
onnxruntime-server
ONNX Runtime Server: The ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference.
Stars: 134
ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference. It aims to offer simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience. Users can provide inference APIs for ONNX models without writing additional code by placing the models in the directory structure. Each session can choose between CPU or CUDA, analyze input/output, and provide Swagger API documentation for easy testing. Ready-to-run Docker images are available, making it convenient to deploy the server.
README:
- ONNX: Open Neural Network Exchange
- The ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference.
- ONNX Runtime Server aims to provide simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience.
- If you have exported ML models trained in various environments as ONNX files, you can provide inference APIs without writing additional code or metadata. Just place the ONNX files into the directory structure.
- Each ONNX session, you can choose to use CPU or CUDA.
- Analyze the input/output of ONNX models to provide type/shape information for your collaborators.
- Built-in Swagger API documentation makes it easy for collaborators to test ML models through the API. (API example)
- Ready-to-run Docker images. No build required.
- ONNX Runtime
- Boost
- CMake, pkg-config
- CUDA(optional, for Nvidia GPU support)
- OpenSSL(optional, for HTTPS)
- Use
download-onnxruntime-linux.shscript- This script downloads the latest version of the binary and install to
/usr/local/onnxruntime. - Also, add
/usr/local/onnxruntime/libto/etc/ld.so.conf.d/onnxruntime.confand runldconfig.
- This script downloads the latest version of the binary and install to
- Or manually download binary from ONNX Runtime Releases.
brew install onnxruntimesudo apt install cmake pkg-config libboost-all-dev libssl-dev- Follow the instructions below to install the CUDA Toolkit and cuDNN.
sudo apt install cuda-toolkit-12 libcudnn9-dev-cuda-12
# optional, for Nvidia GPU support with Docker
sudo apt install nvidia-container-toolkit brew install cmake boost opensslcmake -B build -S . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
cmake --build build --parallel
sudo cmake --install build --prefix /usr/local/onnxruntime-server| OS | Method | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Arch Linux | AUR | yay -S onnxruntime-server |
-
You must enter the path option(
--model-dir) where the models are located.- The onnx model files must be located in the following path:
${model_dir}/${model_name}/${model_version}/model.onnxor${model_dir}/${model_name}/${model_version}.onnx
- The onnx model files must be located in the following path:
Files in --model-dir
|
Create session request body | Get/Execute session API URL path (after created) |
|---|---|---|
model_name/model_version/model.onnx or model_name/model_version.onnx
|
{"model":"model_name", "version":"model_version"} |
/api/sessions/model_name/model_version |
sample/v1/model.onnx or sample/v1.onnx
|
{"model":"sample", "version":"v1"} |
/api/sessions/sample/v1 |
sample/v2/model.onnx or sample/v2.onnx
|
{"model":"sample", "version":"v2"} |
/api/sessions/sample/v2 |
other/20200101/model.onnx or other/20200101.onnx
|
{"model":"other", "version":"20200101"} |
/api/sessions/other/20200101 |
-
You need to enable one of the following backends: TCP, HTTP, or HTTPS.
- If you want to use TCP, you must specify the
--tcp-portoption. - If you want to use HTTP, you must specify the
--http-portoption. - If you want to use HTTPS, you must specify the
--https-port,--https-certand--https-keyoptions. - If you want to use Swagger, you must specify the
--swagger-url-pathoption.
- If you want to use TCP, you must specify the
- Use the
-h,--helpoption to see a full list of options. -
All options can be set as environment variables. This can be useful when operating in a container like Docker.
- Normally, command-line options are prioritized over environment variables, but if
the
ONNX_SERVER_CONFIG_PRIORITY=envenvironment variable exists, environment variables have higher priority. Within a Docker image, environment variables have higher priority.
- Normally, command-line options are prioritized over environment variables, but if
the
| Option | Environment | Description |
|---|---|---|
--workers |
ONNX_SERVER_WORKERS |
Worker thread pool size. Default: 4
|
--request-payload-limit |
ONNX_SERVER_REQUEST_PAYLOAD_LIMIT |
HTTP/HTTPS request payload size limit. Default: 1024 * 1024 * 10(10MB)` |
--model-dir |
ONNX_SERVER_MODEL_DIR |
Model directory path The onnx model files must be located in the following path: ${model_dir}/${model_name}/${model_version}/model.onnx or${model_dir}/${model_name}/${model_version}.onnxDefault: models
|
--prepare-model |
ONNX_SERVER_PREPARE_MODEL |
Pre-create some model sessions at server startup. Format as a space-separated list of model_name:model_version or model_name:model_version(session_options, ...).Available session_options are - cuda=device_id [ or true or false]eg) model1:v1 model2:v9model1:v1(cuda=true) model2:v9(cuda=1)
|
| Option | Environment | Description |
|---|---|---|
--tcp-port |
ONNX_SERVER_TCP_PORT |
Enable TCP backend and which port number to use. |
--http-port |
ONNX_SERVER_HTTP_PORT |
Enable HTTP backend and which port number to use. |
--https-port |
ONNX_SERVER_HTTPS_PORT |
Enable HTTPS backend and which port number to use. |
--https-cert |
ONNX_SERVER_HTTPS_CERT |
SSL Certification file path for HTTPS |
--https-key |
ONNX_SERVER_HTTPS_KEY |
SSL Private key file path for HTTPS |
--swagger-url-path |
ONNX_SERVER_SWAGGER_URL_PATH |
Enable Swagger API document for HTTP/HTTPS backend. This value cannot start with "/api/" and "/health" If not specified, swagger document not provided. eg) /swagger or /api-docs |
| Option | Environment | Description |
|---|---|---|
--log-level |
ONNX_SERVER_LOG_LEVEL |
Log level(debug, info, warn, error, fatal) |
--log-file |
ONNX_SERVER_LOG_FILE |
Log file path. If not specified, logs will be printed to stdout. |
--access-log-file |
ONNX_SERVER_ACCESS_LOG_FILE |
Access log file path. If not specified, logs will be printed to stdout. |
- Docker hub: kibaes/onnxruntime-server
-
1.20.1-linux-cuda12amd64(CUDA 12.x, cuDNN 9.x) -
1.20.1-linux-cpuamd64, arm64
-
DOCKER_IMAGE=kibae/onnxruntime-server:1.20.1-linux-cuda12 # or kibae/onnxruntime-server:1.20.1-linux-cpu
docker pull ${DOCKER_IMAGE}
# simple http backend
docker run --name onnxruntime_server_container -d --rm --gpus all \
-p 80:80 \
-v "/your_model_dir:/app/models" \
-v "/your_log_dir:/app/logs" \
-e "ONNX_SERVER_SWAGGER_URL_PATH=/api-docs" \
${DOCKER_IMAGE}- More information on using Docker images can be found here.
- docker-compose.yml example is available in the repository.
-
HTTP/HTTPS REST API
- API documentation (Swagger) is built in. If you want the server to serve swagger, add
the
--swagger-url-path=/swagger/option at launch. This must be used with the--http-portor--https-portoption../onnxruntime_server --model-dir=YOUR_MODEL_DIR --http-port=8080 --swagger-url-path=/api-docs/
- After running the server as above, you will be able to access the Swagger UI available
at
http://localhost:8080/api-docs/.
- After running the server as above, you will be able to access the Swagger UI available
at
-
- API documentation (Swagger) is built in. If you want the server to serve swagger, add
the
- TCP API
- A few things have been left out to help you get a rough idea of the usage flow.
%%{init: {
'sequence': {'noteAlign': 'left', 'mirrorActors': true}
}}%%
sequenceDiagram
actor A as Administrator
box rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.1) "ONNX Runtime Server"
participant SD as Disk
participant SP as Process
end
actor C as Client
Note right of A: You have 3 models to serve.
A ->> SD: copy model files to disk.<br />"/var/models/model_A/v1/model.onnx"<br />"/var/models/model_A/v2/model.onnx"<br />"/var/models/model_B/20201101/model.onnx"
A ->> SP: Start server with --prepare-model option
activate SP
Note right of A: onnxruntime_server<br />--http-port=8080<br />--model-path=/var/models<br />--prepare-model="model_A:v1(cuda=0) model_A:v2(cuda=0)"
SP -->> SD: Load model
Note over SD, SP: Load model from<br />"/var/models/model_A/v1/model.onnx"
SD -->> SP: Model binary
activate SP
SP -->> SP: Create<br />onnxruntime<br />session
deactivate SP
deactivate SP
rect rgb(100, 100, 100, 0.3)
Note over SD, C: Execute Session
C ->> SP: Execute session request
activate SP
Note over SP, C: POST /api/sessions/model_A/v1<br />{<br />"x": [[1], [2], [3]],<br />"y": [[2], [3], [4]],<br />"z": [[3], [4], [5]]<br />}
activate SP
SP -->> SP: Execute<br />onnxruntime<br />session
deactivate SP
SP ->> C: Execute session response
deactivate SP
Note over SP, C: {<br />"output": [<br />[0.6492120623588562],<br />[0.7610487341880798],<br />[0.8728854656219482]<br />]<br />}
end%%{init: {
'sequence': {'noteAlign': 'left', 'mirrorActors': true}
}}%%
sequenceDiagram
actor A as Administrator
box rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.1) "ONNX Runtime Server"
participant SD as Disk
participant SP as Process
end
actor C as Client
Note right of A: You have 3 models to serve.
A ->> SD: copy model files to disk.<br />"/var/models/model_A/v1/model.onnx"<br />"/var/models/model_A/v2/model.onnx"<br />"/var/models/model_B/20201101/model.onnx"
A ->> SP: Start server
Note right of A: onnxruntime_server<br />--http-port=8080<br />--model-path=/var/models
rect rgb(100, 100, 100, 0.3)
Note over SD, C: Create Session
C ->> SP: Create session request
activate SP
Note over SP, C: POST /api/sessions<br />{"model": "model_A", "version": "v1"}
SP -->> SD: Load model
Note over SD, SP: Load model from<br />"/var/models/model_A/v1/model.onnx"
SD -->> SP: Model binary
activate SP
SP -->> SP: Create<br />onnxruntime<br />session
deactivate SP
SP ->> C: Create session response
deactivate SP
Note over SP, C: {<br />"model": "model_A",<br />"version": "v1",<br />"created_at": 1694228106,<br />"execution_count": 0,<br />"last_executed_at": 0,<br />"inputs": {<br />"x": "float32[-1,1]",<br />"y": "float32[-1,1]",<br />"z": "float32[-1,1]"<br />},<br />"outputs": {<br />"output": "float32[-1,1]"<br />}<br />}
Note right of C: 👌 You can know the type and shape<br />of the input and output.
end
rect rgb(100, 100, 100, 0.3)
Note over SD, C: Execute Session
C ->> SP: Execute session request
activate SP
Note over SP, C: POST /api/sessions/model_A/v1<br />{<br />"x": [[1], [2], [3]],<br />"y": [[2], [3], [4]],<br />"z": [[3], [4], [5]]<br />}
activate SP
SP -->> SP: Execute<br />onnxruntime<br />session
deactivate SP
SP ->> C: Execute session response
deactivate SP
Note over SP, C: {<br />"output": [<br />[0.6492120623588562],<br />[0.7610487341880798],<br />[0.8728854656219482]<br />]<br />}
endFor Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for onnxruntime-server
Similar Open Source Tools

onnxruntime-server
ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference. It aims to offer simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience. Users can provide inference APIs for ONNX models without writing additional code by placing the models in the directory structure. Each session can choose between CPU or CUDA, analyze input/output, and provide Swagger API documentation for easy testing. Ready-to-run Docker images are available, making it convenient to deploy the server.
zeroclaw
ZeroClaw is a fast, small, and fully autonomous AI assistant infrastructure built with Rust. It features a lean runtime, cost-efficient deployment, fast cold starts, and a portable architecture. It is secure by design, fully swappable, and supports OpenAI-compatible provider support. The tool is designed for low-cost boards and small cloud instances, with a memory footprint of less than 5MB. It is suitable for tasks like deploying AI assistants, swapping providers/channels/tools, and pluggable everything.
tokscale
Tokscale is a high-performance CLI tool and visualization dashboard for tracking token usage and costs across multiple AI coding agents. It helps monitor and analyze token consumption from various AI coding tools, providing real-time pricing calculations using LiteLLM's pricing data. Inspired by the Kardashev scale, Tokscale measures token consumption as users scale the ranks of AI-augmented development. It offers interactive TUI mode, multi-platform support, real-time pricing, detailed breakdowns, web visualization, flexible filtering, and social platform features.
LocalAGI
LocalAGI is a powerful, self-hostable AI Agent platform that allows you to design AI automations without writing code. It provides a complete drop-in replacement for OpenAI's Responses APIs with advanced agentic capabilities. With LocalAGI, you can create customizable AI assistants, automations, chat bots, and agents that run 100% locally, without the need for cloud services or API keys. The platform offers features like no-code agents, web-based interface, advanced agent teaming, connectors for various platforms, comprehensive REST API, short & long-term memory capabilities, planning & reasoning, periodic tasks scheduling, memory management, multimodal support, extensible custom actions, fully customizable models, observability, and more.
mcp-context-forge
MCP Context Forge is a powerful tool for generating context-aware data for machine learning models. It provides functionalities to create diverse datasets with contextual information, enhancing the performance of AI algorithms. The tool supports various data formats and allows users to customize the context generation process easily. With MCP Context Forge, users can efficiently prepare training data for tasks requiring contextual understanding, such as sentiment analysis, recommendation systems, and natural language processing.
readme-ai
README-AI is a developer tool that auto-generates README.md files using a combination of data extraction and generative AI. It streamlines documentation creation and maintenance, enhancing developer productivity. This project aims to enable all skill levels, across all domains, to better understand, use, and contribute to open-source software. It offers flexible README generation, supports multiple large language models (LLMs), provides customizable output options, works with various programming languages and project types, and includes an offline mode for generating boilerplate README files without external API calls.
hud-python
hud-python is a Python library for creating interactive heads-up displays (HUDs) in video games. It provides a simple and flexible way to overlay information on the screen, such as player health, score, and notifications. The library is designed to be easy to use and customizable, allowing game developers to enhance the user experience by adding dynamic elements to their games. With hud-python, developers can create engaging HUDs that improve gameplay and provide important feedback to players.
evalplus
EvalPlus is a rigorous evaluation framework for LLM4Code, providing HumanEval+ and MBPP+ tests to evaluate large language models on code generation tasks. It offers precise evaluation and ranking, coding rigorousness analysis, and pre-generated code samples. Users can use EvalPlus to generate code solutions, post-process code, and evaluate code quality. The tool includes tools for code generation and test input generation using various backends.
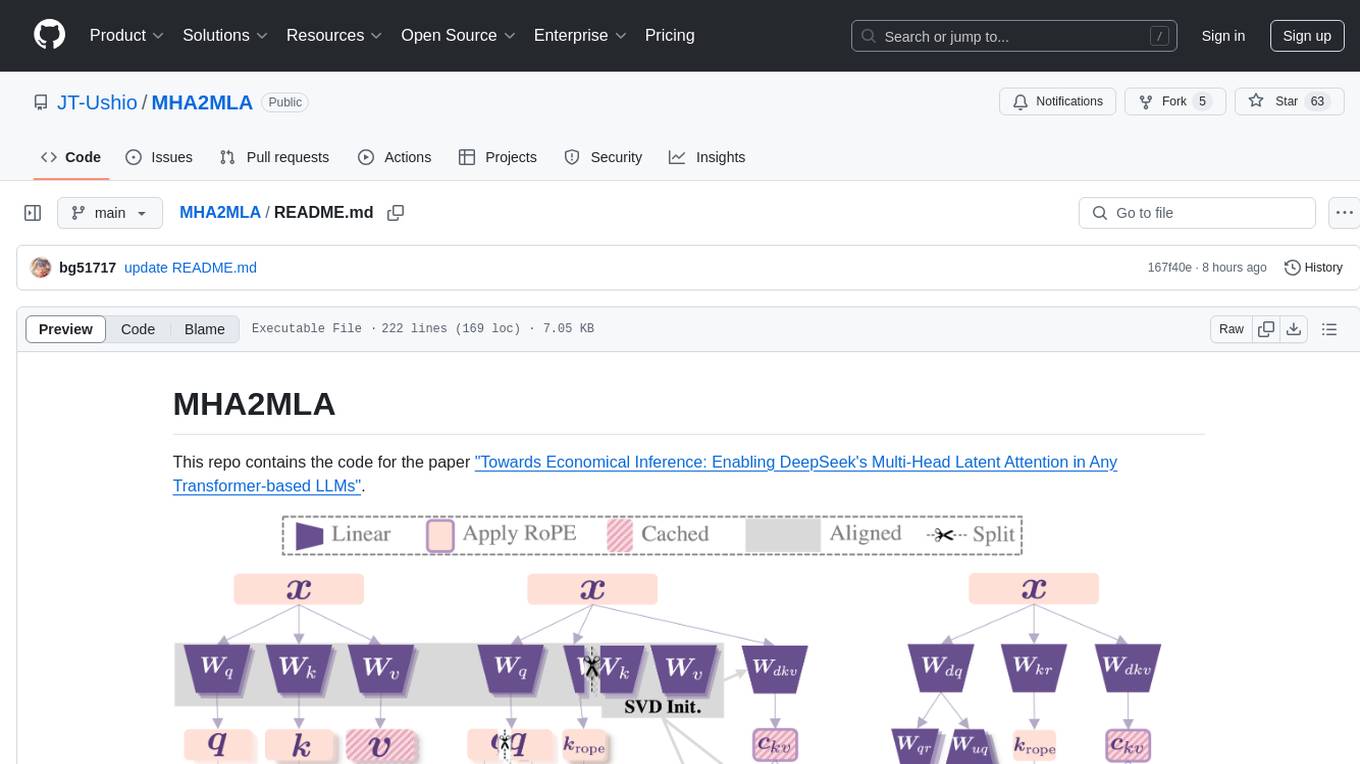
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
mcp-devtools
MCP DevTools is a high-performance server written in Go that replaces multiple Node.js and Python-based servers. It provides access to essential developer tools through a unified, modular interface. The server is efficient, with minimal memory footprint and fast response times. It offers a comprehensive tool suite for agentic coding, including 20+ essential developer agent tools. The tool registry allows for easy addition of new tools. The server supports multiple transport modes, including STDIO, HTTP, and SSE. It includes a security framework for multi-layered protection and a plugin system for adding new tools.

OSA
OSA (Open-Source-Advisor) is a tool designed to improve the quality of scientific open source projects by automating the generation of README files, documentation, CI/CD scripts, and providing advice and recommendations for repositories. It supports various LLMs accessible via API, local servers, or osa_bot hosted on ITMO servers. OSA is currently under development with features like README file generation, documentation generation, automatic implementation of changes, LLM integration, and GitHub Action Workflow generation. It requires Python 3.10 or higher and tokens for GitHub/GitLab/Gitverse and LLM API key. Users can install OSA using PyPi or build from source, and run it using CLI commands or Docker containers.

lingo.dev
Replexica AI automates software localization end-to-end, producing authentic translations instantly across 60+ languages. Teams can do localization 100x faster with state-of-the-art quality, reaching more paying customers worldwide. The tool offers a GitHub Action for CI/CD automation and supports various formats like JSON, YAML, CSV, and Markdown. With lightning-fast AI localization, auto-updates, native quality translations, developer-friendly CLI, and scalability for startups and enterprise teams, Replexica is a top choice for efficient and effective software localization.
dexto
Dexto is a lightweight runtime for creating and running AI agents that turn natural language into real-world actions. It serves as the missing intelligence layer for building AI applications, standalone chatbots, or as the reasoning engine inside larger products. Dexto features a powerful CLI and Web UI for running AI agents, supports multiple interfaces, allows hot-swapping of LLMs from various providers, connects to remote tool servers via the Model Context Protocol, is config-driven with version-controlled YAML, offers production-ready core features, extensibility for custom services, and enables multi-agent collaboration via MCP and A2A.
GPULlama3.java
GPULlama3.java powered by TornadoVM is a Java-native implementation of Llama3 that automatically compiles and executes Java code on GPUs via TornadoVM. It supports Llama3, Mistral, Qwen2.5, Qwen3, and Phi3 models in the GGUF format. The repository aims to provide GPU acceleration for Java code, enabling faster execution and high-performance access to off-heap memory. It offers features like interactive and instruction modes, flexible backend switching between OpenCL and PTX, and cross-platform compatibility with NVIDIA, Intel, and Apple GPUs.
rpaframework
RPA Framework is an open-source collection of libraries and tools for Robotic Process Automation (RPA), designed to be used with Robot Framework and Python. It offers well-documented core libraries for Software Robot Developers, optimized for Robocorp Control Room and Developer Tools, and accepts external contributions. The project includes various libraries for tasks like archiving, browser automation, date/time manipulations, cloud services integration, encryption operations, database interactions, desktop automation, document processing, email operations, Excel manipulation, file system operations, FTP interactions, web API interactions, image manipulation, AI services, and more. The development of the repository is Python-based and requires Python version 3.8+, with tooling based on poetry and invoke for compiling, building, and running the package. The project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
libllm
libLLM is an open-source project designed for efficient inference of large language models (LLM) on personal computers and mobile devices. It is optimized to run smoothly on common devices, written in C++14 without external dependencies, and supports CUDA for accelerated inference. Users can build the tool for CPU only or with CUDA support, and run libLLM from the command line. Additionally, there are API examples available for Python and the tool can export Huggingface models.
For similar tasks
rlhf_trojan_competition
This competition is organized by Javier Rando and Florian Tramèr from the ETH AI Center and SPY Lab at ETH Zurich. The goal of the competition is to create a method that can detect universal backdoors in aligned language models. A universal backdoor is a secret suffix that, when appended to any prompt, enables the model to answer harmful instructions. The competition provides a set of poisoned generation models, a reward model that measures how safe a completion is, and a dataset with prompts to run experiments. Participants are encouraged to use novel methods for red-teaming, automated approaches with low human oversight, and interpretability tools to find the trojans. The best submissions will be offered the chance to present their work at an event during the SaTML 2024 conference and may be invited to co-author a publication summarizing the competition results.

onnxruntime-server
ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference. It aims to offer simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience. Users can provide inference APIs for ONNX models without writing additional code by placing the models in the directory structure. Each session can choose between CPU or CUDA, analyze input/output, and provide Swagger API documentation for easy testing. Ready-to-run Docker images are available, making it convenient to deploy the server.
hallucination-index
LLM Hallucination Index - RAG Special is a comprehensive evaluation of large language models (LLMs) focusing on context length and open vs. closed-source attributes. The index explores the impact of context length on model performance and tests the assumption that closed-source LLMs outperform open-source ones. It also investigates the effectiveness of prompting techniques like Chain-of-Note across different context lengths. The evaluation includes 22 models from various brands, analyzing major trends and declaring overall winners based on short, medium, and long context insights. Methodologies involve rigorous testing with different context lengths and prompting techniques to assess models' abilities in handling extensive texts and detecting hallucinations.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
A-Survey-on-Mixture-of-Experts-in-LLMs
A curated collection of papers and resources on Mixture of Experts in Large Language Models. The repository provides a chronological overview of several representative Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models in recent years, structured according to release dates. It covers MoE models from various domains like Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision, Multimodal, and Recommender Systems. The repository aims to offer insights into Inference Optimization Techniques, Sparsity exploration, Attention mechanisms, and safety enhancements in MoE models.
tool-ahead-of-time
Tool-Ahead-of-Time (TAoT) is a Python package that enables tool calling for any model available through Langchain's ChatOpenAI library, even before official support is provided. It reformats model output into a JSON parser for tool calling. The package supports OpenAI and non-OpenAI models, following LangChain's syntax for tool calling. Users can start using the tool without waiting for official support, providing a more robust solution for tool calling.
UltraBr3aks
UltraBr3aks is a repository designed to share strong AI UltraBr3aks of multiple vendors, specifically focusing on Attention-Breaking technique targeting self-attention mechanisms of Transformer-based models. The method disrupts the model's focus on system guardrails by introducing specific token patterns and contextual noise, allowing for unrestricted generation analysis. The repository is created for educational and research purposes only.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.


