
h2o-llmstudio
H2O LLM Studio - a framework and no-code GUI for fine-tuning LLMs. Documentation: https://docs.h2o.ai/h2o-llmstudio/
Stars: 4110

H2O LLM Studio is a framework and no-code GUI designed for fine-tuning state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). With H2O LLM Studio, you can easily and effectively fine-tune LLMs without the need for any coding experience. The GUI is specially designed for large language models, and you can finetune any LLM using a large variety of hyperparameters. You can also use recent finetuning techniques such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and 8-bit model training with a low memory footprint. Additionally, you can use Reinforcement Learning (RL) to finetune your model (experimental), use advanced evaluation metrics to judge generated answers by the model, track and compare your model performance visually, and easily export your model to the Hugging Face Hub and share it with the community.
README:
Welcome to H2O LLM Studio, a framework and no-code GUI designed for
fine-tuning state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs).
- With H2O LLM Studio, you can
- Quickstart
- What's New
- Setup
- Run H2O LLM Studio GUI
- Run H2O LLM Studio GUI using Docker from a nightly build
- Run H2O LLM Studio GUI by building your own Docker image
- Run H2O LLM Studio with command line interface (CLI)
- Troubleshooting
- Data format and example data
- Training your model
- Example: Run on OASST data via CLI
- Model checkpoints
- Documentation
- Contributing
- License
- easily and effectively fine-tune LLMs without the need for any coding experience.
- use a graphic user interface (GUI) specially designed for large language models.
- finetune any LLM using a large variety of hyperparameters.
- use recent finetuning techniques such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and 8-bit model training with a low memory footprint.
- use Reinforcement Learning (RL) to finetune your model (experimental)
- use advanced evaluation metrics to judge generated answers by the model.
- track and compare your model performance visually. In addition, Neptune and W&B integration can be used.
- chat with your model and get instant feedback on your model performance.
- easily export your model to the Hugging Face Hub and share it with the community.
For questions, discussing, or just hanging out, come and join our Discord!
Use cloud-based runpod.io instance to run the H2O LLM Studio GUI.
Using CLI for fine-tuning LLMs:
- PR 788 New problem type for Causal Regression Modeling allows to train single target regression data using LLMs.
- PR 747 Fully removed RLHF in favor of DPO/IPO/KTO optimization.
-
PR 741 Removing separate max length settings for prompt and answer in favor of a single
max_lengthsettings better resemblingchat_templatefunctionality fromtransformers. -
PR 592 Added
KTOPairLossfor DPO modeling allowing to train models with simple preference data. Data currently needs to be manually prepared by randomly matching positive and negative examples as pairs. - PR 592 Starting to deprecate RLHF in favor of DPO/IPO optimization. Training is disabled, but old experiments are still viewable. RLHF will be fully removed in a future release.
- PR 530 Introduced a new problem type for DPO/IPO optimization. This optimization technique can be used as an alternative to RLHF.
- PR 288 Introduced Deepspeed for sharded training allowing to train larger models on machines with multiple GPUs. Requires NVLink. This feature replaces FSDP and offers more flexibility. Deepspeed requires a system installation of cudatoolkit and we recommend using version 12.1. See Recommended Install.
- PR 449 New problem type for Causal Classification Modeling allows to train binary and multiclass models using LLMs.
- PR 364 User secrets are now handled more securely and flexible. Support for handling secrets using the 'keyring' library was added. User settings are tried to be migrated automatically.
Please note that due to current rapid development we cannot guarantee full backwards compatibility of new functionality. We thus recommend to pin the version of the framework to the one you used for your experiments. For resetting, please delete/backup your data and output folders.
H2O LLM Studio requires a machine with Ubuntu 16.04+ and at least one recent Nvidia GPU with Nvidia drivers version >= 470.57.02. For larger models, we recommend at least 24GB of GPU memory.
For more information about installation prerequisites, see the Set up H2O LLM Studio guide in the documentation.
For a performance comparison of different GPUs, see the H2O LLM Studio performance guide in the documentation.
The recommended way to install H2O LLM Studio is using pipenv with Python 3.10. To install Python 3.10 on Ubuntu 16.04+, execute the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
sudo apt install python3.10
sudo apt-get install python3.10-distutils
curl -sS https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python3.10If deploying on a 'bare metal' machine running Ubuntu, one may need to install the required Nvidia drivers and CUDA. The following commands show how to retrieve the latest drivers for a machine running Ubuntu 20.04 as an example. One can update the following based on their OS.
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu2004/x86_64/cuda-ubuntu2004.pin
sudo mv cuda-ubuntu2004.pin /etc/apt/preferences.d/cuda-repository-pin-600
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/12.1.0/local_installers/cuda-repo-ubuntu2004-12-1-local_12.1.0-530.30.02-1_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu2004-12-1-local_12.1.0-530.30.02-1_amd64.deb
sudo cp /var/cuda-repo-ubuntu2004-12-1-local/cuda-*-keyring.gpg /usr/share/keyrings/
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y install cudaalternatively, one can install cudatoolkits in a conda environment:
conda create -n llmstudio python=3.10
conda activate llmstudio
conda install -c "nvidia/label/cuda-12.1.0" cuda-toolkitWe offer various ways of setting up the necessary python environment.
The following command will create a virtual environment using pipenv and will install the dependencies using pipenv:
make setupIf you are having troubles installing the flash_attn package, consider running
make setup-no-flashinstead. This will install the dependencies without the flash_attn package. Note that this will disable the use of Flash Attention 2 and model training will be slower and consume more memory.
You can also setup a conda virtual environment that can also deviate from the recommended setup. The Makefile contains a command setup-conda-nightly that installs a fresh conda environment with CUDA 12.4 and current nightly PyTorch.
If you wish to use another virtual environment, you can also install the dependencies using the requirements.txt file:
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install flash-attn==2.6.1 --no-build-isolation # optional for Flash Attention 2You can start H2O LLM Studio using the following command:
make llmstudioThis command will start the H2O wave server and app. Navigate to http://localhost:10101/ (we recommend using Chrome) to access H2O LLM Studio and start fine-tuning your models!
If you are running H2O LLM Studio with a custom environment other than Pipenv, you need to start the app as follows:
H2O_WAVE_MAX_REQUEST_SIZE=25MB \
H2O_WAVE_NO_LOG=true \
H2O_WAVE_PRIVATE_DIR="/download/@output/download" \
wave run llm_studio.appIf you are using the nightly conda environment, you can run make llmstudio-conda.
Install Docker first by following instructions from NVIDIA Containers. Make sure to have nvidia-container-toolkit installed on your machine as outlined in the instructions.
H2O LLM Studio images are stored in the h2oai GCR vorvan container repository.
mkdir -p `pwd`/llmstudio_mnt
# make sure to pull latest image if you still have a prior version cached
docker pull gcr.io/vorvan/h2oai/h2o-llmstudio:nightly
# run the container
docker run \
--runtime=nvidia \
--shm-size=64g \
--init \
--rm \
-it \
-u `id -u`:`id -g` \
-p 10101:10101 \
-v `pwd`/llmstudio_mnt:/home/llmstudio/mount \
-v ~/.cache:/home/llmstudio/.cache \
gcr.io/vorvan/h2oai/h2o-llmstudio:nightlyNavigate to http://localhost:10101/ (we recommend using Chrome) to access H2O LLM Studio and start fine-tuning your models!
(Note other helpful docker commands are docker ps and docker kill.)
docker build -t h2o-llmstudio .
mkdir -p `pwd`/llmstudio_mnt
docker run \
--runtime=nvidia \
--shm-size=64g \
--init \
--rm \
-it \
-u `id -u`:`id -g` \
-p 10101:10101 \
-v `pwd`/llmstudio_mnt:/home/llmstudio/mount \
-v ~/.cache:/home/llmstudio/.cache \
h2o-llmstudioAlternatively, you can run H2O LLM Studio GUI by using our self-hosted Docker image available here.
You can also use H2O LLM Studio with the command line interface (CLI) and specify the configuration .yaml file that contains all the experiment parameters. To finetune using H2O LLM Studio with CLI, activate the pipenv environment by running make shell, and then use the following command:
python llm_studio/train.py -Y {path_to_config_yaml_file}To run on multiple GPUs in DDP mode, run the following command:
bash distributed_train.sh {NR_OF_GPUS} -Y {path_to_config_yaml_file}By default, the framework will run on the first k GPUs. If you want to specify specific GPUs to run on, use the CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES environment variable before the command.
To start an interactive chat with your trained model, use the following command:
python llm_studio/prompt.py -e {experiment_name}where experiment_name is the output folder of the experiment you want to chat with (see configuration).
The interactive chat will also work with model that were finetuned using the UI.
To publish the model to Hugging Face, use the following command:
make shell
python llm_studio/publish_to_hugging_face.py -p {path_to_experiment} -d {device} -a {api_key} -u {user_id} -m {model_name} -s {safe_serialization}path_to_experiment is the output folder of the experiment.
device is the target device for running the model, either 'cpu' or 'cuda:0'. Default is 'cuda:0'.
api_key is the Hugging Face API Key. If user logged in, it can be omitted.
user_id is the Hugging Face user ID. If user logged in, it can be omitted.
model_name is the name of the model to be published on Hugging Face. It can be omitted.
safe_serialization is a flag indicating whether safe serialization should be used. Default is True.
If running on cloud based machines such as runpod, you may need to set the following environment variable to allow the H2O Wave server to accept connections from the proxy:
H2O_WAVE_ALLOWED_ORIGINS="*"If you are experiencing timeouts when running the H2O Wave server remotely, you can increase the timeout by setting the following environment variables:
H2O_WAVE_APP_CONNECT_TIMEOUT="15"
H2O_WAVE_APP_WRITE_TIMEOUT="15"
H2O_WAVE_APP_READ_TIMEOUT="15"
H2O_WAVE_APP_POOL_TIMEOUT="15"All default to 5 (seconds). Increase them if you are experiencing timeouts. Use -1 to disable the timeout.
For details on the data format required when importing your data or example data that you can use to try out H2O LLM Studio, see Data format in the H2O LLM Studio documentation.
With H2O LLM Studio, training your large language model is easy and intuitive. First, upload your dataset and then start training your model. Start by creating an experiment. You can then monitor and manage your experiment, compare experiments, or push the model to Hugging Face to share it with the community.
As an example, you can run an experiment on the OASST data via CLI. For instructions, see Run an experiment on the OASST data guide in the H2O LLM Studio documentation.
All open-source datasets and models are posted on H2O.ai's Hugging Face page and our H2OGPT repository.
Detailed documentation and frequently asked questions (FAQs) for H2O LLM Studio can be found at https://docs.h2o.ai/h2o-llmstudio/. If you wish to contribute to the docs, navigate to the /documentation folder of this repo and refer to the README.md for more information.
We are happy to accept contributions to the H2O LLM Studio project. Please refer to the CONTRIBUTING.md file for more information.
H2O LLM Studio is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license. Please see the LICENSE file for more information.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for h2o-llmstudio
Similar Open Source Tools

h2o-llmstudio
H2O LLM Studio is a framework and no-code GUI designed for fine-tuning state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). With H2O LLM Studio, you can easily and effectively fine-tune LLMs without the need for any coding experience. The GUI is specially designed for large language models, and you can finetune any LLM using a large variety of hyperparameters. You can also use recent finetuning techniques such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and 8-bit model training with a low memory footprint. Additionally, you can use Reinforcement Learning (RL) to finetune your model (experimental), use advanced evaluation metrics to judge generated answers by the model, track and compare your model performance visually, and easily export your model to the Hugging Face Hub and share it with the community.
ai-starter-kit
SambaNova AI Starter Kits is a collection of open-source examples and guides designed to facilitate the deployment of AI-driven use cases for developers and enterprises. The kits cover various categories such as Data Ingestion & Preparation, Model Development & Optimization, Intelligent Information Retrieval, and Advanced AI Capabilities. Users can obtain a free API key using SambaNova Cloud or deploy models using SambaStudio. Most examples are written in Python but can be applied to any programming language. The kits provide resources for tasks like text extraction, fine-tuning embeddings, prompt engineering, question-answering, image search, post-call analysis, and more.
LLM_AppDev-HandsOn
This repository showcases how to build a simple LLM-based chatbot for answering questions based on documents using retrieval augmented generation (RAG) technique. It also provides guidance on deploying the chatbot using Podman or on the OpenShift Container Platform. The workshop associated with this repository introduces participants to LLMs & RAG concepts and demonstrates how to customize the chatbot for specific purposes. The software stack relies on open-source tools like streamlit, LlamaIndex, and local open LLMs via Ollama, making it accessible for GPU-constrained environments.
llm
LLM is a CLI utility and Python library for interacting with Large Language Models, both via remote APIs and models that can be installed and run on your own machine. It allows users to run prompts from the command-line, store results in SQLite, generate embeddings, and more. The tool supports self-hosted language models via plugins and provides access to remote and local models. Users can install plugins to access models by different providers, including models that can be installed and run on their own device. LLM offers various options for running Mistral models in the terminal and enables users to start chat sessions with models. Additionally, users can use a system prompt to provide instructions for processing input to the tool.
OSWorld
OSWorld is a benchmarking tool designed to evaluate multimodal agents for open-ended tasks in real computer environments. It provides a platform for running experiments, setting up virtual machines, and interacting with the environment using Python scripts. Users can install the tool on their desktop or server, manage dependencies with Conda, and run benchmark tasks. The tool supports actions like executing commands, checking for specific results, and evaluating agent performance. OSWorld aims to facilitate research in AI by providing a standardized environment for testing and comparing different agent baselines.
torchchat
torchchat is a codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. It allows running LLMs using Python in various environments such as desktop, server, iOS, and Android. The tool supports running models via PyTorch, chatting, generating text, running chat in the browser, and running models on desktop/server without Python. It also provides features like AOT Inductor for faster execution, running in C++ using the runner, and deploying and running on iOS and Android. The tool supports popular hardware and OS including Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS, with various data types and execution modes available.
LARS
LARS is an application that enables users to run Large Language Models (LLMs) locally on their devices, upload their own documents, and engage in conversations where the LLM grounds its responses with the uploaded content. The application focuses on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to increase accuracy and reduce AI-generated inaccuracies. LARS provides advanced citations, supports various file formats, allows follow-up questions, provides full chat history, and offers customization options for LLM settings. Users can force enable or disable RAG, change system prompts, and tweak advanced LLM settings. The application also supports GPU-accelerated inferencing, multiple embedding models, and text extraction methods. LARS is open-source and aims to be the ultimate RAG-centric LLM application.
gpustack
GPUStack is an open-source GPU cluster manager designed for running large language models (LLMs). It supports a wide variety of hardware, scales with GPU inventory, offers lightweight Python package with minimal dependencies, provides OpenAI-compatible APIs, simplifies user and API key management, enables GPU metrics monitoring, and facilitates token usage and rate metrics tracking. The tool is suitable for managing GPU clusters efficiently and effectively.
just-chat
Just-Chat is a containerized application that allows users to easily set up and chat with their AI agent. Users can customize their AI assistant using a YAML file, add new capabilities with Python tools, and interact with the agent through a chat web interface. The tool supports various modern models like DeepSeek Reasoner, ChatGPT, LLAMA3.3, etc. Users can also use semantic search capabilities with MeiliSearch to find and reference relevant information based on meaning. Just-Chat requires Docker or Podman for operation and provides detailed installation instructions for both Linux and Windows users.
safety-tooling
This repository, safety-tooling, is designed to be shared across various AI Safety projects. It provides an LLM API with a common interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google models. The aim is to facilitate collaboration among AI Safety researchers, especially those with limited software engineering backgrounds, by offering a platform for contributing to a larger codebase. The repo can be used as a git submodule for easy collaboration and updates. It also supports pip installation for convenience. The repository includes features for installation, secrets management, linting, formatting, Redis configuration, testing, dependency management, inference, finetuning, API usage tracking, and various utilities for data processing and experimentation.
SWELancer-Benchmark
SWE-Lancer is a benchmark repository containing datasets and code for the paper 'SWE-Lancer: Can Frontier LLMs Earn $1 Million from Real-World Freelance Software Engineering?'. It provides instructions for package management, building Docker images, configuring environment variables, and running evaluations. Users can use this tool to assess the performance of language models in real-world freelance software engineering tasks.
ChatGPT-OpenAI-Smart-Speaker
ChatGPT Smart Speaker is a project that enables speech recognition and text-to-speech functionalities using OpenAI and Google Speech Recognition. It provides scripts for running on PC/Mac and Raspberry Pi, allowing users to interact with a smart speaker setup. The project includes detailed instructions for setting up the required hardware and software dependencies, along with customization options for the OpenAI model engine, language settings, and response randomness control. The Raspberry Pi setup involves utilizing the ReSpeaker hardware for voice feedback and light shows. The project aims to offer an advanced smart speaker experience with features like wake word detection and response generation using AI models.

unitycatalog
Unity Catalog is an open and interoperable catalog for data and AI, supporting multi-format tables, unstructured data, and AI assets. It offers plugin support for extensibility and interoperates with Delta Sharing protocol. The catalog is fully open with OpenAPI spec and OSS implementation, providing unified governance for data and AI with asset-level access control enforced through REST APIs.
labs-ai-tools-for-devs
This repository provides AI tools for developers through Docker containers, enabling agentic workflows. It allows users to create complex workflows using Dockerized tools and Markdown, leveraging various LLM models. The core features include Dockerized tools, conversation loops, multi-model agents, project-first design, and trackable prompts stored in a git repo.
LlamaEdge
The LlamaEdge project makes it easy to run LLM inference apps and create OpenAI-compatible API services for the Llama2 series of LLMs locally. It provides a Rust+Wasm stack for fast, portable, and secure LLM inference on heterogeneous edge devices. The project includes source code for text generation, chatbot, and API server applications, supporting all LLMs based on the llama2 framework in the GGUF format. LlamaEdge is committed to continuously testing and validating new open-source models and offers a list of supported models with download links and startup commands. It is cross-platform, supporting various OSes, CPUs, and GPUs, and provides troubleshooting tips for common errors.

fasttrackml
FastTrackML is an experiment tracking server focused on speed and scalability, fully compatible with MLFlow. It provides a user-friendly interface to track and visualize your machine learning experiments, making it easy to compare different models and identify the best performing ones. FastTrackML is open source and can be easily installed and run with pip or Docker. It is also compatible with the MLFlow Python package, making it easy to integrate with your existing MLFlow workflows.
For similar tasks
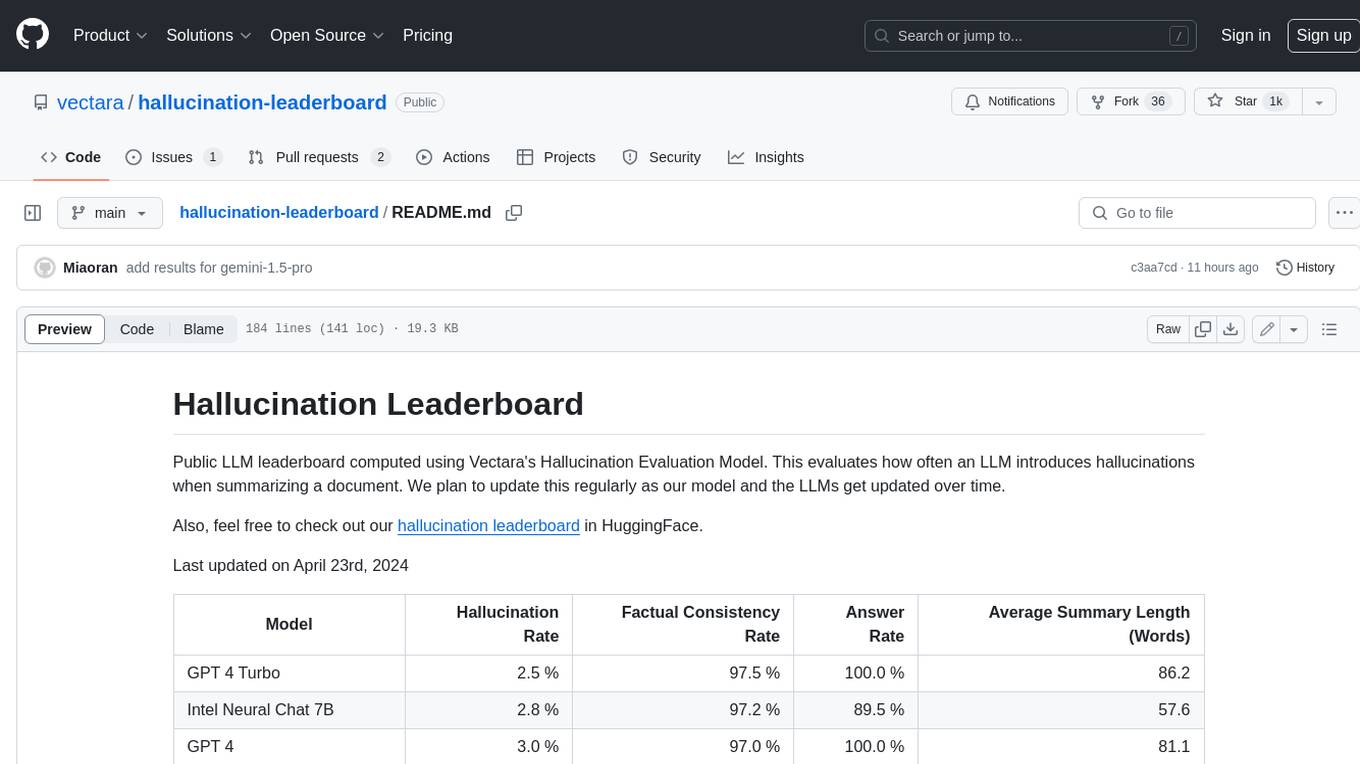
hallucination-leaderboard
This leaderboard evaluates the hallucination rate of various Large Language Models (LLMs) when summarizing documents. It uses a model trained by Vectara to detect hallucinations in LLM outputs. The leaderboard includes models from OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and others. The evaluation is based on 831 documents that were summarized by all the models. The leaderboard shows the hallucination rate, factual consistency rate, answer rate, and average summary length for each model.

h2o-llmstudio
H2O LLM Studio is a framework and no-code GUI designed for fine-tuning state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). With H2O LLM Studio, you can easily and effectively fine-tune LLMs without the need for any coding experience. The GUI is specially designed for large language models, and you can finetune any LLM using a large variety of hyperparameters. You can also use recent finetuning techniques such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and 8-bit model training with a low memory footprint. Additionally, you can use Reinforcement Learning (RL) to finetune your model (experimental), use advanced evaluation metrics to judge generated answers by the model, track and compare your model performance visually, and easily export your model to the Hugging Face Hub and share it with the community.
llm-jp-eval
LLM-jp-eval is a tool designed to automatically evaluate Japanese large language models across multiple datasets. It provides functionalities such as converting existing Japanese evaluation data to text generation task evaluation datasets, executing evaluations of large language models across multiple datasets, and generating instruction data (jaster) in the format of evaluation data prompts. Users can manage the evaluation settings through a config file and use Hydra to load them. The tool supports saving evaluation results and logs using wandb. Users can add new evaluation datasets by following specific steps and guidelines provided in the tool's documentation. It is important to note that using jaster for instruction tuning can lead to artificially high evaluation scores, so caution is advised when interpreting the results.
Awesome-LLM
Awesome-LLM is a curated list of resources related to large language models, focusing on papers, projects, frameworks, tools, tutorials, courses, opinions, and other useful resources in the field. It covers trending LLM projects, milestone papers, other papers, open LLM projects, LLM training frameworks, LLM evaluation frameworks, tools for deploying LLM, prompting libraries & tools, tutorials, courses, books, and opinions. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements and resources in the field of large language models.
bocoel
BoCoEL is a tool that leverages Bayesian Optimization to efficiently evaluate large language models by selecting a subset of the corpus for evaluation. It encodes individual entries into embeddings, uses Bayesian optimization to select queries, retrieves from the corpus, and provides easily managed evaluations. The tool aims to reduce computation costs during evaluation with a dynamic budget, supporting models like GPT2, Pythia, and LLAMA through integration with Hugging Face transformers and datasets. BoCoEL offers a modular design and efficient representation of the corpus to enhance evaluation quality.
cladder
CLadder is a repository containing the CLadder dataset for evaluating causal reasoning in language models. The dataset consists of yes/no questions in natural language that require statistical and causal inference to answer. It includes fields such as question_id, given_info, question, answer, reasoning, and metadata like query_type and rung. The dataset also provides prompts for evaluating language models and example questions with associated reasoning steps. Additionally, it offers dataset statistics, data variants, and code setup instructions for using the repository.
uncheatable_eval
Uncheatable Eval is a tool designed to assess the language modeling capabilities of LLMs on real-time, newly generated data from the internet. It aims to provide a reliable evaluation method that is immune to data leaks and cannot be gamed. The tool supports the evaluation of Hugging Face AutoModelForCausalLM models and RWKV models by calculating the sum of negative log probabilities on new texts from various sources such as recent papers on arXiv, new projects on GitHub, news articles, and more. Uncheatable Eval ensures that the evaluation data is not included in the training sets of publicly released models, thus offering a fair assessment of the models' performance.
llms
The 'llms' repository is a comprehensive guide on Large Language Models (LLMs), covering topics such as language modeling, applications of LLMs, statistical language modeling, neural language models, conditional language models, evaluation methods, transformer-based language models, practical LLMs like GPT and BERT, prompt engineering, fine-tuning LLMs, retrieval augmented generation, AI agents, and LLMs for computer vision. The repository provides detailed explanations, examples, and tools for working with LLMs.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.




