awesome-open-ended
Awesome Open-ended AI
Stars: 171
A curated list of open-ended learning AI resources focusing on algorithms that invent new and complex tasks endlessly, inspired by human advancements. The repository includes papers, safety considerations, surveys, perspectives, and blog posts related to open-ended AI research.
README:
A curated list of open-ended learning AI resources. The aim of open-ended algorithms is to keep on inventing new and ever-more complex tasks and solving them continually, even endlessly. From the invention of the wheel, to farming, vaccines, computers, and even rock and roll. These so-far uniquely human advancements and discoveries are the hallmark of civilization. What does AI need to possess to discover such new paradigms, as only humans have until now? Let's take a look at our progress on this frontier.
When submitting a pull request, please put the new paper at the correct chronological position as the following format:
* **Paper Title** <br>
*Author(s)* <br>
Conference, Year. [[Paper]](link) [[Code]](link) [[Website]](link)
-
Minimal Criterion Coevolution: A New Approach to Open-Ended Search
Jonathan C. Brant, Kenneth O. Stanley
GECCO, 2017. [Paper] [Code] -
Paired Open-Ended Trailblazer (POET): Endlessly Generating Increasingly Complex and Diverse Learning Environments and Their Solutions
Rui Wang, Joel Lehman, Jeff Clune, Kenneth O. Stanley
GECCO, 2019. [Paper] [Code] [Website] -
Enhanced POET: Open-Ended Reinforcement Learning through Unbounded Invention of Learning Challenges and their Solutions
Rui Wang, Joel Lehman, Aditya Rawal, Jiale Zhi, Yulun Li, Jeff Clune, Kenneth O. Stanley
ICML, 2020. [Paper] [Code] [Website] -
Co-generation of game levels and game-playing agents
Aaron Dharna, Julian Togelius, L.B.Soros
AIIDE 2020. [Paper] [Code] -
Emergent Complexity and Zero-shot Transfer via Unsupervised Environment Design
Michael Dennis, Natasha Jaques, Eugene Vinitsky, Alexandre Bayen, Stuart Russell, Andrew Critch, Sergey Levine
NeurIPS, 2020. [Paper] [Code] [Website] -
Co-optimising Robot Morphology and Controller in a Simulated Open-Ended Environment
Emma Hjellbrekke Stensby, Kai Olav Ellefsen, Kyrre Glette
EvoStar 2021. [Paper] [Code] -
Prioritized Level Replay
Minqi Jiang, Edward Grefenstette, Tim Rocktäschel
ICML, 2021. [Paper] [Code] -
Replay-Guided Adversarial Environment Design
Minqi Jiang*, Michael Dennis*, Jack Parker-Holder, Jakob Foerster, Edward Grefenstette, Tim Rocktäschel
NeurIPS, 2021. [Paper] [Code] -
Environment Generation for Zero-Shot Compositional Reinforcement Learning
Izzeddin Gur, Natasha Jaques, Yingjie Miao, Jongwook Choi, Manoj Tiwari, Honglak Lee, Aleksandra Faust
NeurIPS, 2021. [Paper] -
MiniHack the Planet: A Sandbox for Open-Ended Reinforcement Learning Research
Mikayel Samvelyan, Robert Kirk, Vitaly Kurin, Jack Parker-Holder, Minqi Jiang, Eric Hambro, Fabio Petroni, Heinrich Küttler, Edward Grefenstette, Tim Rocktäschel
NeurIPS, 2021. [Paper] [Code] [Website] -
Open-Ended Learning Leads to Generally Capable Agents
Open Ended Learning Team, Adam Stooke, Anuj Mahajan, Catarina Barros, Charlie Deck, Jakob Bauer, Jakub Sygnowski, Maja Trebacz, Max Jaderberg, Michael Mathieu, Nat McAleese, Nathalie Bradley-Schmieg, Nathaniel Wong, Nicolas Porcel, Roberta Raileanu, Steph Hughes-Fitt, Valentin Dalibard, Wojciech Marian Czarnecki
arXiv, 2021. [Paper] [Website] -
SPOTTER: Extending Symbolic Planning Operators through Targeted Reinforcement Learning
Vasanth Sarathy, Daniel Kasenberg, Shivam Goel, Jivko Sinapov, Matthias Scheutz
arXiv, 2021. [Paper] [Code] -
EvoCraft: A New Challenge for Open-Endedness
Djordje Grbic, Rasmus Berg Palm, Elias Najarro, Claire Glanois, Sebastian Risi
EvoStar, 2021. [Paper] [Website] -
Video Games as a Testbed for Open-Ended Phenomena
Sam Earle; Julian Togelius; L. B. Soros
IEEE Conference on Games, 2021. [Paper] -
Open-ended search for environments and adapted agents using map-elites
Emma Stensby Norstein, Kai Olav Ellefsen, Kyrre Glette
EvoStar, 2022. [Paper] [Code] -
Minimal Criterion Artist Collective
Kai Arulkumaran; Thu Nguyen-Phuoc
GECCO, 2022. [Paper] [Code] -
Evolving Curricula with Regret-Based Environment Design
Jack Parker-Holder*, Minqi Jiang*, Michael Dennis, Mikayel Samvelyan, Jakob Foerster, Edward Grefenstette, Tim Rocktäschel
ICML, 2022. [Paper] [Code] [Demo] -
Evolution through Large Models
Joel Lehman, Jonathan Gordon, Shawn Jain, Kamal Ndousse, Cathy Yeh, Kenneth Stanley
arXiv, 2022. [Paper] [Code] -
RAPid-Learn: A Framework for Learning to Recover for Handling Novelties in Open-World Environments
Shivam Goel, Yash Shukla, Vasanth Sarathy, Matthias Scheutz, Jivko Sinapov
arXiv, 2022. [Paper] [Code] -
Transfer Dynamics in Emergent Evolutionary Curricula
Aaron Dharna, Amy K. Hoover, Julian Togelius, Lisa Soros
IEEE Transactions on Games, 2022. [Paper] [Code] -
Watts: Infrastructure for Open-Ended Learning
Aaron Dharna, Charlie Summers, Rohin Dasari, Julian Togelius, Amy K. Hoover
ALOE Workshop 2022 [Paper] [Code] -
MineDojo: Building Open-Ended Embodied Agents with Internet-Scale Knowledge
Linxi Fan, Guanzhi Wang, Yunfan Jiang, Ajay Mandlekar, Yuncong Yang, Haoyi Zhu, Andrew Tang, De-An Huang, Yuke Zhu, Anima Anandkumar
NeurIPS, 2022. [Paper] [Code] [Website] -
Grounding Aleatoric Uncertainty in Unsupervised Environment Design
Minqi Jiang, Michael Dennis, Jack Parker-Holder, Andrei Lupu, Heinrich Küttler, Edward Grefenstette, Tim Rocktäschel, Jakob Foerster
NeurIPS 2022. [Paper] -
Language and Culture Internalisation for Human-Like Autotelic AI
Cédric Colas, Tristan Karch, Clément Moulin-Frier, Pierre-Yves Oudeyer
Nature Machine Intelligence, 2022. [Paper] [Website] -
Flow-Lenia: Towards open-ended evolution in cellular automata through mass conservation and parameter localization
Erwan Plantec, Gautier Hamon, Mayalen Etcheverry, Pierre-Yves Oudeyer, Clément Moulin-Frier, Bert Wang-Chak Chan
ALife 2023. [Paper] -
MAESTRO: Open-Ended Environment Design for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Mikayel Samvelyan, Akbir Khan, Michael Dennis, Minqi Jiang, Jack Parker-Holder, Jakob Foerster, Roberta Raileanu, Tim Rocktäschel
ICLR, 2023. [Paper] [Website] -
Powderworld: A Platform for Understanding Generalization via Rich Task Distributions
Kevin Frans, Philip Isola
ICLR, 2023. [Paper] [Website] [Code] -
Human-Timescale Adaptation in an Open-Ended Task Space
Adaptive Agent Team, Jakob Bauer, Kate Baumli, Satinder Baveja, Feryal Behbahani, Avishkar Bhoopchand, Nathalie Bradley-Schmieg, Michael Chang, Natalie Clay, Adrian Collister, Vibhavari Dasagi, Lucy Gonzalez, Karol Gregor, Edward Hughes, Sheleem Kashem, Maria Loks-Thompson, Hannah Openshaw, Jack Parker-Holder, Shreya Pathak, Nicolas Perez-Nieves, Nemanja Rakicevic, Tim Rocktäschel, Yannick Schroecker, Jakub Sygnowski, Karl Tuyls, Sarah York, Alexander Zacherl, Lei Zhang
ICML, 2023. [Paper] [Website] -
Deep Laplacian-based Options for Temporally-Extended Exploration
Martin Klissarov, Marlos C. Machado
ICML, 2023. [Paper] [Blogpost 1] [Blogpost2] -
Discovering General Reinforcement Learning Algorithms with Adversarial Environment Design
Matthew T. Jackson, Minqi Jiang, Jack Parker-Holder, Risto Vuorio, Chris Lu, Gregory Farquhar, Shimon Whiteson, Jakob N. Foerster
NeurIPS, 2023. [Paper] [Code] -
Voyager: An Open-Ended Embodied Agent with Large Language Models
Guanzhi Wang, Yuqi Xie, Yunfan Jiang, Ajay Mandlekar, Chaowei Xiao, Yuke Zhu, Linxi Fan, Anima Anandkumar
arXiv, 2023. [Paper] [Code] [Website] -
Augmenting Autotelic Agents with Large Language Models
Cédric Colas, Laetitia Teodorescu, Pierre-Yves Oudeyer, Xingdi Yuan, Marc-Alexandre Côté
arXiv, 2023. [Paper] -
Reward-Free Curricula for Training Robust World Models
Marc Rigter, Minqi Jiang, Ingmar Posner
arXiv, 2023. [Paper] -
Promptbreeder: Self-Referential Self-Improvement Via Prompt Evolution
Chrisantha Fernando, Dylan Banarse, Henryk Michalewski, Simon Osindero, Tim Rocktäschel
arXiv, 2023. [Paper] -
Self-Taught Optimizer (STOP): Recursively Self-Improving Code Generation
Eric Zelikman, Eliana Lorch, Lester Mackey, Adam Tauman Kalai
arXiv, 2023. [Paper] -
Motif: Intrinsic Motivation from Artificial Intelligence Feedback
Martin Klissarov, Pierluca D'Oro, Shagun Sodhani, Roberta Raileanu, Pierre-Luc Bacon, Pascal Vincent, Amy Zhang, Mikael Henaff
arXiv, 2023. [Paper] [Code] -
Eureka: Human-Level Reward Design via Coding Large Language Models
Yecheng Jason Ma, William Liang, Guanzhi Wang, De-An Huang, Osbert Bastani, Dinesh Jayaraman, Yuke Zhu, Linxi Fan, Anima Anandkumar
arXiv, 2023. [Paper] [Code] [Website] -
Practical PCG Through Large Language Models
Muhammad U Nasir, Julian Togelius
CoG, 2023. [Paper] -
Augmentative Topology Agents For Open-Ended Learning
Muhammad U. Nasir, Michael Beukman, Steven James, Christopher W. Cleghorn
GECCO, 2023. [Paper] [Code] -
OMNI: Open-endedness via Models of human Notions of Interestingness
Jenny Zhang, Joel Lehman, Kenneth Stanley, Jeff Clune
ICLR, 2024. [Paper] [Code] [Website] -
Quality-Diversity through AI Feedback
Herbie Bradley, Andrew Dai, Hannah Teufel, Jenny Zhang, Koen Oostermeijer, Marco Bellagente, Jeff Clune, Kenneth Stanley, Grégory Schott, Joel Lehman
ICLR, 2024. [Paper] [Website] -
Quality Diversity through Human Feedback
Li Ding, Jenny Zhang, Jeff Clune, Lee Spector, Joel Lehman
ICML, 2024. [Paper] -
OS-Copilot: Towards Generalist Computer Agents with Self-Improvement
Zhiyong Wu, Chengcheng Han*, Zichen Ding, Zhenmin Weng, Zhoumianze Liu, Shunyu Yao, Tao Yu, Lingpeng Kong
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] [Code] [Website] -
Multi-Agent Diagnostics for Robustness via Illuminated Diversity
Mikayel Samvelyan, Davide Paglieri, Minqi Jiang, Jack Parker-Holder, Tim Rocktäschel
AAMAS, 2024. [Paper] [Website] -
Evolutionary Optimization of Model Merging Recipes
Takuya Akiba, Makoto Shing, Yujin Tang, Qi Sun, David Ha
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
Discovering Preference Optimization Algorithms with and for Large Language Models
Chris Lu, Samuel Holt, Claudio Fanconi, Alex J. Chan, Jakob Foerster, Mihaela van der Schaar, Robert Tjarko Lange
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
Generative Design through Quality-Diversity Data Synthesis and Language Models
Adam Gaier, James Stoddart, Lorenzo Villaggi, Shyam Sudhakaran
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
OMNI-EPIC: Open-endedness via Models of human Notions of Interestingness with Environments Programmed in Code
Maxence Faldor, Jenny Zhang, Antoine Cully, Jeff Clune
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] [Website] -
Artificial Generational Intelligence: Cultural Accumulation in Reinforcement Learning
Jonathan Cook, Chris Lu, Edward Hughes, Joel Z. Leibo, Jakob Foerster
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
Computational Life: How Well-formed, Self-replicating Programs Emerge from Simple Interaction
Blaise Agüera y Arcas, Jyrki Alakuijala, James Evans, Ben Laurie, Alexander Mordvintsev, Eyvind Niklasson, Ettore Randazzo, Luca Versari
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
Intelligent Go-Explore: Standing on the Shoulders of Giant Foundation Models
Cong Lu, Shengran Hu, Jeff Clune
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
Genie: Generative Interactive Environments
Jake Bruce, Michael Dennis, Ashley Edwards, Jack Parker-Holder, Yuge Shi, Edward Hughes, Matthew Lai, Aditi Mavalankar, Richie Steigerwald, Chris Apps, Yusuf Aytar, Sarah Bechtle, Feryal Behbahani, Stephanie Chan, Nicolas Heess, Lucy Gonzalez, Simon Osindero, Sherjil Ozair, Scott Reed, Jingwei Zhang, Konrad Zolna, Jeff Clune, Nando de Freitas, Satinder Singh, Tim Rocktäschel
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
Debating with More Persuasive LLMs Leads to More Truthful Answers
Akbir Khan, John Hughes, Dan Valentine, Laura Ruis, Kshitij Sachan, Ansh Radhakrishnan, Edward Grefenstette, Samuel R. Bowman, Tim Rocktäschel, Ethan Perez
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
Toward Artificial Open-Ended Evolution within Lenia using Quality-Diversity
Maxence Faldor, Antoine Cully
ALife, 2024. [Paper] -
Structurally Flexible Neural Networks: Evolving the Building Blocks for General Agents
Joachim Winther Pedersen, Erwan Plantec, Eleni Nisioti, Milton Montero, Sebastian Risi
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
DreamCraft: Text-Guided Generation of Functional 3D Environments in Minecraft
Sam Earle, Filippos Kokkinos, Yuhe Nie, Julian Togelius, Roberta Raileanu
FDG, 2024. [Paper] -
Large Language Models as In-context AI Generators for Quality-Diversity
Bryan Lim, Manon Flageat, Antoine Cully
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] -
Word2World: Generating Stories and Worlds through Large Language Models
Muhammad U. Nasir, Steven James, Julian Togelius
arXiv, 2024. [Paper] [Code]
-
Open Questions in Creating Safe Open-ended AI: Tensions Between Control and Creativity
Adrien Ecoffet, Jeff Clune, Joel Lehman
arXiv, 2020. [Paper] -
Open Questions in Creating Safe Open-ended AI: Tensions Between Control and Creativity
Yoshua Bengio, Geoffrey Hinton, Andrew Yao, Dawn Song, Pieter Abbeel, Trevor Darrell, Yuval Noah Harari, Ya-Qin Zhang, Lan Xue, Shai Shalev-Shwartz, Gillian Hadfield, Jeff Clune, Tegan Maharaj, Frank Hutter, Atılım Güneş Baydin, Sheila McIlraith, Qiqi Gao, Ashwin Acharya, David Krueger, Anca Dragan, Philip Torr, Stuart Russell, Daniel Kahneman, Jan Brauner, Sören Mindermann
Science, 2024. [Paper] -
Rainbow Teaming: Open-Ended Generation of Diverse Adversarial Prompts
Mikayel Samvelyan, Sharath Chandra Raparthy, Andrei Lupu, Eric Hambro, Aram H. Markosyan, Manish Bhatt, Yuning Mao, Minqi Jiang, Jack Parker-Holder, Jakob Foerster, Tim Rocktäschel, Roberta Raileanu
NeurIPS, 2024. [Paper] [Website]
-
Why Greatness Cannot Be Planned: The Myth of the Objective
Kenneth O. Stanley, Joel Lehman
Springer, 2015. [Book] -
Open-endedness: The last grand challenge you’ve never heard of
Kenneth O. Stanley, Joel Lehman, Lisa Soros
O'Reilly Radar, 2017. [Paper] -
AI-GAs: AI-generating algorithms, an alternate paradigm for producing general artificial intelligence
Jeff Clune
arXiv, 2019. [Paper] -
Creative Problem Solving in Artificially Intelligent Agents: A Survey and Framework
Evana Gizzi, Lakshmi Nair, Sonia Chernova, Jivko Sinapov
arXiv, 2022. [Paper] -
Executive Function: A Contrastive Value Policy for Resampling and Relabeling Perceptions via Hindsight Summarization?
Chris Lengerich, Ben Lengerich.
arXiv, 2022. [Paper] -
General Intelligence Requires Rethinking Exploration
Minqi Jiang, Tim Rocktäschel, Edward Grefenstette
Royal Society Open Science, 2023. [Paper] -
Open-Endedness is Essential for Artificial Superhuman Intelligence
Edward Hughes, Michael Dennis, Jack Parker-Holder, Feryal Behbahani, Aditi Mavalankar, Yuge Shi, Tom Schaul, Tim Rocktaschel
ICML, 2024. [Paper]
-
Interactive poetry breeding through Mixtral base model LLMs
Joel Lehman. 2024. [Blog] -
Identifying Life-Changing Books with LLMs
Joel Lehman. 2024. [Blog] -
SerendipityLM: Interactive evolutionary exploration of generative design spaces with large language models
Samim. 2024. [Blog] -
AiWallz: AI Wallpapers
Rach Pradhan, Jenny Zhang. 2024. [App] [Blog]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for awesome-open-ended
Similar Open Source Tools

awesome-open-ended
A curated list of open-ended learning AI resources focusing on algorithms that invent new and complex tasks endlessly, inspired by human advancements. The repository includes papers, safety considerations, surveys, perspectives, and blog posts related to open-ended AI research.
Awesome-LLM-RAG
This repository, Awesome-LLM-RAG, aims to record advanced papers on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in Large Language Models (LLMs). It serves as a resource hub for researchers interested in promoting their work related to LLM RAG by updating paper information through pull requests. The repository covers various topics such as workshops, tutorials, papers, surveys, benchmarks, retrieval-enhanced LLMs, RAG instruction tuning, RAG in-context learning, RAG embeddings, RAG simulators, RAG search, RAG long-text and memory, RAG evaluation, RAG optimization, and RAG applications.
Awesome-LLM-Reasoning-Openai-o1-Survey
The repository 'Awesome LLM Reasoning Openai-o1 Survey' provides a collection of survey papers and related works on OpenAI o1, focusing on topics such as LLM reasoning, self-play reinforcement learning, complex logic reasoning, and scaling law. It includes papers from various institutions and researchers, showcasing advancements in reasoning bootstrapping, reasoning scaling law, self-play learning, step-wise and process-based optimization, and applications beyond math. The repository serves as a valuable resource for researchers interested in exploring the intersection of language models and reasoning techniques.

awesome-generative-information-retrieval
This repository contains a curated list of resources on generative information retrieval, including research papers, datasets, tools, and applications. Generative information retrieval is a subfield of information retrieval that uses generative models to generate new documents or passages of text that are relevant to a given query. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as question answering, summarization, and document generation. The resources in this repository are intended to help researchers and practitioners stay up-to-date on the latest advances in generative information retrieval.
Prompt4ReasoningPapers
Prompt4ReasoningPapers is a repository dedicated to reasoning with language model prompting. It provides a comprehensive survey of cutting-edge research on reasoning abilities with language models. The repository includes papers, methods, analysis, resources, and tools related to reasoning tasks. It aims to support various real-world applications such as medical diagnosis, negotiation, etc.
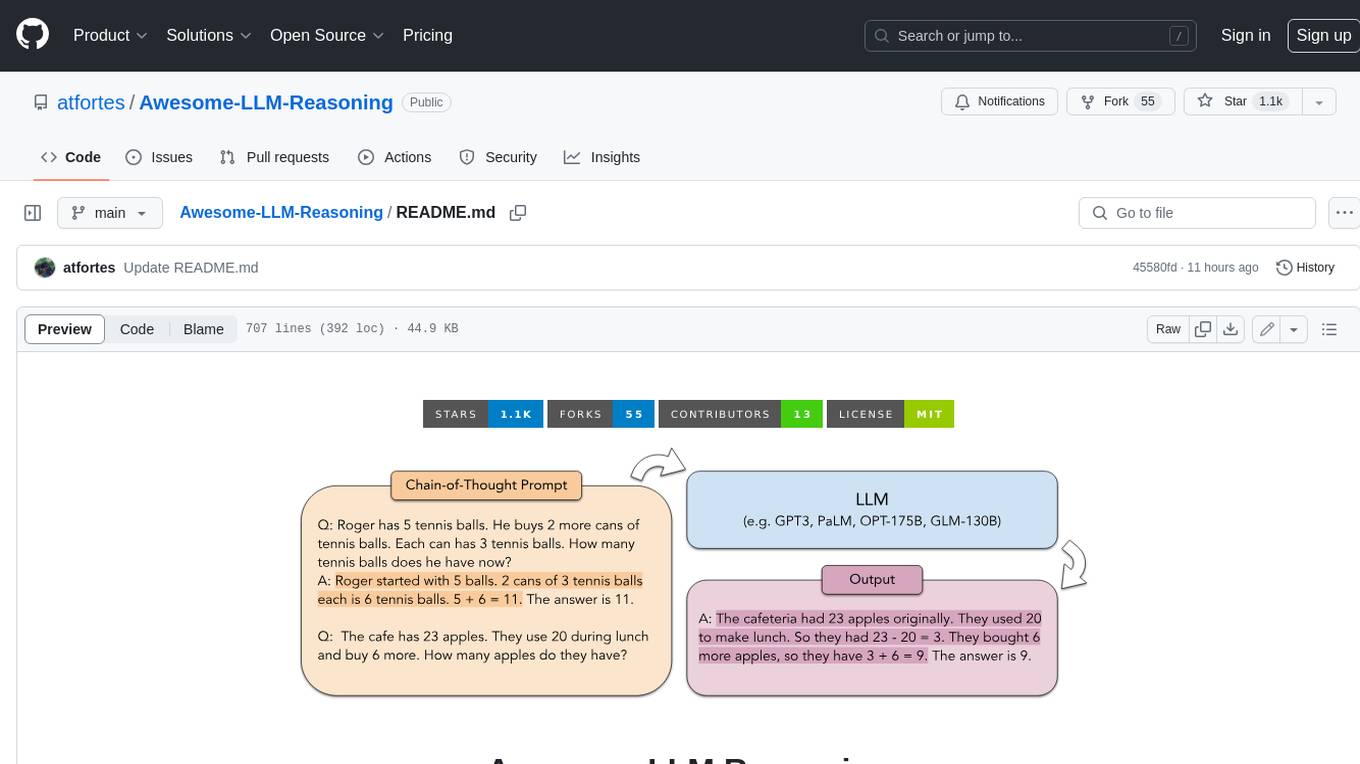
Awesome-LLM-Reasoning
**Curated collection of papers and resources on how to unlock the reasoning ability of LLMs and MLLMs.** **Description in less than 400 words, no line breaks and quotation marks.** Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the NLP landscape, showing improved performance and sample efficiency over smaller models. However, increasing model size alone has not proved sufficient for high performance on challenging reasoning tasks, such as solving arithmetic or commonsense problems. This curated collection of papers and resources presents the latest advancements in unlocking the reasoning abilities of LLMs and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs). It covers various techniques, benchmarks, and applications, providing a comprehensive overview of the field. **5 jobs suitable for this tool, in lowercase letters.** - content writer - researcher - data analyst - software engineer - product manager **Keywords of the tool, in lowercase letters.** - llm - reasoning - multimodal - chain-of-thought - prompt engineering **5 specific tasks user can use this tool to do, in less than 3 words, Verb + noun form, in daily spoken language.** - write a story - answer a question - translate a language - generate code - summarize a document
awesome-llm-role-playing-with-persona
Awesome-llm-role-playing-with-persona is a curated list of resources for large language models for role-playing with assigned personas. It includes papers and resources related to persona-based dialogue systems, personalized response generation, psychology of LLMs, biases in LLMs, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of research papers and tools for exploring role-playing abilities of large language models in various contexts.
LLM4DB
LLM4DB is a repository focused on the intersection of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Database technologies. It covers various aspects such as data processing, data analysis, database optimization, and data management for LLMs. The repository includes research papers, tools, and techniques related to leveraging LLMs for tasks like data cleaning, entity matching, schema matching, data discovery, NL2SQL, data exploration, data visualization, knob tuning, query optimization, and database diagnosis.
Awesome-LLM-Preference-Learning
The repository 'Awesome-LLM-Preference-Learning' is the official repository of a survey paper titled 'Towards a Unified View of Preference Learning for Large Language Models: A Survey'. It contains a curated list of papers related to preference learning for Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository covers various aspects of preference learning, including on-policy and off-policy methods, feedback mechanisms, reward models, algorithms, evaluation techniques, and more. The papers included in the repository explore different approaches to aligning LLMs with human preferences, improving mathematical reasoning in LLMs, enhancing code generation, and optimizing language model performance.
ai4math-papers
The 'ai4math-papers' repository contains a collection of research papers related to AI applications in mathematics, including automated theorem proving, synthetic theorem generation, autoformalization, proof refactoring, premise selection, benchmarks, human-in-the-loop interactions, and constructing examples/counterexamples. The papers cover various topics such as neural theorem proving, reinforcement learning for theorem proving, generative language modeling, formal mathematics statement curriculum learning, and more. The repository serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners interested in the intersection of AI and mathematics.

LLM4DB
LLM4DB is a repository focused on the intersection of Large Language Models (LLM) and Database technologies. It covers various aspects such as data processing, data analysis, database optimization, and data management for LLM. The repository includes works on data cleaning, entity matching, schema matching, data discovery, NL2SQL, data exploration, data visualization, configuration tuning, query optimization, and anomaly diagnosis using LLMs. It aims to provide insights and advancements in leveraging LLMs for improving data processing, analysis, and database management tasks.
LLMAgentPapers
LLM Agents Papers is a repository containing must-read papers on Large Language Model Agents. It covers a wide range of topics related to language model agents, including interactive natural language processing, large language model-based autonomous agents, personality traits in large language models, memory enhancements, planning capabilities, tool use, multi-agent communication, and more. The repository also provides resources such as benchmarks, types of tools, and a tool list for building and evaluating language model agents. Contributors are encouraged to add important works to the repository.
For similar tasks

awesome-open-ended
A curated list of open-ended learning AI resources focusing on algorithms that invent new and complex tasks endlessly, inspired by human advancements. The repository includes papers, safety considerations, surveys, perspectives, and blog posts related to open-ended AI research.
autogen
AutoGen is a framework that enables the development of LLM applications using multiple agents that can converse with each other to solve tasks. AutoGen agents are customizable, conversable, and seamlessly allow human participation. They can operate in various modes that employ combinations of LLMs, human inputs, and tools.
llmesh
LLM Agentic Tool Mesh is a platform by HPE Athonet that democratizes Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) by enabling users to create tools and web applications using Gen AI with Low or No Coding. The platform simplifies the integration process, focuses on key user needs, and abstracts complex libraries into easy-to-understand services. It empowers both technical and non-technical teams to develop tools related to their expertise and provides orchestration capabilities through an agentic Reasoning Engine based on Large Language Models (LLMs) to ensure seamless tool integration and enhance organizational functionality and efficiency.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.