Ling
Ling is a MoE LLM provided and open-sourced by InclusionAI.
Stars: 119
Ling is a MoE LLM provided and open-sourced by InclusionAI. It includes two different sizes, Ling-Lite with 16.8 billion parameters and Ling-Plus with 290 billion parameters. These models show impressive performance and scalability for various tasks, from natural language processing to complex problem-solving. The open-source nature of Ling encourages collaboration and innovation within the AI community, leading to rapid advancements and improvements. Users can download the models from Hugging Face and ModelScope for different use cases. Ling also supports offline batched inference and online API services for deployment. Additionally, users can fine-tune Ling models using Llama-Factory for tasks like SFT and DPO.
README:
🤗 Hugging Face   |   🤖 ModelScope
Ling is a MoE LLM provided and open-sourced by InclusionAI. We introduce two different sizes, which are Ling-Lite and Ling-Plus. Ling-Lite has 16.8 billion parameters with 2.75 billion activated parameters, while Ling-Plus has 290 billion parameters with 28.8 billion activated parameters. Both models demonstrate impressive performance compared to existing models in the industry.
Their structure makes it easy to scale up and down and adapt to different tasks, so users can use these models for a wide range of tasks, from processing natural language to solving complex problems. Furthermore, the open-source nature of Ling promotes collaboration and innovation within the AI community, fostering a diverse range of use cases and enhancements.
As more developers and researchers engage with the platform, we can expect rapid advancements and improvements, leading to even more sophisticated applications. This collaborative approach accelerates development and ensures that the models remain at the forefront of technology, addressing emerging challenges in various fields.
You can download the following table to see the various parameters for your use case. If you are located in mainland China, we also provide the model on ModelScope.cn to speed up the download process.
| Model | #Total Params | #Activated Params | Context Length | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ling-lite-base | 16.8B | 2.75B | 64K |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope |
| Ling-lite | 16.8B | 2.75B | 64K |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope |
| Ling-plus-base | 290B | 28.8B | 64K |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope |
| Ling-plus | 290B | 28.8B | 64K |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope |
| Ling-coder-lite-base | 16.8B | 2.75B | 16K |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope |
| Ling-coder-lite | 16.8B | 2.75B | 16K |
🤗 HuggingFace 🤖 ModelScope |
Detailed evaluation results are reported in our technical report on arxiv or direct link.
Here is a code snippet to show you how to use the chat model with transformers:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "inclusionAI/Ling-lite"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language models."
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are Ling, an assistant created by inclusionAI"},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=512
)
generated_ids = [
output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(model_inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
response = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]If you're in mainland China, we strongly recommend you to use our model from 🤖 ModelScope.
vLLM supports offline batched inference or launching an OpenAI-Compatible API Service for online inference.
Since the Pull Request (PR) has not been submitted to the vLLM community at this stage, please prepare the environment by following the steps below:
git clone -b v0.7.3 https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm.git
cd vllm
git apply Ling/inference/vllm/bailing_moe.patch
pip install -e .from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("inclusionAI/Ling-lite")
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.7, top_p=0.8, repetition_penalty=1.05, max_tokens=512)
llm = LLM(model="inclusionAI/Ling-lite", dtype='bfloat16')
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language models."
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are Ling, an assistant created by inclusionAI"},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
outputs = llm.generate([text], sampling_params)
We utilize YaRN in vLLM to handle long context by add a rope_scaling field to the config.json file of the model. For example,
{
...,
"rope_scaling": {
"factor": 4.0,
"original_max_position_embeddings": 16384,
"type": "yarn"
}
}vllm serve inclusionAI/Ling-lite \
--tensor-parallel-size 2 \
--pipeline-parallel-size 1 \
--use-v2-block-manager \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.90For detailed guidance, please refer to the vLLM instructions.
This topic describes the main steps to run an Ling MoE model based on Huawei NPU cards and the MindIE inference framework
- The MoE Plus model requires at least 2 Atlas 800I A2 (8*64G) servers.
- The MoE Lite model requires at least 1 Atlas 800I A2 (8*64G) server.
Create a model directory on the host for downloading, the directory example is: /root/models', which is used to mount the docker container later.
Download the mindie-related configuration from github:
cd /root/models
git clone [email protected]:inclusionAI/Ling.git# Check the physical link
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -lldp -g | grep Ifname; done
# Check the links
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -link -g ; done
# Check your network health
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -net_health -g ; done
# Check whether the detected IP address is correctly configured
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -netdetect -g ; done
# Check whether the gateway is configured correctly
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -gateway -g ; done
# Check the consistency of the underlying TLS verification behavior of the NPU, recommend that all 0 be
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -tls -g ; done | grep switch
# The underlying TLS check line of the NPU is set to 0
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -tls -s enable 0; doneGo to Ascend Community/Development Resources and pull the mindie image
Image version: 1.0.0-800I-A2-py311-openeuler24.03-lts
The versions of each component are as follows:
| Component | Version |
|---|---|
| MindIE | 1.0.0 |
| CANN | 8.0.0 |
| PTA | 6.0.0.beta1 |
| HDK | 24.1.0 |
Execute the following startup command (reference):
docker run -itd --privileged --name=container name --net=host \
--shm-size 500g \
--device=/dev/davinci0 \
--device=/dev/davinci1 \
--device=/dev/davinci2 \
--device=/dev/davinci3 \
--device=/dev/davinci4 \
--device=/dev/davinci5 \
--device=/dev/davinci6 \
--device=/dev/davinci7 \
--device=/dev/davinci_manager \
--device=/dev/hisi_hdc \
--device /dev/devmm_svm \
-v /usr/local/Ascend/driver:/usr/local/Ascend/driver \
-v /usr/local/Ascend/firmware:/usr/local/Ascend/firmware \
-v /usr/local/sbin/npu-smi:/usr/local/sbin/npu-smi \
-v /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/sbin \
-v /etc/hccn.conf:/etc/hccn.conf \
-v /root/models:/home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend \
mindie: 1.0.0-XXX-800I-A2-arm64-py3.11 (modified according to the name of the loaded image) \
bashIn this case, we use ModelScope to download the model, and install ModelScope first:
pip install modelscopeDownload the model:
# The model takes a long time to download and can be executed in the background
nohup modelscope download --model inclusionAI/Ling-plus --local_dir /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus 2>&1 > /tmp/ling_plus.log &
nohup modelscope download --model inclusionAI/Ling-plus-base --local_dir /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus_base 2>&1 > /tmp/ling_plus_base.log &
nohup modelscope download --model inclusionAI/Ling-lite --local_dir /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite 2>&1 > /tmp/ling_lite.log &
nohup modelscope download --model inclusionAI/Ling-lite-base --local_dir /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_base 2>&1 > /tmp/ling_lite_base.log &After the download is completed, you need to change the file permissions, otherwise an error will be reported when MindIE-Service is started:
chmod -R 750 *.json *.pyThis section applies to the Ling Lite model, the Ling Plus model does not need to worry about this chapter
mindie supports safetensors format weights, if the download weights are not in safetensors format, you need to convert the weights, take Ling Lite as an example, the conversion command is as follows:
# Convert Ling lite
python /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/convert_bin_to_safetensor.py
cd /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite
cp README.md configuration.json config.json special_tokens_map.json modeling_bailing_moe.py tokenizer.json tokenizer_config.json ../Ling_lite_safetensor/
# Convert Ling lite base
python /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/convert_bin_to_safetensor_base.py
cd /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_base
cp README.md configuration.json config.json special_tokens_map.json modeling_bailing_moe.py tokenizer.json tokenizer_config.json ../Ling_lite_base_safetensor/The path of loading the Ling Lite model is changed to '/home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_safetensor', and the path of the Ling Lite Base model is changed to '/home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_base_safetensor'
The default model configuration file (config.json) mindie cannot be loaded directly, and needs to be changed:
# Adapt to mindie's Ling lite model configuration
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_safetensor/config.json /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_safetensor/config.json.bak
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/lite/model_chat_config.json /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_safetensor/config.json
chmod 750 /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_safetensor/config.json
# Adapt to mindie's Ling lite base model configuration
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_base_safetensor/config.json /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_base_safetensor/config.json.bak
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/lite/model_base_config.json /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_base_safetensor/config.json
chmod 750 /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_lite_base_safetensor/config.json
# Adapt to mindie's Ling plus model configuration
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus/config.json /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus/config.json.bak
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/plus/model_chat_config.json /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus/config.json
chmod 750 /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus/config.json
# Adapt to mindie's Ling plus base model configuration
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus_base/config.json /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus_base/config.json.bak
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/plus/model_base_config.json /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus_base/config.json
chmod 750 /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling_plus_base/config.jsonExecute the shell script that adapts the mindie to the Ling model:
bash /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/patch_atb_llm.shSet the underlying environment variables:
source /usr/local/Ascend/atb-models/set_env.shSet different mindie configurations according to the model type:
# Ling Lite
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/lite/config.json /usr/local/Ascend/mindie/latest/mindie-service/conf/config.json
# Ling Lite base
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/lite/config.base.json /usr/local/Ascend/mindie/latest/mindie-service/conf/config.jsonStart the mindie service:
chmod 640 /usr/local/Ascend/mindie/latest/mindie-service/conf/config.json
cd $MIES_INSTALL_PATH
nohup ./bin/mindieservice_daemon > /tmp/service.log 2>&1 &Check /tmp/service.log to check whether the output is Daemon start success!, if so, it means that MindIE-Service has started successfully.
Test if the request is correct:
# Chat model
wget -O- --post-data="{\"messages\":[{\"role\": \"system\", \"content\": \"You are a helpful assistant.\"}, {\"role\": \"user\", \"content\": \"Who are you?\"}], \"stream\": false, \"max_tokens\":100, \"model\": \"bailing_moe\", \"temperature\":0}" \
--header='Content-Type:application/json' \
'http://127.0.0.1:1025/v1/chat/completions'
# base model
wget -O- --post-data='{"inputs":"My name is Olivier and I","stream":false,"parameters":{"temperature":1,"max_new_tokens":100,"do_sample":false}}' \
--header='Content-Type:application/json' \
'http://127.0.0.1:1025/infer'All of the following commands need to be executed simultaneously on all machines.
To enable multi-machine service-based inference, you need to configure a multi-machine ranktable file.
- Get the IP address of each card (on the host)
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -ip -g; done- Configure 'rank_table.json' in the following format and put it in '/root/models' so that it can be mounted to the container
{
"server_count": "...", # Total number of nodes
# The first server in the server_list is the primary node
"server_list": [
{
"device": [
{
"device_id": "...", # The number of the current card, the value range is [0, the number of cards in the machine)
"device_ip": "...", # The IP address of the current card, which can be obtained by hccn_tool command
"rank_id": "..." # The global number of the current card, the value range is [0, total number of cards)
},
...
],
"server_id": "...", # IP address of the current node
"container_ip": "..." # The IP address of the container (required for service-based deployment) is the same as that of the server_id unless otherwise configured
},
...
],
"status": "completed",
"version": "1.0"
}Enter the container and run the following command:
# Set the basic environment variables:
source /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/set_env.sh
# Enable communication environment variables
export ATB_LLM_HCCL_ENABLE=1
export ATB_LLM_COMM_BACKEND="hccl"
export HCCL_CONNECT_TIMEOUT=7200
export WORLD_SIZE=16
export HCCL_EXEC_TIMEOUT=0
# Configure virtual memory environment variables
export PYTORCH_NPU_ALLOC_CONF=expandable_segments:True #开启
# Fixed the issue of slow weight loading
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=1
export RANKTABLEFILE=/home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/rank_table.json
chmod 640 /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/rank_table.json
# To serve, you need to configure the 'container_ip' field in 'ranktable.json', and the configuration of all machines should be consistent, except for the MIES_CONTAINER_IP of the environment variable is the local IP address.
export MIES_CONTAINER_IP=IP address of the container
Set different mindie configurations according to the model type:
# Ling plus
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/plus/config.json /usr/local/Ascend/mindie/latest/mindie-service/conf/config.json
# Ling plus base
cp /home/HwHiAiUser/Ascend/Ling/inference/mindie/plus/config.base.json /usr/local/Ascend/mindie/latest/mindie-service/conf/config.jsonModify the servitization parameters:
cd /usr/local/Ascend/mindie/latest/mindie-service/
vim conf/config.json
# The following configurations need to be changed
# "ipAddress" : "Change to primary node IP",
# "managementIpAddress" : "Change to primary node IP",To set the memory usage ratio:
export NPU_MEMORY_FRACTION=0.95Pull up servitization:
cd $MIES_INSTALL_PATH
nohup ./bin/mindieservice_daemon > /tmp/service.log 2>&1 &When the command is executed, all the parameters used for this startup are first printed, and then until the following output appears:
Daemon start success!
The service is considered to have started successfully.
Test if the request is correct:
# Chat model
wget -O- --post-data="{\"messages\":[{\"role\": \"system\", \"content\": \"You are a helpful assistant.\"}, {\"role\": \"user\", \"content\": \"Who are you?\"}], \"stream\": false, \"max_tokens\":100, \"model\": \"bailing_moe\", \"temperature\":0}" \
--header='Content-Type:application/json' \
'http://<Change to primary node IP>:1025/v1/chat/completions'
# base model
wget -O- --post-data='{"inputs":"My name is Olivier and I","stream":false,"parameters":{"temperature":1,"max_new_tokens":100,"do_sample":false}}' \
--header='Content-Type:application/json' \
'http://<Change to primary node IP>:1025/infer'
We recommend you to use Llama-Factory to finetune Ling with SFT, DPO, etc.
We use identity to demonstrate how to finetune our Ling models by replacing name with Ling and author with inclusionAI.
{
"instruction": "hi",
"input": "",
"output": "Hello! I am Ling, an AI assistant developed by inclusionAI. How can I assist you today?"
}We provide a demo configuration of Llama-Factory to SFT Ling models as follows:
llamafactory-cli train examples/sft/ling_full_sft.yamlThis code repository is licensed under the MIT License.
[TBD]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Ling
Similar Open Source Tools

Ling
Ling is a MoE LLM provided and open-sourced by InclusionAI. It includes two different sizes, Ling-Lite with 16.8 billion parameters and Ling-Plus with 290 billion parameters. These models show impressive performance and scalability for various tasks, from natural language processing to complex problem-solving. The open-source nature of Ling encourages collaboration and innovation within the AI community, leading to rapid advancements and improvements. Users can download the models from Hugging Face and ModelScope for different use cases. Ling also supports offline batched inference and online API services for deployment. Additionally, users can fine-tune Ling models using Llama-Factory for tasks like SFT and DPO.
ai00_server
AI00 RWKV Server is an inference API server for the RWKV language model based upon the web-rwkv inference engine. It supports VULKAN parallel and concurrent batched inference and can run on all GPUs that support VULKAN. No need for Nvidia cards!!! AMD cards and even integrated graphics can be accelerated!!! No need for bulky pytorch, CUDA and other runtime environments, it's compact and ready to use out of the box! Compatible with OpenAI's ChatGPT API interface. 100% open source and commercially usable, under the MIT license. If you are looking for a fast, efficient, and easy-to-use LLM API server, then AI00 RWKV Server is your best choice. It can be used for various tasks, including chatbots, text generation, translation, and Q&A.
onnxruntime-server
ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference. It aims to offer simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience. Users can provide inference APIs for ONNX models without writing additional code by placing the models in the directory structure. Each session can choose between CPU or CUDA, analyze input/output, and provide Swagger API documentation for easy testing. Ready-to-run Docker images are available, making it convenient to deploy the server.
ai-toolkit
The AI Toolkit by Ostris is a collection of tools for machine learning, specifically designed for image generation, LoRA (latent representations of attributes) extraction and manipulation, and model training. It provides a user-friendly interface and extensive documentation to make it accessible to both developers and non-developers. The toolkit is actively under development, with new features and improvements being added regularly. Some of the key features of the AI Toolkit include: - Batch Image Generation: Allows users to generate a batch of images based on prompts or text files, using a configuration file to specify the desired settings. - LoRA (lierla), LoCON (LyCORIS) Extractor: Facilitates the extraction of LoRA and LoCON representations from pre-trained models, enabling users to modify and manipulate these representations for various purposes. - LoRA Rescale: Provides a tool to rescale LoRA weights, allowing users to adjust the influence of specific attributes in the generated images. - LoRA Slider Trainer: Enables the training of LoRA sliders, which can be used to control and adjust specific attributes in the generated images, offering a powerful tool for fine-tuning and customization. - Extensions: Supports the creation and sharing of custom extensions, allowing users to extend the functionality of the toolkit with their own tools and scripts. - VAE (Variational Auto Encoder) Trainer: Facilitates the training of VAEs for image generation, providing users with a tool to explore and improve the quality of generated images. The AI Toolkit is a valuable resource for anyone interested in exploring and utilizing machine learning for image generation and manipulation. Its user-friendly interface, extensive documentation, and active development make it an accessible and powerful tool for both beginners and experienced users.
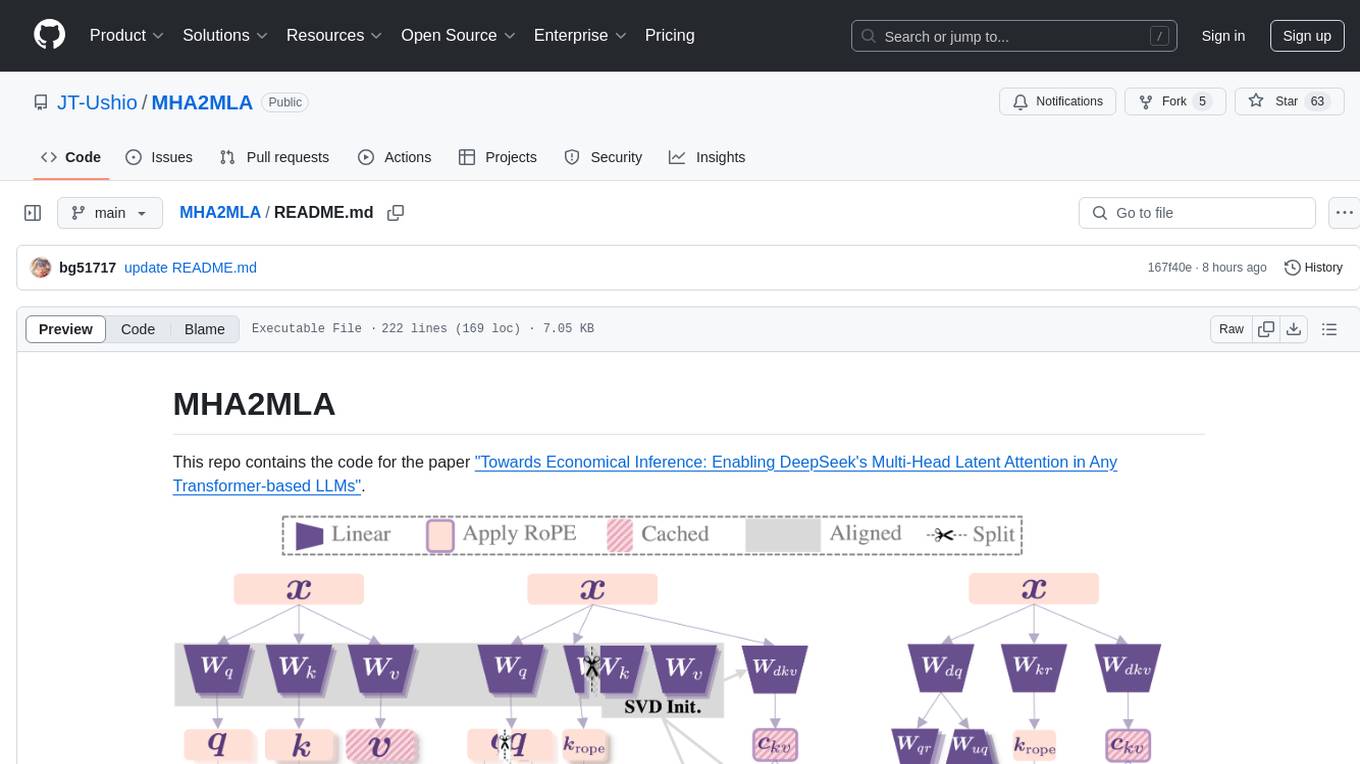
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
candle-vllm
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.
infinity
Infinity is a high-throughput, low-latency REST API for serving vector embeddings, supporting all sentence-transformer models and frameworks. It is developed under the MIT License and powers inference behind Gradient.ai. The API allows users to deploy models from SentenceTransformers, offers fast inference backends utilizing various accelerators, dynamic batching for efficient processing, correct and tested implementation, and easy-to-use API built on FastAPI with Swagger documentation. Users can embed text, rerank documents, and perform text classification tasks using the tool. Infinity supports various models from Huggingface and provides flexibility in deployment via CLI, Docker, Python API, and cloud services like dstack. The tool is suitable for tasks like embedding, reranking, and text classification.
VLM-R1
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.
TheoremExplainAgent
TheoremExplainAgent is an AI system that generates long-form Manim videos to visually explain theorems, proving its deep understanding while uncovering reasoning flaws that text alone often hides. The codebase for the paper 'TheoremExplainAgent: Towards Multimodal Explanations for LLM Theorem Understanding' is available in this repository. It provides a tool for creating multimodal explanations for theorem understanding using AI technology.
LocalAGI
LocalAGI is a powerful, self-hostable AI Agent platform that allows you to design AI automations without writing code. It provides a complete drop-in replacement for OpenAI's Responses APIs with advanced agentic capabilities. With LocalAGI, you can create customizable AI assistants, automations, chat bots, and agents that run 100% locally, without the need for cloud services or API keys. The platform offers features like no-code agents, web-based interface, advanced agent teaming, connectors for various platforms, comprehensive REST API, short & long-term memory capabilities, planning & reasoning, periodic tasks scheduling, memory management, multimodal support, extensible custom actions, fully customizable models, observability, and more.
client-ts
Mistral Typescript Client is an SDK for Mistral AI API, providing Chat Completion and Embeddings APIs. It allows users to create chat completions, upload files, create agent completions, create embedding requests, and more. The SDK supports various JavaScript runtimes and provides detailed documentation on installation, requirements, API key setup, example usage, error handling, server selection, custom HTTP client, authentication, providers support, standalone functions, debugging, and contributions.
mistral-inference
Mistral Inference repository contains minimal code to run 7B, 8x7B, and 8x22B models. It provides model download links, installation instructions, and usage guidelines for running models via CLI or Python. The repository also includes information on guardrailing, model platforms, deployment, and references. Users can interact with models through commands like mistral-demo, mistral-chat, and mistral-common. Mistral AI models support function calling and chat interactions for tasks like testing models, chatting with models, and using Codestral as a coding assistant. The repository offers detailed documentation and links to blogs for further information.
agentops
AgentOps is a toolkit for evaluating and developing robust and reliable AI agents. It provides benchmarks, observability, and replay analytics to help developers build better agents. AgentOps is open beta and can be signed up for here. Key features of AgentOps include: - Session replays in 3 lines of code: Initialize the AgentOps client and automatically get analytics on every LLM call. - Time travel debugging: (coming soon!) - Agent Arena: (coming soon!) - Callback handlers: AgentOps works seamlessly with applications built using Langchain and LlamaIndex.
evalscope
Eval-Scope is a framework designed to support the evaluation of large language models (LLMs) by providing pre-configured benchmark datasets, common evaluation metrics, model integration, automatic evaluation for objective questions, complex task evaluation using expert models, reports generation, visualization tools, and model inference performance evaluation. It is lightweight, easy to customize, supports new dataset integration, model hosting on ModelScope, deployment of locally hosted models, and rich evaluation metrics. Eval-Scope also supports various evaluation modes like single mode, pairwise-baseline mode, and pairwise (all) mode, making it suitable for assessing and improving LLMs.
AnglE
AnglE is a library for training state-of-the-art BERT/LLM-based sentence embeddings with just a few lines of code. It also serves as a general sentence embedding inference framework, allowing for inferring a variety of transformer-based sentence embeddings. The library supports various loss functions such as AnglE loss, Contrastive loss, CoSENT loss, and Espresso loss. It provides backbones like BERT-based models, LLM-based models, and Bi-directional LLM-based models for training on single or multi-GPU setups. AnglE has achieved significant performance on various benchmarks and offers official pretrained models for both BERT-based and LLM-based models.
For similar tasks
cuckoo
Cuckoo is a Decentralized AI Platform that focuses on GPU-sharing for text-to-image generation and LLM inference. It provides a platform for users to generate images using Telegram or Discord.

Ling
Ling is a MoE LLM provided and open-sourced by InclusionAI. It includes two different sizes, Ling-Lite with 16.8 billion parameters and Ling-Plus with 290 billion parameters. These models show impressive performance and scalability for various tasks, from natural language processing to complex problem-solving. The open-source nature of Ling encourages collaboration and innovation within the AI community, leading to rapid advancements and improvements. Users can download the models from Hugging Face and ModelScope for different use cases. Ling also supports offline batched inference and online API services for deployment. Additionally, users can fine-tune Ling models using Llama-Factory for tasks like SFT and DPO.

langbase-examples
Langbase Examples is an open-source repository showcasing projects built using Langbase, a composable AI infrastructure for creating and deploying AI agents with hyper-personalized memory. Langbase offers AI Pipes for building custom AI agents as APIs and Memory (RAG) for managed search engine capabilities. The platform also includes AI Studio for collaboration and deployment of AI projects, providing a complete AI developer platform for teams to work together on building and deploying AI features.

director
Director is a context infrastructure tool for AI agents that simplifies managing MCP servers, prompts, and configurations by packaging them into portable workspaces accessible through a single endpoint. It allows users to define context workspaces once and share them across different AI clients, enabling seamless collaboration, instant context switching, and secure isolation of untrusted servers without cloud dependencies or API keys. Director offers features like workspaces, universal portability, local-first architecture, sandboxing, smart filtering, unified OAuth, observability, multiple interfaces, and compatibility with all MCP clients and servers.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

ray
Ray is a unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications. It consists of a core distributed runtime and a set of AI libraries for simplifying ML compute, including Data, Train, Tune, RLlib, and Serve. Ray runs on any machine, cluster, cloud provider, and Kubernetes, and features a growing ecosystem of community integrations. With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster, making it easy to meet the compute-intensive demands of modern ML workloads.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.

djl
Deep Java Library (DJL) is an open-source, high-level, engine-agnostic Java framework for deep learning. It is designed to be easy to get started with and simple to use for Java developers. DJL provides a native Java development experience and allows users to integrate machine learning and deep learning models with their Java applications. The framework is deep learning engine agnostic, enabling users to switch engines at any point for optimal performance. DJL's ergonomic API interface guides users with best practices to accomplish deep learning tasks, such as running inference and training neural networks.
For similar jobs
ludwig
Ludwig is a declarative deep learning framework designed for scale and efficiency. It is a low-code framework that allows users to build custom AI models like LLMs and other deep neural networks with ease. Ludwig offers features such as optimized scale and efficiency, expert level control, modularity, and extensibility. It is engineered for production with prebuilt Docker containers, support for running with Ray on Kubernetes, and the ability to export models to Torchscript and Triton. Ludwig is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.
wenda
Wenda is a platform for large-scale language model invocation designed to efficiently generate content for specific environments, considering the limitations of personal and small business computing resources, as well as knowledge security and privacy issues. The platform integrates capabilities such as knowledge base integration, multiple large language models for offline deployment, auto scripts for additional functionality, and other practical capabilities like conversation history management and multi-user simultaneous usage.
LLMonFHIR
LLMonFHIR is an iOS application that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to interpret and provide context around patient data in the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. It connects to the OpenAI GPT API to analyze FHIR resources, supports multiple languages, and allows users to interact with their health data stored in the Apple Health app. The app aims to simplify complex health records, provide insights, and facilitate deeper understanding through a conversational interface. However, it is an experimental app for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Users are advised to verify information provided by AI models and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.

Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B
Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B is an open-source project based on Mistral's Mixtral-8x7B model for incremental pre-training of Chinese vocabulary, aiming to advance research on MoE models in the Chinese natural language processing community. The expanded vocabulary significantly improves the model's encoding and decoding efficiency for Chinese, and the model is pre-trained incrementally on a large-scale open-source corpus, enabling it with powerful Chinese generation and comprehension capabilities. The project includes a large model with expanded Chinese vocabulary and incremental pre-training code.
AI-Horde-Worker
AI-Horde-Worker is a repository containing the original reference implementation for a worker that turns your graphics card(s) into a worker for the AI Horde. It allows users to generate or alchemize images for others. The repository provides instructions for setting up the worker on Windows and Linux, updating the worker code, running with multiple GPUs, and stopping the worker. Users can configure the worker using a WebUI to connect to the horde with their username and API key. The repository also includes information on model usage and running the Docker container with specified environment variables.
openshield
OpenShield is a firewall designed for AI models to protect against various attacks such as prompt injection, insecure output handling, training data poisoning, model denial of service, supply chain vulnerabilities, sensitive information disclosure, insecure plugin design, excessive agency granting, overreliance, and model theft. It provides rate limiting, content filtering, and keyword filtering for AI models. The tool acts as a transparent proxy between AI models and clients, allowing users to set custom rate limits for OpenAI endpoints and perform tokenizer calculations for OpenAI models. OpenShield also supports Python and LLM based rules, with upcoming features including rate limiting per user and model, prompts manager, content filtering, keyword filtering based on LLM/Vector models, OpenMeter integration, and VectorDB integration. The tool requires an OpenAI API key, Postgres, and Redis for operation.
VoAPI
VoAPI is a new high-value/high-performance AI model interface management and distribution system. It is a closed-source tool for personal learning use only, not for commercial purposes. Users must comply with upstream AI model service providers and legal regulations. The system offers a visually appealing interface, independent development documentation page support, service monitoring page configuration support, and third-party login support. It also optimizes interface elements, user registration time support, data operation button positioning, and more.
VoAPI
VoAPI is a new high-value/high-performance AI model interface management and distribution system. It is a closed-source tool for personal learning use only, not for commercial purposes. Users must comply with upstream AI model service providers and legal regulations. The system offers a visually appealing interface with features such as independent development documentation page support, service monitoring page configuration support, and third-party login support. Users can manage user registration time, optimize interface elements, and support features like online recharge, model pricing display, and sensitive word filtering. VoAPI also provides support for various AI models and platforms, with the ability to configure homepage templates, model information, and manufacturer information.