
candle-vllm
Efficent platform for inference and serving local LLMs including an OpenAI compatible API server.
Stars: 329
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.
README:
Efficient, easy-to-use platform for inference and serving local LLMs including an OpenAI compatible API server.
- OpenAI compatible API server provided for serving LLMs.
- Highly extensible trait-based system to allow rapid implementation of new module pipelines,
- Streaming support in generation.
- Efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention.
- Continuous batching.
-
In-situquantization (andIn-situmarlin format conversion) -
GPTQ/Marlinformat quantization (4-bit) - Support
Mac/Metaldevices - Support
Multi-GPUinference
Currently, candle-vllm supports chat serving for the following models.
| Model ID | Model Type | Supported | Speed (A100, BF16) |
Throughput (BF16, bs=16) |
Quantized (A100, Q4K or Marlin) |
Throughput (GTPQ/Marlin, bs=16) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | LLAMA | ✅ | 65 tks/s (LLaMa3.1 8B) | 553 tks/s (LLaMa3.1 8B) | 75 tks/s (LLaMa3.1 8B), 115 tks/s (LLaMa3.1 8B, Marlin) | 968 tks/s (LLaMa3.1 8B) |
| #2 | Mistral | ✅ | 70 tks/s (7B) | 585 tks/s (7B) | 96 tks/s (7B), 115 tks/s (7B, Marlin) | 981 tks/s (7B) |
| #3 | Phi (v1, v1.5, v2) | ✅ | 97 tks/s (2.7B, F32+BF16) | TBD | - | TBD |
| #4 | Phi-3 (3.8B, 7B) | ✅ | 107 tks/s (3.8B) | 744 tks/s (3.8B) | 135 tks/s (3.8B) | TBD |
| #5 | Yi | ✅ | 75 tks/s (6B) | 566 tks/s (6B) | 105 tks/s (6B) | TBD |
| #6 | StableLM | ✅ | 99 tks/s (3B) | TBD | - | TBD |
| #7 | BigCode/StarCode | TBD | TBD | TBD | - | TBD |
| #8 | ChatGLM | TBD | TBD | TBD | - | TBD |
| #9 | QWen2 (1.8B, 7B) | ✅ | 148 tks/s (1.8B) | 784 tks/s (1.8B) | - | TBD |
| #10 | Google Gemma | ✅ | 130 tks/s (2B) | TBD | 73 tks/s (Gemma2-9B, Marlin) | 587 tks/s (Gemma2-9B) |
| #11 | DeepSeek-R1-Distill-QWen | TBD | TBD | TBD | 62 tks (QWen 14B) | TBD |
| #12 | DeepSeek-R1-Distill-LLaMa | TBD | TBD | TBD | 108 tks (LLaMa3.1 8B) | TBD |
| #13 | Moondream-2 (Multimodal LLM) | TBD | TBD | TBD | - | TBD |
| #14 | DeepSeek V2/V3/R1 | ✅ | TBD | TBD | - | TBD |
| #15 | QwQ-32B (GGUF) | ✅ | TBD | TBD | 36 tks/s (Q4K) | TBD |
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/66b5b90e-e2ca-4f0b-82d7-99aa9f85568c
See this folder for some examples.
Install dependencies
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
sudo apt install libssl-dev -y
sudo apt install pkg-config -y
git clone [email protected]:EricLBuehler/candle-vllm.git
cd candle-vllm
Run Uncompressed models
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --weight-path /home/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B/ llama3 --temperature 0. --penalty 1.0Note: assume model weights downloaded in folder /home/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B/
Run Marlin-compatible models, e.g., DeepSeek-R1-Distill-QWen-14B (Suggested, fastest approach)
#model format (4-bit GPTQ, 128-group, desc_act=False)
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --dtype bf16 --port 2000 --weight-path /home/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-14B-GPTQ_4bit-128g qwen2 --quant gptq --temperature 0. --penalty 1.0
# If you don't have such model, you can convert Uncompressed model to Marlin-compatible format using the given script
python3 examples/convert_marlin.py --src /home/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-14B/ --dst /home/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-14B-GPTQ_4bit-128gNote: Candle-vLLM will repack the GPTQ model into Marlin format during model loading
Run Marlin-format models,
# If you have Marlin-format model, run it with (--quant marlin)
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --dtype bf16 --port 2000 --weight-path /home/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-14B-GPTQ-Marlin/ qwen2 --quant marlin --penalty 1.0 --temperature 0.You may also run specific model using Huggingface model-id, e.g.,
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --model-id meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf llamacargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --model-id avoroshilov/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-14B-GPTQ_4bit-128g --quant gptq --penalty 1.0 --temperature 0.
Run QwQ-32B GGUF/GGML models on CUDA or Mac/Metal devices
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --model-id Qwen/QwQ-32B --dtype bf16 --weight-path ./ --weight-file qwq-32b-q4_k_m.gguf qwen2 --quant gguf --temperature 0. --penalty 1.0Run GGUF/GGML models on CUDA or Mac/Metal devices (assume gguf model downloaded in /Users/Downloads)
cargo run --release --features metal -- --port 2000 --model-id microsoft/Phi-3.5-mini-instruct --dtype bf16 --weight-path /Users/Downloads --weight-file Phi-3.5-mini-instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf phi3 --quant gguf --temperature 0. --penalty 1.0Note: dtype in gguf/ggml mode is used for kv cache and attention, you may choose f32 or bf16, while, f16 is not recommended.
Run DeepSeek MoE models
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --weight-path /home/DeepSeek-V2-Lite-Chat deep-seek --penalty 1.0 --temperature 0.
Run Multi-GPU inference with NCCL feature
cargo run --release --features cuda,nccl -- --port 2000 --device-ids "0,1" --weight-path /home/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct/ llama3 --temperature 0. --penalty 1.0Run Multi-GPU inference with NCCL feature for quantized models
cargo run --release --features cuda,nccl -- --dtype bf16 --port 2000 --device-ids "0,1" --weight-path /home/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GPTQ-INT4-Marlin/ llama3 --quant gptq --temperature 0. --penalty 1.0If you encountered problems under Multi-GPU settings, you may:
export NCCL_P2P_LEVEL=LOC # use local devices (multiple cards within a server, PCIE, etc.)
export NCCL_P2P_DISABLE=1 # disable p2p cause this feature can cause illegal memory access in certain environments
export NCCL_IB_DISABLE=1 # disable ibnet/infiniband (optional)Note: number of GPUs used must be aligned to 2^n (e.g., 2, 4, or 8).
Install API and chatbot dependencies (openai package is only used for local chat with candle-vllm)
python3 -m pip install openai rich clickChat with the mini chatbot
python3 examples/chat.pyChat demo on GPU (A100, LLaMa3.1 8B)
Chat demo on Apple M4 (Phi3 3.8B)
Install ChatUI and its dependencies:
git clone [email protected]:guoqingbao/candle-vllm-demo.git
cd candle-vllm-demo
apt install npm #install npm if needed
npm install n -g #update node js if needed
n stable #update node js if needed
npm i -g pnpm #install pnpm manager
pnpm install #install ChatUI dependencies
Launching the ChatUI:
pnpm run dev # run the ChatUI
ENOSPC: System limit for number of file watchers reached
echo fs.inotify.max_user_watches=524288 | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf && sudo sysctl -p
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:2000/v1/chat/completions" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "llama7b",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "Explain how to best learn Rust."}
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 128,
"stop": {"Single":"</s>"}
}'Sample response:
{"id":"cmpl-53092967-c9cf-40e0-ae26-d7ac786d59e8","choices":[{"message":{"content":" Learning any programming language requires a combination of theory, practice, and dedication. Here are some steps and resources to help you learn Rust effectively:\n\n1. Start with the basics:\n\t* Understand the syntax and basic structure of Rust programs.\n\t* Learn about variables, data types, loops, and control structures.\n\t* Familiarize yourself with Rust's ownership system and borrowing mechanism.\n2. Read the Rust book:\n\t* The Rust book is an official resource that provides a comprehensive introduction to the language.\n\t* It covers topics such","role":"[INST]"},"finish_reason":"length","index":0,"logprobs":null}],"created":1718784498,"model":"llama7b","object":"chat.completion","usage":{"completion_tokens":129,"prompt_tokens":29,"total_tokens":158}}
In your terminal, install the openai Python package by running pip install openai. I use version 1.3.5.
Then, create a new Python file and write the following code:
import openai
openai.api_key = "EMPTY"
openai.base_url = "http://localhost:2000/v1/"
completion = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="llama",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Explain how to best learn Rust.",
},
],
max_tokens = 64,
)
print(completion.choices[0].message.content)After the candle-vllm service is running, run the Python script and enjoy efficient inference with an OpenAI compatible API server!
Install openai API first
python3 -m pip install openai
Run the benchmark test
python3 examples/benchmark.py --batch 16 --max_tokens 1024Refer to examples/benchmark.py
async def benchmark():
model = "mistral7b"
max_tokens = 1024
# 16 requests
prompts = ["Explain how to best learn Rust.",
"Please talk about deep learning in 100 words.",
"Do you know the capital city of China? Talk the details of you known.",
"Who is the best female actor in the world? Explain why.",
"How to dealing with depression?",
"How to make money in short time?",
"What is the future trend of large language model?",
"The famous tech companies in the world.",
"Explain how to best learn Rust.",
"Please talk about deep learning in 100 words.",
"Do you know the capital city of China? Talk the details of you known.",
"Who is the best female actor in the world? Explain why.",
"How to dealing with depression?",
"How to make money in short time?",
"What is the future trend of large language model?",
"The famous tech companies in the world."]
# send 16 chat requests at the same time
tasks: List[asyncio.Task] = []
for i in range(len(prompts)):
tasks.append(
asyncio.create_task(
chat_completion(model, max_tokens, prompts[i]))
)
# obtain the corresponding stream object for each request
outputs: List[Stream[ChatCompletionChunk]] = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# tasks for streaming chat responses
tasks_stream: List[asyncio.Task] = []
for i in range(len(outputs)):
tasks_stream.append(
asyncio.create_task(
stream_response(i, outputs[i]))
)
# gathering the response texts
outputs: List[(int, str)] = await asyncio.gather(*tasks_stream)
# print the results, you may find chat completion statistics in the backend server (i.e., candle-vllm)
for idx, output in outputs:
print("\n\n Response {}: \n\n {}".format(idx, output))
asyncio.run(benchmark())Candle-vllm now supports GPTQ (Marlin kernel), you may supply the quant (marlin) parameter if you have Marlin format quantized weights, such as:
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --dtype f16 --weight-path /home/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GPTQ-INT4-Marlin/ llama3 --quant marlin --temperature 0. --penalty 1.
You may also use GPTQModel to transform a model to marlin-compatible format using the given script examples/convert_marlin.py.
Note: for using Marlin fast kernel, only 4-bit GPTQ quantization supported at the moment, and the input data type should be bf16 (--dtype bf16) or f16 (--dtype f16).
Candle-vllm now supports in-situ quantization, allowing the transformation of default weights (F32/F16/BF16) or 4-bit GPTQ weights into any GGML format (or marlin format) during model loading. This feature helps conserve GPU memory (or speedup inference performance through marlin kernel), making it more efficient for consumer-grade GPUs (e.g., RTX 4090). To use this feature, simply supply the quant parameter when running candle-vllm.
For unquantized models:
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --weight-path /home/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct/ llama3 --quant q4k
For quantized 4-bit GPTQ model:
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --weight-path /home/mistral_7b-int4/ mistral --quant marlin
Options for quant parameters: ["q4_0", "q4_1", "q5_0", "q5_1", "q8_0", "q2k", "q3k","q4k","q5k","q6k", "marlin", "gguf", "ggml"]
Please note:
-
It may takes few minutes to load F32/F16/BF16 models into quantized;
-
Marlin format in-situ conversion only support 4-bit GPTQ (with
sym=True,groupsize=128or -1,desc_act=False); -
Marlin format only supported in CUDA platform.
For general configuration help, run cargo run -- --help.
For model-specific help, run cargo run --<MODE> --features <PLATFORM> -- --port 2000 <MODEL_TYPE> --help
For local model weights, run cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --weight-path /home/llama2_7b/ llama, change the path when needed.
MODE=["debug", "release"]
PLATFORM=["cuda", "metal"]
MODEL_TYPE = ["llama", "llama3", "mistral", "phi2", "phi3", "qwen2", "gemma", "yi", "stable-lm", "deep-seek"]
WEIGHT_FILE_PATH = Corresponding weight path for the given model type
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --weight-path <WEIGHT_FILE_PATH> <MODEL_TYPE>
or
MODEL_ID = Huggingface model id
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --model-id <MODEL_ID> <MODEL_TYPE>
For kvcache configuration, set kvcache_mem_cpu and kvcache_mem_gpu, default 4GB CPU memory and 4GB GPU memory for kvcache.
For chat history settings, set record_conversation to true to let candle-vllm remember chat history. By default, candle-vllm does not record chat history; instead, the client sends both the messages and the contextual history to candle-vllm. If record_conversation is set to true, the client sends only new chat messages to candle-vllm, and candle-vllm is responsible for recording the previous chat messages. However, this approach requires per-session chat recording, which is not yet implemented, so the default approach record_conversation=false is recommended.
For chat streaming, the stream flag in chat request need to be set to True.
You may supply penalty and temperature to the model to prevent potential repetitions, for example:
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --weight-path /home/mistral_7b/ mistral --repeat-last-n 64 --penalty 1.1 --temperature 0.7
--max-gen-tokens parameter is used to control the maximum output tokens per chat response. The value will be set to 1/5 of max_sequence_len by default.
For consumer GPUs, it is suggested to run the models under GGML formats (or Marlin format), e.g.,
cargo run --release --features cuda -- --port 2000 --weight-path /home/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct/ llama3 --quant q4k
where quant is one of ["q4_0", "q4_1", "q5_0", "q5_1", "q8_0", "q2k", "q3k","q4k","q5k","q6k", "marlin", "gguf", "ggml"].
Installing candle-vllm is as simple as the following steps. If you have any problems, please create an
issue.
The following features are planned to be implemented, but contributions are especially welcome:
- Sampling methods:
- Beam search (huggingface/candle#1319)
- More pipelines (from
candle-transformers)
- Python implementation:
vllm-project vllmpaper
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for candle-vllm
Similar Open Source Tools

candle-vllm
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.
AnglE
AnglE is a library for training state-of-the-art BERT/LLM-based sentence embeddings with just a few lines of code. It also serves as a general sentence embedding inference framework, allowing for inferring a variety of transformer-based sentence embeddings. The library supports various loss functions such as AnglE loss, Contrastive loss, CoSENT loss, and Espresso loss. It provides backbones like BERT-based models, LLM-based models, and Bi-directional LLM-based models for training on single or multi-GPU setups. AnglE has achieved significant performance on various benchmarks and offers official pretrained models for both BERT-based and LLM-based models.
ai00_server
AI00 RWKV Server is an inference API server for the RWKV language model based upon the web-rwkv inference engine. It supports VULKAN parallel and concurrent batched inference and can run on all GPUs that support VULKAN. No need for Nvidia cards!!! AMD cards and even integrated graphics can be accelerated!!! No need for bulky pytorch, CUDA and other runtime environments, it's compact and ready to use out of the box! Compatible with OpenAI's ChatGPT API interface. 100% open source and commercially usable, under the MIT license. If you are looking for a fast, efficient, and easy-to-use LLM API server, then AI00 RWKV Server is your best choice. It can be used for various tasks, including chatbots, text generation, translation, and Q&A.

VITA
VITA is an open-source interactive omni multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) capable of processing video, image, text, and audio inputs simultaneously. It stands out with features like Omni Multimodal Understanding, Non-awakening Interaction, and Audio Interrupt Interaction. VITA can respond to user queries without a wake-up word, track and filter external queries in real-time, and handle various query inputs effectively. The model utilizes state tokens and a duplex scheme to enhance the multimodal interactive experience.
auto-round
AutoRound is an advanced weight-only quantization algorithm for low-bits LLM inference. It competes impressively against recent methods without introducing any additional inference overhead. The method adopts sign gradient descent to fine-tune rounding values and minmax values of weights in just 200 steps, often significantly outperforming SignRound with the cost of more tuning time for quantization. AutoRound is tailored for a wide range of models and consistently delivers noticeable improvements.
rust-genai
genai is a multi-AI providers library for Rust that aims to provide a common and ergonomic single API to various generative AI providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Cohere, Ollama, and Gemini. It focuses on standardizing chat completion APIs across major AI services, prioritizing ergonomics and commonality. The library initially focuses on text chat APIs and plans to expand to support images, function calling, and more in the future versions. Version 0.1.x will have breaking changes in patches, while version 0.2.x will follow semver more strictly. genai does not provide a full representation of a given AI provider but aims to simplify the differences at a lower layer for ease of use.
mistral-inference
Mistral Inference repository contains minimal code to run 7B, 8x7B, and 8x22B models. It provides model download links, installation instructions, and usage guidelines for running models via CLI or Python. The repository also includes information on guardrailing, model platforms, deployment, and references. Users can interact with models through commands like mistral-demo, mistral-chat, and mistral-common. Mistral AI models support function calling and chat interactions for tasks like testing models, chatting with models, and using Codestral as a coding assistant. The repository offers detailed documentation and links to blogs for further information.
Acontext
Acontext is a context data platform designed for production AI agents, offering unified storage, built-in context management, and observability features. It helps agents scale from local demos to production without the need to rebuild context infrastructure. The platform provides solutions for challenges like scattered context data, long-running agents requiring context management, and tracking states from multi-modal agents. Acontext offers core features such as context storage, session management, disk storage, agent skills management, and sandbox for code execution and analysis. Users can connect to Acontext, install SDKs, initialize clients, store and retrieve messages, perform context engineering, and utilize agent storage tools. The platform also supports building agents using end-to-end scripts in Python and Typescript, with various templates available. Acontext's architecture includes client layer, backend with API and core components, infrastructure with PostgreSQL, S3, Redis, and RabbitMQ, and a web dashboard. Join the Acontext community on Discord and follow updates on GitHub.
VLM-R1
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.
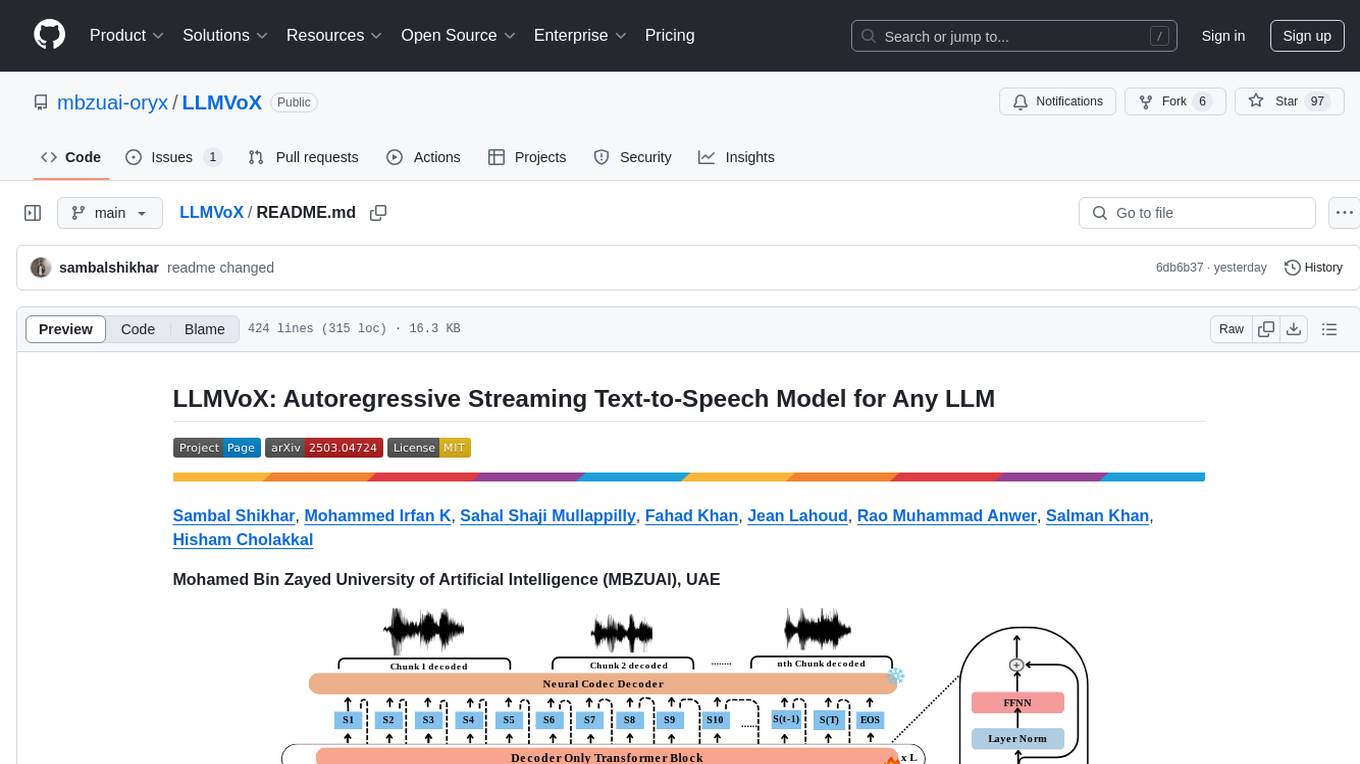
LLMVoX
LLMVoX is a lightweight 30M-parameter, LLM-agnostic, autoregressive streaming Text-to-Speech (TTS) system designed to convert text outputs from Large Language Models into high-fidelity streaming speech with low latency. It achieves significantly lower Word Error Rate compared to speech-enabled LLMs while operating at comparable latency and speech quality. Key features include being lightweight & fast with only 30M parameters, LLM-agnostic for easy integration with existing models, multi-queue streaming for continuous speech generation, and multilingual support for easy adaptation to new languages.
infinity
Infinity is a high-throughput, low-latency REST API for serving vector embeddings, supporting all sentence-transformer models and frameworks. It is developed under the MIT License and powers inference behind Gradient.ai. The API allows users to deploy models from SentenceTransformers, offers fast inference backends utilizing various accelerators, dynamic batching for efficient processing, correct and tested implementation, and easy-to-use API built on FastAPI with Swagger documentation. Users can embed text, rerank documents, and perform text classification tasks using the tool. Infinity supports various models from Huggingface and provides flexibility in deployment via CLI, Docker, Python API, and cloud services like dstack. The tool is suitable for tasks like embedding, reranking, and text classification.
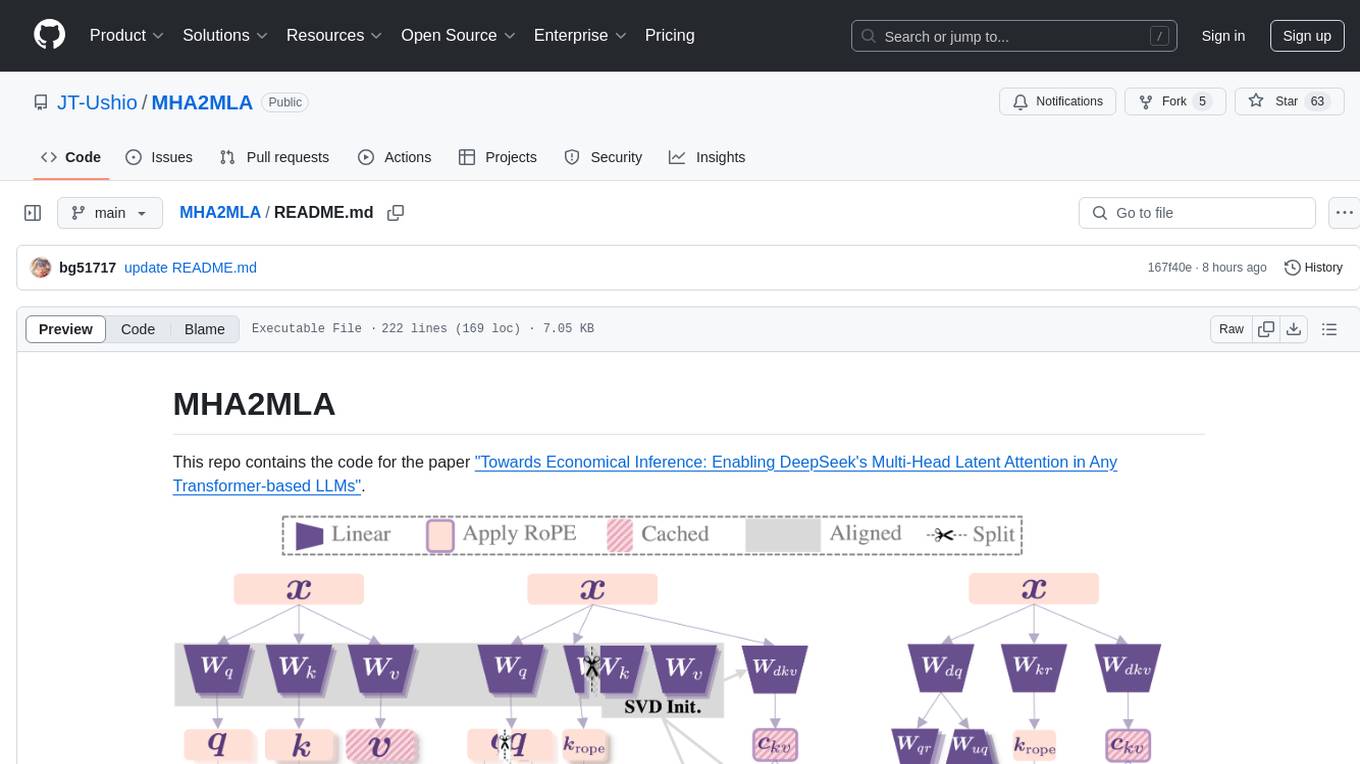
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
docutranslate
Docutranslate is a versatile tool for translating documents efficiently. It supports multiple file formats and languages, making it ideal for businesses and individuals needing quick and accurate translations. The tool uses advanced algorithms to ensure high-quality translations while maintaining the original document's formatting. With its user-friendly interface, Docutranslate simplifies the translation process and saves time for users. Whether you need to translate legal documents, technical manuals, or personal letters, Docutranslate is the go-to solution for all your document translation needs.
dspy.rb
DSPy.rb is a Ruby framework for building reliable LLM applications using composable, type-safe modules. It enables developers to define typed signatures and compose them into pipelines, offering a more structured approach compared to traditional prompting. The framework embraces Ruby conventions and adds innovations like CodeAct agents and enhanced production instrumentation, resulting in scalable LLM applications that are robust and efficient. DSPy.rb is actively developed, with a focus on stability and real-world feedback through the 0.x series before reaching a stable v1.0 API.
agentops
AgentOps is a toolkit for evaluating and developing robust and reliable AI agents. It provides benchmarks, observability, and replay analytics to help developers build better agents. AgentOps is open beta and can be signed up for here. Key features of AgentOps include: - Session replays in 3 lines of code: Initialize the AgentOps client and automatically get analytics on every LLM call. - Time travel debugging: (coming soon!) - Agent Arena: (coming soon!) - Callback handlers: AgentOps works seamlessly with applications built using Langchain and LlamaIndex.
volga
Volga is a general purpose real-time data processing engine in Python for modern AI/ML systems. It aims to be a Python-native alternative to Flink/Spark Streaming with extended functionality for real-time AI/ML workloads. It provides a hybrid push+pull architecture, Entity API for defining data entities and feature pipelines, DataStream API for general data processing, and customizable data connectors. Volga can run on a laptop or a distributed cluster, making it suitable for building custom real-time AI/ML feature platforms or general data pipelines without relying on third-party platforms.
For similar tasks

candle-vllm
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.
semantic-router
Semantic Router is a superfast decision-making layer for your LLMs and agents. Rather than waiting for slow LLM generations to make tool-use decisions, we use the magic of semantic vector space to make those decisions — _routing_ our requests using _semantic_ meaning.
hass-ollama-conversation
The Ollama Conversation integration adds a conversation agent powered by Ollama in Home Assistant. This agent can be used in automations to query information provided by Home Assistant about your house, including areas, devices, and their states. Users can install the integration via HACS and configure settings such as API timeout, model selection, context size, maximum tokens, and other parameters to fine-tune the responses generated by the AI language model. Contributions to the project are welcome, and discussions can be held on the Home Assistant Community platform.
luna-ai
Luna AI is a virtual streamer driven by a 'brain' composed of ChatterBot, GPT, Claude, langchain, chatglm, text-generation-webui, 讯飞星火, 智谱AI. It can interact with viewers in real-time during live streams on platforms like Bilibili, Douyin, Kuaishou, Douyu, or chat with you locally. Luna AI uses natural language processing and text-to-speech technologies like Edge-TTS, VITS-Fast, elevenlabs, bark-gui, VALL-E-X to generate responses to viewer questions and can change voice using so-vits-svc, DDSP-SVC. It can also collaborate with Stable Diffusion for drawing displays and loop custom texts. This project is completely free, and any identical copycat selling programs are pirated, please stop them promptly.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.

cria
Cria is a Python library designed for running Large Language Models with minimal configuration. It provides an easy and concise way to interact with LLMs, offering advanced features such as custom models, streams, message history management, and running multiple models in parallel. Cria simplifies the process of using LLMs by providing a straightforward API that requires only a few lines of code to get started. It also handles model installation automatically, making it efficient and user-friendly for various natural language processing tasks.
beyondllm
Beyond LLM offers an all-in-one toolkit for experimentation, evaluation, and deployment of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It simplifies the process with automated integration, customizable evaluation metrics, and support for various Large Language Models (LLMs) tailored to specific needs. The aim is to reduce LLM hallucination risks and enhance reliability.
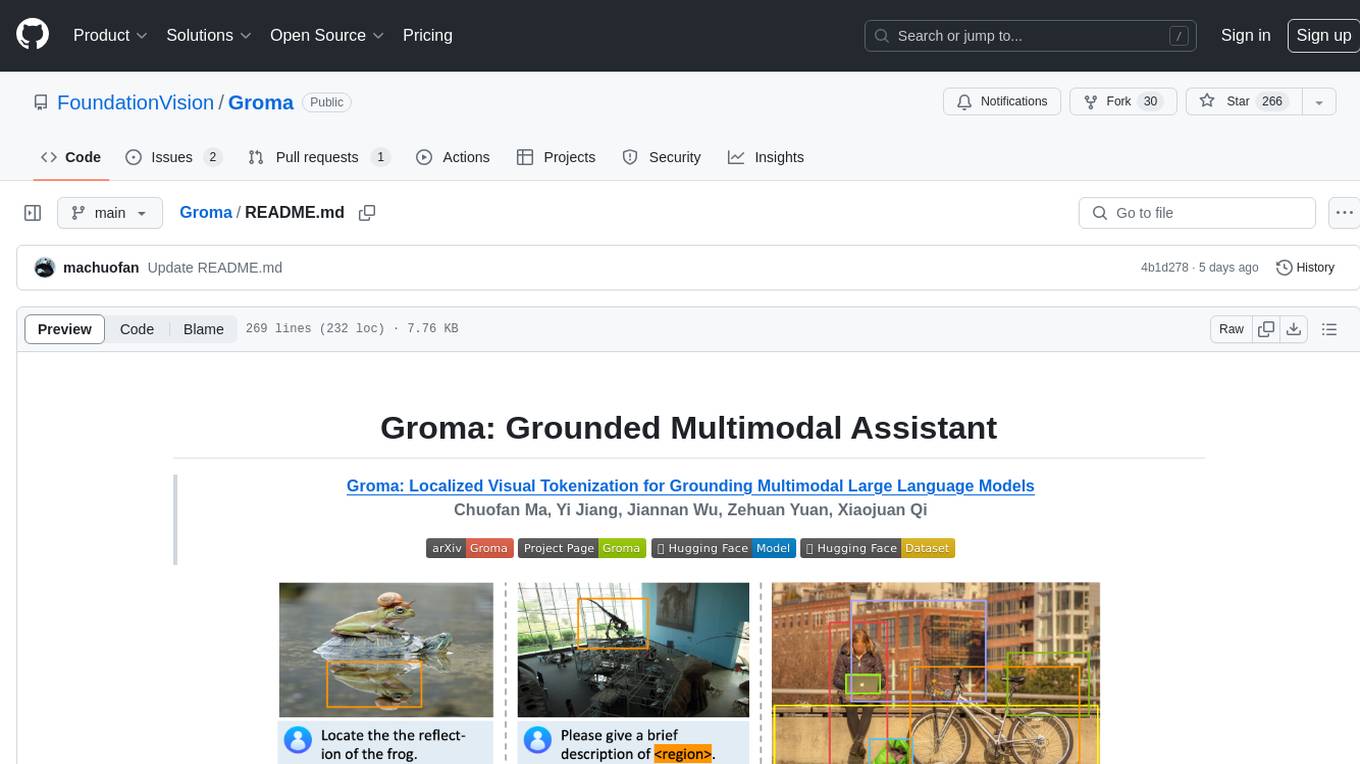
Groma
Groma is a grounded multimodal assistant that excels in region understanding and visual grounding. It can process user-defined region inputs and generate contextually grounded long-form responses. The tool presents a unique paradigm for multimodal large language models, focusing on visual tokenization for localization. Groma achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension benchmarks. The tool provides pretrained model weights and instructions for data preparation, training, inference, and evaluation. Users can customize training by starting from intermediate checkpoints. Groma is designed to handle tasks related to detection pretraining, alignment pretraining, instruction finetuning, instruction following, and more.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.


