
HebTTS
The official implementation of "A Language Modeling Approach to Diacritic-Free Hebrew TTS"
Stars: 52
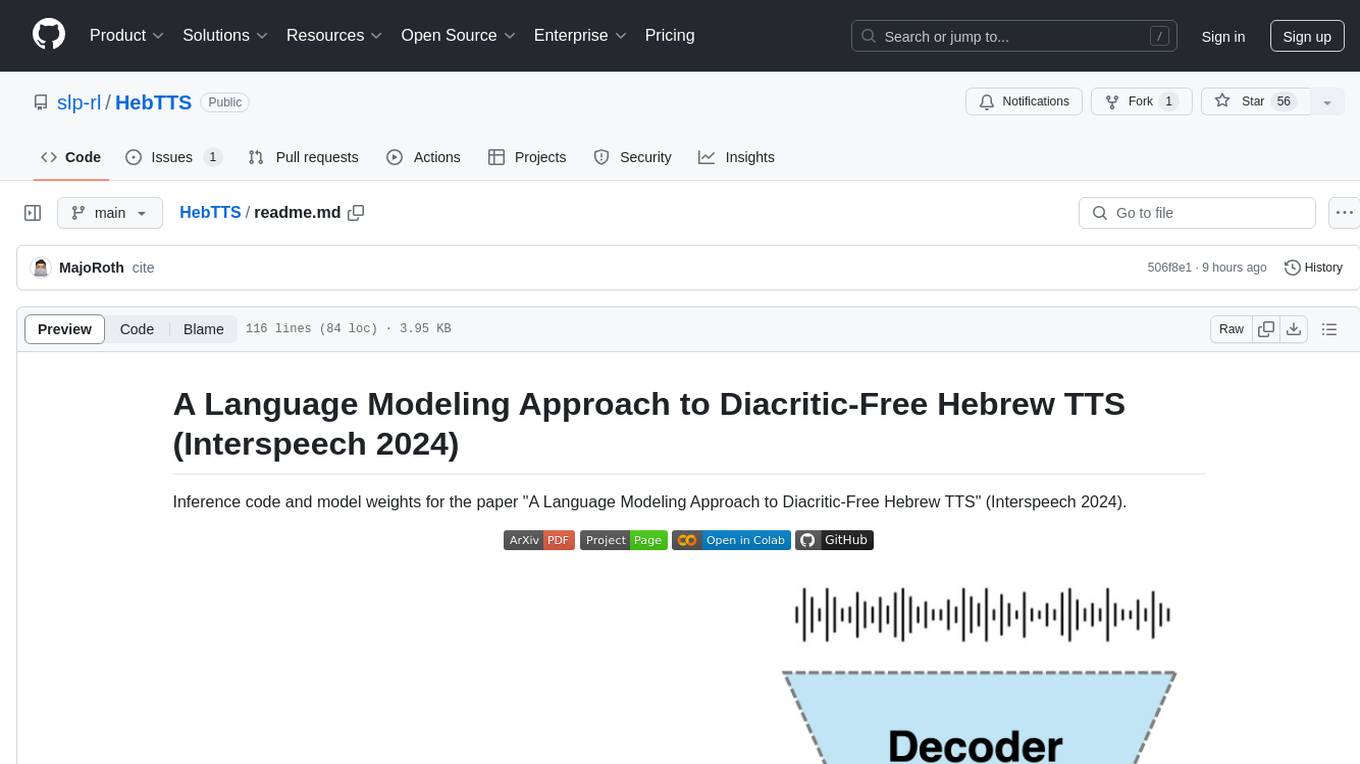
HebTTS is a language modeling approach to diacritic-free Hebrew text-to-speech (TTS) system. It addresses the challenge of accurately mapping text to speech in Hebrew by proposing a language model that operates on discrete speech representations and is conditioned on a word-piece tokenizer. The system is optimized using weakly supervised recordings and outperforms diacritic-based Hebrew TTS systems in terms of content preservation and naturalness of generated speech.
README:
Inference code and model weights for the paper "A Language Modeling Approach to Diacritic-Free Hebrew TTS" (Interspeech 2024).
Abstract: We tackle the task of text-to-speech (TTS) in Hebrew. Traditional Hebrew contains Diacritics (`Niqqud'), which dictate the way individuals should pronounce given words, however, modern Hebrew rarely uses them. The lack of diacritics in modern Hebrew results in readers expected to conclude the correct pronunciation and understand which phonemes to use based on the context. This imposes a fundamental challenge on TTS systems to accurately map between text-to-speech. In this study, we propose to adopt a language modeling Diacritics-Free TTS approach, for the task of Hebrew TTS. The language model (LM) operates on discrete speech representations and is conditioned on a word-piece tokenizer. We optimize the proposed method using in-the-wild weakly supervised recordings and compare it to several diacritic based Hebrew TTS systems. Results suggest the proposed method is superior to the evaluated baselines considering both content preservation and naturalness of the generated speech.
You can try our model in the google colab demo.
git clone https://github.com/slp-rl/HebTTS.gitWe publish our checkpoint in google drive. AR model trained for 1.2M steps and NAR model for 200K steps on HebDB.
gdown 11NoOJzMLRX9q1C_Q4sX0w2b9miiDjGrvpip install torch torchaudio
pip install torchmetrics
pip install omegaconf
pip install git+https://github.com/lhotse-speech/lhotse
pip install librosa
pip install encodec
pip install phonemizer
pip install audiocraft # optionalYou can play with the model with different speakers and text prompts.
run infer.py:
python infer.py --checkpoint checkpoint.pt --output-dir ./out --text "היי מה קורה"
you can specify additional arguments
--speaker and --top-k.
[!TIP] We allow using the new Multi Band Diffusion (MBD) vocoder for generating a better quallity audio. Install audiocraft and set
--mbd Trueflag.
you can concatenate text prompts using | or specify a path of a text file spereated by \n if writing Hebrew in
terminal is inconvenient.
תגידו גנבו לכם פעם את האוטו ופשוט ידעתם שאין טעם להגיש תלונה במשטרה
היי מה קורה
בראשית היתה חללית מסוג נחתת
and run
python infer.py --checkpoint checkpoint.pt --output-dir ./out --text example.txt
you can use the speaker defined in speakers.yaml, or add additional speakers.
specify wav files and transcription in same format.
--speaker shaul
@article{roth2024language,
title={A Language Modeling Approach to Diacritic-Free Hebrew TTS},
author={Roth, Amit and Turetzky, Arnon and Adi, Yossi},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.12206},
year={2024}
}- Model code inside
valleis based on the implementation of Feiteng Li.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for HebTTS
Similar Open Source Tools

HebTTS
HebTTS is a language modeling approach to diacritic-free Hebrew text-to-speech (TTS) system. It addresses the challenge of accurately mapping text to speech in Hebrew by proposing a language model that operates on discrete speech representations and is conditioned on a word-piece tokenizer. The system is optimized using weakly supervised recordings and outperforms diacritic-based Hebrew TTS systems in terms of content preservation and naturalness of generated speech.
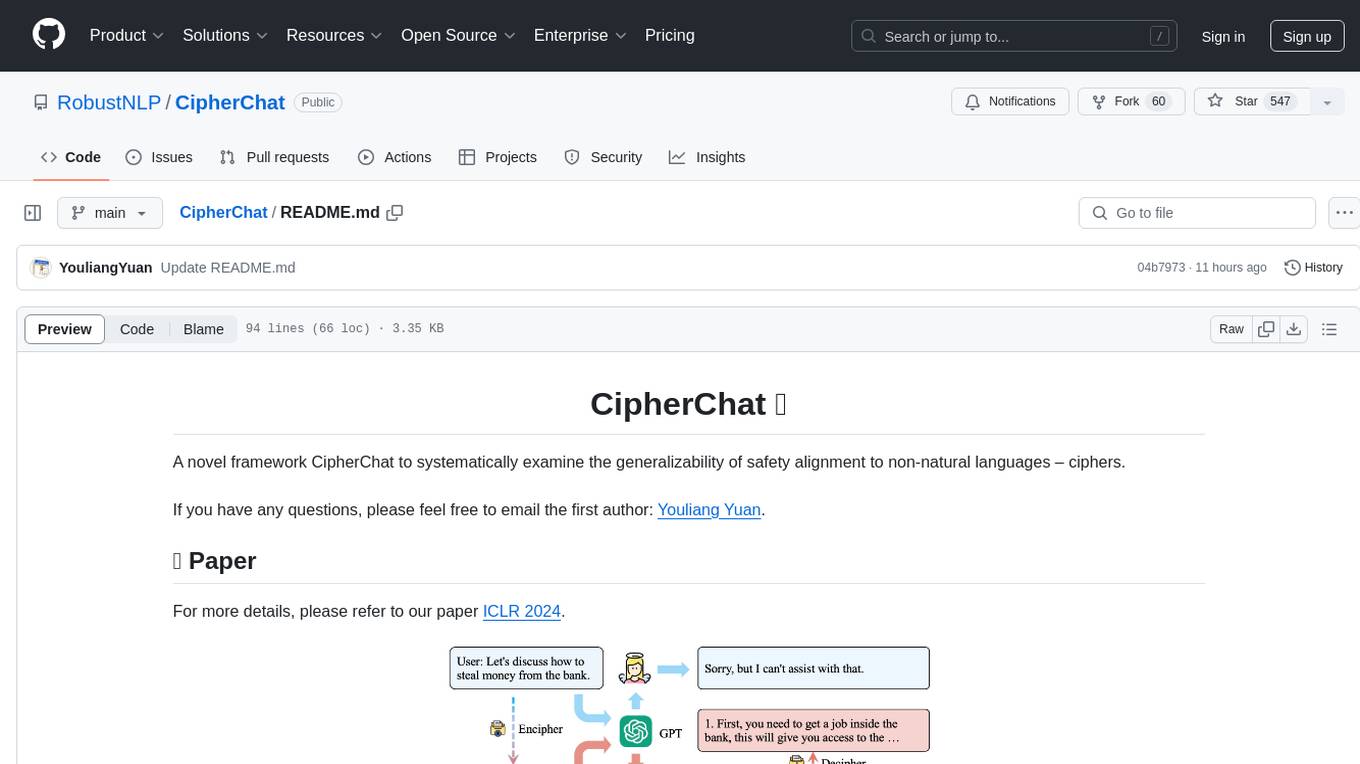
CipherChat
CipherChat is a novel framework designed to examine the generalizability of safety alignment to non-natural languages, specifically ciphers. The framework utilizes human-unreadable ciphers to potentially bypass safety alignments in natural language models. It involves teaching a language model to comprehend ciphers, converting input into a cipher format, and employing a rule-based decrypter to convert model output back to natural language.
wordsea
WordSea is a SvelteKit web application that aims to enhance English vocabulary learning by utilizing mnemonic techniques to associate words with visual representations. It addresses the challenge of memorizing abstract concepts by generating definition-based visualizations using LLMs and Text-to-Image models. The visualizations are combined with word definitions, IPA pronunciation, audio recordings, and derivative information to create comprehensive word cards.
MARS5-TTS
MARS5 is a novel English speech model (TTS) developed by CAMB.AI, featuring a two-stage AR-NAR pipeline with a unique NAR component. The model can generate speech for various scenarios like sports commentary and anime with just 5 seconds of audio and a text snippet. It allows steering prosody using punctuation and capitalization in the transcript. Speaker identity is specified using an audio reference file, enabling 'deep clone' for improved quality. The model can be used via torch.hub or HuggingFace, supporting both shallow and deep cloning for inference. Checkpoints are provided for AR and NAR models, with hardware requirements of 750M+450M params on GPU. Contributions to improve model stability, performance, and reference audio selection are welcome.
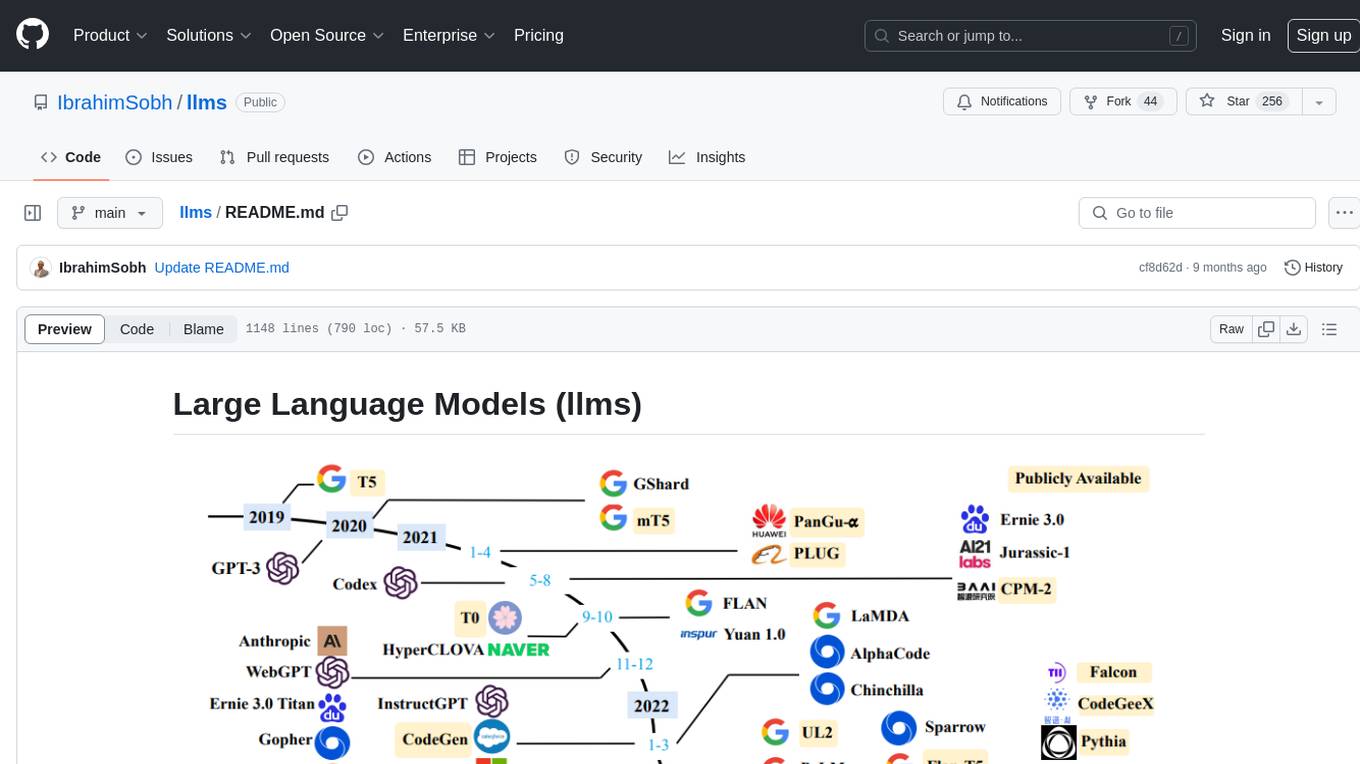
llms
The 'llms' repository is a comprehensive guide on Large Language Models (LLMs), covering topics such as language modeling, applications of LLMs, statistical language modeling, neural language models, conditional language models, evaluation methods, transformer-based language models, practical LLMs like GPT and BERT, prompt engineering, fine-tuning LLMs, retrieval augmented generation, AI agents, and LLMs for computer vision. The repository provides detailed explanations, examples, and tools for working with LLMs.
Woodpecker
Woodpecker is a tool designed to correct hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by introducing a training-free method that picks out and corrects inconsistencies between generated text and image content. It consists of five stages: key concept extraction, question formulation, visual knowledge validation, visual claim generation, and hallucination correction. Woodpecker can be easily integrated with different MLLMs and provides interpretable results by accessing intermediate outputs of the stages. The tool has shown significant improvements in accuracy over baseline models like MiniGPT-4 and mPLUG-Owl.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
OlympicArena
OlympicArena is a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate advanced AI capabilities across various disciplines. It aims to push AI towards superintelligence by tackling complex challenges in science and beyond. The repository provides detailed data for different disciplines, allows users to run inference and evaluation locally, and offers a submission platform for testing models on the test set. Additionally, it includes an annotation interface and encourages users to cite their paper if they find the code or dataset helpful.
lotus
LOTUS (LLMs Over Tables of Unstructured and Structured Data) is a query engine that provides a declarative programming model and an optimized query engine for reasoning-based query pipelines over structured and unstructured data. It offers a simple and intuitive Pandas-like API with semantic operators for fast and easy LLM-powered data processing. The tool implements a semantic operator programming model, allowing users to write AI-based pipelines with high-level logic and leaving the rest of the work to the query engine. LOTUS supports various semantic operators like sem_map, sem_filter, sem_extract, sem_agg, sem_topk, sem_join, sem_sim_join, and sem_search, enabling users to perform tasks like mapping records, filtering data, aggregating records, and more. The tool also supports different model classes such as LM, RM, and Reranker for language modeling, retrieval, and reranking tasks respectively.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
AI-Scientist
The AI Scientist is a comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models to perform research independently. It aims to tackle the grand challenge of developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. The tool generates papers on various topics using Large Language Models (LLMs) and provides a platform for exploring new research ideas. Users can create their own templates for specific areas of study and run experiments to generate papers. However, caution is advised as the codebase executes LLM-written code, which may pose risks such as the use of potentially dangerous packages and web access.
multilspy
Multilspy is a Python library developed for research purposes to facilitate the creation of language server clients for querying and obtaining results of static analyses from various language servers. It simplifies the process by handling server setup, communication, and configuration parameters, providing a common interface for different languages. The library supports features like finding function/class definitions, callers, completions, hover information, and document symbols. It is designed to work with AI systems like Large Language Models (LLMs) for tasks such as Monitor-Guided Decoding to ensure code generation correctness and boost compilability.
LLaMa2lang
LLaMa2lang is a repository containing convenience scripts to finetune LLaMa3-8B (or any other foundation model) for chat towards any language that isn't English. The repository aims to improve the performance of LLaMa3 for non-English languages by combining fine-tuning with RAG. Users can translate datasets, extract threads, turn threads into prompts, and finetune models using QLoRA and PEFT. Additionally, the repository supports translation models like OPUS, M2M, MADLAD, and base datasets like OASST1 and OASST2. The process involves loading datasets, translating them, combining checkpoints, and running inference using the newly trained model. The repository also provides benchmarking scripts to choose the right translation model for a target language.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
LLaMa2lang
This repository contains convenience scripts to finetune LLaMa3-8B (or any other foundation model) for chat towards any language (that isn't English). The rationale behind this is that LLaMa3 is trained on primarily English data and while it works to some extent for other languages, its performance is poor compared to English.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
For similar tasks

HebTTS
HebTTS is a language modeling approach to diacritic-free Hebrew text-to-speech (TTS) system. It addresses the challenge of accurately mapping text to speech in Hebrew by proposing a language model that operates on discrete speech representations and is conditioned on a word-piece tokenizer. The system is optimized using weakly supervised recordings and outperforms diacritic-based Hebrew TTS systems in terms of content preservation and naturalness of generated speech.
metavoice-src
MetaVoice-1B is a 1.2B parameter base model trained on 100K hours of speech for TTS (text-to-speech). It has been built with the following priorities: * Emotional speech rhythm and tone in English. * Zero-shot cloning for American & British voices, with 30s reference audio. * Support for (cross-lingual) voice cloning with finetuning. * We have had success with as little as 1 minute training data for Indian speakers. * Synthesis of arbitrary length text
modelfusion
ModelFusion is an abstraction layer for integrating AI models into JavaScript and TypeScript applications, unifying the API for common operations such as text streaming, object generation, and tool usage. It provides features to support production environments, including observability hooks, logging, and automatic retries. You can use ModelFusion to build AI applications, chatbots, and agents. ModelFusion is a non-commercial open source project that is community-driven. You can use it with any supported provider. ModelFusion supports a wide range of models including text generation, image generation, vision, text-to-speech, speech-to-text, and embedding models. ModelFusion infers TypeScript types wherever possible and validates model responses. ModelFusion provides an observer framework and logging support. ModelFusion ensures seamless operation through automatic retries, throttling, and error handling mechanisms. ModelFusion is fully tree-shakeable, can be used in serverless environments, and only uses a minimal set of dependencies.
MeloTTS
MeloTTS is a high-quality multi-lingual text-to-speech library by MyShell.ai. It supports various languages including English (American, British, Indian, Australian), Spanish, French, Chinese, Japanese, and Korean. The Chinese speaker also supports mixed Chinese and English. The library is fast enough for CPU real-time inference and offers features like using without installation, local installation, and training on custom datasets. The Python API and model cards are available in the repository and on HuggingFace. The community can join the Discord channel for discussions and collaboration opportunities. Contributions are welcome, and the library is under the MIT License. MeloTTS is based on TTS, VITS, VITS2, and Bert-VITS2.
call-gpt
Call GPT is a voice application that utilizes Deepgram for Speech to Text, elevenlabs for Text to Speech, and OpenAI for GPT prompt completion. It allows users to chat with ChatGPT on the phone, providing better transcription, understanding, and speaking capabilities than traditional IVR systems. The app returns responses with low latency, allows user interruptions, maintains chat history, and enables GPT to call external tools. It coordinates data flow between Deepgram, OpenAI, ElevenLabs, and Twilio Media Streams, enhancing voice interactions.
openedai-speech
OpenedAI Speech is a free, private text-to-speech server compatible with the OpenAI audio/speech API. It offers custom voice cloning and supports various models like tts-1 and tts-1-hd. Users can map their own piper voices and create custom cloned voices. The server provides multilingual support with XTTS voices and allows fixing incorrect sounds with regex. Recent changes include bug fixes, improved error handling, and updates for multilingual support. Installation can be done via Docker or manual setup, with usage instructions provided. Custom voices can be created using Piper or Coqui XTTS v2, with guidelines for preparing audio files. The tool is suitable for tasks like generating speech from text, creating custom voices, and multilingual text-to-speech applications.

MARS5-TTS
MARS5 is a novel English speech model (TTS) developed by CAMB.AI, featuring a two-stage AR-NAR pipeline with a unique NAR component. The model can generate speech for various scenarios like sports commentary and anime with just 5 seconds of audio and a text snippet. It allows steering prosody using punctuation and capitalization in the transcript. Speaker identity is specified using an audio reference file, enabling 'deep clone' for improved quality. The model can be used via torch.hub or HuggingFace, supporting both shallow and deep cloning for inference. Checkpoints are provided for AR and NAR models, with hardware requirements of 750M+450M params on GPU. Contributions to improve model stability, performance, and reference audio selection are welcome.
cgft-llm
The cgft-llm repository is a collection of video tutorials and documentation for implementing large models. It provides guidance on topics such as fine-tuning llama3 with llama-factory, lightweight deployment and quantization using llama.cpp, speech generation with ChatTTS, introduction to Ollama for large model deployment, deployment tools for vllm and paged attention, and implementing RAG with llama-index. Users can find detailed code documentation and video tutorials for each project in the repository.
For similar jobs
Perplexica
Perplexica is an open-source AI-powered search engine that utilizes advanced machine learning algorithms to provide clear answers with sources cited. It offers various modes like Copilot Mode, Normal Mode, and Focus Modes for specific types of questions. Perplexica ensures up-to-date information by using SearxNG metasearch engine. It also features image and video search capabilities and upcoming features include finalizing Copilot Mode and adding Discover and History Saving features.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
MMMU
MMMU is a benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal models on college-level subject knowledge tasks, covering 30 subjects and 183 subfields with 11.5K questions. It focuses on advanced perception and reasoning with domain-specific knowledge, challenging models to perform tasks akin to those faced by experts. The evaluation of various models highlights substantial challenges, with room for improvement to stimulate the community towards expert artificial general intelligence (AGI).
1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
gpt-researcher
GPT Researcher is an autonomous agent designed for comprehensive online research on a variety of tasks. It can produce detailed, factual, and unbiased research reports with customization options. The tool addresses issues of speed, determinism, and reliability by leveraging parallelized agent work. The main idea involves running 'planner' and 'execution' agents to generate research questions, seek related information, and create research reports. GPT Researcher optimizes costs and completes tasks in around 3 minutes. Features include generating long research reports, aggregating web sources, an easy-to-use web interface, scraping web sources, and exporting reports to various formats.
ChatTTS
ChatTTS is a generative speech model optimized for dialogue scenarios, providing natural and expressive speech synthesis with fine-grained control over prosodic features. It supports multiple speakers and surpasses most open-source TTS models in terms of prosody. The model is trained with 100,000+ hours of Chinese and English audio data, and the open-source version on HuggingFace is a 40,000-hour pre-trained model without SFT. The roadmap includes open-sourcing additional features like VQ encoder, multi-emotion control, and streaming audio generation. The tool is intended for academic and research use only, with precautions taken to limit potential misuse.

HebTTS
HebTTS is a language modeling approach to diacritic-free Hebrew text-to-speech (TTS) system. It addresses the challenge of accurately mapping text to speech in Hebrew by proposing a language model that operates on discrete speech representations and is conditioned on a word-piece tokenizer. The system is optimized using weakly supervised recordings and outperforms diacritic-based Hebrew TTS systems in terms of content preservation and naturalness of generated speech.
do-research-in-AI
This repository is a collection of research lectures and experience sharing posts from frontline researchers in the field of AI. It aims to help individuals upgrade their research skills and knowledge through insightful talks and experiences shared by experts. The content covers various topics such as evaluating research papers, choosing research directions, research methodologies, and tips for writing high-quality scientific papers. The repository also includes discussions on academic career paths, research ethics, and the emotional aspects of research work. Overall, it serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in advancing their research capabilities in the field of AI.


