
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Official Implementation of "Affordable AI Assistants with Knowledge Graph of Thoughts"
Stars: 139
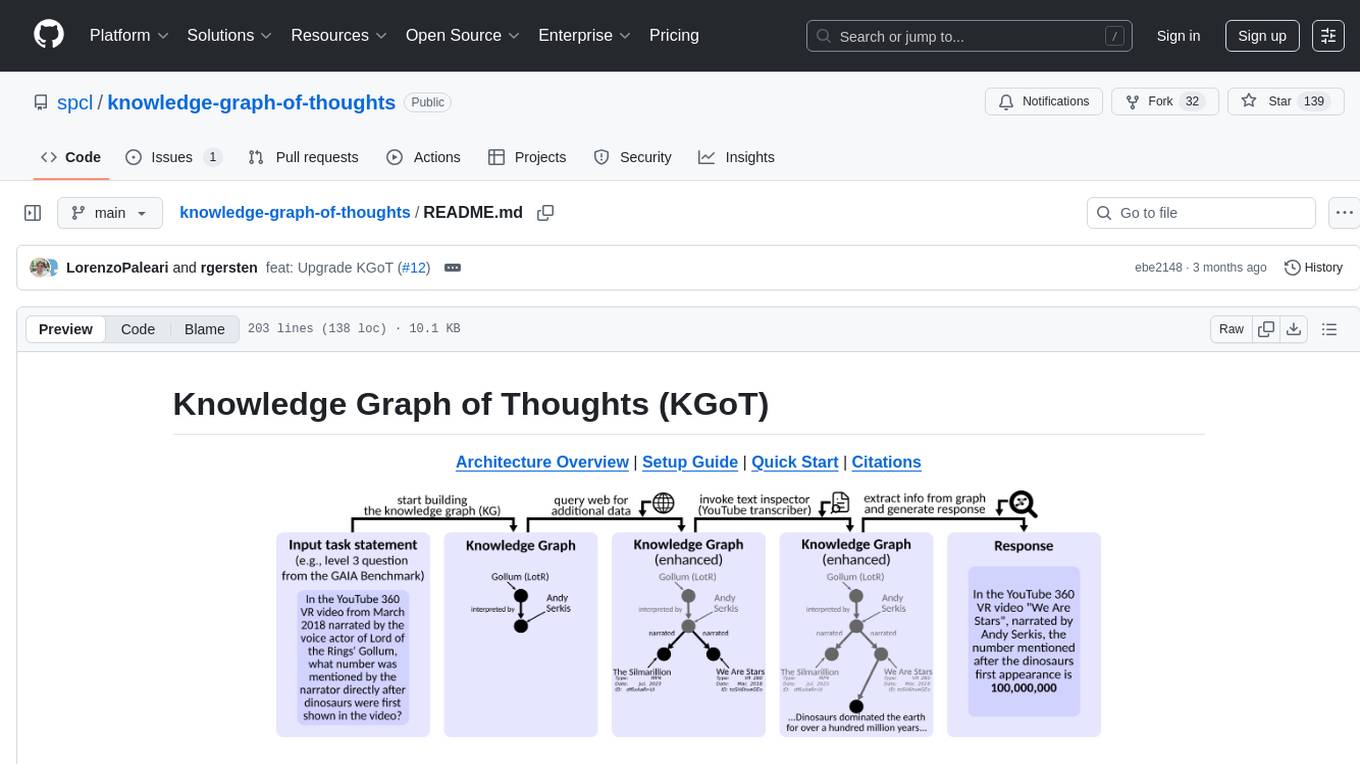
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
README:
This is the official implementation of Affordable AI Assistants with Knowledge Graph of Thoughts.
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively.
The KGoT system is designed as a modular and flexible framework that consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
- The Controller component offers fine-grained control over the customizable parameters in the KGoT pipeline and orchestrates the KG-based reasoning procedure.
- The Graph Store component provides a modular interface for supporting various Knowledge Graph Backends. We initially support Neo4j, NetworkX and RDF4J.
- The Integrated Tools component allows for flexible and extensible Tool Usage and enables the multi-modal reasoning capabilities of the framework.
In order to use this framework, you need to have a working installation of Python 3.10 or newer.
Before running the installation, make sure to activate your Python environment (if any) beforehand.
git clone https://github.com/spcl/knowledge-graph-of-thoughts.git
cd knowledge-graph-of-thoughts/
pip install -e .
playwright installTo get started make a copy of the following template files inside the kgot directory:
kgot/config_llms.template.jsonkgot/config_tools.template.json
Then rename them as follows:
-
config_llms.template.json→config_llms.json -
config_tools.template.json→config_tools.json
Please update the API keys, if necessary, for the language models you intend to use in the kgot/config_llms.json file.
You can also add new models by incorporating their information into the JSON file.
The object key is the language model identifier used in KGoT, and the various attributes contain the information needed to run the model.
Local models are expected to be hosted using Ollama. KGoT assumes that the model is accessible at the default Ollama API endpoint (http://localhost:11434) and integrates with it through ChatOllama via the LangChain framework.
[!NOTE] Please be aware that the values for
num_ctx,num_predict, andnum_batchin the configuration are based on the specific GPU type and VRAM capacity used during our experiments. You may need to adjust these parameters based on your own hardware setup to avoid out-of-memory errors or suboptimal performance.
For the SurferAgent tool we rely on SerpAPI for browsing necessary external information from the Internet.
To use this tool, please set the API key within the kgot/config_tools.json file.
In order to provide a secure & consistent execution environment, we containerize critical modules such as the Neo4j graph database, the RDF4J database and the Python Code Tool. This allows the safe execution of LLM-generated code without security concerns.
We provide a Docker and Sarus setup for the KGoT framework. The Docker setup is recommended for local development, while Sarus is intended for HPC environments.
cd containers/
# Docker
chmod -R 777 ../kgot/knowledge_graph/_snapshots # grant permission for snapshots logging
docker compose up
# Sarus
chmod +x sarus_launcher.sh # grant permission for execution
./sarus_launcher.shThis will build and start the default container images for KGoT, which include:
- Neo4j image
- Python image
cd containers/kgot/
# Docker
docker compose up
# Sarus
chmod +x sarus_launcher.sh # grant permission for execution
./sarus_launcher.shThis will build and start:
- KGoT image
[!NOTE] Further instructions on RDF4J and on customizing the container images can be found under Container Image Setup.
[!WARNING] The initial building phase of the KGoT container image can take a while (15 minutes), so be patient. If you need to make adjustments simply stop the instances and restart them with the following command
docker compose up --buildfrom thecontainers/kgotdirectory. Changes toREADME.md,LICENSE,pyproject.toml,kgot/__init__.pyandkgot/__main__.pywill cause the Docker instance to be rebuilt from scratch.
We primarily evaluated the Knowledge Graph of Thoughts framework with the GAIA and SimpleQA benchmarks, which we discuss first and subsequently alternative ways to run KGoT.
To avoid sharing the GAIA and SimpleQA datasets in a crawlable format, we do not directly provide the datasets inside the repository. Instead, we offer a download script to help you acquire the datasets.
Please refer to the download guide inside the benchmarks directory for further instructions.
We provide two run scripts for evaluating KGoT on the GAIA and SimpleQA datasets.
chmod +x ./run_multiple_gaia.sh # grant permission for logging etc.
./run_multiple_gaia.sh # perform the actual run with default parameters
chmod +x ./run_multiple_simpleqa.sh # grant permission for logging etc.
./run_multiple_simpleqa.sh # perform the actual run with default parametersThe following instructions apply to the run_multiple_gaia.sh script, but are also applicable to the run_multiple_simpleqa.sh script; for more detailed instructions please refer to the complete guide here.
You can run ./run_multiple_gaia.sh --help to check the supported arguments, that generally match the options found here for the gaia.py Python script.
For optimal results, we recommend enabling the '--gaia_formatter' option, which will format the output in a GAIA-compatible format.
The following are the most commonly used arguments:
Arguments:
--log_base_folder - Directory where logs will be stored [path/to/log_folder]
--controller_choice - Type of solver to use [directRetrieve/queryRetrieve]
--backend_choice - Backend database type [neo4j/networkX/rdf4j]
--tool_choice - Tool configuration [tools_v2_3]
--max_iterations - Max iterations for KGoT [integers > 0]
--gaia_formatter - Use GAIA formatter for the output [True/False]
Example: ./run_multiple_gaia.sh --log_base_folder logs/test_1 --controller_choice directRetrieve --backend_choice networkX --tools "tools_v2_3" --max_iterations 5 --gaia_formatter
We offer three choices for storing the knowledge graph (Neo4j, NetworkX and RDF4J) as well as two choices for the retrieval type (direct and query-based retrieval).
We offer two ways to evaluate KGoT on the datasets as well as a way to use KGoT directly with any task description.
As discussed above, you can use the run_multiple_gaia.sh or run_multiple_simpleqa.sh scripts to evaluate KGoT on the GAIA and SimpleQA datasets respectively, which act as frontends for the gaia.py and simpleqa.py Python scripts.
They allow to evaluate multiple subsets of the datasets or to do multiple runs on these subsets, while also transfering the knowledge graph snapshots as well as plotting the results with various metrics.
We further discuss the use of the scripts here.
Please note, that if you use your own Neo4j or RDF4J server instead of the one inside the Docker container, the transfer of the knowledge graph snapshots will fail or needs to be adapted.
You can also directly run the Python script gaia.py, which we further discuss here. This Python script will however not plot the resulting data nor move the snapshots of the knowledge graph.
You can also directly use the command kgot, which is fully configurable and can be used to solve a single task:
kgot single -p "What is a knowledge graph?"You can also, for example, select a desirable backend and pass files via the command line:
kgot --db_choice neo4j --controller_choice directRetrieve single --p "Could you summarize the content of these files for me?" --files [path/to/file1] [path/to/file2]If you find this repository useful, please consider giving it a star! If you have any questions or feedback, don't hesitate to reach out and open an issue.
When using this in your work, please reference us with the citation provided below:
@misc{besta2025kgot,
title = {{Affordable AI Assistants with Knowledge Graph of Thoughts}},
author = {Besta, Maciej and Paleari, Lorenzo and Jiang, Jia Hao Andrea and Gerstenberger, Robert and Wu, You and Hannesson, Jón Gunnar and Iff, Patrick and Kubicek, Ales and Nyczyk, Piotr and Khimey, Diana and Blach, Nils and Zhang, Haiqiang and Zhang, Tao and Ma, Peiran and Kwaśniewski, Grzegorz and Copik, Marcin and Niewiadomski, Hubert and Hoefler, Torsten},
year = 2025,
month = Jun,
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2504.02670},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/2504.02670},
eprinttype = {arXiv},
eprint = {2504.02670}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Similar Open Source Tools

knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
warc-gpt
WARC-GPT is an experimental retrieval augmented generation pipeline for web archive collections. It allows users to interact with WARC files, extract text, generate text embeddings, visualize embeddings, and interact with a web UI and API. The tool is highly customizable, supporting various LLMs, providers, and embedding models. Users can configure the application using environment variables, ingest WARC files, start the server, and interact with the web UI and API to search for content and generate text completions. WARC-GPT is designed for exploration and experimentation in exploring web archives using AI.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
aici
The Artificial Intelligence Controller Interface (AICI) lets you build Controllers that constrain and direct output of a Large Language Model (LLM) in real time. Controllers are flexible programs capable of implementing constrained decoding, dynamic editing of prompts and generated text, and coordinating execution across multiple, parallel generations. Controllers incorporate custom logic during the token-by-token decoding and maintain state during an LLM request. This allows diverse Controller strategies, from programmatic or query-based decoding to multi-agent conversations to execute efficiently in tight integration with the LLM itself.
pgai
pgai simplifies the process of building search and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) AI applications with PostgreSQL. It brings embedding and generation AI models closer to the database, allowing users to create embeddings, retrieve LLM chat completions, reason over data for classification, summarization, and data enrichment directly from within PostgreSQL in a SQL query. The tool requires an OpenAI API key and a PostgreSQL client to enable AI functionality in the database. Users can install pgai from source, run it in a pre-built Docker container, or enable it in a Timescale Cloud service. The tool provides functions to handle API keys using psql or Python, and offers various AI functionalities like tokenizing, detokenizing, embedding, chat completion, and content moderation.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.

cognita
Cognita is an open-source framework to organize your RAG codebase along with a frontend to play around with different RAG customizations. It provides a simple way to organize your codebase so that it becomes easy to test it locally while also being able to deploy it in a production ready environment. The key issues that arise while productionizing RAG system from a Jupyter Notebook are: 1. **Chunking and Embedding Job** : The chunking and embedding code usually needs to be abstracted out and deployed as a job. Sometimes the job will need to run on a schedule or be trigerred via an event to keep the data updated. 2. **Query Service** : The code that generates the answer from the query needs to be wrapped up in a api server like FastAPI and should be deployed as a service. This service should be able to handle multiple queries at the same time and also autoscale with higher traffic. 3. **LLM / Embedding Model Deployment** : Often times, if we are using open-source models, we load the model in the Jupyter notebook. This will need to be hosted as a separate service in production and model will need to be called as an API. 4. **Vector DB deployment** : Most testing happens on vector DBs in memory or on disk. However, in production, the DBs need to be deployed in a more scalable and reliable way. Cognita makes it really easy to customize and experiment everything about a RAG system and still be able to deploy it in a good way. It also ships with a UI that makes it easier to try out different RAG configurations and see the results in real time. You can use it locally or with/without using any Truefoundry components. However, using Truefoundry components makes it easier to test different models and deploy the system in a scalable way. Cognita allows you to host multiple RAG systems using one app. ### Advantages of using Cognita are: 1. A central reusable repository of parsers, loaders, embedders and retrievers. 2. Ability for non-technical users to play with UI - Upload documents and perform QnA using modules built by the development team. 3. Fully API driven - which allows integration with other systems. > If you use Cognita with Truefoundry AI Gateway, you can get logging, metrics and feedback mechanism for your user queries. ### Features: 1. Support for multiple document retrievers that use `Similarity Search`, `Query Decompostion`, `Document Reranking`, etc 2. Support for SOTA OpenSource embeddings and reranking from `mixedbread-ai` 3. Support for using LLMs using `Ollama` 4. Support for incremental indexing that ingests entire documents in batches (reduces compute burden), keeps track of already indexed documents and prevents re-indexing of those docs.

MegatronApp
MegatronApp is a toolchain built around the Megatron-LM training framework, offering performance tuning, slow-node detection, and training-process visualization. It includes modules like MegaScan for anomaly detection, MegaFBD for forward-backward decoupling, MegaDPP for dynamic pipeline planning, and MegaScope for visualization. The tool aims to enhance large-scale distributed training by providing valuable capabilities and insights.
OlympicArena
OlympicArena is a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate advanced AI capabilities across various disciplines. It aims to push AI towards superintelligence by tackling complex challenges in science and beyond. The repository provides detailed data for different disciplines, allows users to run inference and evaluation locally, and offers a submission platform for testing models on the test set. Additionally, it includes an annotation interface and encourages users to cite their paper if they find the code or dataset helpful.
neuron-ai
Neuron is a PHP framework for creating and orchestrating AI Agents, providing tools for the entire agentic application development lifecycle. It allows integration of AI entities in existing PHP applications with a powerful and flexible architecture. Neuron offers tutorials and educational content to help users get started using AI Agents in their projects. The framework supports various LLM providers, tools, and toolkits, enabling users to create fully functional agents for tasks like data analysis, chatbots, and structured output. Neuron also facilitates monitoring and debugging of AI applications, ensuring control over agent behavior and decision-making processes.
LLMeBench
LLMeBench is a flexible framework designed for accelerating benchmarking of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP). It supports evaluation of various NLP tasks using model providers like OpenAI, HuggingFace Inference API, and Petals. The framework is customizable for different NLP tasks, LLM models, and datasets across multiple languages. It features extensive caching capabilities, supports zero- and few-shot learning paradigms, and allows on-the-fly dataset download and caching. LLMeBench is open-source and continuously expanding to support new models accessible through APIs.
lmql
LMQL is a programming language designed for large language models (LLMs) that offers a unique way of integrating traditional programming with LLM interaction. It allows users to write programs that combine algorithmic logic with LLM calls, enabling model reasoning capabilities within the context of the program. LMQL provides features such as Python syntax integration, rich control-flow options, advanced decoding techniques, powerful constraints via logit masking, runtime optimization, sync and async API support, multi-model compatibility, and extensive applications like JSON decoding and interactive chat interfaces. The tool also offers library integration, flexible tooling, and output streaming options for easy model output handling.
safety-tooling
This repository, safety-tooling, is designed to be shared across various AI Safety projects. It provides an LLM API with a common interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google models. The aim is to facilitate collaboration among AI Safety researchers, especially those with limited software engineering backgrounds, by offering a platform for contributing to a larger codebase. The repo can be used as a git submodule for easy collaboration and updates. It also supports pip installation for convenience. The repository includes features for installation, secrets management, linting, formatting, Redis configuration, testing, dependency management, inference, finetuning, API usage tracking, and various utilities for data processing and experimentation.
BTGenBot
BTGenBot is a tool that generates behavior trees for robots using lightweight large language models (LLMs) with a maximum of 7 billion parameters. It fine-tunes on a specific dataset, compares multiple LLMs, and evaluates generated behavior trees using various methods. The tool demonstrates the potential of LLMs with a limited number of parameters in creating effective and efficient robot behaviors.
AI-Scientist
The AI Scientist is a comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models to perform research independently. It aims to tackle the grand challenge of developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. The tool generates papers on various topics using Large Language Models (LLMs) and provides a platform for exploring new research ideas. Users can create their own templates for specific areas of study and run experiments to generate papers. However, caution is advised as the codebase executes LLM-written code, which may pose risks such as the use of potentially dangerous packages and web access.
eval-dev-quality
DevQualityEval is an evaluation benchmark and framework designed to compare and improve the quality of code generation of Language Model Models (LLMs). It provides developers with a standardized benchmark to enhance real-world usage in software development and offers users metrics and comparisons to assess the usefulness of LLMs for their tasks. The tool evaluates LLMs' performance in solving software development tasks and measures the quality of their results through a point-based system. Users can run specific tasks, such as test generation, across different programming languages to evaluate LLMs' language understanding and code generation capabilities.
For similar tasks
GeminiChatUp
Gemini ChatUp is a chat application utilizing the Google GeminiPro API Key. It supports responsive layout and can store multiple sets of conversations with customizable parameters for each set. Users can log in with a test account or provide their own API Key to deploy the feature. The application also offers user authentication through Edge config in Vercel, allowing users to add usernames and passwords in JSON format. Local deployment is possible by installing dependencies, setting up environment variables, and running the application locally.

knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
ai-tech-interview
This repository contains a collection of interview questions related to various topics such as statistics, machine learning, deep learning, Python, networking, operating systems, data structures, and algorithms. The questions cover a wide range of concepts and are suitable for individuals preparing for technical interviews in the field of artificial intelligence and data science.
free-ai-tips
Free AI Tips is a GitHub repository that provides weekly tips on Generative AI and Machine Learning. Users can register to receive these tips for free. The repository aims to offer valuable insights and knowledge in the field of AI and ML to help individuals enhance their skills and stay updated with the latest trends and developments.

ragflow
RAGFlow is an open-source Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) engine that combines deep document understanding with Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide accurate question-answering capabilities. It offers a streamlined RAG workflow for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to extract knowledge from unstructured data in various formats, including Word documents, slides, Excel files, images, and more. RAGFlow's key features include deep document understanding, template-based chunking, grounded citations with reduced hallucinations, compatibility with heterogeneous data sources, and an automated and effortless RAG workflow. It supports multiple recall paired with fused re-ranking, configurable LLMs and embedding models, and intuitive APIs for seamless integration with business applications.
Agent
Agent is a RustSBI specialized domain knowledge quiz LLM tool that extracts domain knowledge from various sources such as Rust Documentation, RISC-V Documentation, Bouffalo Docs, Bouffalo SDK, and Xiangshan Docs. It also provides resources for LLM prompt engineering and RAG engineering, including guides and existing projects related to retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems.
vault-ai
OP Vault is a tool that leverages the OP Stack (OpenAI + Pinecone Vector Database) to allow users to upload custom knowledgebase files and ask questions about their contents. It provides a user-friendly Golang server and React frontend for querying human-readable content like books and documents, making it valuable for knowledge extraction and question-answering. Users can upload entire libraries, receive specific answers with file and section references, and explore the power of the OP Stack in a practical interface.
MemoryBear
MemoryBear is a next-generation AI memory system developed by RedBear AI, focusing on overcoming limitations in knowledge storage and multi-agent collaboration. It empowers AI with human-like memory capabilities, enabling deep knowledge understanding and cognitive collaboration. The system addresses challenges such as knowledge forgetting, memory gaps in multi-agent collaboration, and semantic ambiguity during reasoning. MemoryBear's core features include memory extraction engine, graph storage, hybrid search, memory forgetting engine, self-reflection engine, and FastAPI services. It offers a standardized service architecture for efficient integration and invocation across applications.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
