
rank_llm
RankLLM is a Python toolkit for reproducible information retrieval research using rerankers, with a focus on listwise reranking.
Stars: 411
RankLLM is a suite of prompt-decoders compatible with open source LLMs like Vicuna and Zephyr. It allows users to create custom ranking models for various NLP tasks, such as document reranking, question answering, and summarization. The tool offers a variety of features, including the ability to fine-tune models on custom datasets, use different retrieval methods, and control the context size and variable passages. RankLLM is easy to use and can be integrated into existing NLP pipelines.
README:
We offer a suite of rerankers - pointwise models like MonoT5, pairwise models like DuoT5 and listwise models with a focus on open source LLMs compatible with vLLM, SGLang, or TensorRT-LLM. We also support RankGPT and RankGemini variants, which are proprietary listwise rerankers. Addtionally, we support reranking with the first-token logits only to improve inference efficiency. Some of the code in this repository is borrowed from RankGPT, PyGaggle, and LiT5!
current_version = 0.21.0
- Installation
- Quick Start
- End-to-end Run and 2CR
- Model Zoo
- Training
- Community Contribution
- References and Citations
- Acknowledgments
⚠️ RankLLM is not compatible with macOS, regardless of whether you are using an Intel-based Mac or Apple Silicon (M-series). We recommend using Linux or Windows instead.
As rank_llm relies on Anserini, it is required that you have JDK 21 installed. Please note that using JDK 11 is not supported and may lead to errors.
conda create -n rankllm python=3.10
conda activate rankllmpip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121conda install -c conda-forge openjdk=21 maven -ypip install -r requirements.txtpip install -e .[sglang] # local installation for development
pip install rank-llm[sglang] # or pip installationRemember to install flashinfer to use SGLang backend.
pip install flashinfer -i https://flashinfer.ai/whl/cu121/torch2.4/pip install -e .[tensorrt-llm] # local installation for development
pip install rank-llm[tensorrt-llm] # or pip installationThe following code snippet is a minimal walk through of retrieval, reranking, evalaution, and invocations analysis of top 100 retrieved documents for queries from DL19. In this example BM25 is used as the retriever and RankZephyr as the reranker. Additional sample snippets are available to run under the src/rank_llm/demo directory.
from pathlib import Path
from rank_llm.analysis.response_analysis import ResponseAnalyzer
from rank_llm.data import DataWriter
from rank_llm.evaluation.trec_eval import EvalFunction
from rank_llm.rerank import Reranker, get_openai_api_key
from rank_llm.rerank.listwise import (
SafeOpenai,
VicunaReranker,
ZephyrReranker,
)
from rank_llm.retrieve.retriever import Retriever
from rank_llm.retrieve.topics_dict import TOPICS
# -------- Retrieval --------
# By default BM25 is used for retrieval of top 100 candidates.
dataset_name = "dl19"
retrieved_results = Retriever.from_dataset_with_prebuilt_index(dataset_name)
# Users can specify other retrieval methods and number of retrieved candidates.
# retrieved_results = Retriever.from_dataset_with_prebuilt_index(
# dataset_name, RetrievalMethod.SPLADE_P_P_ENSEMBLE_DISTIL, k=50
# )
# ---------------------------
# --------- Rerank ----------
# Rank Zephyr model
reranker = ZephyrReranker()
# Rank Vicuna model
# reranker = VicunaReranker()
# RankGPT
# model_coordinator = SafeOpenai("gpt-4o-mini", 4096, keys=get_openai_api_key())
# reranker = Reranker(model_coordinator)
rerank_results = reranker.rerank_batch(requests=retrieved_results)
# ---------------------------
# ------- Evaluation --------
# Evaluate retrieved results.
ndcg_10_retrieved = EvalFunction.from_results(retrieved_results, TOPICS[dataset_name])
print(ndcg_10_retrieved)
# Evaluate rerank results.
ndcg_10_rerank = EvalFunction.from_results(rerank_results, TOPICS[dataset_name])
print(ndcg_10_rerank)
# By default ndcg@10 is the eval metric, other value can be specified:
# eval_args = ["-c", "-m", "map_cut.100", "-l2"]
# map_100_rerank = EvalFunction.from_results(rerank_results, topics, eval_args)
# print(map_100_rerank)
# eval_args = ["-c", "-m", "recall.20"]
# recall_20_rerank = EvalFunction.from_results(rerank_results, topics, eval_args)
# print(recall_20_rerank)
# ---------------------------
# --- Analyze invocations ---
analyzer = ResponseAnalyzer.from_inline_results(rerank_results)
error_counts = analyzer.count_errors(verbose=True)
print(error_counts)
# ---------------------------
# ------ Save results -------
writer = DataWriter(rerank_results)
Path(f"demo_outputs/").mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
writer.write_in_jsonl_format(f"demo_outputs/rerank_results.jsonl")
writer.write_in_trec_eval_format(f"demo_outputs/rerank_results.txt")
writer.write_inference_invocations_history(
f"demo_outputs/inference_invocations_history.json"
)
# ---------------------------If you are interested in running retrieval and reranking end-to-end or reproducing the results from the reference papers, run_rank_llm.py is a convinent wrapper script that combines these two steps.
The comperehensive list of our two-click reproduction commands are available on MS MARCO V1 and MS MARCO V2 webpages for DL19 and DL20 and DL21-23 datasets, respectively. Moving forward, we plan to cover more datasets and retrievers in our 2CR pages. The rest of this session provides some sample e2e runs.
We can run the RankZephyr model with the following command:
python src/rank_llm/scripts/run_rank_llm.py --model_path=castorini/rank_zephyr_7b_v1_full --top_k_candidates=100 --dataset=dl20 \
--retrieval_method=SPLADE++_EnsembleDistil_ONNX --prompt_mode=rank_GPT --context_size=4096 --variable_passagesIncluding the --sglang_batched flag will allow you to run the model in batched mode using the SGLang library.
Including the --tensorrt_batched flag will allow you to run the model in batched mode using the TensorRT-LLM library.
If you want to run multiple passes of the model, you can use the --num_passes flag.
We can run the RankGPT4-o model with the following command:
python src/rank_llm/scripts/run_rank_llm.py --model_path=gpt-4o --top_k_candidates=100 --dataset=dl20 \
--retrieval_method=bm25 --prompt_mode=rank_GPT_APEER --context_size=4096 --use_azure_openaiNote that the --prompt_mode is set to rank_GPT_APEER to use the LLM refined prompt from APEER.
This can be changed to rank_GPT to use the original prompt.
We can run the LiT5-Distill V2 model (which could rerank 100 documents in a single pass) with the following command:
python src/rank_llm/scripts/run_rank_llm.py --model_path=castorini/LiT5-Distill-large-v2 --top_k_candidates=100 --dataset=dl19 \
--retrieval_method=bm25 --prompt_mode=LiT5 --context_size=150 --batch_size=4 \
--variable_passages --window_size=100We can run the LiT5-Distill original model (which works with a window size of 20) with the following command:
python src/rank_llm/scripts/run_rank_llm.py --model_path=castorini/LiT5-Distill-large --top_k_candidates=100 --dataset=dl19 \
--retrieval_method=bm25 --prompt_mode=LiT5 --context_size=150 --batch_size=32 \
--variable_passagesWe can run the LiT5-Score model with the following command:
python src/rank_llm/scripts/run_rank_llm.py --model_path=castorini/LiT5-Score-large --top_k_candidates=100 --dataset=dl19 \
--retrieval_method=bm25 --prompt_mode=LiT5 --context_size=150 --batch_size=8 \
--window_size=100 --variable_passagesThe following runs the 3B variant of MonoT5 trained for 10K steps:
python src/rank_llm/scripts/run_rank_llm.py --model_path=castorini/monot5-3b-msmarco-10k --top_k_candidates=1000 --dataset=dl19 \
--retrieval_method=bm25 --prompt_mode=monot5 --context_size=512Note that we usually rerank 1K candidates with MonoT5.
The following runs the #B variant of DuoT5 trained for 10K steps:
python src/rank_llm/scripts/run_rank_llm.py --model_path=castorini/duot5-3b-msmarco-10k --top_k_candidates=50 --dataset=dl19 \
--retrieval_method=bm25 --prompt_mode=duot5Since Duo's pairwise comparison has $O(n^2) runtime complexity, we recommend reranking top 50 candidates using DuoT5 models.
We can run the FirstMistral model, reranking using the first-token logits only with the following command:
python src/rank_llm/scripts/run_rank_llm.py --model_path=castorini/first_mistral --top_k_candidates=100 --dataset=dl20 --retrieval_method=SPLADE++_EnsembleDistil_ONNX --prompt_mode=rank_GPT --context_size=4096 --variable_passages --use_logits --use_alpha --num_gpus 1
Omit --use_logits if you wish to perform traditional listwise reranking.
First install genai:
pip install -e .[genai] # local installation for development
pip install rank-llm[genai] # or pip installationThen run the following command:
python src/rank_llm/scripts/run_rank_llm.py --model_path=gemini-2.0-flash-001 --top_k_candidates=100 --dataset=dl20 \
--retrieval_method=SPLADE++_EnsembleDistil_ONNX --prompt_mode=rank_GPT_APEER --context_size=4096The following is a table of the listwise models our repository was primarily built to handle (with the models hosted on HuggingFace):
vLLM, SGLang, and TensorRT-LLM backends are only supported for RankZephyr and RankVicuna models.
| Model Name | Hugging Face Identifier/Link |
|---|---|
| RankZephyr 7B V1 - Full - BF16 | castorini/rank_zephyr_7b_v1_full |
| RankVicuna 7B - V1 | castorini/rank_vicuna_7b_v1 |
| RankVicuna 7B - V1 - No Data Augmentation | castorini/rank_vicuna_7b_v1_noda |
| RankVicuna 7B - V1 - FP16 | castorini/rank_vicuna_7b_v1_fp16 |
| RankVicuna 7B - V1 - No Data Augmentation - FP16 | castorini/rank_vicuna_7b_v1_noda_fp16 |
We also officially support the following rerankers built by our group:
The following is a table specifically for our LiT5 suite of models hosted on HuggingFace:
| Model Name | 🤗 Hugging Face Identifier/Link |
|---|---|
| LiT5 Distill base | castorini/LiT5-Distill-base |
| LiT5 Distill large | castorini/LiT5-Distill-large |
| LiT5 Distill xl | castorini/LiT5-Distill-xl |
| LiT5 Distill base v2 | castorini/LiT5-Distill-base-v2 |
| LiT5 Distill large v2 | castorini/LiT5-Distill-large-v2 |
| LiT5 Distill xl v2 | castorini/LiT5-Distill-xl-v2 |
| LiT5 Score base | castorini/LiT5-Score-base |
| LiT5 Score large | castorini/LiT5-Score-large |
| LiT5 Score xl | castorini/LiT5-Score-xl |
Now you can run top-100 reranking with the v2 model in a single pass while maintaining efficiency!
The following is a table specifically for our monoT5 suite of models hosted on HuggingFace:
| Model Name | 🤗 Hugging Face Identifier/Link |
|---|---|
| monoT5 Small MSMARCO 10K | castorini/monot5-small-msmarco-10k |
| monoT5 Small MSMARCO 100K | castorini/monot5-small-msmarco-100k |
| monoT5 Base MSMARCO | castorini/monot5-base-msmarco |
| monoT5 Base MSMARCO 10K | castorini/monot5-base-msmarco-10k |
| monoT5 Large MSMARCO 10K | castorini/monot5-large-msmarco-10k |
| monoT5 Large MSMARCO | castorini/monot5-large-msmarco |
| monoT5 3B MSMARCO 10K | castorini/monot5-3b-msmarco-10k |
| monoT5 3B MSMARCO | castorini/monot5-3b-msmarco |
| monoT5 Base Med MSMARCO | castorini/monot5-base-med-msmarco |
| monoT5 3B Med MSMARCO | castorini/monot5-3b-med-msmarco |
We recommend the Med models for biomedical retrieval. We also provide both 10K (generally better OOD effectiveness) and 100K checkpoints (better in-domain).
Please check the training directory for finetuning open-source listwise rerankers.
If you would like to contribute to the project, please refer to the contribution guidelines.
If you use RankLLM, please cite the following relevant papers:
@ARTICLE{pradeep2023rankvicuna,
title = {{RankVicuna}: Zero-Shot Listwise Document Reranking with Open-Source Large Language Models},
author = {Ronak Pradeep and Sahel Sharifymoghaddam and Jimmy Lin},
year = {2023},
journal = {arXiv:2309.15088}
}
[2312.02724] RankZephyr: Effective and Robust Zero-Shot Listwise Reranking is a Breeze!
@ARTICLE{pradeep2023rankzephyr,
title = {{RankZephyr}: Effective and Robust Zero-Shot Listwise Reranking is a Breeze!},
author = {Ronak Pradeep and Sahel Sharifymoghaddam and Jimmy Lin},
year = {2023},
journal = {arXiv:2312.02724}
}
If you use one of the LiT5 models please cite the following relevant paper:
@ARTICLE{tamber2023scaling,
title = {Scaling Down, LiTting Up: Efficient Zero-Shot Listwise Reranking with Seq2seq Encoder-Decoder Models},
author = {Manveer Singh Tamber and Ronak Pradeep and Jimmy Lin},
year = {2023},
journal = {arXiv:2312.16098}
}
If you use one of the monoT5 models please cite the following relevant paper:
@ARTICLE{pradeep2021emd,
title = {The Expando-Mono-Duo Design Pattern for Text Ranking with Pretrained Sequence-to-Sequence Models},
author = {Ronak Pradeep and Rodrigo Nogueira and Jimmy Lin},
year = {2021},
journal = {arXiv:2101.05667},
}
If you use the FirstMistral model, please consider citing:
@ARTICLE{chen2024firstrepro,
title = title={An Early FIRST Reproduction and Improvements to Single-Token Decoding for Fast Listwise Reranking},
author = {Zijian Chen and Ronak Pradeep and Jimmy Lin},
year = {2024},
journal = {arXiv:2411.05508}
}
If you would like to cite the FIRST methodology, please consider citing:
[2406.15657] FIRST: Faster Improved Listwise Reranking with Single Token Decoding
@ARTICLE{reddy2024first,
title = {FIRST: Faster Improved Listwise Reranking with Single Token Decoding},
author = {Reddy, Revanth Gangi and Doo, JaeHyeok and Xu, Yifei and Sultan, Md Arafat and Swain, Deevya and Sil, Avirup and Ji, Heng},
year = {2024}
journal = {arXiv:2406.15657},
}
This research is supported in part by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for rank_llm
Similar Open Source Tools

rank_llm
RankLLM is a suite of prompt-decoders compatible with open source LLMs like Vicuna and Zephyr. It allows users to create custom ranking models for various NLP tasks, such as document reranking, question answering, and summarization. The tool offers a variety of features, including the ability to fine-tune models on custom datasets, use different retrieval methods, and control the context size and variable passages. RankLLM is easy to use and can be integrated into existing NLP pipelines.
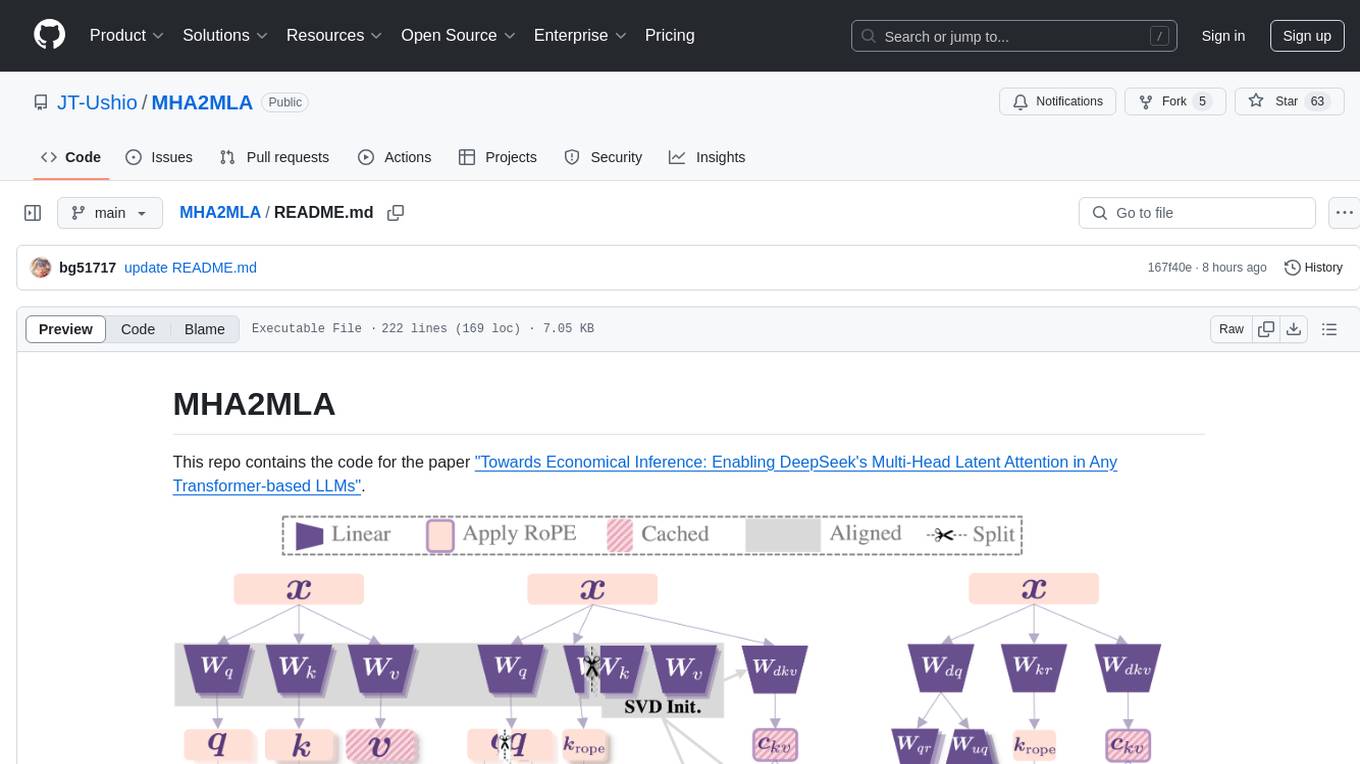
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
Online-RLHF
This repository, Online RLHF, focuses on aligning large language models (LLMs) through online iterative Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It aims to bridge the gap in existing open-source RLHF projects by providing a detailed recipe for online iterative RLHF. The workflow presented here has shown to outperform offline counterparts in recent LLM literature, achieving comparable or better results than LLaMA3-8B-instruct using only open-source data. The repository includes model releases for SFT, Reward model, and RLHF model, along with installation instructions for both inference and training environments. Users can follow step-by-step guidance for supervised fine-tuning, reward modeling, data generation, data annotation, and training, ultimately enabling iterative training to run automatically.

CodeTF
CodeTF is a Python transformer-based library for code large language models (Code LLMs) and code intelligence. It provides an interface for training and inferencing on tasks like code summarization, translation, and generation. The library offers utilities for code manipulation across various languages, including easy extraction of code attributes. Using tree-sitter as its core AST parser, CodeTF enables parsing of function names, comments, and variable names. It supports fast model serving, fine-tuning of LLMs, various code intelligence tasks, preprocessed datasets, model evaluation, pretrained and fine-tuned models, and utilities to manipulate source code. CodeTF aims to facilitate the integration of state-of-the-art Code LLMs into real-world applications, ensuring a user-friendly environment for code intelligence tasks.
LongLoRA
LongLoRA is a tool for efficient fine-tuning of long-context large language models. It includes LongAlpaca data with long QA data collected and short QA sampled, models from 7B to 70B with context length from 8k to 100k, and support for GPTNeoX models. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning, context extension, and improved LoRA fine-tuning. It provides pre-trained weights, fine-tuning instructions, evaluation methods, local and online demos, streaming inference, and data generation via Pdf2text. LongLoRA is licensed under Apache License 2.0, while data and weights are under CC-BY-NC 4.0 License for research use only.
AutoGPTQ
AutoGPTQ is an easy-to-use LLM quantization package with user-friendly APIs, based on GPTQ algorithm (weight-only quantization). It provides a simple and efficient way to quantize large language models (LLMs) to reduce their size and computational cost while maintaining their performance. AutoGPTQ supports a wide range of LLM models, including GPT-2, GPT-J, OPT, and BLOOM. It also supports various evaluation tasks, such as language modeling, sequence classification, and text summarization. With AutoGPTQ, users can easily quantize their LLM models and deploy them on resource-constrained devices, such as mobile phones and embedded systems.
AnglE
AnglE is a library for training state-of-the-art BERT/LLM-based sentence embeddings with just a few lines of code. It also serves as a general sentence embedding inference framework, allowing for inferring a variety of transformer-based sentence embeddings. The library supports various loss functions such as AnglE loss, Contrastive loss, CoSENT loss, and Espresso loss. It provides backbones like BERT-based models, LLM-based models, and Bi-directional LLM-based models for training on single or multi-GPU setups. AnglE has achieved significant performance on various benchmarks and offers official pretrained models for both BERT-based and LLM-based models.
TheoremExplainAgent
TheoremExplainAgent is an AI system that generates long-form Manim videos to visually explain theorems, proving its deep understanding while uncovering reasoning flaws that text alone often hides. The codebase for the paper 'TheoremExplainAgent: Towards Multimodal Explanations for LLM Theorem Understanding' is available in this repository. It provides a tool for creating multimodal explanations for theorem understanding using AI technology.
star-vector
StarVector is a multimodal vision-language model for Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) generation. It can be used to perform image2SVG and text2SVG generation. StarVector works directly in the SVG code space, leveraging visual understanding to apply accurate SVG primitives. It achieves state-of-the-art performance in producing compact and semantically rich SVGs. The tool provides Hugging Face model checkpoints for image2SVG vectorization, with models like StarVector-8B and StarVector-1B. It also offers datasets like SVG-Stack, SVG-Fonts, SVG-Icons, SVG-Emoji, and SVG-Diagrams for evaluation. StarVector can be trained using Deepspeed or FSDP for tasks like Image2SVG and Text2SVG generation. The tool provides a demo with options for HuggingFace generation or VLLM backend for faster generation speed.

OSA
OSA (Open-Source-Advisor) is a tool designed to improve the quality of scientific open source projects by automating the generation of README files, documentation, CI/CD scripts, and providing advice and recommendations for repositories. It supports various LLMs accessible via API, local servers, or osa_bot hosted on ITMO servers. OSA is currently under development with features like README file generation, documentation generation, automatic implementation of changes, LLM integration, and GitHub Action Workflow generation. It requires Python 3.10 or higher and tokens for GitHub/GitLab/Gitverse and LLM API key. Users can install OSA using PyPi or build from source, and run it using CLI commands or Docker containers.
infinity
Infinity is a high-throughput, low-latency REST API for serving vector embeddings, supporting all sentence-transformer models and frameworks. It is developed under the MIT License and powers inference behind Gradient.ai. The API allows users to deploy models from SentenceTransformers, offers fast inference backends utilizing various accelerators, dynamic batching for efficient processing, correct and tested implementation, and easy-to-use API built on FastAPI with Swagger documentation. Users can embed text, rerank documents, and perform text classification tasks using the tool. Infinity supports various models from Huggingface and provides flexibility in deployment via CLI, Docker, Python API, and cloud services like dstack. The tool is suitable for tasks like embedding, reranking, and text classification.
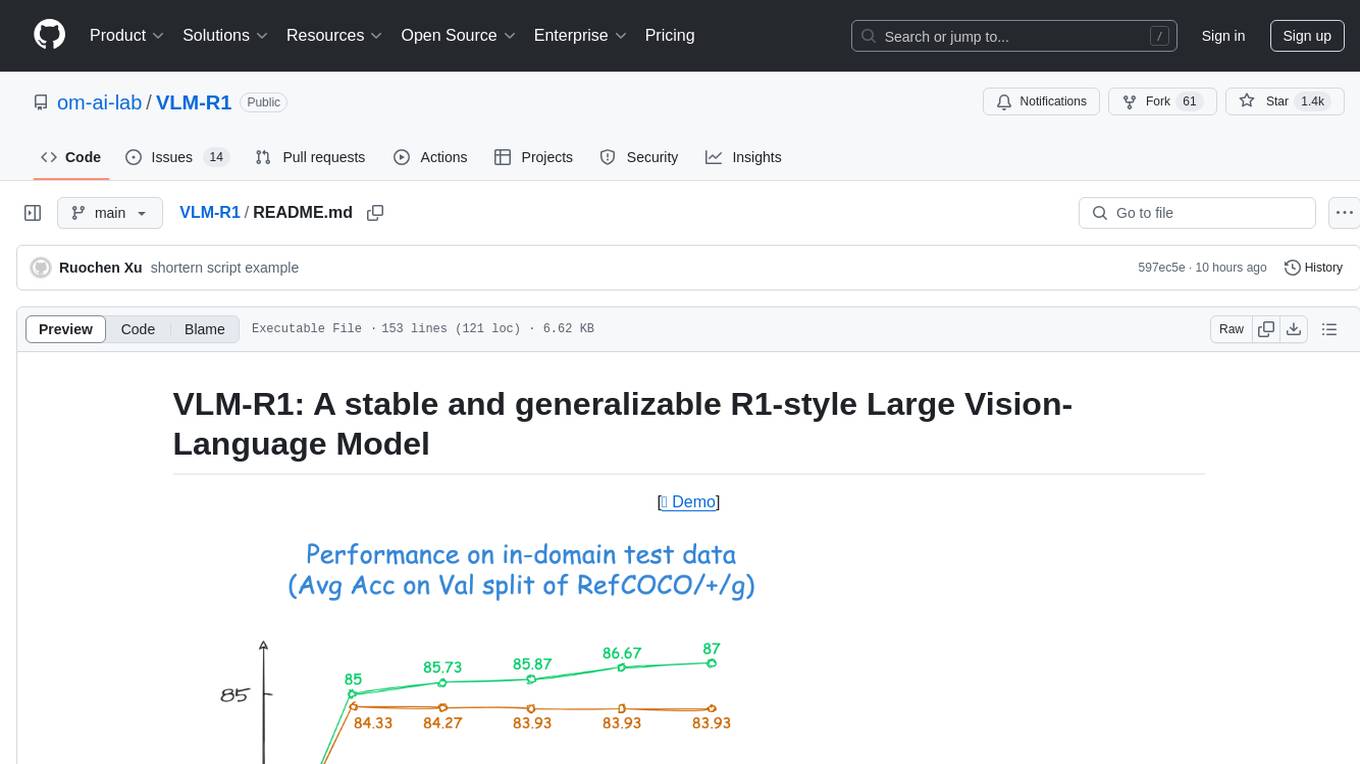
VLM-R1
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.
candle-vllm
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.
LTEngine
LTEngine is a free and open-source local AI machine translation API written in Rust. It is self-hosted and compatible with LibreTranslate. LTEngine utilizes large language models (LLMs) via llama.cpp, offering high-quality translations that rival or surpass DeepL for certain languages. It supports various accelerators like CUDA, Metal, and Vulkan, with the largest model 'gemma3-27b' fitting on a single consumer RTX 3090. LTEngine is actively developed, with a roadmap outlining future enhancements and features.
superlinked
Superlinked is a compute framework for information retrieval and feature engineering systems, focusing on converting complex data into vector embeddings for RAG, Search, RecSys, and Analytics stack integration. It enables custom model performance in machine learning with pre-trained model convenience. The tool allows users to build multimodal vectors, define weights at query time, and avoid postprocessing & rerank requirements. Users can explore the computational model through simple scripts and python notebooks, with a future release planned for production usage with built-in data infra and vector database integrations.
Scrapegraph-ai
ScrapeGraphAI is a web scraping Python library that utilizes LLM and direct graph logic to create scraping pipelines for websites and local documents. It offers various standard scraping pipelines like SmartScraperGraph, SearchGraph, SpeechGraph, and ScriptCreatorGraph. Users can extract information by specifying prompts and input sources. The library supports different LLM APIs such as OpenAI, Groq, Azure, and Gemini, as well as local models using Ollama. ScrapeGraphAI is designed for data exploration and research purposes, providing a versatile tool for extracting information from web pages and generating outputs like Python scripts, audio summaries, and search results.
For similar tasks

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.

jupyter-ai
Jupyter AI connects generative AI with Jupyter notebooks. It provides a user-friendly and powerful way to explore generative AI models in notebooks and improve your productivity in JupyterLab and the Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, Jupyter AI offers: * An `%%ai` magic that turns the Jupyter notebook into a reproducible generative AI playground. This works anywhere the IPython kernel runs (JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab, Kaggle, VSCode, etc.). * A native chat UI in JupyterLab that enables you to work with generative AI as a conversational assistant. * Support for a wide range of generative model providers, including AI21, Anthropic, AWS, Cohere, Gemini, Hugging Face, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. * Local model support through GPT4All, enabling use of generative AI models on consumer grade machines with ease and privacy.

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.





