WarAgent): Large Language Model-based Multi-Agent Simulation of World Wars, 2023.11, [paper], [code].
- Emergence of Social Norms in Large Language Model-based Agent Societies, 2024.03, [paper], [code].
- Large Content And Behavior Models To Understand, Simulate, And Optimize Content And Behavior, ICLR-2024, [paper]
- The benefits, risks and bounds of personalizing the alignment of large language models to individuals, 2024.04, Nature Machine Intelligence, [paper].
- A social path to human-like artificial intelligence, 2023.11, Nature Machine Intelligence, [paper].
- Using large language models in psychology, 2023.10, Nature reviews psychology, [paper].
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
Similar Open Source Tools

Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science is a repository that compiles papers evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) from a social science perspective. It includes papers on evaluating, aligning, and simulating LLMs, as well as enhancing tools in social science research. The repository categorizes papers based on their focus on attitudes, opinions, values, personality, morality, and more. It aims to contribute to discussions on the potential and challenges of using LLMs in social science research.
LLM-Agent-Survey
LLM-Agent-Survey is a comprehensive repository that provides a curated list of papers related to Large Language Model (LLM) agents. The repository categorizes papers based on LLM-Profiled Roles and includes high-quality publications from prestigious conferences and journals. It aims to offer a systematic understanding of LLM-based agents, covering topics such as tool use, planning, and feedback learning. The repository also includes unpublished papers with insightful analysis and novelty, marked for future updates. Users can explore a wide range of surveys, tool use cases, planning workflows, and benchmarks related to LLM agents.
MedLLMsPracticalGuide
This repository serves as a practical guide for Medical Large Language Models (Medical LLMs) and provides resources, surveys, and tools for building, fine-tuning, and utilizing LLMs in the medical domain. It covers a wide range of topics including pre-training, fine-tuning, downstream biomedical tasks, clinical applications, challenges, future directions, and more. The repository aims to provide insights into the opportunities and challenges of LLMs in medicine and serve as a practical resource for constructing effective medical LLMs.
ABigSurveyOfLLMs
ABigSurveyOfLLMs is a repository that compiles surveys on Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide a comprehensive overview of the field. It includes surveys on various aspects of LLMs such as transformers, alignment, prompt learning, data management, evaluation, societal issues, safety, misinformation, attributes of LLMs, efficient LLMs, learning methods for LLMs, multimodal LLMs, knowledge-based LLMs, extension of LLMs, LLMs applications, and more. The repository aims to help individuals quickly understand the advancements and challenges in the field of LLMs through a collection of recent surveys and research papers.
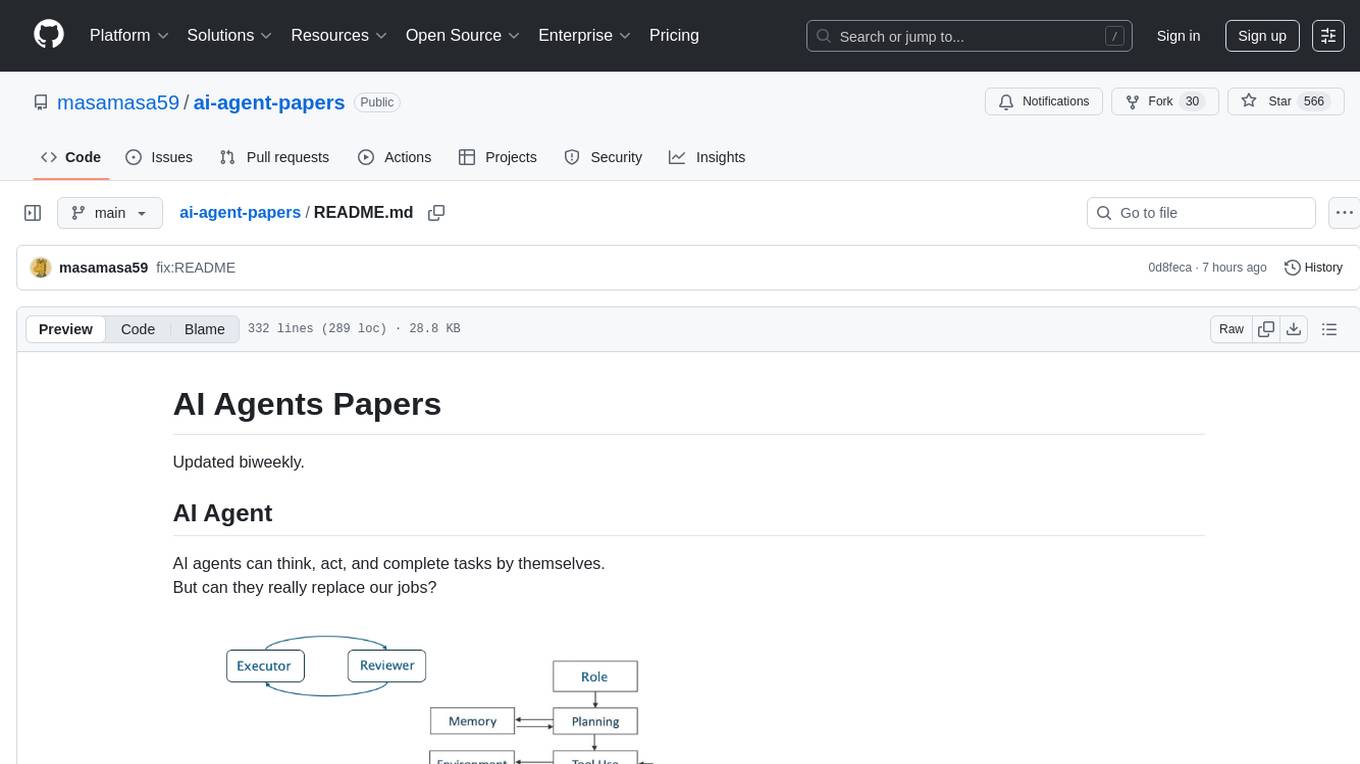
ai-agent-papers
The AI Agents Papers repository provides a curated collection of papers focusing on AI agents, covering topics such as agent capabilities, applications, architectures, and presentations. It includes a variety of papers on ideation, decision making, long-horizon tasks, learning, memory-based agents, self-evolving agents, and more. The repository serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners interested in AI agent technologies and advancements.
LLM-Tool-Survey
This repository contains a collection of papers related to tool learning with large language models (LLMs). The papers are organized according to the survey paper 'Tool Learning with Large Language Models: A Survey'. The survey focuses on the benefits and implementation of tool learning with LLMs, covering aspects such as task planning, tool selection, tool calling, response generation, benchmarks, evaluation, challenges, and future directions in the field. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of tool learning with LLMs and inspire further exploration in this emerging area.
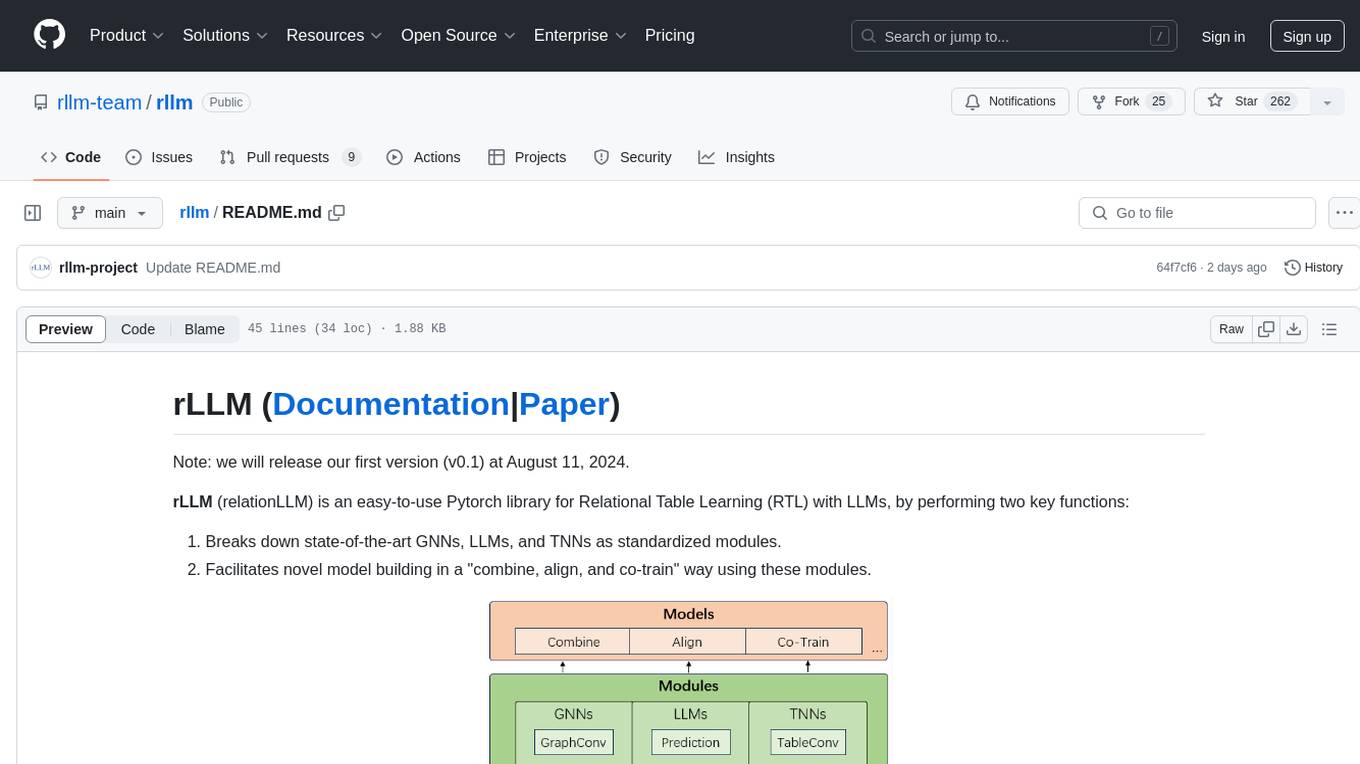
rllm
rLLM (relationLLM) is a Pytorch library for Relational Table Learning (RTL) with LLMs. It breaks down state-of-the-art GNNs, LLMs, and TNNs as standardized modules and facilitates novel model building in a 'combine, align, and co-train' way using these modules. The library is LLM-friendly, processes various graphs as multiple tables linked by foreign keys, introduces new relational table datasets, and is supported by students and teachers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Tsinghua University.
awesome-tool-llm
This repository focuses on exploring tools that enhance the performance of language models for various tasks. It provides a structured list of literature relevant to tool-augmented language models, covering topics such as tool basics, tool use paradigm, scenarios, advanced methods, and evaluation. The repository includes papers, preprints, and books that discuss the use of tools in conjunction with language models for tasks like reasoning, question answering, mathematical calculations, accessing knowledge, interacting with the world, and handling non-textual modalities.
llm.hunyuan.T1
Hunyuan-T1 is a cutting-edge large-scale hybrid Mamba reasoning model driven by reinforcement learning. It has been officially released as an upgrade to the Hunyuan Thinker-1-Preview model. The model showcases exceptional performance in deep reasoning tasks, leveraging the TurboS base and Mamba architecture to enhance inference capabilities and align with human preferences. With a focus on reinforcement learning training, the model excels in various reasoning tasks across different domains, showcasing superior abilities in mathematical, logical, scientific, and coding reasoning. Through innovative training strategies and alignment with human preferences, Hunyuan-T1 demonstrates remarkable performance in public benchmarks and internal evaluations, positioning itself as a leading model in the field of reasoning.
OpenRedTeaming
OpenRedTeaming is a repository focused on red teaming for generative models, specifically large language models (LLMs). The repository provides a comprehensive survey on potential attacks on GenAI and robust safeguards. It covers attack strategies, evaluation metrics, benchmarks, and defensive approaches. The repository also implements over 30 auto red teaming methods. It includes surveys, taxonomies, attack strategies, and risks related to LLMs. The goal is to understand vulnerabilities and develop defenses against adversarial attacks on large language models.
DriveLM
DriveLM is a multimodal AI model that enables autonomous driving by combining computer vision and natural language processing. It is designed to understand and respond to complex driving scenarios using visual and textual information. DriveLM can perform various tasks related to driving, such as object detection, lane keeping, and decision-making. It is trained on a massive dataset of images and text, which allows it to learn the relationships between visual cues and driving actions. DriveLM is a powerful tool that can help to improve the safety and efficiency of autonomous vehicles.
LLM-on-Tabular-Data-Prediction-Table-Understanding-Data-Generation
This repository serves as a comprehensive survey on the application of Large Language Models (LLMs) on tabular data, focusing on tasks such as prediction, data generation, and table understanding. It aims to consolidate recent progress in this field by summarizing key techniques, metrics, datasets, models, and optimization approaches. The survey identifies strengths, limitations, unexplored territories, and gaps in the existing literature, providing insights for future research directions. It also offers code and dataset references to empower readers with the necessary tools and knowledge to address challenges in this rapidly evolving domain.
language-ai-engineering-lab
The Language AI Engineering Lab is a structured repository focusing on Generative AI, guiding users from language fundamentals to production-ready Language AI systems. It covers topics like NLP, Transformers, Large Language Models, and offers hands-on learning paths, practical implementations, and end-to-end projects. The repository includes in-depth concepts, diagrams, code examples, and videos to support learning. It also provides learning objectives for various areas of Language AI engineering, such as NLP, Transformers, LLM training, prompt engineering, context management, RAG pipelines, context engineering, evaluation, model context protocol, LLM orchestration, agentic AI systems, multimodal models, MLOps, LLM data engineering, and domain applications like IVR and voice systems.
Awesome-Trustworthy-Embodied-AI
The Awesome Trustworthy Embodied AI repository focuses on the development of safe and trustworthy Embodied Artificial Intelligence (EAI) systems. It addresses critical challenges related to safety and trustworthiness in EAI, proposing a unified research framework and defining levels of safety and resilience. The repository provides a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art solutions, benchmarks, and evaluation metrics, aiming to bridge the gap between capability advancement and safety mechanisms in EAI development.
awesome-azure-openai-llm
This repository is a collection of references to Azure OpenAI, Large Language Models (LLM), and related services and libraries. It provides information on various topics such as RAG, Azure OpenAI, LLM applications, agent design patterns, semantic kernel, prompting, finetuning, challenges & abilities, LLM landscape, surveys & references, AI tools & extensions, datasets, and evaluations. The content covers a wide range of topics related to AI, machine learning, and natural language processing, offering insights into the latest advancements in the field.
llms-interview-questions
This repository contains a comprehensive collection of 63 must-know Large Language Models (LLMs) interview questions. It covers topics such as the architecture of LLMs, transformer models, attention mechanisms, training processes, encoder-decoder frameworks, differences between LLMs and traditional statistical language models, handling context and long-term dependencies, transformers for parallelization, applications of LLMs, sentiment analysis, language translation, conversation AI, chatbots, and more. The readme provides detailed explanations, code examples, and insights into utilizing LLMs for various tasks.
For similar tasks

Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science is a repository that compiles papers evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) from a social science perspective. It includes papers on evaluating, aligning, and simulating LLMs, as well as enhancing tools in social science research. The repository categorizes papers based on their focus on attitudes, opinions, values, personality, morality, and more. It aims to contribute to discussions on the potential and challenges of using LLMs in social science research.
For similar jobs
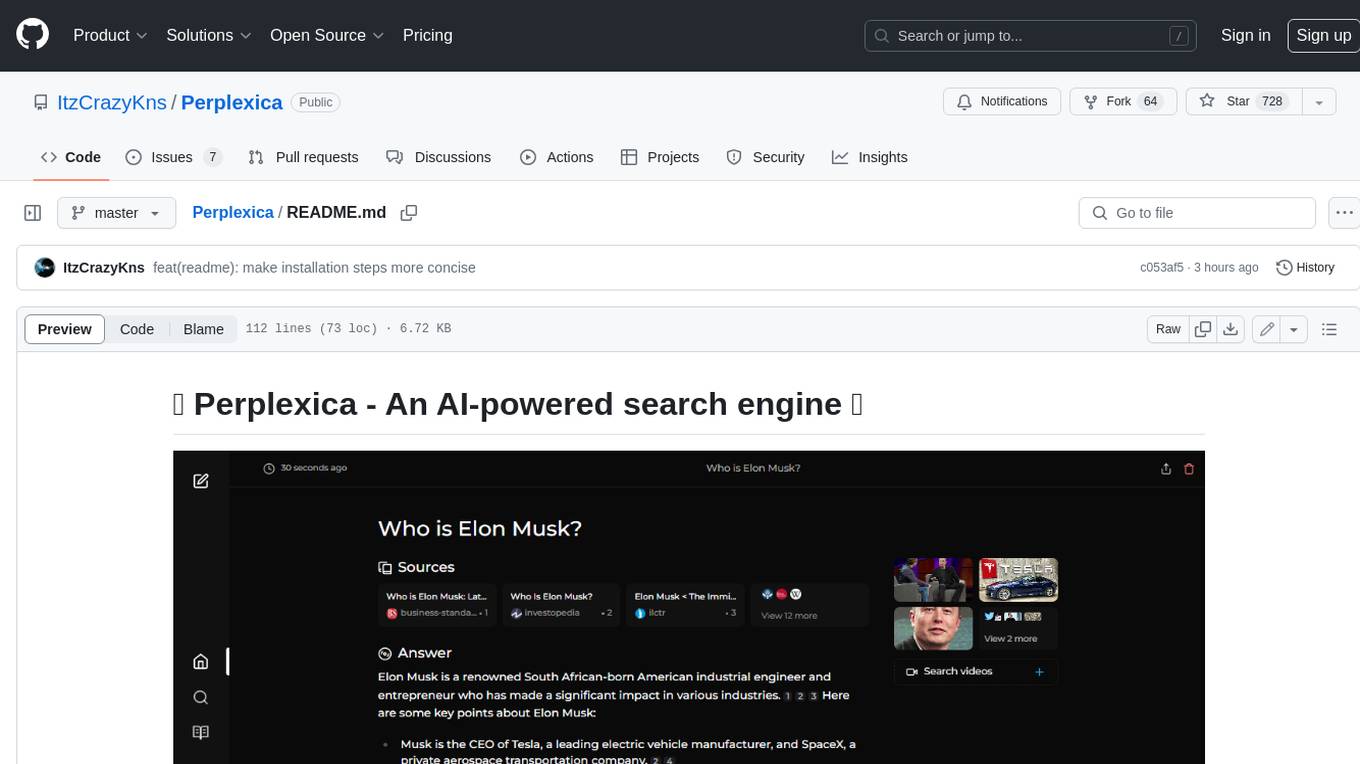
Perplexica
Perplexica is an open-source AI-powered search engine that utilizes advanced machine learning algorithms to provide clear answers with sources cited. It offers various modes like Copilot Mode, Normal Mode, and Focus Modes for specific types of questions. Perplexica ensures up-to-date information by using SearxNG metasearch engine. It also features image and video search capabilities and upcoming features include finalizing Copilot Mode and adding Discover and History Saving features.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
MMMU
MMMU is a benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal models on college-level subject knowledge tasks, covering 30 subjects and 183 subfields with 11.5K questions. It focuses on advanced perception and reasoning with domain-specific knowledge, challenging models to perform tasks akin to those faced by experts. The evaluation of various models highlights substantial challenges, with room for improvement to stimulate the community towards expert artificial general intelligence (AGI).
1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
gpt-researcher
GPT Researcher is an autonomous agent designed for comprehensive online research on a variety of tasks. It can produce detailed, factual, and unbiased research reports with customization options. The tool addresses issues of speed, determinism, and reliability by leveraging parallelized agent work. The main idea involves running 'planner' and 'execution' agents to generate research questions, seek related information, and create research reports. GPT Researcher optimizes costs and completes tasks in around 3 minutes. Features include generating long research reports, aggregating web sources, an easy-to-use web interface, scraping web sources, and exporting reports to various formats.
ChatTTS
ChatTTS is a generative speech model optimized for dialogue scenarios, providing natural and expressive speech synthesis with fine-grained control over prosodic features. It supports multiple speakers and surpasses most open-source TTS models in terms of prosody. The model is trained with 100,000+ hours of Chinese and English audio data, and the open-source version on HuggingFace is a 40,000-hour pre-trained model without SFT. The roadmap includes open-sourcing additional features like VQ encoder, multi-emotion control, and streaming audio generation. The tool is intended for academic and research use only, with precautions taken to limit potential misuse.
HebTTS
HebTTS is a language modeling approach to diacritic-free Hebrew text-to-speech (TTS) system. It addresses the challenge of accurately mapping text to speech in Hebrew by proposing a language model that operates on discrete speech representations and is conditioned on a word-piece tokenizer. The system is optimized using weakly supervised recordings and outperforms diacritic-based Hebrew TTS systems in terms of content preservation and naturalness of generated speech.
do-research-in-AI
This repository is a collection of research lectures and experience sharing posts from frontline researchers in the field of AI. It aims to help individuals upgrade their research skills and knowledge through insightful talks and experiences shared by experts. The content covers various topics such as evaluating research papers, choosing research directions, research methodologies, and tips for writing high-quality scientific papers. The repository also includes discussions on academic career paths, research ethics, and the emotional aspects of research work. Overall, it serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in advancing their research capabilities in the field of AI.