guidellm
Evaluate and Enhance Your LLM Deployments for Real-World Inference Needs
Stars: 844

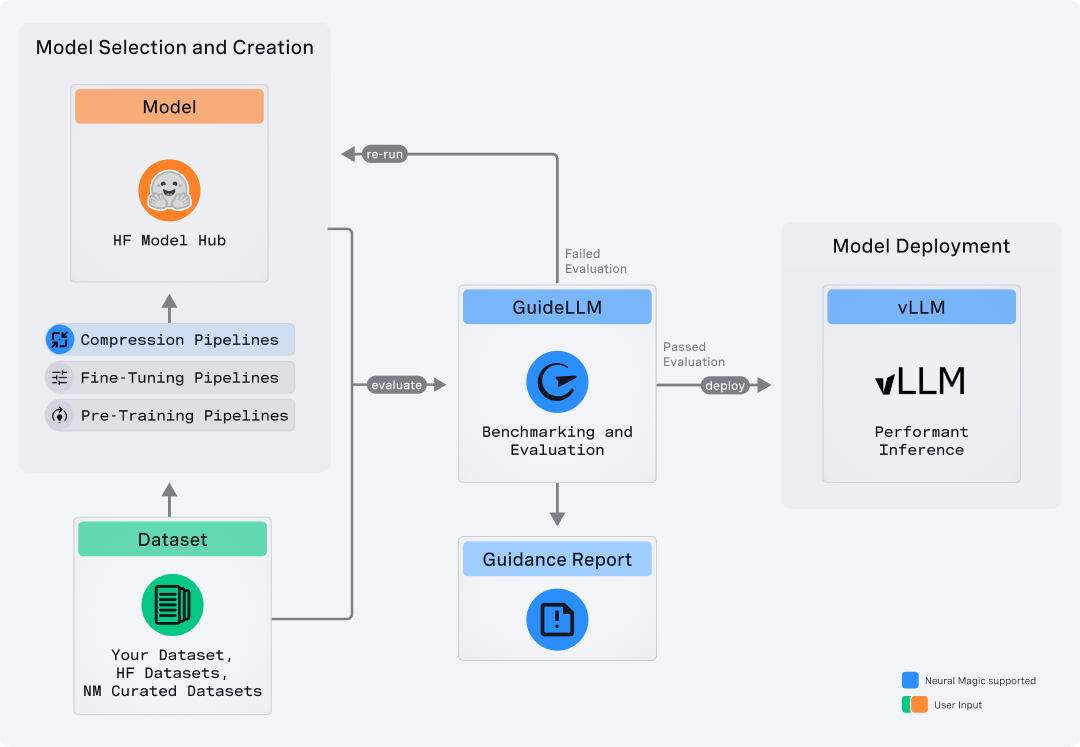
GuideLLM is a platform for evaluating and optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs). By simulating real-world inference workloads, GuideLLM enables users to assess the performance, resource requirements, and cost implications of deploying LLMs on various hardware configurations. This approach ensures efficient, scalable, and cost-effective LLM inference serving while maintaining high service quality. The tool provides features for performance evaluation, resource optimization, cost estimation, and scalability testing.
README:
GuideLLM is a platform for evaluating how language models perform under real workloads and configurations. It simulates end-to-end interactions with OpenAI-compatible and vLLM-native servers, generates workload patterns that reflect production usage, and produces detailed reports that help teams understand system behavior, resource needs, and operational limits. GuideLLM supports real and synthetic datasets, multimodal inputs, and flexible execution profiles, giving engineering and ML teams a consistent framework for assessing model behavior, tuning deployments, and planning capacity as their systems evolve.
GuideLLM gives teams a clear picture of performance, efficiency, and reliability when deploying LLMs in production-like environments.
- Captures complete latency and token-level statistics for SLO-driven evaluation, including full distributions for TTFT, ITL, and end-to-end behavior.
- Generates realistic, configurable traffic patterns across synchronous, concurrent, and rate-based modes, including reproducible sweeps to identify safe operating ranges.
- Supports both real and synthetic multimodal datasets, enabling controlled experiments and production-style evaluations in one framework.
- Produces standardized, exportable reports for dashboards, analysis, and regression tracking, ensuring consistency across teams and workflows.
- Delivers high-throughput, extensible benchmarking with multiprocessing, threading, async execution, and a flexible CLI/API for customization or quickstarts.
Many tools benchmark endpoints, not models, and miss the details that matter for LLMs. GuideLLM focuses exclusively on LLM-specific workloads, measuring TTFT, ITL, output distributions, and dataset-driven variation. It fits into everyday engineering tasks by using standard Python interfaces and HuggingFace datasets instead of custom formats or research-only pipelines. It is also built for performance, supporting high-rate load generation and accurate scheduling far beyond simple scripts or example benchmarks. The table below highlights how this approach compares to other options.
| Tool | CLI | API | High Perf | Full Metrics | Data Modalities | Data Sources | Profiles | Backends | Endpoints | Output Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GuideLLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Text, Image, Audio, Video | HuggingFace, Files, Synthetic, Custom | Synchronous, Concurrent, Throughput, Constant, Poisson, Sweep | OpenAI-compatible | /completions, /chat/completions, /audio/translation, /audio/transcription | console, json, csv, html |
| inference-perf | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | Text | Synthetic, Specific Datasets | Concurrent, Constant, Poisson, Sweep | OpenAI-compatible | /completions, /chat/completions | json, png |
| genai-bench | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | Text, Image, Embedding, ReRank | Synthetic, File | Concurrent | OpenAI-compatible, Hosted Cloud | /chat/completions, /embeddings | console, xlsx, png |
| llm-perf | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | Text | Synthetic | Concurrent | OpenAI-compatible, Hosted Cloud | /chat/completions | json |
| ollama-benchmark | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | Text | Synthetic | Synchronous | Ollama | /completions | console, json |
| vllm/benchmarks | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | Text | Synthetic, Specific Datasets | Synchronous, Throughput, Constant, Sweep | OpenAI-compatible, vLLM API | /completions, /chat/completions | console, png |
This section summarizes the newest capabilities available to users and outlines the current areas of development. It helps readers understand how the platform is evolving and what to expect next.
Recent Additions
- New refactored architecture enabling high-rate load generation at scale and a more extensible interface for additional backends, data pipelines, load generation schedules, benchmarking constraints, and output formats.
- Added multimodal benchmarking support for image, video, and audio workloads across chat completions, transcription, and translation APIs.
- Broader metrics collection, including richer statistics for visual, audio, and text inputs such as image sizes, audio lengths, video frame counts, and word-level data.
Active Development
- Generation of synthetic multimodal datasets for controlled experimentation across images, audio, and video.
- Extended prefixing options for testing system-prompt and user-prompt variations.
- Multi-turn conversation capabilities for benchmarking chat agents and dialogue systems.
- Speculative decoding specific views and outputs.
The Quick Start shows how to install GuideLLM, launch a server, and run your first benchmark in a few minutes.
Before installing, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- OS: Linux or MacOS
- Python: 3.10 - 3.13
Install the latest GuideLLM release from PyPi using pip :
pip install guidellm[recommended]Or install from source:
pip install git+https://github.com/vllm-project/guidellm.gitOr run the latest container from ghcr.io/vllm-project/guidellm:
podman run \
--rm -it \
-v "./results:/results:rw" \
-e GUIDELLM_TARGET=http://localhost:8000 \
-e GUIDELLM_PROFILE=sweep \
-e GUIDELLM_MAX_SECONDS=30 \
-e GUIDELLM_DATA="prompt_tokens=256,output_tokens=128" \
ghcr.io/vllm-project/guidellm:latestStart any OpenAI-compatible endpoint. For vLLM:
vllm serve "neuralmagic/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-quantized.w4a16"Verify the server is running at http://localhost:8000.
Run a sweep that identifies the maximum performance and maximum rates for the model:
guidellm benchmark \
--target "http://localhost:8000" \
--profile sweep \
--max-seconds 30 \
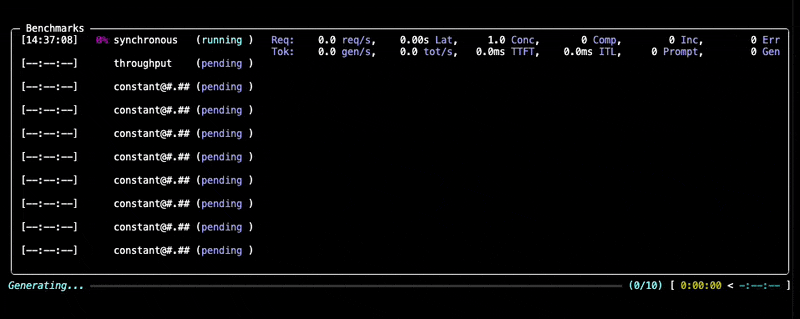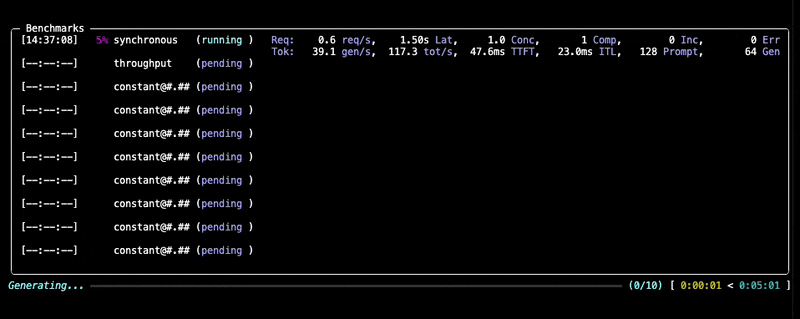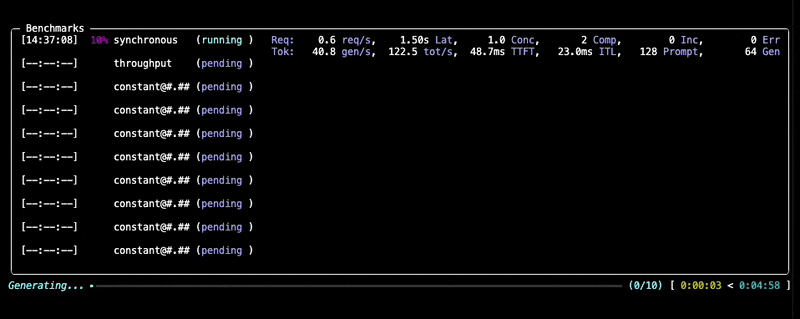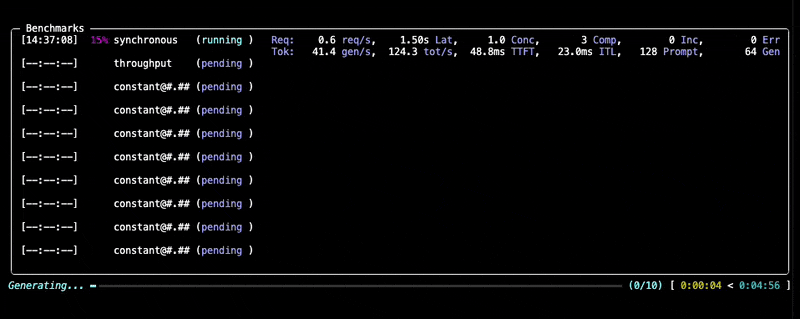
--data "prompt_tokens=256,output_tokens=128"You will see progress updates and per-benchmark summaries during the run, as given below:
After the benchmark completes, GuideLLM saves all results into the output directory you specified (default: the current directory). You'll see a summary printed in the console along with a set of file locations (.json, .csv, .html) that contain the full results of the run.
The following section, Output Files and Reports, explains what each file contains and how to use them for analysis, visualization, or automation.
After running the Quick Start benchmark, GuideLLM writes several output files to the directory you specified. Each one focuses on a different layer of analysis, ranging from a quick on-screen summary to fully structured data for dashboards and regression pipelines.
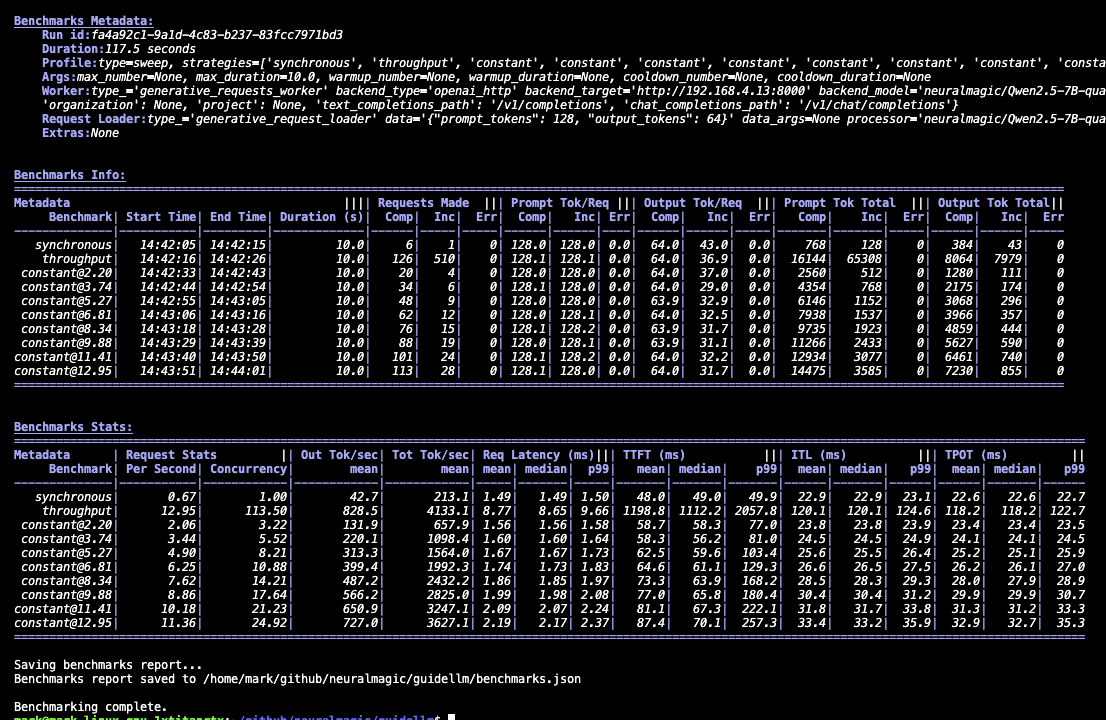
Console Output
The console provides a lightweight summary with high-level statistics for each benchmark in the run. It's useful for quick checks to confirm that the server responded correctly, the load sweep completed, and the system behaved as expected. Additionally, the output tables can be copied and pasted into spreadsheet software using | as the delimiter. The sections will look similar to the following:
benchmarks.json
This file is the authoritative record of the entire benchmark session. It includes configuration, metadata, per-benchmark statistics, and sample request entries with individual request timings. Use it for debugging, deeper analysis, or loading into Python with GenerativeBenchmarksReport.
Alternatively, a yaml version of this file can be generated for easier human readability with the same content as benchmarks.json using the --outputs yaml argument.
benchmarks.csv
This file provides a compact tabular view of each benchmark with the fields most commonly used for reporting—throughput, latency percentiles, token counts, and rate information. It opens cleanly in spreadsheets and BI tools and is well-suited for comparisons across runs.
benchmarks.html
The HTML report provides a visual summary of results, including charts of latency distributions, throughput behavior, and generation patterns. It's ideal for quick exploration or sharing with teammates without requiring them to parse JSON.
GuideLLM supports a wide range of LLM benchmarking workflows. The examples below show how to run typical scenarios and highlight the parameters that matter most. For a complete list of arguments, details, and options, run guidellm benchmark run --help
Simmulating different applications requires different traffic shapes. This example demonstrates rate-based load testing using a constant profile at 10 requests per second, running for 20 seconds with synthetic data of 128 prompt tokens and 256 output tokens.
guidellm benchmark \
--target http://localhost:8000 \
--profile constant \
--rate 10 \
--max-seconds 20 \
--data "prompt_tokens=128,output_tokens=256"Key parameters:
-
--profile: Defines the traffic pattern - options includesynchronous(sequential requests),concurrent(parallel users),throughput(maximum capacity),constant(fixed requests/sec),poisson(randomized requests/sec), orsweep(automatic rate exploration) -
--rate: The numeric rate value whose meaning depends on profile - forsweepit's the number of benchmarks, forconcurrentit's simultaneous requests, forconstant/poissonit's requests per second -
--max-seconds: Maximum duration in seconds for each benchmark run (can also use--max-requeststo limit by request count instead)
GuideLLM supports HuggingFace datasets, local files, and synthetic data. This example loads the CNN DailyMail dataset from HuggingFace and maps the article column to prompts while using the summary token count column to determine output lengths.
guidellm benchmark run \
--target http://localhost:8000 \
--data "abisee/cnn_dailymail" \
--data-args '{"name": "3.0.0"}' \
--data-column-mapper '{"text_column":"article"}'Key parameters:
-
--data: Data source specification - accepts HuggingFace dataset IDs (prefix withhf:), local file paths (.json,.csv,.jsonl,.txt), or synthetic data configs (JSON object orkey=valuepairs likeprompt_tokens=256,output_tokens=128) -
--data-args: Arguments for loading the dataset. Seedatasets.load_datasetfor valid options. -
--data-column-mapper: JSON object of arguments for dataset creation - commonly used to specify column mappings liketext_column,output_tokens_count_column, or HuggingFace dataset parameters -
--data-samples: Number of samples to use from the dataset - use-1(default) for all samples with dynamic generation, or specify a positive integer to limit sample count -
--processor: Tokenizer or processor name used for generating synthetic data - if not provided and required for the dataset, automatically loads from the model; accepts HuggingFace model IDs or local paths
You can benchmark chat completions, text completions, or other supported request types. This example configures the benchmark to test chat completions API using a custom dataset file, with GuideLLM automatically formatting requests to match the chat completions schema.
guidellm benchmark \
--target http://localhost:8000 \
--request-type chat_completions \
--data path/to/data.jsonKey parameters:
-
--request-type: Specifies the API endpoint format - options includechat_completions(chat API format),completions(text completion format),audio_transcription(audio transcription), andaudio_translation(audio translation).
Built-in scenarios bundle schedules, dataset settings, and request formatting to standardize common testing patterns. This example uses the pre-configured chat scenario which includes appropriate defaults for chat model evaluation, with any additional CLI arguments overriding the scenario's settings.
guidellm benchmark --scenario chat --target http://localhost:8000Key parameters:
-
--scenario: Built-in scenario name or path to a custom scenario configuration file - built-in options include pre-configured testing patterns for common use cases; CLI options passed alongside this will override the scenario's default settings
Warm-up, cooldown, and maximum limits help ensure stable, repeatable measurements. This example runs a concurrent benchmark with 16 parallel requests, using 10% warmup and cooldown periods to exclude initialization and shutdown effects, while limiting the test to stop if more than 5 errors occur.
guidellm benchmark \
--target http://localhost:8000 \
--profile concurrent \
--rate 16 \
--warmup 0.1 \
--cooldown 0.1 \
--max-errors 5
--detect-saturationKey parameters:
-
--warmup: Warm-up specification - values between 0 and 1 represent a percentage of total requests/time, values ≥1 represent absolute request or time units. -
--cooldown: Cool-down specification - same format as warmup, excludes final portion of benchmark from analysis to avoid shutdown effects -
--max-seconds: Maximum duration in seconds for each benchmark before automatic termination -
--max-requests: Maximum number of requests per benchmark before automatic termination -
--max-errors: Maximum number of individual errors before stopping the benchmark entirely -
--detect-saturation: Enable over-saturation detection to automatically stop benchmarks when the model becomes over-saturated (see also--over-saturationfor more advanced control)
Developers interested in extending GuideLLM can use the project's established development workflow. Local setup, environment activation, and testing instructions are outlined in DEVELOPING.md. This guide explains how to run the benchmark suite, validate changes, and work with the CLI or API during development. Contribution standards are documented in CONTRIBUTING.md, including coding conventions, commit structure, and review guidelines. These standards help maintain stability as the platform evolves. The CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md outlines expectations for respectful and constructive participation across all project spaces. For contributors who want deeper reference material, the documentation covers installation, backends, datasets, metrics, output types, and architecture. Reviewing these topics is useful when adding new backends, request types, or data integrations. Release notes and changelogs are linked from the GitHub Releases page and provide historical context for ongoing work.
The complete documentation provides the details that do not fit in this README. It includes installation steps, backend configuration, dataset handling, metrics definitions, output formats, tutorials, and an architecture overview. These references help you explore the platform more deeply or integrate it into existing workflows.
Notable docs are given below:
- Installation Guide - This guide provides step-by-step instructions for installing GuideLLM, including prerequisites and setup tips.
- Backends Guide - A comprehensive overview of supported backends and how to set them up for use with GuideLLM.
- Data/Datasets Guide - Information on supported datasets, including how to use them for benchmarking.
- Metrics Guide - Detailed explanations of the metrics used in GuideLLM, including definitions and how to interpret them.
- Outputs Guide - Information on the different output formats supported by GuideLLM and how to use them.
- Architecture Overview - A detailed look at GuideLLM's design, components, and how they interact.
GuideLLM is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
If you find GuideLLM helpful in your research or projects, please consider citing it:
@misc{guidellm2024,
title={GuideLLM: Scalable Inference and Optimization for Large Language Models},
author={Neural Magic, Inc.},
year={2024},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/vllm-project/guidellm}},
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for guidellm
Similar Open Source Tools

guidellm
GuideLLM is a platform for evaluating and optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs). By simulating real-world inference workloads, GuideLLM enables users to assess the performance, resource requirements, and cost implications of deploying LLMs on various hardware configurations. This approach ensures efficient, scalable, and cost-effective LLM inference serving while maintaining high service quality. The tool provides features for performance evaluation, resource optimization, cost estimation, and scalability testing.
atropos
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.

guidellm
GuideLLM is a powerful tool for evaluating and optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs). By simulating real-world inference workloads, GuideLLM helps users gauge the performance, resource needs, and cost implications of deploying LLMs on various hardware configurations. This approach ensures efficient, scalable, and cost-effective LLM inference serving while maintaining high service quality. Key features include performance evaluation, resource optimization, cost estimation, and scalability testing.
evidently
Evidently is an open-source Python library designed for evaluating, testing, and monitoring machine learning (ML) and large language model (LLM) powered systems. It offers a wide range of functionalities, including working with tabular, text data, and embeddings, supporting predictive and generative systems, providing over 100 built-in metrics for data drift detection and LLM evaluation, allowing for custom metrics and tests, enabling both offline evaluations and live monitoring, and offering an open architecture for easy data export and integration with existing tools. Users can utilize Evidently for one-off evaluations using Reports or Test Suites in Python, or opt for real-time monitoring through the Dashboard service.
MPLSandbox
MPLSandbox is an out-of-the-box multi-programming language sandbox designed to provide unified and comprehensive feedback from compiler and analysis tools for LLMs. It simplifies code analysis for researchers and can be seamlessly integrated into LLM training and application processes to enhance performance in a range of code-related tasks. The sandbox environment ensures safe code execution, the code analysis module offers comprehensive analysis reports, and the information integration module combines compilation feedback and analysis results for complex code-related tasks.
RainbowGPT
RainbowGPT is a versatile tool that offers a range of functionalities, including Stock Analysis for financial decision-making, MySQL Management for database navigation, and integration of AI technologies like GPT-4 and ChatGlm3. It provides a user-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, ensuring seamless information flow and continuous expansion of emerging technologies. The tool enhances adaptability, creativity, and insight, making it a valuable asset for various projects and tasks.
llm-d-inference-sim
The `llm-d-inference-sim` is a lightweight, configurable, and real-time simulator designed to mimic the behavior of vLLM without the need for GPUs or running heavy models. It operates as an OpenAI-compliant server, allowing developers to test clients, schedulers, and infrastructure using realistic request-response cycles, token streaming, and latency patterns. The simulator offers modes of operation, response generation from predefined text or real datasets, latency simulation, tokenization options, LoRA management, KV cache simulation, failure injection, and deployment options for standalone or Kubernetes testing. It supports a subset of standard vLLM Prometheus metrics for observability.
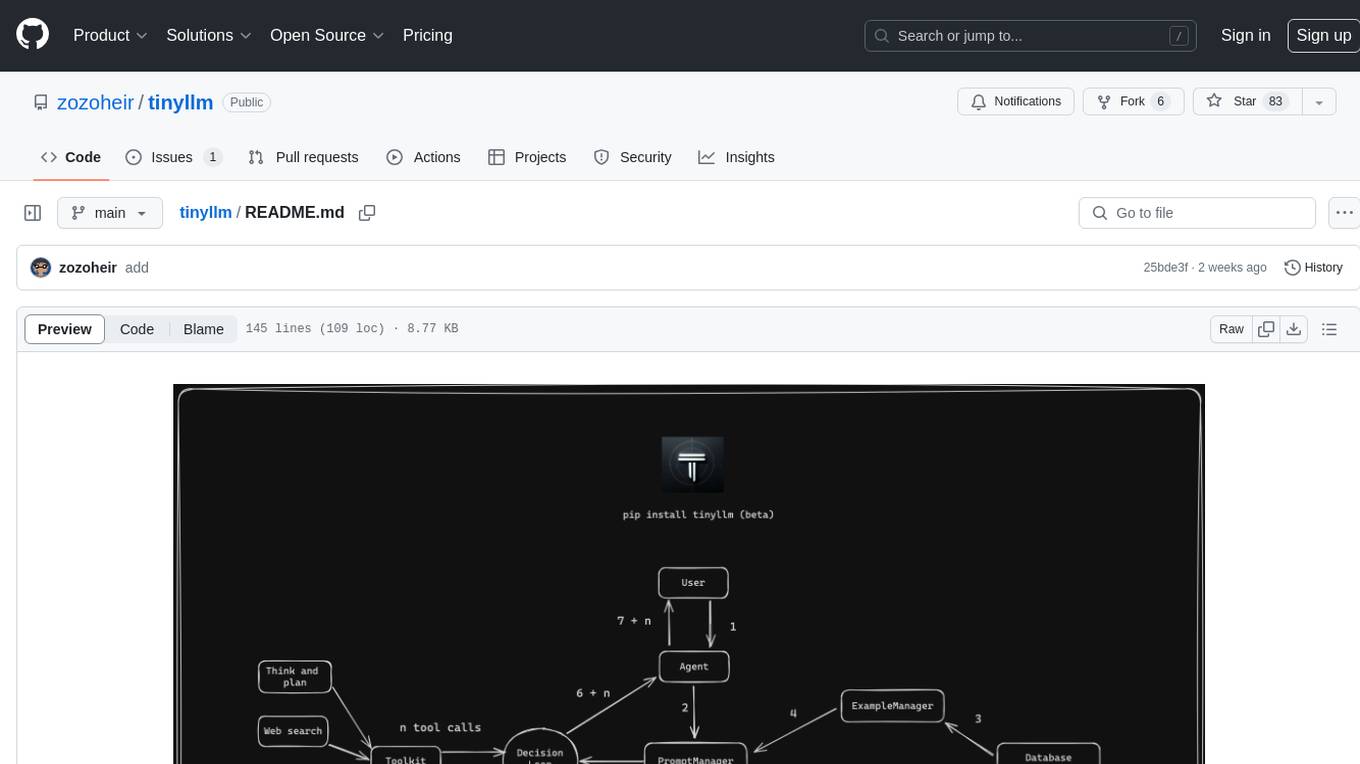
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.

helix-db
HelixDB is a database designed specifically for AI applications, providing a single platform to manage all components needed for AI applications. It supports graph + vector data model and also KV, documents, and relational data. Key features include built-in tools for MCP, embeddings, knowledge graphs, RAG, security, logical isolation, and ultra-low latency. Users can interact with HelixDB using the Helix CLI tool and SDKs in TypeScript and Python. The roadmap includes features like organizational auth, server code improvements, 3rd party integrations, educational content, and binary quantisation for better performance. Long term projects involve developing in-house tools for knowledge graph ingestion, graph-vector storage engine, and network protocol & serdes libraries.
open-unlearning
OpenUnlearning is an easily extensible framework that unifies LLM unlearning evaluation benchmarks. It provides efficient implementations of TOFU and MUSE unlearning benchmarks, supporting 5 unlearning methods, 3+ datasets, 6+ evaluation metrics, and 7+ LLMs. Users can easily extend the framework to incorporate more variants, collaborate by adding new benchmarks, unlearning methods, datasets, and evaluation metrics, and drive progress in the field.
qlib
Qlib is an open-source, AI-oriented quantitative investment platform that supports diverse machine learning modeling paradigms, including supervised learning, market dynamics modeling, and reinforcement learning. It covers the entire chain of quantitative investment, from alpha seeking to order execution. The platform empowers researchers to explore ideas and implement productions using AI technologies in quantitative investment. Qlib collaboratively solves key challenges in quantitative investment by releasing state-of-the-art research works in various paradigms. It provides a full ML pipeline for data processing, model training, and back-testing, enabling users to perform tasks such as forecasting market patterns, adapting to market dynamics, and modeling continuous investment decisions.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
Upsonic
Upsonic offers a cutting-edge enterprise-ready framework for orchestrating LLM calls, agents, and computer use to complete tasks cost-effectively. It provides reliable systems, scalability, and a task-oriented structure for real-world cases. Key features include production-ready scalability, task-centric design, MCP server support, tool-calling server, computer use integration, and easy addition of custom tools. The framework supports client-server architecture and allows seamless deployment on AWS, GCP, or locally using Docker.

OneKE
OneKE is a flexible dockerized system for schema-guided knowledge extraction, capable of extracting information from the web and raw PDF books across multiple domains like science and news. It employs a collaborative multi-agent approach and includes a user-customizable knowledge base to enable tailored extraction. OneKE offers various IE tasks support, data sources support, LLMs support, extraction method support, and knowledge base configuration. Users can start with examples using YAML, Python, or Web UI, and perform tasks like Named Entity Recognition, Relation Extraction, Event Extraction, Triple Extraction, and Open Domain IE. The tool supports different source formats like Plain Text, HTML, PDF, Word, TXT, and JSON files. Users can choose from various extraction models like OpenAI, DeepSeek, LLaMA, Qwen, ChatGLM, MiniCPM, and OneKE for information extraction tasks. Extraction methods include Schema Agent, Extraction Agent, and Reflection Agent. The tool also provides support for schema repository and case repository management, along with solutions for network issues. Contributors to the project include Ningyu Zhang, Haofen Wang, Yujie Luo, Xiangyuan Ru, Kangwei Liu, Lin Yuan, Mengshu Sun, Lei Liang, Zhiqiang Zhang, Jun Zhou, Lanning Wei, Da Zheng, and Huajun Chen.
codellm-devkit
Codellm-devkit (CLDK) is a Python library that serves as a multilingual program analysis framework bridging traditional static analysis tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for code (CodeLLMs). It simplifies the process of analyzing codebases across multiple programming languages, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights and facilitating LLM-based code analysis. The library provides a unified interface for integrating outputs from various analysis tools and preparing them for effective use by CodeLLMs. Codellm-devkit aims to enable the development and experimentation of robust analysis pipelines that combine traditional program analysis tools and CodeLLMs, reducing friction in multi-language code analysis and ensuring compatibility across different tools and LLM platforms. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with popular analysis tools like WALA, Tree-sitter, LLVM, and CodeQL, acting as a crucial intermediary layer for efficient communication between these tools and CodeLLMs. The project is continuously evolving to include new tools and frameworks, maintaining its versatility for code analysis and LLM integration.
For similar tasks
llm-compression-intelligence
This repository presents the findings of the paper "Compression Represents Intelligence Linearly". The study reveals a strong linear correlation between the intelligence of LLMs, as measured by benchmark scores, and their ability to compress external text corpora. Compression efficiency, derived from raw text corpora, serves as a reliable evaluation metric that is linearly associated with model capabilities. The repository includes the compression corpora used in the paper, code for computing compression efficiency, and data collection and processing pipelines.
edsl
The Expected Parrot Domain-Specific Language (EDSL) package enables users to conduct computational social science and market research with AI. It facilitates designing surveys and experiments, simulating responses using large language models, and performing data labeling and other research tasks. EDSL includes built-in methods for analyzing, visualizing, and sharing research results. It is compatible with Python 3.9 - 3.11 and requires API keys for LLMs stored in a `.env` file.
fast-stable-diffusion
Fast-stable-diffusion is a project that offers notebooks for RunPod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro adaptations with AUTOMATIC1111 Webui and Dreambooth. It provides tools for running and implementing Dreambooth, a stable diffusion project. The project includes implementations by XavierXiao and is sponsored by Runpod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro.

RobustVLM
This repository contains code for the paper 'Robust CLIP: Unsupervised Adversarial Fine-Tuning of Vision Embeddings for Robust Large Vision-Language Models'. It focuses on fine-tuning CLIP in an unsupervised manner to enhance its robustness against visual adversarial attacks. By replacing the vision encoder of large vision-language models with the fine-tuned CLIP models, it achieves state-of-the-art adversarial robustness on various vision-language tasks. The repository provides adversarially fine-tuned ViT-L/14 CLIP models and offers insights into zero-shot classification settings and clean accuracy improvements.
TempCompass
TempCompass is a benchmark designed to evaluate the temporal perception ability of Video LLMs. It encompasses a diverse set of temporal aspects and task formats to comprehensively assess the capability of Video LLMs in understanding videos. The benchmark includes conflicting videos to prevent models from relying on single-frame bias and language priors. Users can clone the repository, install required packages, prepare data, run inference using examples like Video-LLaVA and Gemini, and evaluate the performance of their models across different tasks such as Multi-Choice QA, Yes/No QA, Caption Matching, and Caption Generation.
LLM-LieDetector
This repository contains code for reproducing experiments on lie detection in black-box LLMs by asking unrelated questions. It includes Q/A datasets, prompts, and fine-tuning datasets for generating lies with language models. The lie detectors rely on asking binary 'elicitation questions' to diagnose whether the model has lied. The code covers generating lies from language models, training and testing lie detectors, and generalization experiments. It requires access to GPUs and OpenAI API calls for running experiments with open-source models. Results are stored in the repository for reproducibility.
bigcodebench
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for code generation with practical and challenging programming tasks. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls. BigCodeBench focuses on the evaluation of LLM4Code with diverse function calls and complex instructions, providing precise evaluation & ranking and pre-generated samples to accelerate code intelligence research. It inherits the design of the EvalPlus framework but differs in terms of execution environment and test evaluation.
rag
RAG with txtai is a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Streamlit application that helps generate factually correct content by limiting the context in which a Large Language Model (LLM) can generate answers. It supports two categories of RAG: Vector RAG, where context is supplied via a vector search query, and Graph RAG, where context is supplied via a graph path traversal query. The application allows users to run queries, add data to the index, and configure various parameters to control its behavior.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.