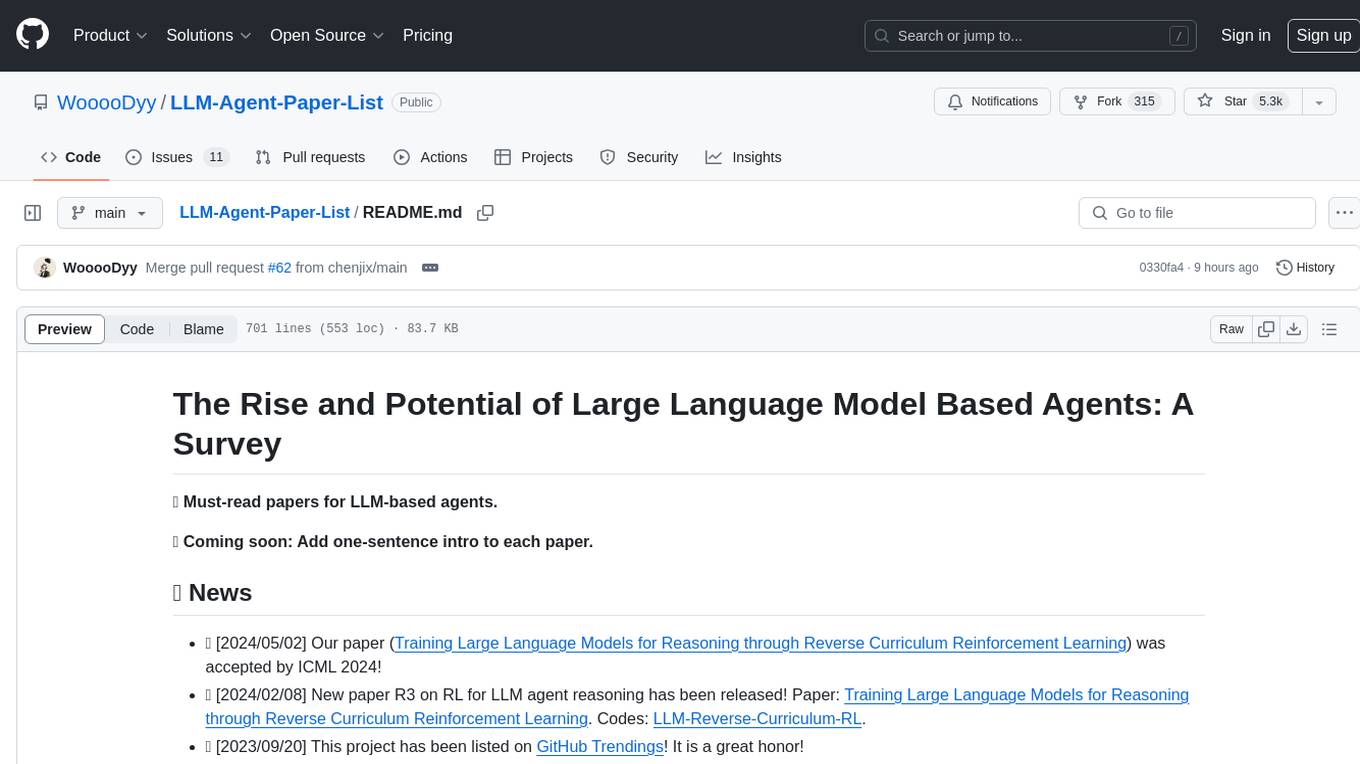
awesome-large-audio-models
Collection of resources on the applications of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Audio AI.
Stars: 481
This repository is a curated list of awesome large AI models in audio signal processing, focusing on the application of large language models to audio tasks. It includes survey papers, popular large audio models, automatic speech recognition, neural speech synthesis, speech translation, other speech applications, large audio models in music, and audio datasets. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive overview of recent advancements and challenges in applying large language models to audio signal processing, showcasing the efficacy of transformer-based architectures in various audio tasks.
README:
This repo supplements our survey paper: Sparks of Large Audio Models: A Survey and Outlook.
Authors: Siddique Latif, Moazzam Shoukat, Fahad Shamshad, Muhammad Usama, Yi Ren, Heriberto Cuayahuitl, Xulong Zhang, Roberto Togneri, Wenwu Wang, Bjorn Schuller.
Abstract:
This survey paper provides a comprehensive overview of the recent advancements and challenges in applying large language models to the field of audio signal processing. Audio processing, with its diverse signal representations and a wide range of sources--from human voices to musical instruments and environmental sounds--poses challenges distinct from those found in traditional Natural Language Processing scenarios. Nevertheless, Large Audio Models, epitomized by transformer-based architectures, have shown marked efficacy in this sphere. By leveraging massive amounts of data, these models have demonstrated prowess in a variety of audio tasks, spanning from Automatic Speech Recognition and Text-To-Speech to Music Generation, among others. Notably, recently these Foundational Audio Models, like SeamlessM4T, have started showing abilities to act as universal translators, supporting multiple speech tasks for up to 100 languages without any reliance on separate task-specific systems. This paper presents an in-depth analysis of state-of-the-art methodologies regarding Foundational Large Audio Models, their performance benchmarks, and their applicability to real-world scenarios. We also highlight current limitations and provide insights into potential future research directions in the realm of Large Audio Models with the intent to spark further discussion, thereby fostering innovation in the next generation of audio-processing systems.
Awesome Large Language Models in Audio AI
A curated list of awesome large AI models in audio signal processing, inspired by the other awesome initiatives. We intend to regularly update the relevant latest papers and their open-source implementations on this page.
- Popular Large Audio Models
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
- Neural Speech Synthesis
- Speech Translation (ST)
- Other Speech Applications
- Large Audio Models in Music
- Audio Datasets
A review of deep learning techniques for speech processing [2023].
Ambuj Mehrish, Navonil Majumder, Rishabh Bharadwaj, Rada Mihalcea, Soujanya Poria
[PDF]
A survey on deep reinforcement learning for audio-based applications [2023].
Latif, Siddique and Cuayáhuitl, Heriberto and Pervez, Farrukh and Shamshad, Fahad and Ali, Hafiz Shehbaz and Cambria, Erik
[PDF]
A Survey of Large Language Models [2023].
Wayne Xin Zhao, Kun Zhou, Junyi Li, Tianyi Tang, Xiaolei Wang, Yupeng Hou, Yingqian Min, Beichen Zhang, Junjie Zhang, Zican Dong, Yifan Du, Chen Yang, Yushuo Chen, Zhipeng Chen, Jinhao Jiang, Ruiyang Ren, Yifan Li, Xinyu Tang, Zikang Liu, Peiyu Liu, Jian-Yun Nie, Ji-Rong Wen
[PDF]
A survey on evaluation of large language models [2023].
Yupeng Chang, Xu Wang, Jindong Wang, Yuan Wu, Linyi Yang, Kaijie Zhu, Hao Chen, Xiaoyuan Yi, Cunxiang Wang, Yidong Wang, Wei Ye, Yue Zhang, Yi Chang, Philip S. Yu, Qiang Yang, Xing Xie
[PDF]
Challenges and Applications of Large Language Models [2023].
Kaddour, Jean and Harris, Joshua and Mozes, Maximilian and Bradley, Herbie and Raileanu, Roberta and McHardy, Robert
[PDF]
Aligning Large Language Models with Human: A Survey [2023].
Yufei Wang, Wanjun Zhong, Liangyou Li, Fei Mi, Xingshan Zeng, Wenyong Huang, Lifeng Shang, Xin Jiang, Qun Liu
[PDF]
A Comprehensive Survey on Segment Anything Model for Vision and Beyond [2023].
Zhang, Chunhui and Liu, Li and Cui, Yawen and Huang, Guanjie and Lin, Weilin and Yang, Yiqian and Hu, Yuehong
[PDF]
Vision-language models for vision tasks: A survey [2023].
Zhang, Jingyi and Huang, Jiaxing and Jin, Sheng and Lu, Shijian
[PDF]
Foundational Models Defining a New Era in Vision: A Survey and Outlook [2023].
Awais, Muhammad and Naseer, Muzammal and Khan, Salman and Anwer, Rao Muhammad and Cholakkal, Hisham and Shah, Mubarak and Yang, Ming-Hsuan and Khan, Fahad Shahbaz
[PDF]
Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models [2023].
Tiffany H. Kung, Morgan Cheatham, Arielle Medenilla, Czarina Sillos, Lorie De Leon, Camille Elepaño, Maria Madriaga, Rimel Aggabao, Giezel Diaz-Candido, James Maningo, Victor Tseng
[PDF]
Engineering education in the era of ChatGPT: Promise and pitfalls of generative AI for education [2023].
Junaid Qadir
[PDF]
ChatGPT: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? [2023].
Jürgen Rudolph, Samson Tan, Shannon Tan
[PDF]
Foundation models for generalist medical artificial intelligence [2023].
Moor, Michael and Banerjee, Oishi and Abad, Zahra Shakeri Hossein and Krumholz, Harlan M and Leskovec, Jure and Topol, Eric J and Rajpurkar, Pranav
[PDF]
Large AI models in health informatics: Applications, challenges, and the future [2023].
Jianing Qiu, Lin Li, Jiankai Sun, Jiachuan Peng, Peilun Shi, Ruiyang Zhang, Yinzhao Dong, Kyle Lam, Frank P.-W. Lo, Bo Xiao, Wu Yuan, Dong Xu, Benny Lo
[PDF]
The shaky foundations of large language models and foundation models for electronic health records [2023].
Michael Wornow, Yizhe Xu, Rahul Thapa, Birju Patel, Ethan Steinberg, Scott Fleming, Michael A. Pfeffer, Jason Fries & Nigam H. Shah
[PDF]
On the Challenges and Perspectives of Foundation Models for Medical Image Analysis [2023].
Shaoting Zhang, Dimitris Metaxas
[PDF]
Survey of Protein Sequence Embedding Models [2023].
Chau Tran, Siddharth Khadkikar, Aleksey Porollo
[PDF]
A Short Survey of Viewing Large Language Models in Legal Aspect [2023].
Zhongxiang Sun
[PDF]
Large Language Models as Tax Attorneys: A Case Study in Legal Capabilities Emergence [2023].
John J. Nay, David Karamardian, Sarah B. Lawsky, Wenting Tao, Meghana Bhat, Raghav Jain, Aaron Travis Lee, Jonathan H. Choi, Jungo Kasai
[PDF]
Foundation Models for Decision Making: Problems, Methods, and Opportunities [2023].
Sherry Yang, Ofir Nachum, Yilun Du, Jason Wei, Pieter Abbeel, Dale Schuurmans
[PDF]
Transformers in speech processing: A survey [2022].
Siddique Latif, Aun Zaidi, Heriberto Cuayahuitl, Fahad Shamshad, Moazzam Shoukat, Junaid Qadir
[PDF]
On the opportunities and risks of foundation models [2022].
*Rishi Bommasani, Drew A. Hudson, Ehsan Adeli, Russ Altman, Simran Arora, Sydney von Arx et. al. *
[PDF]
Vision-language pre-training: Basics, recent advances, and future trends [2022].
Zhe Gan, Linjie Li, Chunyuan Li, Lijuan Wang, Zicheng Liu, Jianfeng Gao
[PDF]
ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education [2022].
Enkelejda Kasneci, Kathrin Sessler, Stefan Küchemann, Maria Bannert, Daryna Dementieva, Frank Fischer, Urs Gasser, Georg Groh, Stephan Günnemann, Eyke Hüllermeier, Stephan Krusche, Gitta Kutyniok, Tilman Michaeli, Claudia Nerdel, Jürgen Pfeffer, Oleksandra Poquet, Michael Sailer, Albrecht Schmidt, Tina Seidel, Matthias Stadler, Jochen Weller, Jochen Kuhn, Gjergji Kasneci
[PDF]
Protein language models and structure prediction: Connection and progression [2022].
Bozhen Hu, Jun Xia, Jiangbin Zheng, Cheng Tan, Yufei Huang, Yongjie Xu, Stan Z. Li
[PDF]
A human being wrote this law review article: GPT-3 and the practice of law [2022].
Amy B. Cyphert
[PDF]
A comparative study on transformer vs rnn in speech applications [2019].
Shigeki Karita, Nanxin Chen, Tomoki Hayashi, Takaaki Hori, Hirofumi Inaguma, Ziyan Jiang, Masao Someki, Nelson Enrique Yalta Soplin, Ryuichi Yamamoto, Xiaofei Wang, Shinji Watanabe, Takenori Yoshimura, Wangyou Zhang
[PDF]
Speechgpt: Empowering large language models with intrinsic cross-modal conversational abilities. [2023].
Zhang, Dong, Shimin Li, Xin Zhang, Jun Zhan, Pengyu Wang, Yaqian Zhou, and Xipeng Qiu.
[PDF]
AudioPaLM: A Large Language Model That Can Speak and Listen. [2023].
Rubenstein, Paul K., Chulayuth Asawaroengchai, Duc Dung Nguyen, Ankur Bapna, Zalán Borsos, Félix de Chaumont Quitry, Peter Chen et al.
[PDF]
AudioLM: A Language Modeling Approach to Audio Generation [2023].
Zalán Borsos, Raphaël Marinier, Damien Vincent, Eugene Kharitonov, Olivier Pietquin, Matt Sharifi, Dominik Roblek, Olivier Teboul, David Grangier, Marco Tagliasacchi, Neil Zeghidour
[PDF]
Listen, Think, and Understand [2023].
Yuan Gong, Hongyin Luo, Alexander H. Liu, Leonid Karlinsky, James Glass
[PDF]
VioLA: Unified Codec Language Models for Speech Recognition, Synthesis, and Translation [2023].
Tianrui Wang, Long Zhou, Ziqiang Zhang, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Yashesh Gaur, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Furu Wei
[PDF]
Audiogen: Textually guided audio generation [2022].
Felix Kreuk, Gabriel Synnaeve, Adam Polyak, Uriel Singer, Alexandre Défossez, Jade Copet, Devi Parikh, Yaniv Taigman, Yossi Adi
[PDF]
Simple and Controllable Music Generation [2023].
Jade Copet, Felix Kreuk, Itai Gat, Tal Remez, David Kant, Gabriel Synnaeve, Yossi Adi, Alexandre Défossez
[PDF]
MusicLM: Generating Music From Text [2023].
Andrea Agostinelli, Timo I. Denk, Zalán Borsos, Jesse Engel, Mauro Verzetti, Antoine Caillon, Qingqing Huang, Aren Jansen, Adam Roberts, Marco Tagliasacchi, Matt Sharifi, Neil Zeghidour, Christian Frank
[PDF]
SeamlessM4T—Massively Multilingual & Multimodal Machine Translation [2023].
Seamless Communication, Loic Barrault, Andy Chung, David Dale, Ning Dong (AI), Paul-Ambroise Duquenne, Hady Elsahar et. al.
[PDF]
SALMONN: Towards Generic Hearing Abilities for Large Language Models [2023].
Changli Tang, Wenyi Yu, Guangzhi Sun, Xiaozhao Chen, Tian Tan, Wei Li, Lu Lu, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
[PDF][Github]
On decoder-only architecture for speech-to-text and large language model integration [2023].
Jian Wu, Yashesh Gaur, Zhuo Chen, Long Zhou, Yimeng Zhu, Tianrui Wang, Jinyu Li, Shujie Liu, Bo Ren, Linquan Liu, Yu Wu
[PDF]
X-LLM: Bootstrapping Advanced Large Language Models by Treating Multi-Modalities as Foreign Languages [2023].
Feilong Chen, Minglun Han, Haozhi Zhao, Qingyang Zhang, Jing Shi, Shuang Xu, Bo Xu
[PDF][Github]
Adapting Large Language Model with Speech for Fully Formatted End-to-End Speech Recognition [2023].
Shaoshi Ling, Yuxuan Hu, Shuangbei Qian, Guoli Ye, Yao Qian, Yifan Gong, Ed Lin, Michael Zeng
[PDF]
Semantic Segmentation with Bidirectional Language Models Improves Long-form ASR [2023].
W. Ronny Huang, Hao Zhang, Shankar Kumar, Shuo-yiin Chang, Tara N. Sainath
[PDF]
Prompting Large Language Models with Speech Recognition Abilities [2023].
Yassir Fathullah, Chunyang Wu, Egor Lakomkin, Junteng Jia, Yuan Shangguan, Ke Li, Jinxi Guo, Wenhan Xiong, Jay Mahadeokar, Ozlem Kalinli, Christian Fuegen, Mike Seltzer
[PDF]
Connecting Speech Encoder and Large Language Model for ASR [2023].
Wenyi Yu, Changli Tang, Guangzhi Sun, Xiaozhao Chen, Tian Tan, Wei Li, Lu Lu, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
[PDF]
SALMONN: Towards Generic Hearing Abilities for Large Language Models [2023].
Changli Tang, Wenyi Yu, Guangzhi Sun, Xiaozhao Chen, Tian Tan, Wei Li, Lu Lu, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
[PDF][Github]
Investigating the Utility of Surprisal from Large Language Models for Speech Synthesis Prosody [2023].
Sofoklis Kakouros, Juraj Šimko, Martti Vainio, Antti Suni
[PDF]
Neural Codec Language Models are Zero-Shot Text to Speech Synthesizers [2023].
Chengyi Wang, Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Ziqiang Zhang, Long Zhou, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Yanqing Liu, Huaming Wang, Jinyu Li, Lei He, Sheng Zhao, Furu Wei
[PDF]
Speak, read and prompt: High-fidelity text-to-speech with minimal supervision [2023].
Eugene Kharitonov, Damien Vincent, Zalán Borsos, Raphaël Marinier, Sertan Girgin, Olivier Pietquin, Matt Sharifi, Marco Tagliasacchi, Neil Zeghidour
[PDF]
Speechlmscore: Evaluating Speech Generation Using Speech Language Model [2023].
Soumi Maiti, Yifan Peng, Takaaki Saeki, Shinji Watanabe
[PDF]
LM-VC: Zero-shot Voice Conversion via Speech Generation based on Language Models [2023].
Zhichao Wang, Yuanzhe Chen, Lei Xie, Qiao Tian, Yuping Wang
[PDF]
Assessing Phrase Break of ESL Speech with Pre-trained Language Models and Large Language Models [2023].
Zhiyi Wang, Shaoguang Mao, Wenshan Wu, Yan Xia, Yan Deng, Jonathan Tien
[PDF]
SeamlessM4T—Massively Multilingual & Multimodal Machine Translation [2023].
Seamless Communication, Loic Barrault, Andy Chung, David Dale, Ning Dong (AI), Paul-Ambroise Duquenne, Hady Elsahar, Hongyu Gong, Kevin Heffernan, John Hoffman, Christopher Klaiber, Peng-Jen Chen, Daniel Licht, Jean Maillard, Alice Rakotoarison, Kaushik Ram Sadagopan, Guillaume Wenzek, Abinesh Ramakrishnan, Alexandre Mourachko, Amanda Kallet, Ann Lee, Anna Sun, Bapi Akula, Benjamin Peloquin, Bernie Huang, Bokai Yu, Brian Ellis, Can Balioglu, Carleigh Wood, Changhan Wang, Christophe Ropers, Cynthia Gao, Daniel Li (FAIR), Elahe Kalbassi, Ethan Ye, Gabriel Mejia Gonzalez, Hirofumi Inaguma, Holger Schwenk, Igor Tufanov, Ilia Kulikov, Janice Lam, Jeff Wang (PM - AI), Juan Pino, Justin Haaheim, Justine Kao, Prangthip Hasanti, Kevin Tran, Maha Elbayad, Marta R. Costa-jussa, Mohamed Ramadan, Naji El Hachem, Onur Çelebi, Paco Guzmán, Paden Tomasello, Pengwei Li, Pierre Andrews, Ruslan Mavlyutov, Russ Howes, Safiyyah Saleem, Skyler Wang, Somya Jain, Sravya Popuri, Tuan Tran, Vish Vogeti, Xutai Ma, Yilin Yang
[PDF]
PolyVoice: Language Models for Speech to Speech Translation [2023].
Qianqian Dong, Zhiying Huang, Qiao Tian, Chen Xu, Tom Ko, Yunlong Zhao, Siyuan Feng, Tang Li, Kexin Wang, Xuxin Cheng, Fengpeng Yue, Ye Bai, Xi Chen, Lu Lu, Zejun Ma, Yuping Wang, Mingxuan Wang, Yuxuan Wang
[PDF]
AudioPaLM: A Large Language Model That Can Speak and Listen [2023].
Paul K. Rubenstein, Chulayuth Asawaroengchai, Duc Dung Nguyen, Ankur Bapna, Zalán Borsos, Félix de Chaumont Quitry, Peter Chen, Dalia El Badawy, Wei Han, Eugene Kharitonov, Hannah Muckenhirn, Dirk Padfield, James Qin, Danny Rozenberg, Tara Sainath, Johan Schalkwyk, Matt Sharifi, Michelle Tadmor Ramanovich, Marco Tagliasacchi, Alexandru Tudor, Mihajlo Velimirović, Damien Vincent, Jiahui Yu, Yongqiang Wang, Vicky Zayats, Neil Zeghidour, Yu Zhang, Zhishuai Zhang, Lukas Zilka, Christian Frank
[PDF]
SALMONN: Towards Generic Hearing Abilities for Large Language Models [2023].
Changli Tang, Wenyi Yu, Guangzhi Sun, Xiaozhao Chen, Tian Tan, Wei Li, Lu Lu, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
[PDF][Github]
SpeechX: Neural Codec Language Model as a Versatile Speech Transformer [2023].
Xiaofei Wang, Manthan Thakker, Zhuo Chen, Naoyuki Kanda, Sefik Emre Eskimez, Sanyuan Chen, Min Tang, Shujie Liu, Jinyu Li, Takuya Yoshioka
[PDF]
Audiogpt: Understanding and generating speech, music, sound, and talking head [2023].
Rongjie Huang, Mingze Li, Dongchao Yang, Jiatong Shi, Xuankai Chang, Zhenhui Ye, Yuning Wu, Zhiqing Hong, Jiawei Huang, Jinglin Liu, Yi Ren, Zhou Zhao, Shinji Watanabe
[PDF]
X-LLM: Bootstrapping Advanced Large Language Models by Treating Multi-Modalities as Foreign Languages [2023].
Feilong Chen, Minglun Han, Haozhi Zhao, Qingyang Zhang, Jing Shi, Shuang Xu, Bo Xu
[PDF][Github]
Can Large Language Models Aid in Annotating Speech Emotional Data? Uncovering New Frontiers [2023].
Siddique Latif, Muhammad Usama, Mohammad Ibrahim Malik, Björn W. Schuller
[PDF]
LLaSM: Large Language and Speech Model [2023].
Yu Shu, Siwei Dong, Guangyao Chen, Wenhao Huang, Ruihua Zhang, Daochen Shi, Qiqi Xiang, Yemin Shi
[PDF]
SALMONN: Towards Generic Hearing Abilities for Large Language Models [2023].
Changli Tang, Wenyi Yu, Guangzhi Sun, Xiaozhao Chen, Tian Tan, Wei Li, Lu Lu, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
[PDF][Github]
MusicGen: Simple and Controllable Music Generation [2023].
Jade Copet, Felix Kreuk, Itai Gat, Tal Remez, David Kant, Gabriel Synnaeve, Yossi Adi, Alexandre Défossez
[PDF]
JEN-1: Text-Guided Universal Music Generation with Omnidirectional Diffusion Models [2023].
Peike Li, Boyu Chen, Yao Yao, Yikai Wang, Allen Wang, Alex Wang
[PDF]
VampNet: Music Generation via Masked Acoustic Token Modeling [2023].
Hugo Flores Garcia, Prem Seetharaman, Rithesh Kumar, Bryan Pardo
[PDF]
Text-to-Audio Generation using Instruction-Tuned LLM and Latent Diffusion Model [2023].
Deepanway Ghosal, Navonil Majumder, Ambuj Mehrish, Soujanya Poria
[PDF]
WavJourney: Compositional Audio Creation with Large Language Models [2023].
Xubo Liu, Zhongkai Zhu, Haohe Liu, Yi Yuan, Meng Cui, Qiushi Huang, Jinhua Liang, Yin Cao, Qiuqiang Kong, Mark D. Plumbley, Wenwu Wang
[PDF]
MusicLDM: Enhancing Novelty in Text-to-Music Generation Using Beat-Synchronous Mixup Strategies [2023].
Ke Chen, Yusong Wu, Haohe Liu, Marianna Nezhurina, Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick, Shlomo Dubnov
[PDF]
Exploring the efficacy of pre-trained checkpoints in text-to-music generation task [2022].
Shangda Wu, Maosong Sun
[PDF]
SingSong: Generating musical accompaniments from singing [2023].
Chris Donahue, Antoine Caillon, Adam Roberts, Ethan Manilow, Philippe Esling, Andrea Agostinelli, Mauro Verzetti, Ian Simon, Olivier Pietquin, Neil Zeghidour, Jesse Engel
[PDF]
LOAF-M2L: Joint Learning of Wording and Formatting for Singable Melody-to-Lyric Generation [2023].
Longshen Ou, Xichu Ma, Ye Wang
[PDF]
Efficient Neural Music Generation [2023].
Max W. Y. Lam, Qiao Tian, Tang Li, Zongyu Yin, Siyuan Feng, Ming Tu, Yuliang Ji, Rui Xia, Mingbo Ma, Xuchen Song, Jitong Chen, Yuping Wang, Yuxuan Wang
[PDF]
MuseCoco: Generating Symbolic Music from Text [2023].
Peiling Lu, Xin Xu, Chenfei Kang, Botao Yu, Chengyi Xing, Xu Tan, Jiang Bian
[PDF]
LaunchpadGPT: Language Model as Music Visualization Designer on Launchpad [2023].
Siting Xu, Yunlong Tang, Feng Zheng
[PDF]
Music Understanding LLaMA: Advancing Text-to-Music Generation with Question Answering and Captioning [2023].
Shansong Liu, Atin Sakkeer Hussain, Chenshuo Sun, Ying Shan
[PDF][Github]
SALMONN: Towards Generic Hearing Abilities for Large Language Models [2023].
Changli Tang, Wenyi Yu, Guangzhi Sun, Xiaozhao Chen, Tian Tan, Wei Li, Lu Lu, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
[PDF][Github]
Mustango: Toward Controllable Text-to-Music Generation [2023].
Jan Melechovsky, Zixun Guo, Deepanway Ghosal, Navonil Majumder, Dorien Herremans, Soujanya Poria
[PDF][Github]
| Title | Full Name | Size | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| CommonVoice 11 | CommonVoice: A Massively Multilingual Speech Corpus | 58250 Voices of 2508 hours | Download |
| Libri-Light | Libri-Light: A Benchmark for ASR with Limited or No Supervision | 60000 Hours | Download |
| Wenetspeech | Wenetspeech: A 10000+ hours multi-domain mandarin corpus for speech recognition | 10000 Hours | Download |
| Gigaspeech | Gigaspeech: An evolving, multi-domain asr corpus with 10,000 hours of transcribed audio | 50000 Hours | Download |
| MuST-C | MuST-C: a Multilingual Speech Translation Corpus | 3600 Hours | Download |
| VoxPopuli | VoxPopuli: A Large-Scale Multilingual Speech Corpus for Representation Learning, Semi-Supervised Learning and Interpretation | 400k Hours | Download |
| CoVoST | CoVoST: A Large-Scale Multilingual Speech-To-Text Translation Corpus | 2280 Hours | Download |
| CVSS | CVSS: A Massively Multilingual Speech-to-Speech Translation Corpus | 3909 Hours | Download |
| EMIME | The EMIME bilingual database | - | Download |
| Audiocaps | Audiocaps: Generating captions for audios in the wild | 46000 Audios | Download |
| Clotho | Clotho: An audio captioning dataset | 4981 audios 24905 captions | Download |
| Audio set | Audio set: An ontology and human-labeled dataset for audio events | 5.8k hours | Download |
| Emopia | Emopia: A multi-modal pop piano dataset for emotion recognition and emotion-based music generation | 387 piano solo sounds | Download |
| MetaMIDI | Building the MetaMIDI Dataset: Linking Symbolic and Audio Musical Data | 436631 MIDI files | Download |
| DALI2 | Creating DALI, a Large Dataset of Synchronized Audio, Lyrics, and Notes | 7756 Songs | Download |
| MillionMIDI | Million MIDI Dataset (MMD) | 100k Songs | Download |
| Vggsound | Vggsound: A Large-Scale Audio-Visual Dataset | 200k Videos | Download |
| FSD50K | FSD50K: An Open Dataset of Human-Labeled Sound Events | 51197 Sound Clips | Download |
| Symphony | Symphony generation with permutation invariant language model | 46359 MIDI files | Download |
| MusicCaps | MusicLM: Generating Music From Text | 5521 music-text pairs | Download |
| Jamendo | The MTG-Jamendo dataset for automatic music tagging | 55525 Tracks | Download |
| MusicBench | Mustango: Toward Controllable Text-to-Music Generation | 53168 Tracks | Download |
If you find the listing and survey useful for your work, please cite the paper:
@article{latif2023sparks,
title={Sparks of Large Audio Models: A Survey and Outlook},
author={Latif, Siddique and Shoukat, Moazzam and Shamshad, Fahad and Usama, Muhammad and Cuay{\'a}huitl, Heriberto and Schuller, Bj{\"o}rn W},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12792},
year={2023}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for awesome-large-audio-models
Similar Open Source Tools

awesome-large-audio-models
This repository is a curated list of awesome large AI models in audio signal processing, focusing on the application of large language models to audio tasks. It includes survey papers, popular large audio models, automatic speech recognition, neural speech synthesis, speech translation, other speech applications, large audio models in music, and audio datasets. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive overview of recent advancements and challenges in applying large language models to audio signal processing, showcasing the efficacy of transformer-based architectures in various audio tasks.
Awesome-Segment-Anything
Awesome-Segment-Anything is a powerful tool for segmenting and extracting information from various types of data. It provides a user-friendly interface to easily define segmentation rules and apply them to text, images, and other data formats. The tool supports both supervised and unsupervised segmentation methods, allowing users to customize the segmentation process based on their specific needs. With its versatile functionality and intuitive design, Awesome-Segment-Anything is ideal for data analysts, researchers, content creators, and anyone looking to efficiently extract valuable insights from complex datasets.
Awesome-Story-Generation
Awesome-Story-Generation is a repository that curates a comprehensive list of papers related to Story Generation and Storytelling, focusing on the era of Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository includes papers on various topics such as Literature Review, Large Language Model, Plot Development, Better Storytelling, Story Character, Writing Style, Story Planning, Controllable Story, Reasonable Story, and Benchmark. It aims to provide a chronological collection of influential papers in the field, with a focus on citation counts for LLMs-era papers and some earlier influential papers. The repository also encourages contributions and feedback from the community to improve the collection.
Odyssey
Odyssey is a framework designed to empower agents with open-world skills in Minecraft. It provides an interactive agent with a skill library, a fine-tuned LLaMA-3 model, and an open-world benchmark for evaluating agent capabilities. The framework enables agents to explore diverse gameplay opportunities in the vast Minecraft world by offering primitive and compositional skills, extensive training data, and various long-term planning tasks. Odyssey aims to advance research on autonomous agent solutions by providing datasets, model weights, and code for public use.
VILA
VILA is a family of open Vision Language Models optimized for efficient video understanding and multi-image understanding. It includes models like NVILA, LongVILA, VILA-M3, VILA-U, and VILA-1.5, each offering specific features and capabilities. The project focuses on efficiency, accuracy, and performance in various tasks related to video, image, and language understanding and generation. VILA models are designed to be deployable on diverse NVIDIA GPUs and support long-context video understanding, medical applications, and multi-modal design.
RLHF-Reward-Modeling
This repository, RLHF-Reward-Modeling, is dedicated to training reward models for DRL-based RLHF (PPO), Iterative SFT, and iterative DPO. It provides state-of-the-art performance in reward models with a base model size of up to 13B. The installation instructions involve setting up the environment and aligning the handbook. Dataset preparation requires preprocessing conversations into a standard format. The code can be run with Gemma-2b-it, and evaluation results can be obtained using provided datasets. The to-do list includes various reward models like Bradley-Terry, preference model, regression-based reward model, and multi-objective reward model. The repository is part of iterative rejection sampling fine-tuning and iterative DPO.
LearnPrompt
LearnPrompt is a permanent, free, open-source AIGC course platform that currently supports various tools like ChatGPT, Agent, Midjourney, Runway, Stable Diffusion, AI digital humans, AI voice & music, and large model fine-tuning. The platform offers features such as multilingual support, comment sections, daily selections, and submissions. Users can explore different modules, including sound cloning, RAG, GPT-SoVits, and OpenAI Sora world model. The platform aims to continuously update and provide tutorials, examples, and knowledge systems related to AI technologies.
Awesome-TimeSeries-SpatioTemporal-LM-LLM
Awesome-TimeSeries-SpatioTemporal-LM-LLM is a curated list of Large (Language) Models and Foundation Models for Temporal Data, including Time Series, Spatio-temporal, and Event Data. The repository aims to summarize recent advances in Large Models and Foundation Models for Time Series and Spatio-Temporal Data with resources such as papers, code, and data. It covers various applications like General Time Series Analysis, Transportation, Finance, Healthcare, Event Analysis, Climate, Video Data, and more. The repository also includes related resources, surveys, and papers on Large Language Models, Foundation Models, and their applications in AIOps.
LocalAI
LocalAI is a free and open-source OpenAI alternative that acts as a drop-in replacement REST API compatible with OpenAI (Elevenlabs, Anthropic, etc.) API specifications for local AI inferencing. It allows users to run LLMs, generate images, audio, and more locally or on-premises with consumer-grade hardware, supporting multiple model families and not requiring a GPU. LocalAI offers features such as text generation with GPTs, text-to-audio, audio-to-text transcription, image generation with stable diffusion, OpenAI functions, embeddings generation for vector databases, constrained grammars, downloading models directly from Huggingface, and a Vision API. It provides a detailed step-by-step introduction in its Getting Started guide and supports community integrations such as custom containers, WebUIs, model galleries, and various bots for Discord, Slack, and Telegram. LocalAI also offers resources like an LLM fine-tuning guide, instructions for local building and Kubernetes installation, projects integrating LocalAI, and a how-tos section curated by the community. It encourages users to cite the repository when utilizing it in downstream projects and acknowledges the contributions of various software from the community.

sailor-llm
Sailor is a suite of open language models tailored for South-East Asia (SEA), focusing on languages such as Indonesian, Thai, Vietnamese, Malay, and Lao. Developed with careful data curation, Sailor models are designed to understand and generate text across diverse linguistic landscapes of the SEA region. Built from Qwen 1.5, Sailor encompasses models of varying sizes, spanning from 0.5B to 7B versions for different requirements. Benchmarking results demonstrate Sailor's proficiency in tasks such as question answering, commonsense reasoning, reading comprehension, and more in SEA languages.
MiniCPM-V-CookBook
MiniCPM-V & o Cookbook is a comprehensive repository for building multimodal AI applications effortlessly. It provides easy-to-use documentation, supports a wide range of users, and offers versatile deployment scenarios. The repository includes live demonstrations, inference recipes for vision and audio capabilities, fine-tuning recipes, serving recipes, quantization recipes, and a framework support matrix. Users can customize models, deploy them efficiently, and compress models to improve efficiency. The repository also showcases awesome works using MiniCPM-V & o and encourages community contributions.
AI-Notes
AI-Notes is a repository dedicated to practical applications of artificial intelligence and deep learning. It covers concepts such as data mining, machine learning, natural language processing, and AI. The repository contains Jupyter Notebook examples for hands-on learning and experimentation. It explores the development stages of AI, from narrow artificial intelligence to general artificial intelligence and superintelligence. The content delves into machine learning algorithms, deep learning techniques, and the impact of AI on various industries like autonomous driving and healthcare. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of AI technologies and their real-world applications.
chronos-forecasting
Chronos is a family of pretrained time series forecasting models based on language model architectures. A time series is transformed into a sequence of tokens via scaling and quantization, and a language model is trained on these tokens using the cross-entropy loss. Once trained, probabilistic forecasts are obtained by sampling multiple future trajectories given the historical context. Chronos models have been trained on a large corpus of publicly available time series data, as well as synthetic data generated using Gaussian processes.
flash-tokenizer
FlashTokenizer is a high-performance CPU tokenizer library implemented in C++ for LLM inference serving. It is 10 times faster than BertTokenizerFast in transformers, offering the highest speed and accuracy. Developed to be faster, more accurate, and easier to use than existing tokenizers like BertTokenizerFast, FlashTokenizer is implemented in C++ for straightforward maintenance. It supports parallel processing at the C++ level for batch encoding, delivering outstanding speed. The tokenizer is based on the LinMax Tokenizer proposed in Fast WordPiece Tokenization, enabling tokenization in linear time.
For similar tasks

awesome-large-audio-models
This repository is a curated list of awesome large AI models in audio signal processing, focusing on the application of large language models to audio tasks. It includes survey papers, popular large audio models, automatic speech recognition, neural speech synthesis, speech translation, other speech applications, large audio models in music, and audio datasets. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive overview of recent advancements and challenges in applying large language models to audio signal processing, showcasing the efficacy of transformer-based architectures in various audio tasks.

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.
suno-api
Suno AI API is an open-source project that allows developers to integrate the music generation capabilities of Suno.ai into their own applications. The API provides a simple and convenient way to generate music, lyrics, and other audio content using Suno.ai's powerful AI models. With Suno AI API, developers can easily add music generation functionality to their apps, websites, and other projects.
openvino-plugins-ai-audacity
OpenVINO™ AI Plugins for Audacity* are a set of AI-enabled effects, generators, and analyzers for Audacity®. These AI features run 100% locally on your PC -- no internet connection necessary! OpenVINO™ is used to run AI models on supported accelerators found on the user's system such as CPU, GPU, and NPU. * **Music Separation**: Separate a mono or stereo track into individual stems -- Drums, Bass, Vocals, & Other Instruments. * **Noise Suppression**: Removes background noise from an audio sample. * **Music Generation & Continuation**: Uses MusicGen LLM to generate snippets of music, or to generate a continuation of an existing snippet of music. * **Whisper Transcription**: Uses whisper.cpp to generate a label track containing the transcription or translation for a given selection of spoken audio or vocals.
SunoApi
SunoAPI is an unofficial client for Suno AI, built on Python and Streamlit. It supports functions like generating music and obtaining music information. Users can set up multiple account information to be saved for use. The tool also features built-in maintenance and activation functions for tokens, eliminating concerns about token expiration. It supports multiple languages and allows users to upload pictures for generating songs based on image content analysis.
awesome-generative-ai
Awesome Generative AI is a curated list of modern Generative Artificial Intelligence projects and services. Generative AI technology creates original content like images, sounds, and texts using machine learning algorithms trained on large data sets. It can produce unique and realistic outputs such as photorealistic images, digital art, music, and writing. The repo covers a wide range of applications in art, entertainment, marketing, academia, and computer science.
ai-audio-datasets
AI Audio Datasets List (AI-ADL) is a comprehensive collection of datasets consisting of speech, music, and sound effects, used for Generative AI, AIGC, AI model training, and audio applications. It includes datasets for speech recognition, speech synthesis, music information retrieval, music generation, audio processing, sound synthesis, and more. The repository provides a curated list of diverse datasets suitable for various AI audio tasks.

YuE
YuE (乐) is an open-source foundation model designed for music generation, specifically transforming lyrics into full songs. It can generate complete songs in various genres and vocal styles, ensuring a polished and cohesive result. The model requires significant GPU memory for generating long sequences and recommends specific configurations for optimal performance. Users can customize the number of sessions for memory usage. The tool provides a quickstart guide for generating music using Transformers and includes tips for execution time and tag selection. The project is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial 4.0.
For similar jobs
metavoice-src
MetaVoice-1B is a 1.2B parameter base model trained on 100K hours of speech for TTS (text-to-speech). It has been built with the following priorities: * Emotional speech rhythm and tone in English. * Zero-shot cloning for American & British voices, with 30s reference audio. * Support for (cross-lingual) voice cloning with finetuning. * We have had success with as little as 1 minute training data for Indian speakers. * Synthesis of arbitrary length text

suno-api
Suno AI API is an open-source project that allows developers to integrate the music generation capabilities of Suno.ai into their own applications. The API provides a simple and convenient way to generate music, lyrics, and other audio content using Suno.ai's powerful AI models. With Suno AI API, developers can easily add music generation functionality to their apps, websites, and other projects.
bark.cpp
Bark.cpp is a C/C++ implementation of the Bark model, a real-time, multilingual text-to-speech generation model. It supports AVX, AVX2, and AVX512 for x86 architectures, and is compatible with both CPU and GPU backends. Bark.cpp also supports mixed F16/F32 precision and 4-bit, 5-bit, and 8-bit integer quantization. It can be used to generate realistic-sounding audio from text prompts.
NSMusicS
NSMusicS is a local music software that is expected to support multiple platforms with AI capabilities and multimodal features. The goal of NSMusicS is to integrate various functions (such as artificial intelligence, streaming, music library management, cross platform, etc.), which can be understood as similar to Navidrome but with more features than Navidrome. It wants to become a plugin integrated application that can almost have all music functions.
ai-voice-cloning
This repository provides a tool for AI voice cloning, allowing users to generate synthetic speech that closely resembles a target speaker's voice. The tool is designed to be user-friendly and accessible, with a graphical user interface that guides users through the process of training a voice model and generating synthetic speech. The tool also includes a variety of features that allow users to customize the generated speech, such as the pitch, volume, and speaking rate. Overall, this tool is a valuable resource for anyone interested in creating realistic and engaging synthetic speech.
RVC_CLI
**RVC_CLI: Retrieval-based Voice Conversion Command Line Interface** This command-line interface (CLI) provides a comprehensive set of tools for voice conversion, enabling you to modify the pitch, timbre, and other characteristics of audio recordings. It leverages advanced machine learning models to achieve realistic and high-quality voice conversions. **Key Features:** * **Inference:** Convert the pitch and timbre of audio in real-time or process audio files in batch mode. * **TTS Inference:** Synthesize speech from text using a variety of voices and apply voice conversion techniques. * **Training:** Train custom voice conversion models to meet specific requirements. * **Model Management:** Extract, blend, and analyze models to fine-tune and optimize performance. * **Audio Analysis:** Inspect audio files to gain insights into their characteristics. * **API:** Integrate the CLI's functionality into your own applications or workflows. **Applications:** The RVC_CLI finds applications in various domains, including: * **Music Production:** Create unique vocal effects, harmonies, and backing vocals. * **Voiceovers:** Generate voiceovers with different accents, emotions, and styles. * **Audio Editing:** Enhance or modify audio recordings for podcasts, audiobooks, and other content. * **Research and Development:** Explore and advance the field of voice conversion technology. **For Jobs:** * Audio Engineer * Music Producer * Voiceover Artist * Audio Editor * Machine Learning Engineer **AI Keywords:** * Voice Conversion * Pitch Shifting * Timbre Modification * Machine Learning * Audio Processing **For Tasks:** * Convert Pitch * Change Timbre * Synthesize Speech * Train Model * Analyze Audio

openvino-plugins-ai-audacity
OpenVINO™ AI Plugins for Audacity* are a set of AI-enabled effects, generators, and analyzers for Audacity®. These AI features run 100% locally on your PC -- no internet connection necessary! OpenVINO™ is used to run AI models on supported accelerators found on the user's system such as CPU, GPU, and NPU. * **Music Separation**: Separate a mono or stereo track into individual stems -- Drums, Bass, Vocals, & Other Instruments. * **Noise Suppression**: Removes background noise from an audio sample. * **Music Generation & Continuation**: Uses MusicGen LLM to generate snippets of music, or to generate a continuation of an existing snippet of music. * **Whisper Transcription**: Uses whisper.cpp to generate a label track containing the transcription or translation for a given selection of spoken audio or vocals.
WavCraft
WavCraft is an LLM-driven agent for audio content creation and editing. It applies LLM to connect various audio expert models and DSP function together. With WavCraft, users can edit the content of given audio clip(s) conditioned on text input, create an audio clip given text input, get more inspiration from WavCraft by prompting a script setting and let the model do the scriptwriting and create the sound, and check if your audio file is synthesized by WavCraft.