
empirical
Test and evaluate LLMs and model configurations, across all the scenarios that matter for your application
Stars: 134
Empirical is a tool that allows you to test different LLMs, prompts, and other model configurations across all the scenarios that matter for your application. With Empirical, you can run your test datasets locally against off-the-shelf models, test your own custom models and RAG applications, view, compare, and analyze outputs on a web UI, score your outputs with scoring functions, and run tests on CI/CD.
README:
Empirical is the fastest way to test different LLMs and model configurations, across all the scenarios that matter for your application.
With Empirical, you can
- Run your test datasets locally against off-the-shelf or custom models
- Compare model outputs on a web UI, and test changes quickly
- Score your outputs with scoring functions
- Run tests on CI/CD
https://github.com/empirical-run/empirical/assets/284612/65d96ecc-12a2-474d-a81e-bbddb71106b6
Empirical bundles together a test runner and a web app. These can be used through the CLI in your terminal window.
Empirical relies on a configuration file, typically located at empiricalrc.js
which describes the test to run.
In this example, we will ask an LLM to extract entities from user messages and
give us a structured JSON output. For example, "I'm Alice from Maryland" will
become {name: 'Alice', location: 'Maryland'}.
Our test will succeed if the model outputs valid JSON.
-
Use the CLI to create a sample configuration file called
empiricalrc.js.npm init empiricalrun # For TypeScript npm init empiricalrun -- --using-ts -
Run the example dataset against the selected models.
npx empiricalrun
This step requires the
OPENAI_API_KEYenvironment variable to authenticate with OpenAI. This execution will cost $0.0026, based on the selected models. -
Use the
uicommand to open the reporter web app and see side-by-side results.npx empiricalrun ui
Edit the empiricalrc.js file to make Empirical work for your use-case.
- Configure which models to use
- Configure your test dataset
- Configure scoring functions to grade output quality
See development docs.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for empirical
Similar Open Source Tools

empirical
Empirical is a tool that allows you to test different LLMs, prompts, and other model configurations across all the scenarios that matter for your application. With Empirical, you can run your test datasets locally against off-the-shelf models, test your own custom models and RAG applications, view, compare, and analyze outputs on a web UI, score your outputs with scoring functions, and run tests on CI/CD.
autoarena
AutoArena is a tool designed to create leaderboards ranking Language Model outputs against one another using automated judge evaluation. It allows users to rank outputs from different LLMs, RAG setups, and prompts to find the best configuration of their system. Users can perform automated head-to-head evaluation using judges from various platforms like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Cohere. Additionally, users can define and run custom judges, connect to internal services, or implement bespoke logic. AutoArena enables users to run the application locally, providing full control over their environment and data.
open-deep-research
Open Deep Research is an open-source project that serves as a clone of Open AI's Deep Research experiment. It utilizes Firecrawl's extract and search method along with a reasoning model to conduct in-depth research on the web. The project features Firecrawl Search + Extract, real-time data feeding to AI via search, structured data extraction from multiple websites, Next.js App Router for advanced routing, React Server Components and Server Actions for server-side rendering, AI SDK for generating text and structured objects, support for various model providers, styling with Tailwind CSS, data persistence with Vercel Postgres and Blob, and simple and secure authentication with NextAuth.js.

pytest-evals
pytest-evals is a minimalistic pytest plugin designed to help evaluate the performance of Language Model (LLM) outputs against test cases. It allows users to test and evaluate LLM prompts against multiple cases, track metrics, and integrate easily with pytest, Jupyter notebooks, and CI/CD pipelines. Users can scale up by running tests in parallel with pytest-xdist and asynchronously with pytest-asyncio. The tool focuses on simplifying evaluation processes without the need for complex frameworks, keeping tests and evaluations together, and emphasizing logic over infrastructure.
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
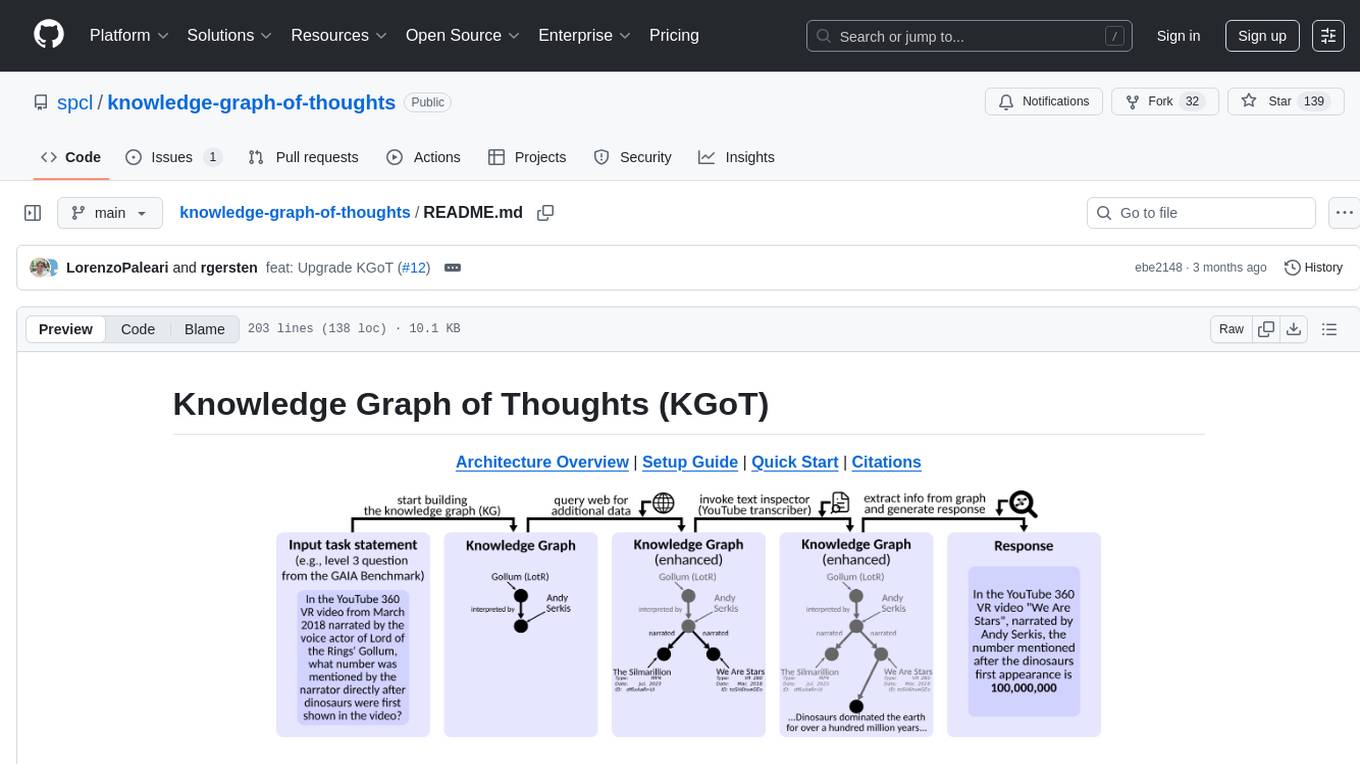
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
OlympicArena
OlympicArena is a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate advanced AI capabilities across various disciplines. It aims to push AI towards superintelligence by tackling complex challenges in science and beyond. The repository provides detailed data for different disciplines, allows users to run inference and evaluation locally, and offers a submission platform for testing models on the test set. Additionally, it includes an annotation interface and encourages users to cite their paper if they find the code or dataset helpful.

svelte-bench
SvelteBench is an LLM benchmark tool for evaluating Svelte components generated by large language models. It supports multiple LLM providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and OpenRouter. Users can run predefined test suites to verify the functionality of the generated components. The tool allows configuration of API keys for different providers and offers debug mode for faster development. Users can provide a context file to improve component generation. Benchmark results are saved in JSON format for analysis and visualization.
ai-starter-kit
SambaNova AI Starter Kits is a collection of open-source examples and guides designed to facilitate the deployment of AI-driven use cases for developers and enterprises. The kits cover various categories such as Data Ingestion & Preparation, Model Development & Optimization, Intelligent Information Retrieval, and Advanced AI Capabilities. Users can obtain a free API key using SambaNova Cloud or deploy models using SambaStudio. Most examples are written in Python but can be applied to any programming language. The kits provide resources for tasks like text extraction, fine-tuning embeddings, prompt engineering, question-answering, image search, post-call analysis, and more.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

physical-AI-interpretability
Physical AI Interpretability is a toolkit for transformer-based Physical AI and robotics models, providing tools for attention mapping, feature extraction, and out-of-distribution detection. It includes methods for post-hoc attention analysis, applying Dictionary Learning into robotics, and training sparse autoencoders. The toolkit aims to enhance interpretability and understanding of AI models in physical environments.
llm-benchmark
LLM SQL Generation Benchmark is a tool for evaluating different Large Language Models (LLMs) on their ability to generate accurate analytical SQL queries for Tinybird. It measures SQL query correctness, execution success, performance metrics, error handling, and recovery. The benchmark includes an automated retry mechanism for error correction. It supports various providers and models through OpenRouter and can be extended to other models. The benchmark is based on a GitHub dataset with 200M rows, where each LLM must produce SQL from 50 natural language prompts. Results are stored in JSON files and presented in a web application. Users can benchmark new models by following provided instructions.
AI-Scientist
The AI Scientist is a comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models to perform research independently. It aims to tackle the grand challenge of developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. The tool generates papers on various topics using Large Language Models (LLMs) and provides a platform for exploring new research ideas. Users can create their own templates for specific areas of study and run experiments to generate papers. However, caution is advised as the codebase executes LLM-written code, which may pose risks such as the use of potentially dangerous packages and web access.

MegatronApp
MegatronApp is a toolchain built around the Megatron-LM training framework, offering performance tuning, slow-node detection, and training-process visualization. It includes modules like MegaScan for anomaly detection, MegaFBD for forward-backward decoupling, MegaDPP for dynamic pipeline planning, and MegaScope for visualization. The tool aims to enhance large-scale distributed training by providing valuable capabilities and insights.
dlio_benchmark
DLIO is an I/O benchmark tool designed for Deep Learning applications. It emulates modern deep learning applications using Benchmark Runner, Data Generator, Format Handler, and I/O Profiler modules. Users can configure various I/O patterns, data loaders, data formats, datasets, and parameters. The tool is aimed at emulating the I/O behavior of deep learning applications and provides a modular design for flexibility and customization.
eval-dev-quality
DevQualityEval is an evaluation benchmark and framework designed to compare and improve the quality of code generation of Language Model Models (LLMs). It provides developers with a standardized benchmark to enhance real-world usage in software development and offers users metrics and comparisons to assess the usefulness of LLMs for their tasks. The tool evaluates LLMs' performance in solving software development tasks and measures the quality of their results through a point-based system. Users can run specific tasks, such as test generation, across different programming languages to evaluate LLMs' language understanding and code generation capabilities.
For similar tasks

empirical
Empirical is a tool that allows you to test different LLMs, prompts, and other model configurations across all the scenarios that matter for your application. With Empirical, you can run your test datasets locally against off-the-shelf models, test your own custom models and RAG applications, view, compare, and analyze outputs on a web UI, score your outputs with scoring functions, and run tests on CI/CD.
promptfoo
Promptfoo is a tool for testing and evaluating LLM output quality. With promptfoo, you can build reliable prompts, models, and RAGs with benchmarks specific to your use-case, speed up evaluations with caching, concurrency, and live reloading, score outputs automatically by defining metrics, use as a CLI, library, or in CI/CD, and use OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, HuggingFace, open-source models like Llama, or integrate custom API providers for any LLM API.
bench
Bench is a tool for evaluating LLMs for production use cases. It provides a standardized workflow for LLM evaluation with a common interface across tasks and use cases. Bench can be used to test whether open source LLMs can do as well as the top closed-source LLM API providers on specific data, and to translate the rankings on LLM leaderboards and benchmarks into scores that are relevant for actual use cases.
truss
Truss is a tool that simplifies the process of serving AI/ML models in production. It provides a consistent and easy-to-use interface for packaging, testing, and deploying models, regardless of the framework they were created with. Truss also includes a live reload server for fast feedback during development, and a batteries-included model serving environment that eliminates the need for Docker and Kubernetes configuration.
LLMinator
LLMinator is a Gradio-based tool with an integrated chatbot designed to locally run and test Language Model Models (LLMs) directly from HuggingFace. It provides an easy-to-use interface made with Gradio, LangChain, and Torch, offering features such as context-aware streaming chatbot, inbuilt code syntax highlighting, loading any LLM repo from HuggingFace, support for both CPU and CUDA modes, enabling LLM inference with llama.cpp, and model conversion capabilities.
onnxruntime-server
ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference. It aims to offer simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience. Users can provide inference APIs for ONNX models without writing additional code by placing the models in the directory structure. Each session can choose between CPU or CUDA, analyze input/output, and provide Swagger API documentation for easy testing. Ready-to-run Docker images are available, making it convenient to deploy the server.
llm-vscode
llm-vscode is an extension designed for all things LLM, utilizing llm-ls as its backend. It offers features such as code completion with 'ghost-text' suggestions, the ability to choose models for code generation via HTTP requests, ensuring prompt size fits within the context window, and code attribution checks. Users can configure the backend, suggestion behavior, keybindings, llm-ls settings, and tokenization options. Additionally, the extension supports testing models like Code Llama 13B, Phind/Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2, and WizardLM/WizardCoder-Python-34B-V1.0. Development involves cloning llm-ls, building it, and setting up the llm-vscode extension for use.
mistral-inference
Mistral Inference repository contains minimal code to run 7B, 8x7B, and 8x22B models. It provides model download links, installation instructions, and usage guidelines for running models via CLI or Python. The repository also includes information on guardrailing, model platforms, deployment, and references. Users can interact with models through commands like mistral-demo, mistral-chat, and mistral-common. Mistral AI models support function calling and chat interactions for tasks like testing models, chatting with models, and using Codestral as a coding assistant. The repository offers detailed documentation and links to blogs for further information.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

