
MHA2MLA
Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs
Stars: 145
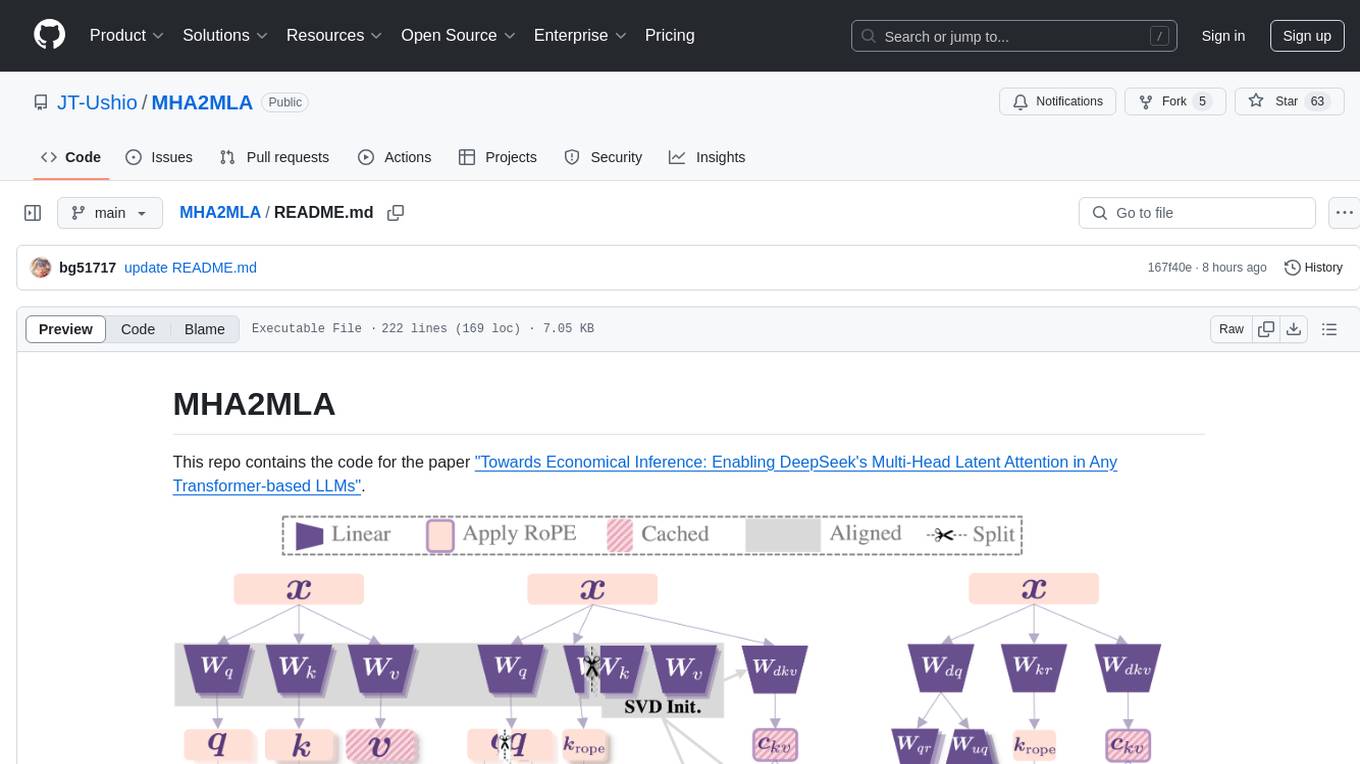
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
README:
This repo contains the code for the paper "Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs".
- [2025.03.12] Released the inference code implemented using PyTorch (support for FlashMLA inference requires additional development time).
- [2025.03.04] The four MLA checkpoints ($d_{kv}$=8/16/32/128) derived from
SmolLM-135M/360M/1B7are publicly available. - [2025.03.03] The four MLA checkpoints ($d_{kv}$=16/32/64/256) derived from
Llama-2-7Bare publicly available. - [2025.02.21] The paper of MHA2MLA is publicly available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.14837
- [2025.02.19] Released the first version of the MHA2MLA code, providing usage code for Llama fine-tuning and evaluating.
- [ ]
Provide the code for incorporating the projection matrix and inference. - [ ] Thanks to DeepSeek for open-sourcing the FlashMLA inference framework. It’s theoretically possible to save more GPU memory usage using this framework. Let’s see how economical MHA2MLA + FlashMLA (+ KV quanto) can be!
- [x] Release the code of MHA2MLA based on HuggingFace
Transformers
- SmolLM: https://huggingface.co/blog/smollm
- Llama-2-7b-hf: https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf
First download the datasets.
- smollm-corpus(fineweb-edu-dedup, cosmopedia-v2, python-edu): https://huggingface.co/datasets/HuggingFaceTB/smollm-corpus
- open-web-math: https://huggingface.co/datasets/open-web-math/open-web-math
- stackoverflow: https://huggingface.co/datasets/bigcode/stackoverflow-clean
Secondly, process the datasets according to https://github.com/huggingface/nanotron/blob/main/docs/nanoset.md.
Install pytorch and other packages.
conda create -n mla-ft python=3.11
pip install torch==2.4.0 torchvision==0.19.0
pip install -r requirements.txtThe research presented in our paper was conducted using nanotron framework. Since there are differences between
transformersandnanotron, hyperparameter search might be necessary. For exact reproduction of the paper's results, we recommend using nanotron for fine tuneing which refer to Our README for MHA2MLA using nanotron.
First, prepare three configuration files:
- A general configuration file referencing 135M_4GPU.yaml
- A partial-RoPE configuration file referencing rope_v4_topk4.yaml
- A SVD configuration file referencing svd_method7_rank8.yaml
The available strategies for each method are listed below:
| Partial-RoPE version | Strategy |
|---|---|
| 0 | full-RoPE |
| 1 | $\mathcal{S}_{\text{high}}$ |
| 2 | $\mathcal{S}_{\text{uniform}}$ |
| 4 | $\mathcal{S}_{\text{2-norm}}$ |
| 5 | $\mathcal{S}_{\text{low}}$ |
| SVD version | Strategy |
|---|---|
| 2 | $SVD_{split}$ |
| 7 | $SVD_{joint}$ |
Then, use the following command for MLA fine-tuning:
torchrun --nproc_per_node 4 \
../src/mha2mla/run_train.py \
--config_file ../configs_hf/rope/135M_4GPU.yaml \
--partial_rope_config ../configs_hf/rope/rope_v4_topk4.yaml \
--svd_config ../configs_hf/rope/svd_method7_rank8.yamlIf you want to use the partial-RoPE version 4, you should get the
qk_tensorfirst. Using the following command, you can get theqk_tensor:torchrun --nproc_per_node 1 \ ../src/mha2mla/2_norm.py \ --config_file ../configs_hf/rope/135M_4GPU.yaml \ --output_dir ./qk_tensor_hf_test.pth \ --sample_size 1024
For the MLA evaluation, you can use the following command:
accelerate launch --multi_gpu --num_processes=4 \
../src/mha2mla/eval.py --is_mla \
accelerate \
--model_args "pretrained=${model_name_or_path},revision=main,dtype=bfloat16,max_length=2048" \
--override_batch_size 48 \
--custom_tasks "../src/mha2mla/tasks.py" \
--tasks "../src/mha2mla/smollm1_base.txt" \
--output_dir "../eval_results/"If you want to evaluate the
partial_ropeckpt withoutlow rank approx, you should change--is_mlato--is_partial_rope.
For the baseline evaluation, you can use the following command:
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 \
../src/mha2mla/longbench.py \
--model_path ${model_name_or_path} \
--tokenizer_path ${model_name_or_path} \
--longbench True \
--lb_max_tokens 2048 \
--lb_batch_size 16 \
--output_dir /longbench/bf16 \
--dtype "bfloat16"For the MLA model, you should add the parameter --is_mla to the command.
If you want to use the quantized KV cache, you can use the following command:
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 \
../src/mha2mla/longbench.py \
--model_path ${model_name_or_path} \
--tokenizer_path ${model_name_or_path} \
--longbench True \
--lb_max_tokens 2048 \
--lb_batch_size 16 \
--output_dir /longbench/${model_name_or_path}_hqq_int4 \
--dtype "bfloat16" \
--cache_implementation "quantized" \
--backend "HQQ" \
--nbits 4 \
--residual_length 128 \- Step 1: Download the monkey patch file.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JT-Ushio/MHA2MLA/refs/heads/main/src/mha2mla/monkey_patch.py- Step 2(Option): For MHA2MLA models using Partial-RoPE 2-nrom method, Download the qk_2-norm file.
Take
qk_tensor_1.7B.pthas an example:
wget https://github.com/JT-Ushio/MHA2MLA/raw/refs/heads/main/utils/qk_tensor_1.7B.pth- Step 3: Download the MHA2MLA models and run inference.
Take
fnlp/SmolLM-1B7-MLA-d_kv_16as an example:
import torch
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoTokenizer, LlamaForCausalLM
from monkey_patch import infer_monkey_patch
model_name = "fnlp/SmolLM-1B7-MLA-d_kv_16"
# Monkey Patch: MHA -> MLA
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_name)
if "RoPE" in config:
config.RoPE["qk_tensor_path"] = "qk_tensor_1.7B.pth" # Configuration for Specific Models
infer_monkey_patch(config.RoPE)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, config=config, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).cuda()
# Generate
text = "Which American-born Sinclair won the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1930?"
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
generation_kwargs = {"do_sample": False, "use_cache": True, "max_new_tokens": 128}
output = model.generate(**inputs, **generation_kwargs)
print(tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
# - Sinclair Lewis@misc{ji2025economicalinferenceenablingdeepseeks,
title={Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs},
author={Tao Ji and Bin Guo and Yuanbin Wu and Qipeng Guo and Lixing Shen and Zhan Chen and Xipeng Qiu and Qi Zhang and Tao Gui},
year={2025},
eprint={2502.14837},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.14837},
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for MHA2MLA
Similar Open Source Tools

MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
rank_llm
RankLLM is a suite of prompt-decoders compatible with open source LLMs like Vicuna and Zephyr. It allows users to create custom ranking models for various NLP tasks, such as document reranking, question answering, and summarization. The tool offers a variety of features, including the ability to fine-tune models on custom datasets, use different retrieval methods, and control the context size and variable passages. RankLLM is easy to use and can be integrated into existing NLP pipelines.
VLM-R1
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.
dspy.rb
DSPy.rb is a Ruby framework for building reliable LLM applications using composable, type-safe modules. It enables developers to define typed signatures and compose them into pipelines, offering a more structured approach compared to traditional prompting. The framework embraces Ruby conventions and adds innovations like CodeAct agents and enhanced production instrumentation, resulting in scalable LLM applications that are robust and efficient. DSPy.rb is actively developed, with a focus on stability and real-world feedback through the 0.x series before reaching a stable v1.0 API.

starcoder2-self-align
StarCoder2-Instruct is an open-source pipeline that introduces StarCoder2-15B-Instruct-v0.1, a self-aligned code Large Language Model (LLM) trained with a fully permissive and transparent pipeline. It generates instruction-response pairs to fine-tune StarCoder-15B without human annotations or data from proprietary LLMs. The tool is primarily finetuned for Python code generation tasks that can be verified through execution, with potential biases and limitations. Users can provide response prefixes or one-shot examples to guide the model's output. The model may have limitations with other programming languages and out-of-domain coding tasks.
candle-vllm
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.

CodeTF
CodeTF is a Python transformer-based library for code large language models (Code LLMs) and code intelligence. It provides an interface for training and inferencing on tasks like code summarization, translation, and generation. The library offers utilities for code manipulation across various languages, including easy extraction of code attributes. Using tree-sitter as its core AST parser, CodeTF enables parsing of function names, comments, and variable names. It supports fast model serving, fine-tuning of LLMs, various code intelligence tasks, preprocessed datasets, model evaluation, pretrained and fine-tuned models, and utilities to manipulate source code. CodeTF aims to facilitate the integration of state-of-the-art Code LLMs into real-world applications, ensuring a user-friendly environment for code intelligence tasks.
AnglE
AnglE is a library for training state-of-the-art BERT/LLM-based sentence embeddings with just a few lines of code. It also serves as a general sentence embedding inference framework, allowing for inferring a variety of transformer-based sentence embeddings. The library supports various loss functions such as AnglE loss, Contrastive loss, CoSENT loss, and Espresso loss. It provides backbones like BERT-based models, LLM-based models, and Bi-directional LLM-based models for training on single or multi-GPU setups. AnglE has achieved significant performance on various benchmarks and offers official pretrained models for both BERT-based and LLM-based models.
Tutel
Tutel MoE is an optimized Mixture-of-Experts implementation that offers a parallel solution with 'No-penalty Parallism/Sparsity/Capacity/Switching' for modern training and inference. It supports Pytorch framework (version >= 1.10) and various GPUs including CUDA and ROCm. The tool enables Full Precision Inference of MoE-based Deepseek R1 671B on AMD MI300. Tutel provides features like all-to-all benchmarking, tensorcore option, NCCL timeout settings, Megablocks solution, and dynamic switchable configurations. Users can run Tutel in distributed mode across multiple GPUs and machines. The tool allows for custom MoE implementations and offers detailed usage examples and reference documentation.
repomix
Repomix is a powerful tool that packs your entire repository into a single, AI-friendly file. It is designed to format your codebase for easy understanding by AI tools like Large Language Models (LLMs), Claude, ChatGPT, and Gemini. Repomix offers features such as AI optimization, token counting, simplicity in usage, customization options, Git awareness, and security-focused checks using Secretlint. It allows users to pack their entire repository or specific directories/files using glob patterns, and even supports processing remote Git repositories. The tool generates output in plain text, XML, or Markdown formats, with options for including/excluding files, removing comments, and performing security checks. Repomix also provides a global configuration option, custom instructions for AI context, and a security check feature to detect sensitive information in files.
LocalAGI
LocalAGI is a powerful, self-hostable AI Agent platform that allows you to design AI automations without writing code. It provides a complete drop-in replacement for OpenAI's Responses APIs with advanced agentic capabilities. With LocalAGI, you can create customizable AI assistants, automations, chat bots, and agents that run 100% locally, without the need for cloud services or API keys. The platform offers features like no-code agents, web-based interface, advanced agent teaming, connectors for various platforms, comprehensive REST API, short & long-term memory capabilities, planning & reasoning, periodic tasks scheduling, memory management, multimodal support, extensible custom actions, fully customizable models, observability, and more.
ScaleLLM
ScaleLLM is a cutting-edge inference system engineered for large language models (LLMs), meticulously designed to meet the demands of production environments. It extends its support to a wide range of popular open-source models, including Llama3, Gemma, Bloom, GPT-NeoX, and more. ScaleLLM is currently undergoing active development. We are fully committed to consistently enhancing its efficiency while also incorporating additional features. Feel free to explore our **_Roadmap_** for more details. ## Key Features * High Efficiency: Excels in high-performance LLM inference, leveraging state-of-the-art techniques and technologies like Flash Attention, Paged Attention, Continuous batching, and more. * Tensor Parallelism: Utilizes tensor parallelism for efficient model execution. * OpenAI-compatible API: An efficient golang rest api server that compatible with OpenAI. * Huggingface models: Seamless integration with most popular HF models, supporting safetensors. * Customizable: Offers flexibility for customization to meet your specific needs, and provides an easy way to add new models. * Production Ready: Engineered with production environments in mind, ScaleLLM is equipped with robust system monitoring and management features to ensure a seamless deployment experience.
onnxruntime-server
ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference. It aims to offer simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience. Users can provide inference APIs for ONNX models without writing additional code by placing the models in the directory structure. Each session can choose between CPU or CUDA, analyze input/output, and provide Swagger API documentation for easy testing. Ready-to-run Docker images are available, making it convenient to deploy the server.
FDAbench
FDABench is a benchmark tool designed for evaluating data agents' reasoning ability over heterogeneous data in analytical scenarios. It offers 2,007 tasks across various data sources, domains, difficulty levels, and task types. The tool provides ready-to-use data agent implementations, a DAG-based evaluation system, and a framework for agent-expert collaboration in dataset generation. Key features include data agent implementations, comprehensive evaluation metrics, multi-database support, different task types, extensible framework for custom agent integration, and cost tracking. Users can set up the environment using Python 3.10+ on Linux, macOS, or Windows. FDABench can be installed with a one-command setup or manually. The tool supports API configuration for LLM access and offers quick start guides for database download, dataset loading, and running examples. It also includes features like dataset generation using the PUDDING framework, custom agent integration, evaluation metrics like accuracy and rubric score, and a directory structure for easy navigation.
docutranslate
Docutranslate is a versatile tool for translating documents efficiently. It supports multiple file formats and languages, making it ideal for businesses and individuals needing quick and accurate translations. The tool uses advanced algorithms to ensure high-quality translations while maintaining the original document's formatting. With its user-friendly interface, Docutranslate simplifies the translation process and saves time for users. Whether you need to translate legal documents, technical manuals, or personal letters, Docutranslate is the go-to solution for all your document translation needs.
libllm
libLLM is an open-source project designed for efficient inference of large language models (LLM) on personal computers and mobile devices. It is optimized to run smoothly on common devices, written in C++14 without external dependencies, and supports CUDA for accelerated inference. Users can build the tool for CPU only or with CUDA support, and run libLLM from the command line. Additionally, there are API examples available for Python and the tool can export Huggingface models.
For similar tasks
Ollama-Colab-Integration
Ollama Colab Integration V4 is a tool designed to enhance the interaction and management of large language models. It allows users to quantize models within their notebook environment, access a variety of models through a user-friendly interface, and manage public endpoints efficiently. The tool also provides features like LiteLLM proxy control, model insights, and customizable model file templating. Users can troubleshoot model loading issues, CPU fallback strategies, and manage VRAM and RAM effectively. Additionally, the tool offers functionalities for downloading model files from Hugging Face, model conversion with high precision, model quantization using Q and Kquants, and securely uploading converted models to Hugging Face.
rknn-llm
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.
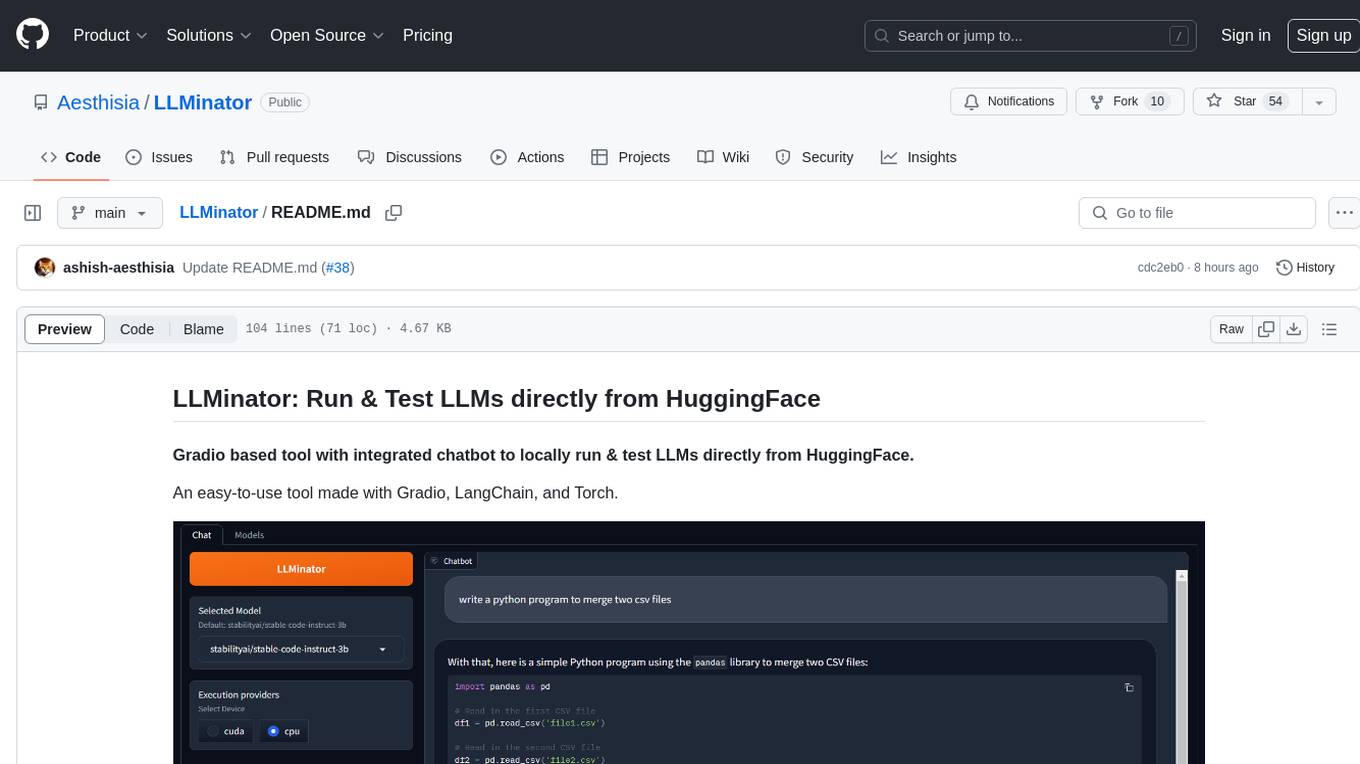
LLMinator
LLMinator is a Gradio-based tool with an integrated chatbot designed to locally run and test Language Model Models (LLMs) directly from HuggingFace. It provides an easy-to-use interface made with Gradio, LangChain, and Torch, offering features such as context-aware streaming chatbot, inbuilt code syntax highlighting, loading any LLM repo from HuggingFace, support for both CPU and CUDA modes, enabling LLM inference with llama.cpp, and model conversion capabilities.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
BodhiApp
Bodhi App runs Open Source Large Language Models locally, exposing LLM inference capabilities as OpenAI API compatible REST APIs. It leverages llama.cpp for GGUF format models and huggingface.co ecosystem for model downloads. Users can run fine-tuned models for chat completions, create custom aliases, and convert Huggingface models to GGUF format. The CLI offers commands for environment configuration, model management, pulling files, serving API, and more.
lm.rs
lm.rs is a tool that allows users to run inference on Language Models locally on the CPU using Rust. It supports LLama3.2 1B and 3B models, with a WebUI also available. The tool provides benchmarks and download links for models and tokenizers, with recommendations for quantization options. Users can convert models from Google/Meta on huggingface using provided scripts. The tool can be compiled with cargo and run with various arguments for model weights, tokenizer, temperature, and more. Additionally, a backend for the WebUI can be compiled and run to connect via the web interface.
LiteRT
LiteRT is Google's open-source high-performance runtime for on-device AI, previously known as TensorFlow Lite. The repository is currently not intended for open-source development, but aims to evolve to allow direct building and contributions. LiteRT supports Python versions 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 on Linux and MacOS. It ensures compatibility with existing .tflite file extension and format, offering conversion tools and continued active development under the name LiteRT.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
