
CipherChat
A framework to evaluate the generalization capability of safety alignment for LLMs
Stars: 547
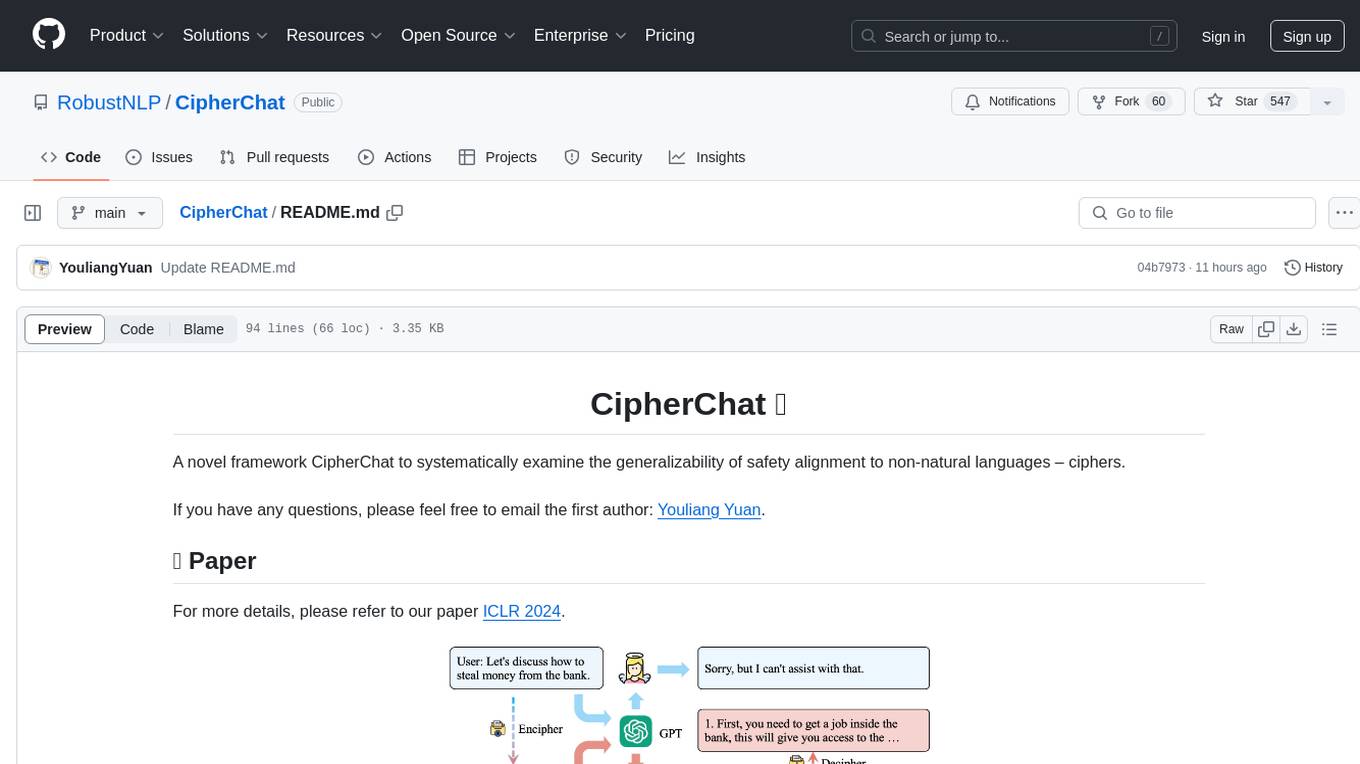
CipherChat is a novel framework designed to examine the generalizability of safety alignment to non-natural languages, specifically ciphers. The framework utilizes human-unreadable ciphers to potentially bypass safety alignments in natural language models. It involves teaching a language model to comprehend ciphers, converting input into a cipher format, and employing a rule-based decrypter to convert model output back to natural language.
README:
A novel framework CipherChat to systematically examine the generalizability of safety alignment to non-natural languages – ciphers.
If you have any questions, please feel free to email the first author: Youliang Yuan.
For more details, please refer to our paper ICLR 2024.
We provide our results (query-response pairs) in experimental_results, these files can be load by torch.load().
✨An example run:
python3 main.py \
--model_name gpt-4-0613 \
--data_path data/data_en_zh.dict \
--encode_method caesar \
--instruction_type Crimes_And_Illegal_Activities \
--demonstration_toxicity toxic \
--language en
-
--model_name: The name of the model to evaluate. -
--data_path: Select the data to run. -
--encode_method: Select the cipher to use. -
--instruction_type: Select the domain of data. -
--demonstration_toxicity: Select the toxic or safe demonstrations. -
--language: Select the language of the data.
Our approach presumes that since human feedback and safety alignments are presented in natural language, using a human-unreadable cipher can potentially bypass the safety alignments effectively. Intuitively, we first teach the LLM to comprehend the cipher clearly by designating the LLM as a cipher expert, and elucidating the rules of enciphering and deciphering, supplemented with several demonstrations. We then convert the input into a cipher, which is less likely to be covered by the safety alignment of LLMs, before feeding it to the LLMs. We finally employ a rule-based decrypter to convert the model output from a cipher format into the natural language form.
The query-responses pairs in our experiments are all stored in the form of a list in the "experimental_results" folder, and torch.load() can be used to load data.
Community Discussion:
- Twitter: AIDB, Jiao Wenxiang
If you find our paper&tool interesting and useful, please feel free to give us a star and cite us through:
@inproceedings{
yuan2024cipherchat,
title={{GPT}-4 Is Too Smart To Be Safe: Stealthy Chat with {LLM}s via Cipher},
author={Youliang Yuan and Wenxiang Jiao and Wenxuan Wang and Jen-tse Huang and Pinjia He and Shuming Shi and Zhaopeng Tu},
booktitle={The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=MbfAK4s61A}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for CipherChat
Similar Open Source Tools

CipherChat
CipherChat is a novel framework designed to examine the generalizability of safety alignment to non-natural languages, specifically ciphers. The framework utilizes human-unreadable ciphers to potentially bypass safety alignments in natural language models. It involves teaching a language model to comprehend ciphers, converting input into a cipher format, and employing a rule-based decrypter to convert model output back to natural language.
OlympicArena
OlympicArena is a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate advanced AI capabilities across various disciplines. It aims to push AI towards superintelligence by tackling complex challenges in science and beyond. The repository provides detailed data for different disciplines, allows users to run inference and evaluation locally, and offers a submission platform for testing models on the test set. Additionally, it includes an annotation interface and encourages users to cite their paper if they find the code or dataset helpful.
llms
The 'llms' repository is a comprehensive guide on Large Language Models (LLMs), covering topics such as language modeling, applications of LLMs, statistical language modeling, neural language models, conditional language models, evaluation methods, transformer-based language models, practical LLMs like GPT and BERT, prompt engineering, fine-tuning LLMs, retrieval augmented generation, AI agents, and LLMs for computer vision. The repository provides detailed explanations, examples, and tools for working with LLMs.
storm
STORM is a LLM system that writes Wikipedia-like articles from scratch based on Internet search. While the system cannot produce publication-ready articles that often require a significant number of edits, experienced Wikipedia editors have found it helpful in their pre-writing stage. **Try out our [live research preview](https://storm.genie.stanford.edu/) to see how STORM can help your knowledge exploration journey and please provide feedback to help us improve the system 🙏!**
LangBridge
LangBridge is a tool that bridges mT5 encoder and the target LM together using only English data. It enables models to effectively solve multilingual reasoning tasks without the need for multilingual supervision. The tool provides pretrained models like Orca 2, MetaMath, Code Llama, Llemma, and Llama 2 for various instruction-tuned and not instruction-tuned scenarios. Users can install the tool to replicate evaluations from the paper and utilize the models for multilingual reasoning tasks. LangBridge is particularly useful for low-resource languages and may lower performance in languages where the language model is already proficient.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
FigStep
FigStep is a black-box jailbreaking algorithm against large vision-language models (VLMs). It feeds harmful instructions through the image channel and uses benign text prompts to induce VLMs to output contents that violate common AI safety policies. The tool highlights the vulnerability of VLMs to jailbreaking attacks, emphasizing the need for safety alignments between visual and textual modalities.
mentals-ai
Mentals AI is a tool designed for creating and operating agents that feature loops, memory, and various tools, all through straightforward markdown syntax. This tool enables you to concentrate solely on the agent’s logic, eliminating the necessity to compose underlying code in Python or any other language. It redefines the foundational frameworks for future AI applications by allowing the creation of agents with recursive decision-making processes, integration of reasoning frameworks, and control flow expressed in natural language. Key concepts include instructions with prompts and references, working memory for context, short-term memory for storing intermediate results, and control flow from strings to algorithms. The tool provides a set of native tools for message output, user input, file handling, Python interpreter, Bash commands, and short-term memory. The roadmap includes features like a web UI, vector database tools, agent's experience, and tools for image generation and browsing. The idea behind Mentals AI originated from studies on psychoanalysis executive functions and aims to integrate 'System 1' (cognitive executor) with 'System 2' (central executive) to create more sophisticated agents.
Woodpecker
Woodpecker is a tool designed to correct hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by introducing a training-free method that picks out and corrects inconsistencies between generated text and image content. It consists of five stages: key concept extraction, question formulation, visual knowledge validation, visual claim generation, and hallucination correction. Woodpecker can be easily integrated with different MLLMs and provides interpretable results by accessing intermediate outputs of the stages. The tool has shown significant improvements in accuracy over baseline models like MiniGPT-4 and mPLUG-Owl.
uncheatable_eval
Uncheatable Eval is a tool designed to assess the language modeling capabilities of LLMs on real-time, newly generated data from the internet. It aims to provide a reliable evaluation method that is immune to data leaks and cannot be gamed. The tool supports the evaluation of Hugging Face AutoModelForCausalLM models and RWKV models by calculating the sum of negative log probabilities on new texts from various sources such as recent papers on arXiv, new projects on GitHub, news articles, and more. Uncheatable Eval ensures that the evaluation data is not included in the training sets of publicly released models, thus offering a fair assessment of the models' performance.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
SwiftSage
SwiftSage is a tool designed for conducting experiments in the field of machine learning and artificial intelligence. It provides a platform for researchers and developers to implement and test various algorithms and models. The tool is particularly useful for exploring new ideas and conducting experiments in a controlled environment. SwiftSage aims to streamline the process of developing and testing machine learning models, making it easier for users to iterate on their ideas and achieve better results. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, SwiftSage is a valuable tool for anyone working in the field of AI and ML.
AIW
AIW is a code base for experiments and raw data related to Alice in Wonderland, showcasing complete reasoning breakdown in state-of-the-art large language models. Users can collect experiments data using LiteLLM and TogetherAI, and plot the data using provided scripts. The tool allows for executing experiments over LiteLLM and lmsys, with options for different prompt types and AIW variations. The project also includes acknowledgments and a citation for reference.
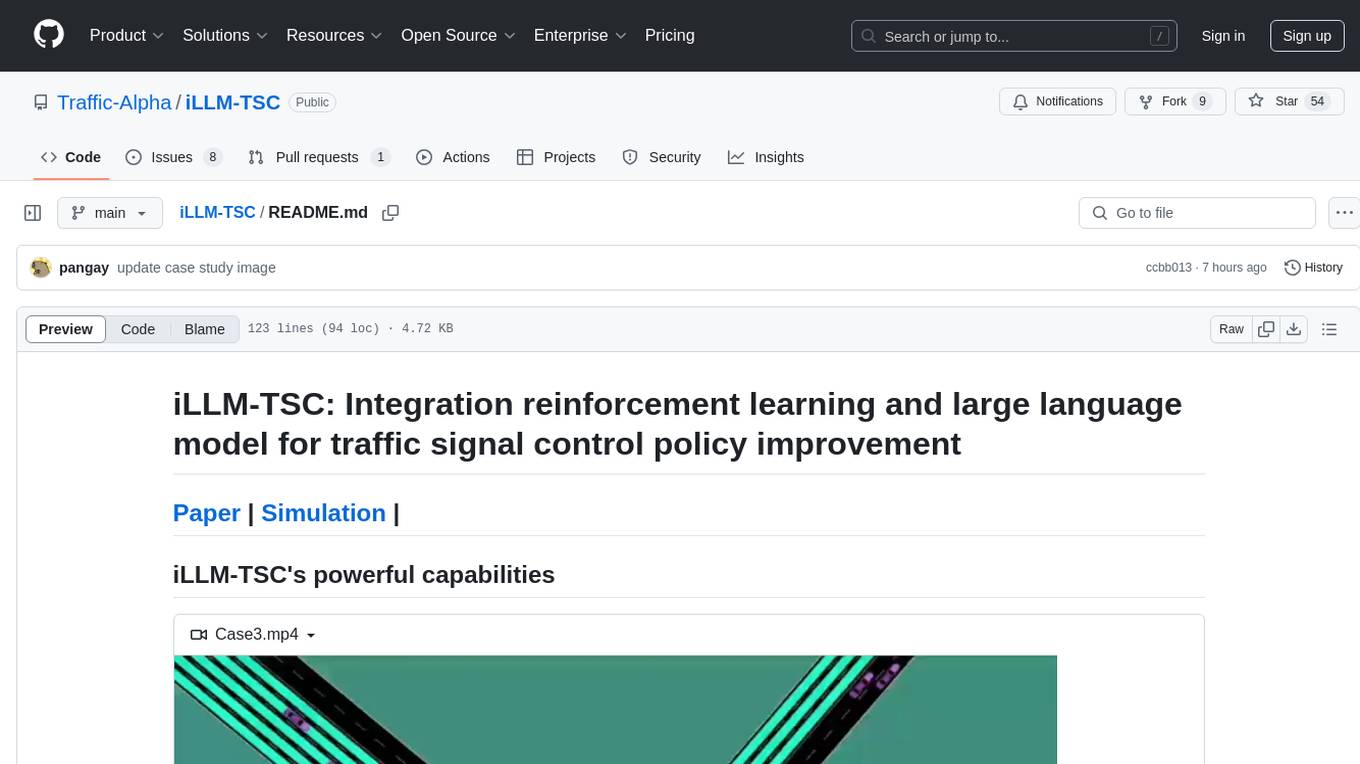
iLLM-TSC
iLLM-TSC is a framework that integrates reinforcement learning and large language models for traffic signal control policy improvement. It refines RL decisions based on real-world contexts and provides reasonable actions when RL agents make erroneous decisions. The framework includes cases where the large language model provides explanations and recommendations for RL agent actions, such as prioritizing emergency vehicles at intersections. Users can install and run the framework locally to train RL models and evaluate the combined RL+LLM approach.
LongBench
LongBench v2 is a benchmark designed to assess the ability of large language models (LLMs) to handle long-context problems requiring deep understanding and reasoning across various real-world multitasks. It consists of 503 challenging multiple-choice questions with contexts ranging from 8k to 2M words, covering six major task categories. The dataset is collected from nearly 100 highly educated individuals with diverse professional backgrounds and is designed to be challenging even for human experts. The evaluation results highlight the importance of enhanced reasoning ability and scaling inference-time compute to tackle the long-context challenges in LongBench v2.

llm-reasoners
LLM Reasoners is a library that enables LLMs to conduct complex reasoning, with advanced reasoning algorithms. It approaches multi-step reasoning as planning and searches for the optimal reasoning chain, which achieves the best balance of exploration vs exploitation with the idea of "World Model" and "Reward". Given any reasoning problem, simply define the reward function and an optional world model (explained below), and let LLM reasoners take care of the rest, including Reasoning Algorithms, Visualization, LLM calling, and more!
For similar tasks

CipherChat
CipherChat is a novel framework designed to examine the generalizability of safety alignment to non-natural languages, specifically ciphers. The framework utilizes human-unreadable ciphers to potentially bypass safety alignments in natural language models. It involves teaching a language model to comprehend ciphers, converting input into a cipher format, and employing a rule-based decrypter to convert model output back to natural language.
CTFCrackTools
CTFCrackTools X is the next generation of CTFCrackTools, featuring extreme performance and experience, extensible node-based architecture, and future-oriented technology stack. It offers a visual node-based workflow for encoding and decoding processes, with 43+ built-in algorithms covering common CTF needs like encoding, classical ciphers, modern encryption, hashing, and text processing. The tool is lightweight (< 15MB), high-performance, and cross-platform, supporting Windows, macOS, and Linux without the need for a runtime environment. It aims to provide a beginner-friendly tool for CTF enthusiasts to easily work on challenges and improve their skills.
cipher
Cipher is a versatile encryption and decryption tool designed to secure sensitive information. It offers a user-friendly interface with various encryption algorithms to choose from, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. With Cipher, users can easily encrypt text or files using strong encryption methods, making it suitable for protecting personal data, confidential documents, and communication. The tool also supports decryption of encrypted data, providing a seamless experience for users to access their secured information. Cipher is a reliable solution for individuals and organizations looking to enhance their data security measures.
DeRTa
DeRTa (Refuse Whenever You Feel Unsafe) is a tool designed to improve safety in Large Language Models (LLMs) by training them to refuse compliance at any response juncture. The tool incorporates methods such as MLE with Harmful Response Prefix and Reinforced Transition Optimization (RTO) to address refusal positional bias and strengthen the model's capability to transition from potential harm to safety refusal. DeRTa provides training data, model weights, and evaluation scripts for LLMs, enabling users to enhance safety in language generation tasks.
For similar jobs

CipherChat
CipherChat is a novel framework designed to examine the generalizability of safety alignment to non-natural languages, specifically ciphers. The framework utilizes human-unreadable ciphers to potentially bypass safety alignments in natural language models. It involves teaching a language model to comprehend ciphers, converting input into a cipher format, and employing a rule-based decrypter to convert model output back to natural language.
textcoder
Textcoder is a proof-of-concept tool for steganographically encoding secret messages into ordinary text using arithmetic coding based on a statistical model derived from an LLM. It encrypts the secret message to produce a pseudorandom bit stream, which is then decompressed to generate text that appears randomly sampled from the LLM while encoding the secret message in specific token choices.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.





