
easydist
Automated Parallelization System and Infrastructure for Multiple Ecosystems
Stars: 70
EasyDist is an automated parallelization system and infrastructure designed for multiple ecosystems. It offers usability by making parallelizing training or inference code effortless with just a single line of change. It ensures ecological compatibility by serving as a centralized source of truth for SPMD rules at the operator-level for various machine learning frameworks. EasyDist decouples auto-parallel algorithms from specific frameworks and IRs, allowing for the development and benchmarking of different auto-parallel algorithms in a flexible manner. The architecture includes MetaOp, MetaIR, and the ShardCombine Algorithm for SPMD sharding rules without manual annotations.
README:
EasyDist is an automated parallelization system and infrastructure designed for multiple ecosystems, offering the following key features:
-
Usability. With EasyDist, parallelizing your training or inference code to a larger scale becomes effortless with just a single line of change.
-
Ecological Compatibility. EasyDist serves as a centralized source of truth for SPMD rules at the operator-level for various machine learning frameworks. Currently, EasyDist currently supports PyTorch, Jax natively, and the TVM Tensor Expression operator for SPMD rules.
-
Infrastructure. EasyDist decouples auto-parallel algorithms from specific machine learning frameworks and IRs. This design choice allows for the development and benchmarking of different auto-parallel algorithms in a more flexible manner, leveraging the capabilities and abstractions provided by EasyDist.
To parallelize your training loop using EasyDist, you can use the easydist_compile decorator. Here's an example of how it can be used with PyTorch:
@easydist_compile()
def train_step(net, optimizer, inputs, labels):
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
return lossThis one-line decorator parallelizes the training step. You can find more examples in the ./examples/ directory.
EasyDist introduces the concept of MetaOp and MetaIR to decouple automatic parallelization methods from specific intermediate representations (IR) and frameworks. Additionally, it presents the ShardCombine Algorithm, which defines operator Single-Program, Multiple-Data (SPMD) sharding rules without requiring manual annotations. The architecture of EasyDist is as follows:
To install EasyDist, you can use pip and install from PyPI:
# For PyTorch users
pip install pai-easydist[torch]
# For Jax users
pip install pai-easydist[jax] -f https://storage.googleapis.com/jax-releases/jax_cuda_releases.htmlIf you prefer to install EasyDist from source, you can clone the GitHub repository and then install it with the appropriate extras:
git clone https://github.com/alibaba/easydist.git && cd easydist
# EasyDist with PyTorch installation
pip install -e '.[torch]'
# EasyDist with Jax installation
pip install -e '.[jax]' -f https://storage.googleapis.com/jax-releases/jax_cuda_releases.htmlSee CONTRIBUTING.md for details.
EasyDist is developed by Alibaba Group and NUS HPC-AI Lab. This work is supported by Alibaba Innovative Research(AIR).
EasyDist is licensed under the Apache License (Version 2.0). See LICENSE file. This product contains some third-party testcases under other open source licenses. See the NOTICE file for more information.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for easydist
Similar Open Source Tools

easydist
EasyDist is an automated parallelization system and infrastructure designed for multiple ecosystems. It offers usability by making parallelizing training or inference code effortless with just a single line of change. It ensures ecological compatibility by serving as a centralized source of truth for SPMD rules at the operator-level for various machine learning frameworks. EasyDist decouples auto-parallel algorithms from specific frameworks and IRs, allowing for the development and benchmarking of different auto-parallel algorithms in a flexible manner. The architecture includes MetaOp, MetaIR, and the ShardCombine Algorithm for SPMD sharding rules without manual annotations.
llm-on-ray
LLM-on-Ray is a comprehensive solution for building, customizing, and deploying Large Language Models (LLMs). It simplifies complex processes into manageable steps by leveraging the power of Ray for distributed computing. The tool supports pretraining, finetuning, and serving LLMs across various hardware setups, incorporating industry and Intel optimizations for performance. It offers modular workflows with intuitive configurations, robust fault tolerance, and scalability. Additionally, it provides an Interactive Web UI for enhanced usability, including a chatbot application for testing and refining models.
ai-data-analysis-MulitAgent
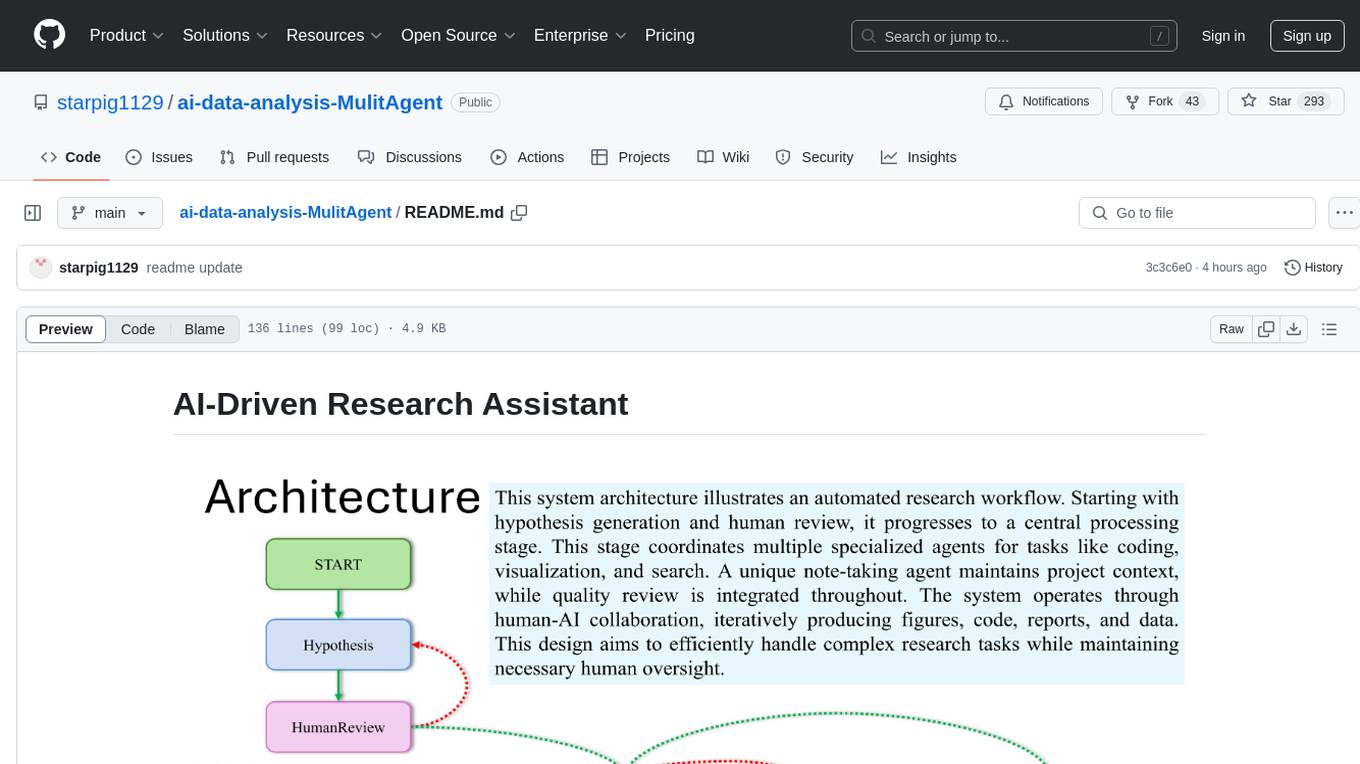
AI-Driven Research Assistant is an advanced AI-powered system utilizing specialized agents for data analysis, visualization, and report generation. It integrates LangChain, OpenAI's GPT models, and LangGraph for complex research processes. Key features include hypothesis generation, data processing, web search, code generation, and report writing. The system's unique Note Taker agent maintains project state, reducing overhead and improving context retention. System requirements include Python 3.10+ and Jupyter Notebook environment. Installation involves cloning the repository, setting up a Conda virtual environment, installing dependencies, and configuring environment variables. Usage instructions include setting data, running Jupyter Notebook, customizing research tasks, and viewing results. Main components include agents for hypothesis generation, process supervision, visualization, code writing, search, report writing, quality review, and note-taking. Workflow involves hypothesis generation, processing, quality review, and revision. Customization is possible by modifying agent creation and workflow definition. Current issues include OpenAI errors, NoteTaker efficiency, runtime optimization, and refiner improvement. Contributions via pull requests are welcome under the MIT License.
GhostOS
GhostOS is an AI Agent framework designed to replace JSON Schema with a Turing-complete code interaction interface (Moss Protocol). It aims to create intelligent entities capable of continuous learning and growth through code generation and project management. The framework supports various capabilities such as turning Python files into web agents, real-time voice conversation, body movements control, and emotion expression. GhostOS is still in early experimental development and focuses on out-of-the-box capabilities for AI agents.
blades
Blades is a multimodal AI Agent framework in Go, supporting custom models, tools, memory, middleware, and more. It is well-suited for multi-turn conversations, chain reasoning, and structured output. The framework provides core components like Agent, Prompt, Chain, ModelProvider, Tool, Memory, and Middleware, enabling developers to build intelligent applications with flexible configuration and high extensibility. Blades leverages the characteristics of Go to achieve high decoupling and efficiency, making it easy to integrate different language model services and external tools. The project is in its early stages, inviting Go developers and AI enthusiasts to contribute and explore the possibilities of building AI applications in Go.

llm_client
llm_client is a Rust interface designed for Local Large Language Models (LLMs) that offers automated build support for CPU, CUDA, MacOS, easy model presets, and a novel cascading prompt workflow for controlled generation. It provides a breadth of configuration options and API support for various OpenAI compatible APIs. The tool is primarily focused on deterministic signals from probabilistic LLM vibes, enabling specialized workflows for specific tasks and reproducible outcomes.
council
Council is an open-source platform designed for the rapid development and deployment of customized generative AI applications using teams of agents. It extends the LLM tool ecosystem by providing advanced control flow and scalable oversight for AI agents. Users can create sophisticated agents with predictable behavior by leveraging Council's powerful approach to control flow using Controllers, Filters, Evaluators, and Budgets. The framework allows for automated routing between agents, comparing, evaluating, and selecting the best results for a task. Council aims to facilitate packaging and deploying agents at scale on multiple platforms while enabling enterprise-grade monitoring and quality control.
CompressAI-Vision
CompressAI-Vision is a tool that helps you develop, test, and evaluate compression models with standardized tests in the context of compression methods optimized for machine tasks algorithms such as Neural-Network (NN)-based detectors. It currently focuses on two types of pipeline: Video compression for remote inference (`compressai-remote-inference`), which corresponds to the MPEG "Video Coding for Machines" (VCM) activity. Split inference (`compressai-split-inference`), which includes an evaluation framework for compressing intermediate features produced in the context of split models. The software supports all the pipelines considered in the related MPEG activity: "Feature Compression for Machines" (FCM).
aici
The Artificial Intelligence Controller Interface (AICI) lets you build Controllers that constrain and direct output of a Large Language Model (LLM) in real time. Controllers are flexible programs capable of implementing constrained decoding, dynamic editing of prompts and generated text, and coordinating execution across multiple, parallel generations. Controllers incorporate custom logic during the token-by-token decoding and maintain state during an LLM request. This allows diverse Controller strategies, from programmatic or query-based decoding to multi-agent conversations to execute efficiently in tight integration with the LLM itself.
DistServe
DistServe improves the performance of large language models serving by disaggregating the prefill and decoding computation. It allows setting parallelism configs and scheduling strategies for the two phases independently, handling KV-Cache communication and memory management automatically. Utilizes a high-performance C++ Transformer inference library SwiftTransformer with features like model/pipeline parallelism, FlashAttention, Continuous Batching, and PagedAttention. Supports GPT-2, OPT, and LLaMA2 models.
pathway
Pathway is a Python data processing framework for analytics and AI pipelines over data streams. It's the ideal solution for real-time processing use cases like streaming ETL or RAG pipelines for unstructured data. Pathway comes with an **easy-to-use Python API** , allowing you to seamlessly integrate your favorite Python ML libraries. Pathway code is versatile and robust: **you can use it in both development and production environments, handling both batch and streaming data effectively**. The same code can be used for local development, CI/CD tests, running batch jobs, handling stream replays, and processing data streams. Pathway is powered by a **scalable Rust engine** based on Differential Dataflow and performs incremental computation. Your Pathway code, despite being written in Python, is run by the Rust engine, enabling multithreading, multiprocessing, and distributed computations. All the pipeline is kept in memory and can be easily deployed with **Docker and Kubernetes**. You can install Pathway with pip: `pip install -U pathway` For any questions, you will find the community and team behind the project on Discord.
wandbot
Wandbot is a question-answering bot designed for Weights & Biases documentation. It employs Retrieval Augmented Generation with a ChromaDB backend for efficient responses. The bot features periodic data ingestion, integration with Discord and Slack, and performance monitoring through logging. It has a fallback mechanism for model selection and is evaluated based on retrieval accuracy and model-generated responses. The implementation includes creating document embeddings, constructing the Q&A RAGPipeline, model selection, deployment on FastAPI, Discord, and Slack, logging and analysis with Weights & Biases Tables, and performance evaluation.
MemoryBear
MemoryBear is a next-generation AI memory system developed by RedBear AI, focusing on overcoming limitations in knowledge storage and multi-agent collaboration. It empowers AI with human-like memory capabilities, enabling deep knowledge understanding and cognitive collaboration. The system addresses challenges such as knowledge forgetting, memory gaps in multi-agent collaboration, and semantic ambiguity during reasoning. MemoryBear's core features include memory extraction engine, graph storage, hybrid search, memory forgetting engine, self-reflection engine, and FastAPI services. It offers a standardized service architecture for efficient integration and invocation across applications.
BitMat
BitMat is a Python package designed to optimize matrix multiplication operations by utilizing custom kernels written in Triton. It leverages the principles outlined in the "1bit-LLM Era" paper, specifically utilizing packed int8 data to enhance computational efficiency and performance in deep learning and numerical computing tasks.
radicalbit-ai-monitoring
The Radicalbit AI Monitoring Platform provides a comprehensive solution for monitoring Machine Learning and Large Language models in production. It helps proactively identify and address potential performance issues by analyzing data quality, model quality, and model drift. The repository contains files and projects for running the platform, including UI, API, SDK, and Spark components. Installation using Docker compose is provided, allowing deployment with a K3s cluster and interaction with a k9s container. The platform documentation includes a step-by-step guide for installation and creating dashboards. Community engagement is encouraged through a Discord server. The roadmap includes adding functionalities for batch and real-time workloads, covering various model types and tasks.
ArcticTraining
ArcticTraining is a framework designed to simplify and accelerate the post-training process for large language models (LLMs). It offers modular trainer designs, simplified code structures, and integrated pipelines for creating and cleaning synthetic data, enabling users to enhance LLM capabilities like code generation and complex reasoning with greater efficiency and flexibility.
For similar tasks

easydist
EasyDist is an automated parallelization system and infrastructure designed for multiple ecosystems. It offers usability by making parallelizing training or inference code effortless with just a single line of change. It ensures ecological compatibility by serving as a centralized source of truth for SPMD rules at the operator-level for various machine learning frameworks. EasyDist decouples auto-parallel algorithms from specific frameworks and IRs, allowing for the development and benchmarking of different auto-parallel algorithms in a flexible manner. The architecture includes MetaOp, MetaIR, and the ShardCombine Algorithm for SPMD sharding rules without manual annotations.
edgen
Edgen is a local GenAI API server that serves as a drop-in replacement for OpenAI's API. It provides multi-endpoint support for chat completions and speech-to-text, is model agnostic, offers optimized inference, and features model caching. Built in Rust, Edgen is natively compiled for Windows, MacOS, and Linux, eliminating the need for Docker. It allows users to utilize GenAI locally on their devices for free and with data privacy. With features like session caching, GPU support, and support for various endpoints, Edgen offers a scalable, reliable, and cost-effective solution for running GenAI applications locally.
Awesome_LLM_System-PaperList
Since the emergence of chatGPT in 2022, the acceleration of Large Language Model has become increasingly important. Here is a list of papers on LLMs inference and serving.
LLM-Viewer
LLM-Viewer is a tool for visualizing Language and Learning Models (LLMs) and analyzing performance on different hardware platforms. It enables network-wise analysis, considering factors such as peak memory consumption and total inference time cost. With LLM-Viewer, users can gain valuable insights into LLM inference and performance optimization. The tool can be used in a web browser or as a command line interface (CLI) for easy configuration and visualization. The ongoing project aims to enhance features like showing tensor shapes, expanding hardware platform compatibility, and supporting more LLMs with manual model graph configuration.

ServerlessLLM
ServerlessLLM is a fast, affordable, and easy-to-use library designed for multi-LLM serving, optimized for environments with limited GPU resources. It supports loading various leading LLM inference libraries, achieving fast load times, and reducing model switching overhead. The library facilitates easy deployment via Ray Cluster and Kubernetes, integrates with the OpenAI Query API, and is actively maintained by contributors.
sarathi-serve
Sarathi-Serve is the official OSDI'24 artifact submission for paper #444, focusing on 'Taming Throughput-Latency Tradeoff in LLM Inference'. It is a research prototype built on top of CUDA 12.1, designed to optimize throughput-latency tradeoff in Large Language Models (LLM) inference. The tool provides a Python environment for users to install and reproduce results from the associated experiments. Users can refer to specific folders for individual figures and are encouraged to cite the paper if they use the tool in their work.

aphrodite-engine
Aphrodite is the official backend engine for PygmalionAI, serving as the inference endpoint for the website. It allows serving Hugging Face-compatible models with fast speeds. Features include continuous batching, efficient K/V management, optimized CUDA kernels, quantization support, distributed inference, and 8-bit KV Cache. The engine requires Linux OS and Python 3.8 to 3.12, with CUDA >= 11 for build requirements. It supports various GPUs, CPUs, TPUs, and Inferentia. Users can limit GPU memory utilization and access full commands via CLI.
uTensor
uTensor is an extremely light-weight machine learning inference framework built on Tensorflow and optimized for Arm targets. It consists of a runtime library and an offline tool that handles most of the model translation work. The core runtime is only ~2KB. The workflow involves constructing and training a model in Tensorflow, then using uTensor to produce C++ code for inferencing. The runtime ensures system safety, guarantees RAM usage, and focuses on clear, concise, and debuggable code. The high-level API simplifies tensor handling and operator execution for embedded systems.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.