
warc-gpt
WARC + AI - Experimental Retrieval Augmented Generation Pipeline for Web Archive Collections.
Stars: 219
WARC-GPT is an experimental retrieval augmented generation pipeline for web archive collections. It allows users to interact with WARC files, extract text, generate text embeddings, visualize embeddings, and interact with a web UI and API. The tool is highly customizable, supporting various LLMs, providers, and embedding models. Users can configure the application using environment variables, ingest WARC files, start the server, and interact with the web UI and API to search for content and generate text completions. WARC-GPT is designed for exploration and experimentation in exploring web archives using AI.
README:
WARC + AI: Experimental Retrieval Augmented Generation Pipeline for Web Archive Collections.
More info:
- "WARC-GPT: An Open-Source Tool for Exploring Web Archives Using AI". Feb 12 2024 - lil.law.harvard.edu
https://github.com/harvard-lil/warc-gpt/assets/625889/8ea3da4a-62a1-4ffa-a510-ef3e35699237
- Features
- Installation
- Configuring the application
- Ingesting WARCs
- Starting the server
- Interacting with the Web UI
- Interacting with the API
- Visualizing Embeddings
- Disclaimer
- Retrieval Augmented Generation pipeline for WARC files
- Highly customizable, can interact with many different LLMs, providers and embedding models
- REST API
- Web UI
- Embeddings visualization
WARC-GPT requires the following machine-level dependencies to be installed.
Use the following commands to clone the project and install its dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/harvard-lil/warc-gpt.git
cd warc-gpt
poetry env use 3.11
poetry installIf you don't want to use Poetry, or are in some context where that doesn't work, you can clone the repo, create a virtual environment, and install the dependencies like this:
git clone https://github.com/harvard-lil/warc-gpt.git
cd warc-gpt
python3 -m venv env
. env/bin/activate
pip install .If you choose this method, remove the prefix poetry run from the
commands below.
This program uses environment variables to handle settings.
Copy .env.example into a new .env file and edit it as needed.
cp .env.example .envSee details for individual settings in .env.example.
A few notes:
- WARC-GPT can interact with both the OpenAI API and Ollama for local inference.
- Both can be used at the same time, but at least one is needed.
- By default, the program will try to communicate with Ollama's API at
http://localhost:11434. - It is also possible to use OpenAI's client to interact with compatible providers, such as HuggingFace's Message API or vLLM. To do so, set values for both
OPENAI_BASE_URLandOPENAI_COMPATIBLE_MODELenvironment variables.
- Prompts can be edited directly in the configuration file.
Place the WARC files you would to explore with WARC-GPT under ./warc and run the following command to:
- Extract text from all the
text/htmlandapplication/pdfresponse records present in the WARC files. - Generate text embeddings for this text. WARC-GPT will automatically split text based on the embedding model's context window.
- Store these embeddings in a vector store, so it can be used as WARC-GPT's knowledge base.
poetry run flask ingest
# May help with performance in certain cases: only ingest 1 chunk of text at a time.
poetry run flask ingest --batch-size 1Note: Running ingest clears the ./chromadb folder.
The following command will start WARC-GPT's server on port 5000.
poetry run flask run
# Not: Use --port to use a different portOnce the server is started, the application's web UI should be available on http://localhost:5000.
Unless RAG search is disabled in settings, the system will try to find relevant excerpts in its knowledge base - populated ahead of time using WARC files and the ingest command - to answer the questions it is asked.
The interface also automatically handles a basic chat history, allowing for few-shots / chain-of-thoughts prompting.
Returns a list of available models as JSON.
Performs search against the vector store for a given message.
Accepts a JSON body with the following properties:
-
message: User prompt (required)
Returns a JSON array of objects containing the following properties:
-
[].warc_filename: Filename of the WARC from which that excerpt is from. -
[].warc_record_content_type: Can start with eithertext/htmlorapplication/pdf. -
[].warc_record_id: Individual identifier of the WARC record within the WARC file. -
[].warc_record_date: Date at which the WARC record was created. -
[].warc_record_target_uri: Filename of the WARC from which that excerpt is from. -
[].warc_record_text: Text excerpt.
Uses an LLM to generate a text completion.
Accepts a JSON body with the following properties:
-
model: One of the models/api/modelslists (required) -
message: User prompt (required) -
temperature: Defaults to 0.0 -
max_tokens: If provided, caps number of tokens that will be generated in response. -
search_results: Array, output of/api/search. -
history: A list of chat completion objects representing the chat history. Each object must containuserandcontent.
Returns RAW text stream as output.
WARC-GPT allows for generating basic interactive T-SNE 2D scatter plots of the vector stores it generates.
Use the visualize command to do so:
poetry run flask visualizevisualize takes a --questions option which allows to place questions on the plot:
poetry run flask visualize --questions="Who am I?;Who are you?"The Library Innovation Lab is an organization based at the Harvard Law School Library. We are a cross-functional group of software developers, librarians, lawyers, and researchers doing work at the edges of technology and digital information.
Our work is rooted in library principles including longevity, authenticity, reliability, and privacy. Any work that we produce takes these principles as a primary lens. However due to the nature of exploration and a desire to prototype our work with real users, we do not guarantee service or performance at the level of a production-grade platform for all of our releases. This includes WARC-GPT, which is an experimental boilerplate released under MIT License.
Successful experimentation hinges on user feedback, so we encourage anyone interested in trying out our work to do so. It is all open-source and available on Github.
Please keep in mind:
- We are an innovation lab leveraging our resources and flexibility to conduct explorations for a broader field. Projects may be eventually passed off to another group, take a totally unexpected turn, or be sunset completely.
- While we always have priorities set around security and privacy each of those topics is complex in its own right and often requires grand scale work. Experiments can sometimes initially prioritize closed-loop feedback over broader questions of security. We will always disclose when this is the case.
- There are some experiments that are destined to become mainstays in our established platforms and tools. We will also disclose when that’s the case.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for warc-gpt
Similar Open Source Tools

warc-gpt
WARC-GPT is an experimental retrieval augmented generation pipeline for web archive collections. It allows users to interact with WARC files, extract text, generate text embeddings, visualize embeddings, and interact with a web UI and API. The tool is highly customizable, supporting various LLMs, providers, and embedding models. Users can configure the application using environment variables, ingest WARC files, start the server, and interact with the web UI and API to search for content and generate text completions. WARC-GPT is designed for exploration and experimentation in exploring web archives using AI.
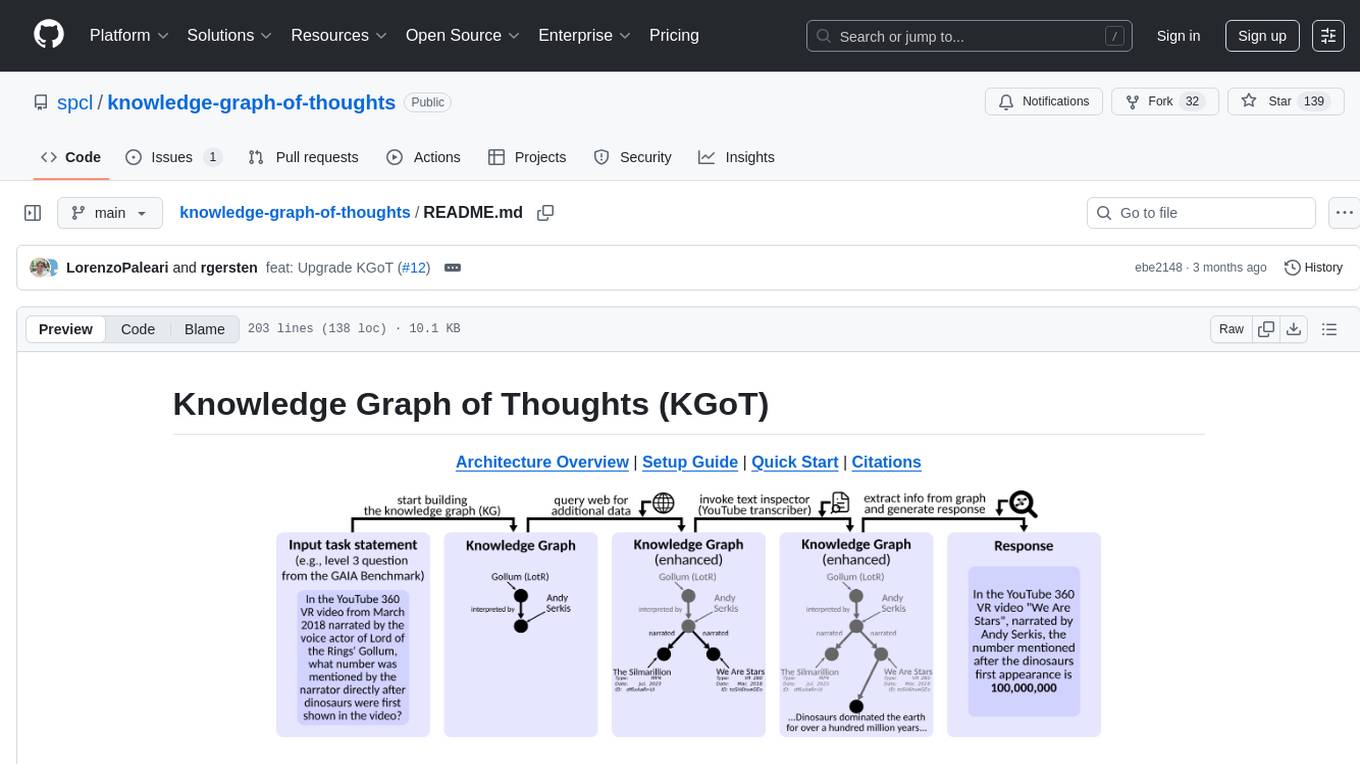
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
gpt-subtrans
GPT-Subtrans is an open-source subtitle translator that utilizes large language models (LLMs) as translation services. It supports translation between any language pairs that the language model supports. Note that GPT-Subtrans requires an active internet connection, as subtitles are sent to the provider's servers for translation, and their privacy policy applies.
llm-subtrans
LLM-Subtrans is an open source subtitle translator that utilizes LLMs as a translation service. It supports translating subtitles between any language pairs supported by the language model. The application offers multiple subtitle formats support through a pluggable system, including .srt, .ssa/.ass, and .vtt files. Users can choose to use the packaged release for easy usage or install from source for more control over the setup. The tool requires an active internet connection as subtitles are sent to translation service providers' servers for translation.
PolyMind
PolyMind is a multimodal, function calling powered LLM webui designed for various tasks such as internet searching, image generation, port scanning, Wolfram Alpha integration, Python interpretation, and semantic search. It offers a plugin system for adding extra functions and supports different models and endpoints. The tool allows users to interact via function calling and provides features like image input, image generation, and text file search. The application's configuration is stored in a `config.json` file with options for backend selection, compatibility mode, IP address settings, API key, and enabled features.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
curategpt
CurateGPT is a prototype web application and framework designed for general purpose AI-guided curation and curation-related operations over collections of objects. It provides functionalities for loading example data, building indexes, interacting with knowledge bases, and performing tasks such as chatting with a knowledge base, querying Pubmed, interacting with a GitHub issue tracker, term autocompletion, and all-by-all comparisons. The tool is built to work best with the OpenAI gpt-4 model and OpenAI ada-text-embedding-002 for embedding, but also supports alternative models through a plugin architecture.
pgai
pgai simplifies the process of building search and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) AI applications with PostgreSQL. It brings embedding and generation AI models closer to the database, allowing users to create embeddings, retrieve LLM chat completions, reason over data for classification, summarization, and data enrichment directly from within PostgreSQL in a SQL query. The tool requires an OpenAI API key and a PostgreSQL client to enable AI functionality in the database. Users can install pgai from source, run it in a pre-built Docker container, or enable it in a Timescale Cloud service. The tool provides functions to handle API keys using psql or Python, and offers various AI functionalities like tokenizing, detokenizing, embedding, chat completion, and content moderation.
aisheets
Hugging Face AI Sheets is an open-source tool for building, enriching, and transforming datasets using AI models with no code. It can be deployed locally or on the Hub, providing access to thousands of open models. Users can easily generate datasets, run data generation scripts, and customize inference endpoints for text generation. The tool supports custom LLMs and offers advanced configuration options for authentication, inference, and miscellaneous settings. With AI Sheets, users can leverage the power of AI models without writing any code, making dataset management and transformation efficient and accessible.
AI-Scientist
The AI Scientist is a comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models to perform research independently. It aims to tackle the grand challenge of developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. The tool generates papers on various topics using Large Language Models (LLMs) and provides a platform for exploring new research ideas. Users can create their own templates for specific areas of study and run experiments to generate papers. However, caution is advised as the codebase executes LLM-written code, which may pose risks such as the use of potentially dangerous packages and web access.
curate-gpt
CurateGPT is a prototype web application and framework for performing general purpose AI-guided curation and curation-related operations over collections of objects. It allows users to load JSON, YAML, or CSV data, build vector database indexes for ontologies, and interact with various data sources like GitHub, Google Drives, Google Sheets, and more. The tool supports ontology curation, knowledge base querying, term autocompletion, and all-by-all comparisons for objects in a collection.
ai-town
AI Town is a virtual town where AI characters live, chat, and socialize. This project provides a deployable starter kit for building and customizing your own version of AI Town. It features a game engine, database, vector search, auth, text model, deployment, pixel art generation, background music generation, and local inference. You can customize your own simulation by creating characters and stories, updating spritesheets, changing the background, and modifying the background music.

HackBot
HackBot is an AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide accurate answers to cybersecurity-related queries, conduct code analysis, and scan analysis. It utilizes the Meta-LLama2 AI model through the 'LlamaCpp' library to respond coherently. The chatbot offers features like local AI/Runpod deployment support, cybersecurity chat assistance, interactive interface, clear output presentation, static code analysis, and vulnerability analysis. Users can interact with HackBot through a command-line interface and utilize it for various cybersecurity tasks.
LongRAG
This repository contains the code for LongRAG, a framework that enhances retrieval-augmented generation with long-context LLMs. LongRAG introduces a 'long retriever' and a 'long reader' to improve performance by using a 4K-token retrieval unit, offering insights into combining RAG with long-context LLMs. The repo provides instructions for installation, quick start, corpus preparation, long retriever, and long reader.
qb
QANTA is a system and dataset for question answering tasks. It provides a script to download datasets, preprocesses questions, and matches them with Wikipedia pages. The system includes various datasets, training, dev, and test data in JSON and SQLite formats. Dependencies include Python 3.6, `click`, and NLTK models. Elastic Search 5.6 is needed for the Guesser component. Configuration is managed through environment variables and YAML files. QANTA supports multiple guesser implementations that can be enabled/disabled. Running QANTA involves using `cli.py` and Luigi pipelines. The system accesses raw Wikipedia dumps for data processing. The QANTA ID numbering scheme categorizes datasets based on events and competitions.
eval-dev-quality
DevQualityEval is an evaluation benchmark and framework designed to compare and improve the quality of code generation of Language Model Models (LLMs). It provides developers with a standardized benchmark to enhance real-world usage in software development and offers users metrics and comparisons to assess the usefulness of LLMs for their tasks. The tool evaluates LLMs' performance in solving software development tasks and measures the quality of their results through a point-based system. Users can run specific tasks, such as test generation, across different programming languages to evaluate LLMs' language understanding and code generation capabilities.
For similar tasks
bce-qianfan-sdk
The Qianfan SDK provides best practices for large model toolchains, allowing AI workflows and AI-native applications to access the Qianfan large model platform elegantly and conveniently. The core capabilities of the SDK include three parts: large model reasoning, large model training, and general and extension: * `Large model reasoning`: Implements interface encapsulation for reasoning of Yuyan (ERNIE-Bot) series, open source large models, etc., supporting dialogue, completion, Embedding, etc. * `Large model training`: Based on platform capabilities, it supports end-to-end large model training process, including training data, fine-tuning/pre-training, and model services. * `General and extension`: General capabilities include common AI development tools such as Prompt/Debug/Client. The extension capability is based on the characteristics of Qianfan to adapt to common middleware frameworks.
freeGPT
freeGPT provides free access to text and image generation models. It supports various models, including gpt3, gpt4, alpaca_7b, falcon_40b, prodia, and pollinations. The tool offers both asynchronous and non-asynchronous interfaces for text completion and image generation. It also features an interactive Discord bot that provides access to all the models in the repository. The tool is easy to use and can be integrated into various applications.
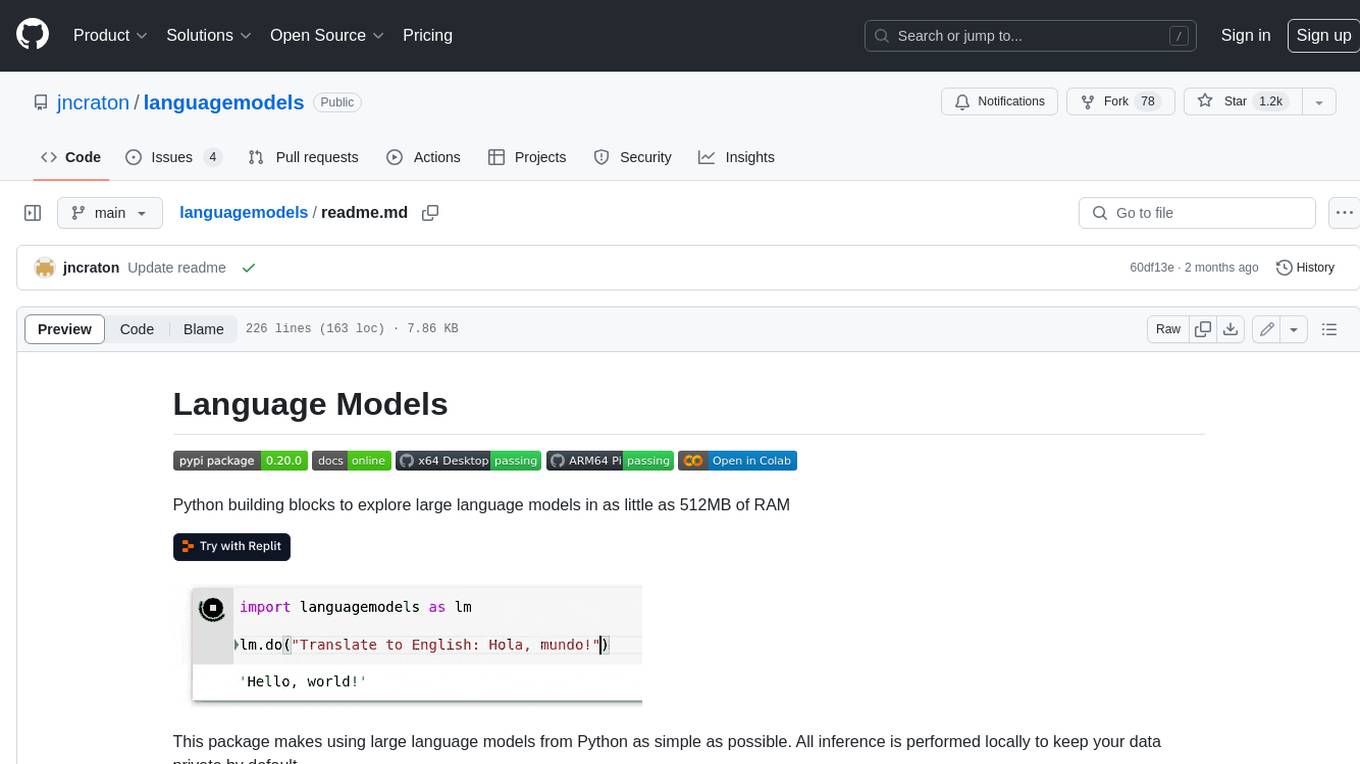
languagemodels
Language Models is a Python package that provides building blocks to explore large language models with as little as 512MB of RAM. It simplifies the usage of large language models from Python, ensuring all inference is performed locally to keep data private. The package includes features such as text completions, chat capabilities, code completions, external text retrieval, semantic search, and more. It outperforms Hugging Face transformers for CPU inference and offers sensible default models with varying parameters based on memory constraints. The package is suitable for learners and educators exploring the intersection of large language models with modern software development.
RWKV-Runner
RWKV Runner is a project designed to simplify the usage of large language models by automating various processes. It provides a lightweight executable program and is compatible with the OpenAI API. Users can deploy the backend on a server and use the program as a client. The project offers features like model management, VRAM configurations, user-friendly chat interface, WebUI option, parameter configuration, model conversion tool, download management, LoRA Finetune, and multilingual localization. It can be used for various tasks such as chat, completion, composition, and model inspection.

warc-gpt
WARC-GPT is an experimental retrieval augmented generation pipeline for web archive collections. It allows users to interact with WARC files, extract text, generate text embeddings, visualize embeddings, and interact with a web UI and API. The tool is highly customizable, supporting various LLMs, providers, and embedding models. Users can configure the application using environment variables, ingest WARC files, start the server, and interact with the web UI and API to search for content and generate text completions. WARC-GPT is designed for exploration and experimentation in exploring web archives using AI.
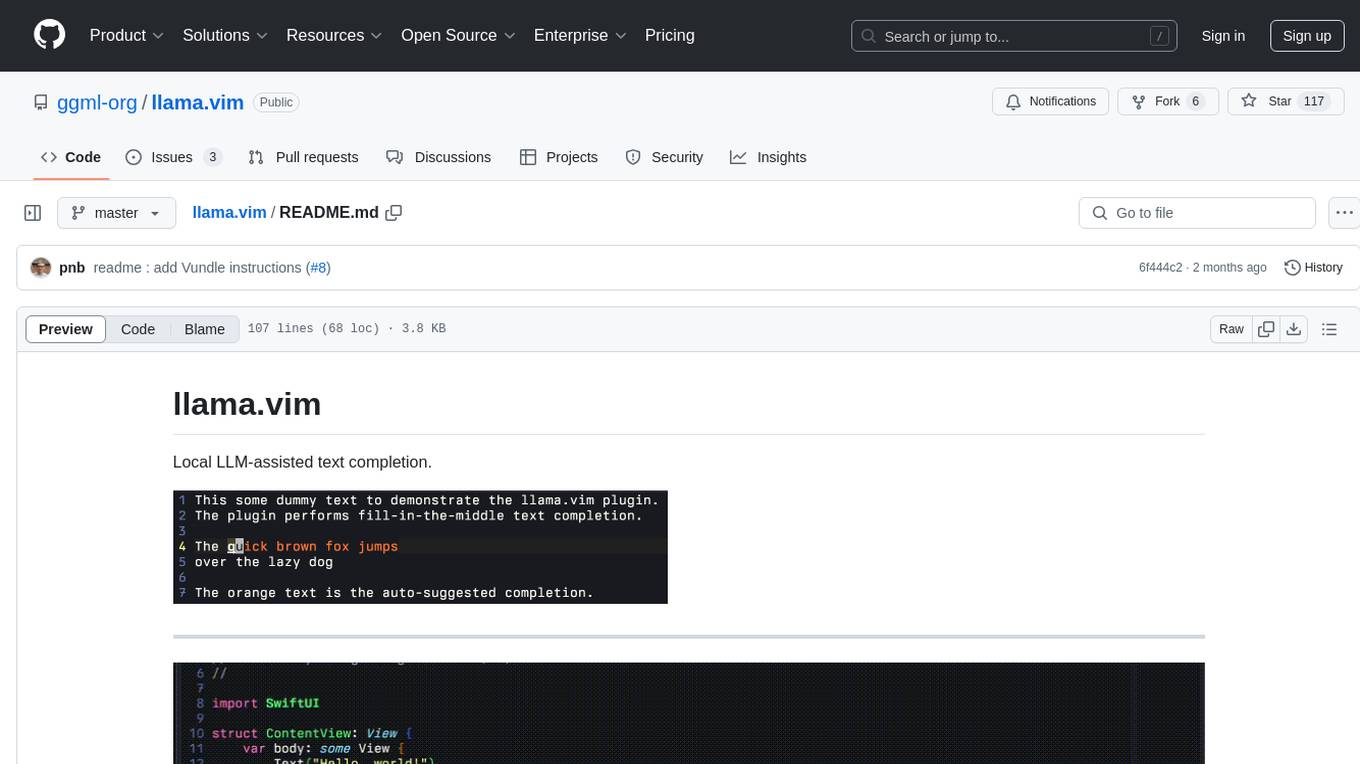
llama.vim
llama.vim is a plugin that provides local LLM-assisted text completion for Vim users. It offers features such as auto-suggest on cursor movement, manual suggestion toggling, suggestion acceptance with Tab and Shift+Tab, control over text generation time, context configuration, ring context with chunks from open and edited files, and performance stats display. The plugin requires a llama.cpp server instance to be running and supports FIM-compatible models. It aims to be simple, lightweight, and provide high-quality and performant local FIM completions even on consumer-grade hardware.
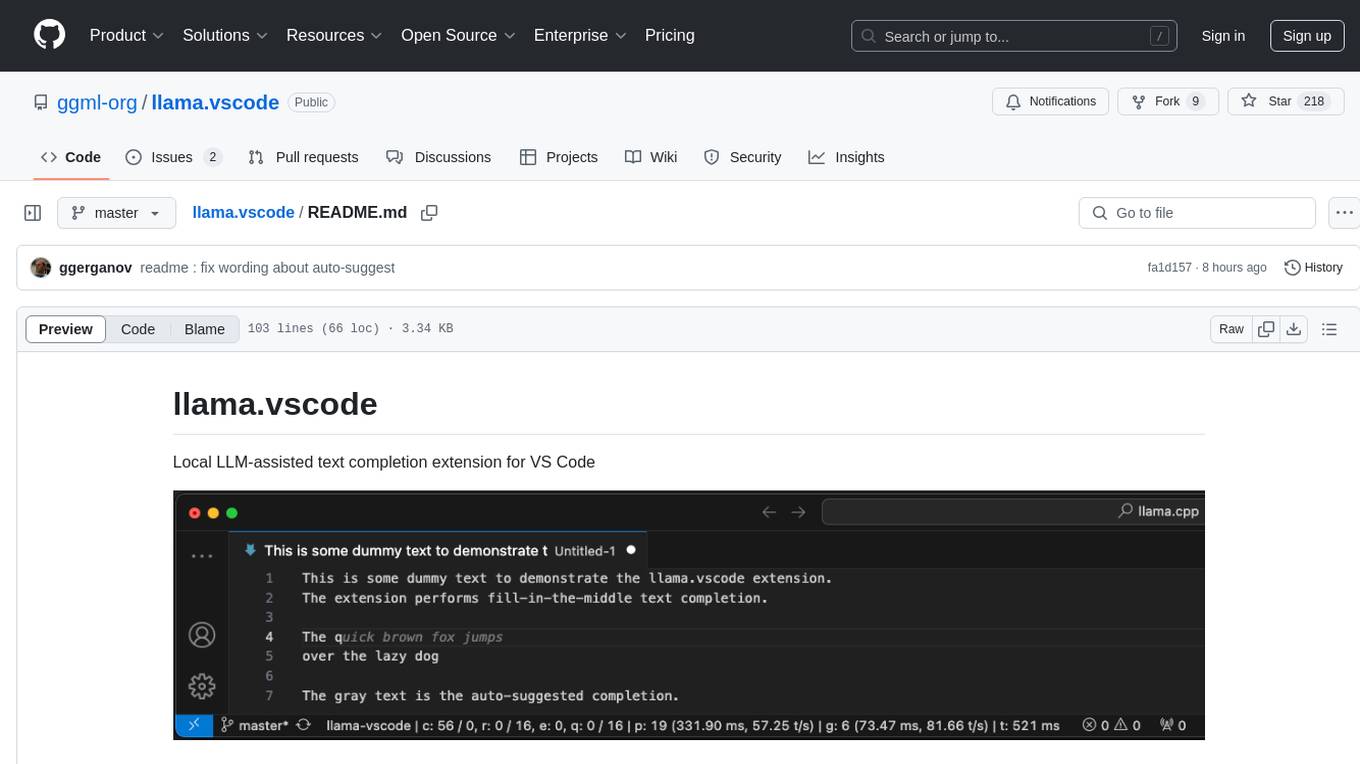
llama.vscode
llama.vscode is a local LLM-assisted text completion extension for Visual Studio Code. It provides auto-suggestions on input, allows accepting suggestions with shortcuts, and offers various features to enhance text completion. The extension is designed to be lightweight and efficient, enabling high-quality completions even on low-end hardware. Users can configure the scope of context around the cursor and control text generation time. It supports very large contexts and displays performance statistics for better user experience.
illume
Illume is a scriptable command line program designed for interfacing with an OpenAI-compatible LLM API. It acts as a unix filter, sending standard input to the LLM and streaming its response to standard output. Users can interact with the LLM through text editors like Vim or Emacs, enabling seamless communication with the AI model for various tasks.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.