UMbreLLa
LLM Inference on consumer devices
Stars: 94
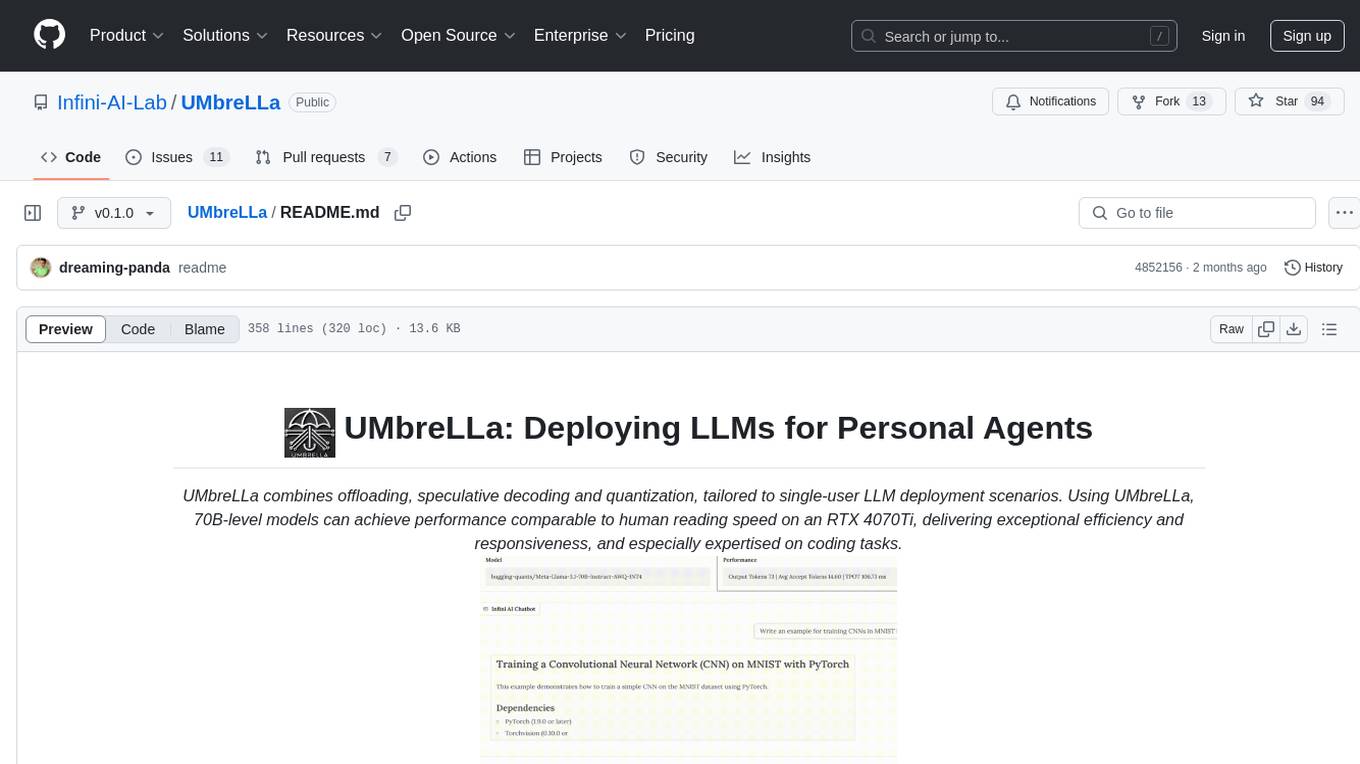
UMbreLLa is a tool designed for deploying Large Language Models (LLMs) for personal agents. It combines offloading, speculative decoding, and quantization to optimize single-user LLM deployment scenarios. With UMbreLLa, 70B-level models can achieve performance comparable to human reading speed on an RTX 4070Ti, delivering exceptional efficiency and responsiveness, especially for coding tasks. The tool supports deploying models on various GPUs and offers features like code completion and CLI/Gradio chatbots. Users can configure the LLM engine for optimal performance based on their hardware setup.
README:
The throughput is measured with a batch size of 1 to directly mirror the user experience.
| GPU | Model | Draft | Throughput (tokens/sec) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stochastic | Greedy | |||
| RTX 4090 | Llama3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | 7.2 | 8.6 |
| Llama3.3-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | 7.0 | 7.4 | |
| Llama3.1-8B-Instruct | Llama3.2-1B-Instruct | 100.7 | 108.1 | |
| RTX 4080 SUPER | Llama3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | 7.4 | 8.4 |
| Llama3.3-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | 6.7 | 7.2 | |
| RTX 4070 Ti | Llama3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.2-1B-Instruct | 5.5 | 6.1 |
| Llama3.3-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.2-1B-Instruct | 5.2 | 5.5 | |
| L40 | Llama3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.2-1B-Instruct | 37.0 | 38.5 |
| Llama3.3-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.2-1B-Instruct | 36.3 | 37.1 | |
Evaluated on ananyarn/Algorithm_and_Python_Source_Code.
| GPU | Model | Draft | Throughput (tokens/sec) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RTX 4090 | Llama3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | 11.4 |
| Llama3.3-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | 11.2 | |
| Llama3.1-8B-Instruct | CodeDrafter-500M | 174.8 | |
| RTX 4080 SUPER | Llama3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | 12.2 |
| Llama3.3-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | 12.1 | |
| Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | CodeDrafter-500M | 195.3 | |
| RTX 4070 Ti | Llama3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.2-1B-Instruct | 9.7 |
| Llama3.3-70B-Instruct-AWQ | Llama3.2-1B-Instruct | 9.6 | |
| Llama3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ | CodeDrafter-500M | 162.3 | |
| L40 | Llama3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ | CodeDrafter-500M | 45.6 |
| Llama3.3-70B-Instruct-AWQ | CodeDrafter-500M | 45.0 |
Offloading experiments heavily rely on the status of PCIE, and may vary across instances.
❌ UMbreLLa is not designed for large-scale LLM serving.
conda create -n umbrella python=3.10
bash install.shcd app
python chatbot.py --configuration ../configs/chat_config_24gb.jsonThen you can chat with the LLM specified in chat_config_24gb.json.
cd app
python gradio_chat.py --configuration ../configs/chat_config_24gb.jsonThen you can chat with the LLM specified in chat_config_24gb.json in Gradio.
cd app
python api.py --configuration ../configs/chat_config_24gb.json --max_client 1 --port 65432configuration specifies the LLM and speculative decoding details.
max_client is the maximum clients that can connect to the server.
port is the port of the server.
After the server is started, Client can be started and connect to the server by
from umbrella.api.client import APIClient
client = APIClient(port=port) #port should be the same as the server
client.run()To get the LLM output,
input1 = {"context": text1, "max_new_tokens": 512, "temperature": 0.0}
output1 = client.get_output(**input1){
"model": "hugging-quants/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ-INT4",
"draft_model": "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct",
"offload": true,
"cuda_graph": false,
"max_length": 4096,
"num_cache_layers": 0,
"generation_length": 256,
"max_turns": 12,
"topk": 32,
"temperature": 0.6,
"topp": 0.9,
"repetition_penalty": 1.05,
"growmap_path": "../umbrella/trees/sequoia_tree-3x4.json",
"width": 16,
"num_beams": 24,
"depth": 16,
"engine": "dynamic",
"template": "meta-llama3"
}-
model: Specifies the target LLM to serve, e.g.,
"hugging-quants/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-AWQ-INT4". -
draft_model: Lightweight draft model, e.g.,
"meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct". -
offload: Enables offloading of the target model to host memory or disk (
trueorfalse). - cuda_graph: Toggles CUDA graph optimization for the draft model (currently unsupported for AWQ models).
- max_length: The maximum token length for input and output combined.
- num_cache_layers: Sets the number of layers cached during inference (e.g., for memory optimization).
- generation_length: Maximum length of generated responses in tokens.
- max_turns: Limits the number of conversational turns retained in memory.
-
topk: Limits token selection during generation to the top
kmost likely tokens. - temperature: Controls randomness in token selection (lower values = more deterministic outputs).
-
topp: Enables nucleus sampling by limiting token selection to those with cumulative probability ≤
p. - repetition_penalty: Penalizes repetitive text generation (values > 1 discourage repetition).
-
growmap_path: Path to the speculative decoding tree used by the static engine (e.g.,
"../umbrella/trees/sequoia_tree-3x4.json").
-
engine: Defines the decoding strategy. Choose between:
-
"static": Optimized for on-device execution. -
"dynamic": Designed for offloading scenarios.
-
- width, num_beams, depth: Hyperparameters for speculative decoding in dynamic engines.
-
template: Defines the structure for input prompts. Supported values include:
-
"llama3-code": Optimized for code-related tasks. -
"meta-llama3": General-purpose instruction-following template.
-
./configs and ./umbrella/trees.
from umbrella.speculation.auto_engine import AutoEngine
DEVICE = "cuda:0"
engine = AutoEngine.from_config(device=DEVICE, **config)
engine.initialize()GEN_LEN = 512
text1 = "Tell me what you know about Reinforcement Learning in 100 words."
text2 = "Tell me what you know about LSH in 100 words."
engine.prefill(text1) # The first operation must be prefilling
engine.speculative_decoding(max_new_tokens=GEN_LEN)
engine.append(text2)
engine.speculative_decoding(max_new_tokens=GEN_LEN)output = engine.generate(
context=prompt,
max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
temperature=temperature,
top_p=top_p,
repetition_penalty=repetition_penalty,
)
# return a dict containing token ids and detokenized texts
# context=prompt (str) can be replaced by input_ids=tokens list[int]
stream = engine.generate_stream(
context=prompt,
max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
temperature=temperature,
top_p=top_p,
repetition_penalty=repetition_penalty,
)
# return a stream containing detokenized texts
# context=prompt (str) can be replaced by input_ids=tokens list[int]@article{chen2024sequoia,
title={Sequoia: Scalable, Robust, and Hardware-aware Speculative Decoding},
author={Chen, Zhuoming and May, Avner and Svirschevski, Ruslan and Huang, Yuhsun and Ryabinin, Max and Jia, Zhihao and Chen, Beidi},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.12374},
year={2024}
}
@article{svirschevski2024specexec,
title={SpecExec: Massively Parallel Speculative Decoding for Interactive LLM Inference on Consumer Devices},
author={Svirschevski, Ruslan and May, Avner and Chen, Zhuoming and Chen, Beidi and Jia, Zhihao and Ryabinin, Max},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.02532},
year={2024}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for UMbreLLa
Similar Open Source Tools

UMbreLLa
UMbreLLa is a tool designed for deploying Large Language Models (LLMs) for personal agents. It combines offloading, speculative decoding, and quantization to optimize single-user LLM deployment scenarios. With UMbreLLa, 70B-level models can achieve performance comparable to human reading speed on an RTX 4070Ti, delivering exceptional efficiency and responsiveness, especially for coding tasks. The tool supports deploying models on various GPUs and offers features like code completion and CLI/Gradio chatbots. Users can configure the LLM engine for optimal performance based on their hardware setup.
adk-rust
ADK-Rust is a comprehensive and production-ready Rust framework for building AI agents. It features type-safe agent abstractions with async execution and event streaming, multiple agent types including LLM agents, workflow agents, and custom agents, realtime voice agents with bidirectional audio streaming, a tool ecosystem with function tools, Google Search, and MCP integration, production features like session management, artifact storage, memory systems, and REST/A2A APIs, and a developer-friendly experience with interactive CLI, working examples, and comprehensive documentation. The framework follows a clean layered architecture and is production-ready and actively maintained.
dexto
Dexto is a lightweight runtime for creating and running AI agents that turn natural language into real-world actions. It serves as the missing intelligence layer for building AI applications, standalone chatbots, or as the reasoning engine inside larger products. Dexto features a powerful CLI and Web UI for running AI agents, supports multiple interfaces, allows hot-swapping of LLMs from various providers, connects to remote tool servers via the Model Context Protocol, is config-driven with version-controlled YAML, offers production-ready core features, extensibility for custom services, and enables multi-agent collaboration via MCP and A2A.
Neosgenesis
Neogenesis System is an advanced AI decision-making framework that enables agents to 'think about how to think'. It implements a metacognitive approach with real-time learning, tool integration, and multi-LLM support, allowing AI to make expert-level decisions in complex environments. Key features include metacognitive intelligence, tool-enhanced decisions, real-time learning, aha-moment breakthroughs, experience accumulation, and multi-LLM support.

mistral.rs
Mistral.rs is a fast LLM inference platform written in Rust. We support inference on a variety of devices, quantization, and easy-to-use application with an Open-AI API compatible HTTP server and Python bindings.
auto-round
AutoRound is an advanced weight-only quantization algorithm for low-bits LLM inference. It competes impressively against recent methods without introducing any additional inference overhead. The method adopts sign gradient descent to fine-tune rounding values and minmax values of weights in just 200 steps, often significantly outperforming SignRound with the cost of more tuning time for quantization. AutoRound is tailored for a wide range of models and consistently delivers noticeable improvements.
alphora
Alphora is a full-stack framework for building production AI agents, providing agent orchestration, prompt engineering, tool execution, memory management, streaming, and deployment with an async-first, OpenAI-compatible design. It offers features like agent derivation, reasoning-action loop, async streaming, visual debugger, OpenAI compatibility, multimodal support, tool system with zero-config tools and type safety, prompt engine with dynamic prompts, memory and storage management, sandbox for secure execution, deployment as API, and more. Alphora allows users to build sophisticated AI agents easily and efficiently.
augustus
Augustus is a Go-based LLM vulnerability scanner designed for security professionals to test large language models against a wide range of adversarial attacks. It integrates with 28 LLM providers, covers 210+ adversarial attacks including prompt injection, jailbreaks, encoding exploits, and data extraction, and produces actionable vulnerability reports. The tool is built for production security testing with features like concurrent scanning, rate limiting, retry logic, and timeout handling out of the box.
TempCompass
TempCompass is a benchmark designed to evaluate the temporal perception ability of Video LLMs. It encompasses a diverse set of temporal aspects and task formats to comprehensively assess the capability of Video LLMs in understanding videos. The benchmark includes conflicting videos to prevent models from relying on single-frame bias and language priors. Users can clone the repository, install required packages, prepare data, run inference using examples like Video-LLaVA and Gemini, and evaluate the performance of their models across different tasks such as Multi-Choice QA, Yes/No QA, Caption Matching, and Caption Generation.
GPULlama3.java
GPULlama3.java powered by TornadoVM is a Java-native implementation of Llama3 that automatically compiles and executes Java code on GPUs via TornadoVM. It supports Llama3, Mistral, Qwen2.5, Qwen3, and Phi3 models in the GGUF format. The repository aims to provide GPU acceleration for Java code, enabling faster execution and high-performance access to off-heap memory. It offers features like interactive and instruction modes, flexible backend switching between OpenCL and PTX, and cross-platform compatibility with NVIDIA, Intel, and Apple GPUs.

flashinfer
FlashInfer is a library for Language Languages Models that provides high-performance implementation of LLM GPU kernels such as FlashAttention, PageAttention and LoRA. FlashInfer focus on LLM serving and inference, and delivers state-the-art performance across diverse scenarios.
z-ai-sdk-python
Z.ai Open Platform Python SDK is the official Python SDK for Z.ai's large model open interface, providing developers with easy access to Z.ai's open APIs. The SDK offers core features like chat completions, embeddings, video generation, audio processing, assistant API, and advanced tools. It supports various functionalities such as speech transcription, text-to-video generation, image understanding, and structured conversation handling. Developers can customize client behavior, configure API keys, and handle errors efficiently. The SDK is designed to simplify AI interactions and enhance AI capabilities for developers.
libllm
libLLM is an open-source project designed for efficient inference of large language models (LLM) on personal computers and mobile devices. It is optimized to run smoothly on common devices, written in C++14 without external dependencies, and supports CUDA for accelerated inference. Users can build the tool for CPU only or with CUDA support, and run libLLM from the command line. Additionally, there are API examples available for Python and the tool can export Huggingface models.
ScaleLLM
ScaleLLM is a cutting-edge inference system engineered for large language models (LLMs), meticulously designed to meet the demands of production environments. It extends its support to a wide range of popular open-source models, including Llama3, Gemma, Bloom, GPT-NeoX, and more. ScaleLLM is currently undergoing active development. We are fully committed to consistently enhancing its efficiency while also incorporating additional features. Feel free to explore our **_Roadmap_** for more details. ## Key Features * High Efficiency: Excels in high-performance LLM inference, leveraging state-of-the-art techniques and technologies like Flash Attention, Paged Attention, Continuous batching, and more. * Tensor Parallelism: Utilizes tensor parallelism for efficient model execution. * OpenAI-compatible API: An efficient golang rest api server that compatible with OpenAI. * Huggingface models: Seamless integration with most popular HF models, supporting safetensors. * Customizable: Offers flexibility for customization to meet your specific needs, and provides an easy way to add new models. * Production Ready: Engineered with production environments in mind, ScaleLLM is equipped with robust system monitoring and management features to ensure a seamless deployment experience.
ai
The react-native-ai repository allows users to run Large Language Models (LLM) locally in a React Native app using the Universal MLC LLM Engine with compatibility for Vercel AI SDK. Please note that this project is experimental and not ready for production. The repository is licensed under MIT and was created with create-react-native-library.
pyllms
PyLLMs is a minimal Python library designed to connect to various Language Model Models (LLMs) such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, AI21, Cohere, Aleph Alpha, and HuggingfaceHub. It provides a built-in model performance benchmark for fast prototyping and evaluating different models. Users can easily connect to top LLMs, get completions from multiple models simultaneously, and evaluate models on quality, speed, and cost. The library supports asynchronous completion, streaming from compatible models, and multi-model initialization for testing and comparison. Additionally, it offers features like passing chat history, system messages, counting tokens, and benchmarking models based on quality, speed, and cost.
For similar tasks

UMbreLLa
UMbreLLa is a tool designed for deploying Large Language Models (LLMs) for personal agents. It combines offloading, speculative decoding, and quantization to optimize single-user LLM deployment scenarios. With UMbreLLa, 70B-level models can achieve performance comparable to human reading speed on an RTX 4070Ti, delivering exceptional efficiency and responsiveness, especially for coding tasks. The tool supports deploying models on various GPUs and offers features like code completion and CLI/Gradio chatbots. Users can configure the LLM engine for optimal performance based on their hardware setup.

glide
Glide is a cloud-native LLM gateway that provides a unified REST API for accessing various large language models (LLMs) from different providers. It handles LLMOps tasks such as model failover, caching, key management, and more, making it easy to integrate LLMs into applications. Glide supports popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock (Titan), Cohere, Google Gemini, OctoML, and Ollama. It offers high availability, performance, and observability, and provides SDKs for Python and NodeJS to simplify integration.
agents-flex
Agents-Flex is a LLM Application Framework like LangChain base on Java. It provides a set of tools and components for building LLM applications, including LLM Visit, Prompt and Prompt Template Loader, Function Calling Definer, Invoker and Running, Memory, Embedding, Vector Storage, Resource Loaders, Document, Splitter, Loader, Parser, LLMs Chain, and Agents Chain.
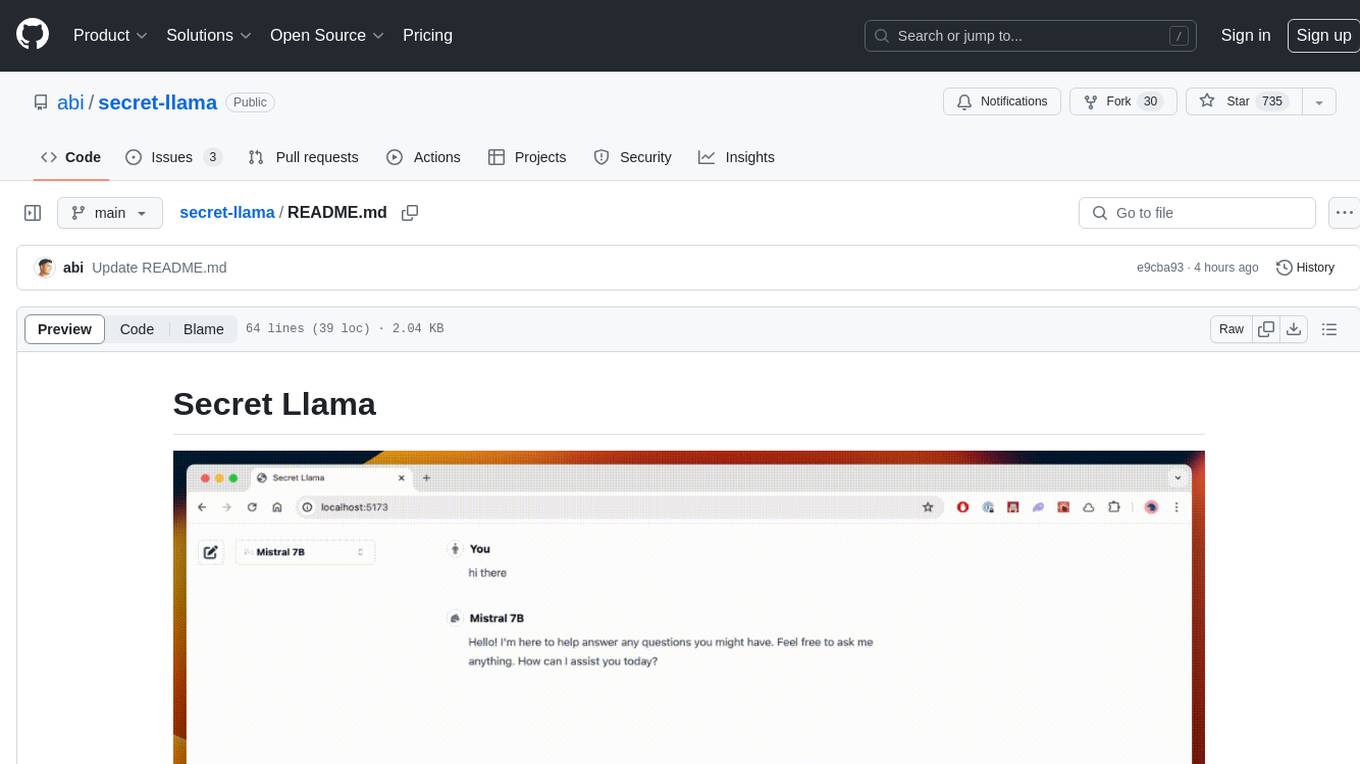
secret-llama
Entirely-in-browser, fully private LLM chatbot supporting Llama 3, Mistral and other open source models. Fully private = No conversation data ever leaves your computer. Runs in the browser = No server needed and no install needed! Works offline. Easy-to-use interface on par with ChatGPT, but for open source LLMs. System requirements include a modern browser with WebGPU support. Supported models include TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v0.4-q4f32_1-1k, Llama-3-8B-Instruct-q4f16_1, Phi1.5-q4f16_1-1k, and Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2-q4f16_1. Looking for contributors to improve the interface, support more models, speed up initial model loading time, and fix bugs.
shellgpt
ShellGPT is a tool that allows users to chat with a large language model (LLM) in the terminal. It can be used for various purposes such as generating shell commands, telling stories, and interacting with Linux terminal. The tool provides different modes of usage including direct mode for asking questions, REPL mode for chatting with LLM, and TUI mode tailored for inferring shell commands. Users can customize the tool by setting up different language model backends such as Ollama or using OpenAI compatible API endpoints. Additionally, ShellGPT comes with built-in system contents for general questions, correcting typos, generating URL slugs, programming questions, shell command inference, and git commit message generation. Users can define their own content or share customized contents in the discuss section.
Open-LLM-VTuber
Open-LLM-VTuber is a project in early stages of development that allows users to interact with Large Language Models (LLM) using voice commands and receive responses through a Live2D talking face. The project aims to provide a minimum viable prototype for offline use on macOS, Linux, and Windows, with features like long-term memory using MemGPT, customizable LLM backends, speech recognition, and text-to-speech providers. Users can configure the project to chat with LLMs, choose different backend services, and utilize Live2D models for visual representation. The project supports perpetual chat, offline operation, and GPU acceleration on macOS, addressing limitations of existing solutions on macOS.
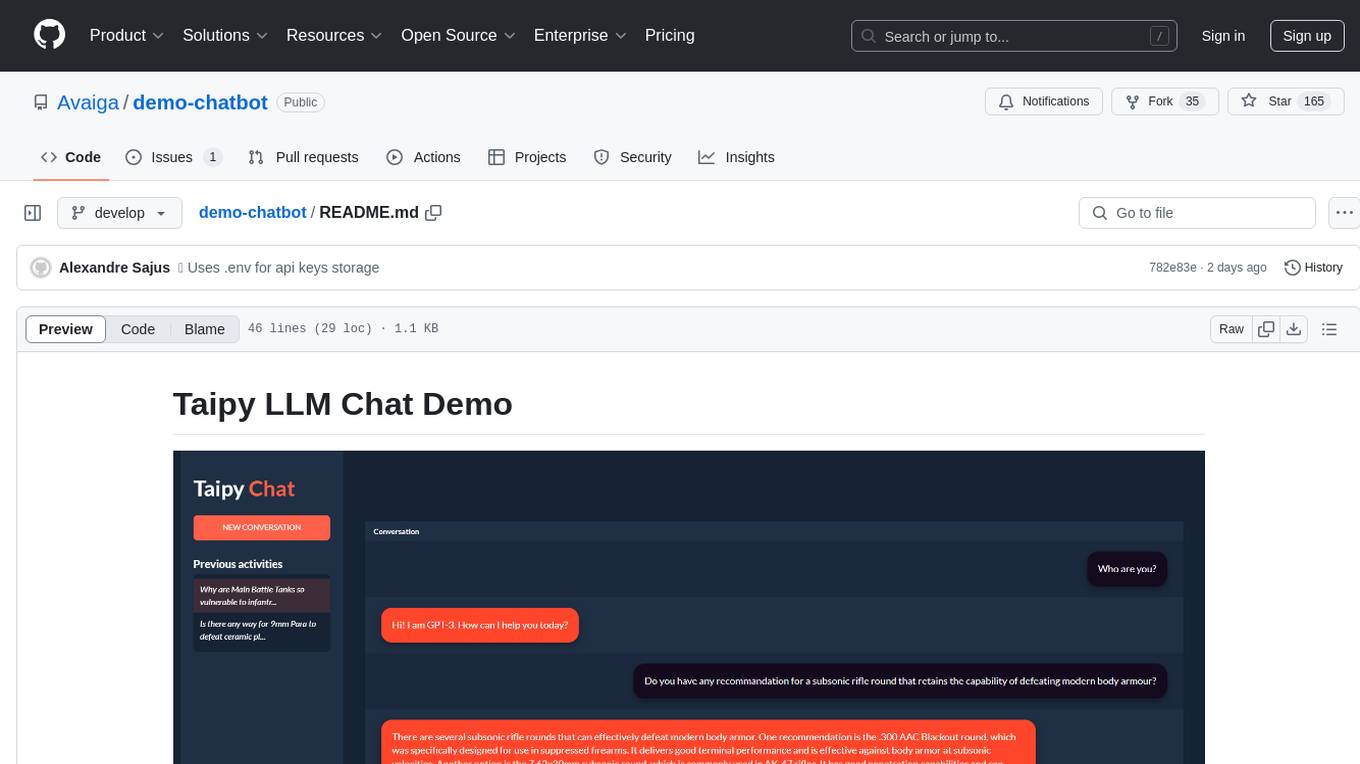
demo-chatbot
The demo-chatbot repository contains a simple app to chat with an LLM, allowing users to create any LLM Inference Web Apps using Python. The app utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 API to generate responses to user messages, with the flexibility to switch to other APIs or models. The repository includes a tutorial in the Taipy documentation for creating the app. Users need an OpenAI account with an active API key to run the app by cloning the repository, installing dependencies, setting up the API key in a .env file, and running the main.py file.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.