
AnglE
Train and Infer Powerful Sentence Embeddings with AnglE | 🔥 SOTA on STS and MTEB Leaderboard
Stars: 519
AnglE is a library for training state-of-the-art BERT/LLM-based sentence embeddings with just a few lines of code. It also serves as a general sentence embedding inference framework, allowing for inferring a variety of transformer-based sentence embeddings. The library supports various loss functions such as AnglE loss, Contrastive loss, CoSENT loss, and Espresso loss. It provides backbones like BERT-based models, LLM-based models, and Bi-directional LLM-based models for training on single or multi-GPU setups. AnglE has achieved significant performance on various benchmarks and offers official pretrained models for both BERT-based and LLM-based models.
README:
EN | 简体中文
Sponsored by Mixedbread
For more detailed usage, please read the 📘 document: https://angle.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html



📢 Train/Infer Powerful Sentence Embeddings with AnglE. This library is from the paper: AnglE: Angle-optimized Text Embeddings. It allows for training state-of-the-art BERT/LLM-based sentence embeddings with just a few lines of code. AnglE is also a general sentence embedding inference framework, allowing for infering a variety of transformer-based sentence embeddings.
Loss:
- 📐 AnglE loss (ACL24)
- ⚖ Contrastive loss
- 📏 CoSENT loss
- ☕️ Espresso loss (ICLR 2025, a.k.a 2DMSE, detail: README_ESE)
Backbones:
- BERT-based models (BERT, RoBERTa, ELECTRA, ALBERT, etc.)
- LLM-based models (LLaMA, Mistral, Qwen, etc.)
- Bi-directional LLM-based models (LLaMA, Mistral, Qwen, OpenELMo, etc.. refer to: https://github.com/WhereIsAI/BiLLM)
Training:
- Single-GPU training
- Multi-GPU training
📅 May 16, 2024 | Paper "AnglE: Angle-optimized Text Embeddings" is accepted by ACL 2024 Main Conference.
📅 Mar 13, 2024 | Paper "BeLLM: Backward Dependency Enhanced Large Language Model for Sentence Embeddings" is accepted by NAACL 2024 Main Conference.
📅 Mar 8, 2024 | 🍞 mixedbread's embedding (mixedbread-ai/mxbai-embed-large-v1) achieves SOTA on the MTEB Leaderboard with an average score of 64.68! The model is trained using AnglE. Congrats mixedbread!
📅 Dec 4, 2023 | Our universal sentence embedding WhereIsAI/UAE-Large-V1 achieves SOTA on the MTEB Leaderboard with an average score of 64.64! The model is trained using AnglE.
📅 Dec, 2023 | AnglE achieves SOTA performance on the STS Bechmark Semantic Textual Similarity!
BERT-based models:
| 🤗 HF | Max Tokens | Pooling Strategy | Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| WhereIsAI/UAE-Large-V1 | 512 | cls | English, General-purpose |
| WhereIsAI/UAE-Code-Large-V1 | 512 | cls | Code Similarity |
| WhereIsAI/pubmed-angle-base-en | 512 | cls | Medical Similarity |
| WhereIsAI/pubmed-angle-large-en | 512 | cls | Medical Similarity |
LLM-based models:
| 🤗 HF (lora weight) | Backbone | Max Tokens | Prompts | Pooling Strategy | Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeanLee97/angle-llama-13b-nli | NousResearch/Llama-2-13b-hf | 4096 | Prompts.A |
last token | English, Similarity Measurement |
| SeanLee97/angle-llama-7b-nli-v2 | NousResearch/Llama-2-7b-hf | 4096 | Prompts.A |
last token | English, Similarity Measurement |
💡 You can find more third-party embeddings trained with AnglE in HuggingFace Collection
python -m pip install -U angle-emb-
With Prompts: You can specify a prompt with
prompt=YOUR_PROMPTinencodemethod. If set a prompt, the inputs should be a list of dict or a single dict with keytext, wheretextis the placeholder in the prompt for the input text. You can use other placeholder names. We provide a set of predefined prompts inPromptsclass, you can check them viaPrompts.list_prompts().
from angle_emb import AnglE, Prompts
from angle_emb.utils import cosine_similarity
angle = AnglE.from_pretrained('WhereIsAI/UAE-Large-V1', pooling_strategy='cls').cuda()
# For retrieval tasks, we use `Prompts.C` as the prompt for the query when using UAE-Large-V1 (no need to specify prompt for documents).
# When specify prompt, the inputs should be a list of dict with key 'text'
qv = angle.encode({'text': 'what is the weather?'}, to_numpy=True, prompt=Prompts.C)
doc_vecs = angle.encode([
'The weather is great!',
'it is rainy today.',
'i am going to bed'
], to_numpy=True)
for dv in doc_vecs:
print(cosine_similarity(qv[0], dv))- Without Prompts: no need to specify a prompt. Just input a list of strings or a single string.
from angle_emb import AnglE
from angle_emb.utils import cosine_similarity
angle = AnglE.from_pretrained('WhereIsAI/UAE-Large-V1', pooling_strategy='cls').cuda()
# for non-retrieval tasks, we don't need to specify prompt when using UAE-Large-V1.
doc_vecs = angle.encode([
'The weather is great!',
'The weather is very good!',
'i am going to bed'
])
for i, dv1 in enumerate(doc_vecs):
for dv2 in doc_vecs[i+1:]:
print(cosine_similarity(dv1, dv2))If the pretrained weight is a LoRA-based model, you need to specify the backbone via model_name_or_path and specify the LoRA path via the pretrained_lora_path in from_pretrained method.
import torch
from angle_emb import AnglE, Prompts
from angle_emb.utils import cosine_similarity
angle = AnglE.from_pretrained('NousResearch/Llama-2-7b-hf',
pretrained_lora_path='SeanLee97/angle-llama-7b-nli-v2',
pooling_strategy='last',
is_llm=True,
torch_dtype=torch.float16).cuda()
print('All predefined prompts:', Prompts.list_prompts())
doc_vecs = angle.encode([
{'text': 'The weather is great!'},
{'text': 'The weather is very good!'},
{'text': 'i am going to bed'}
], prompt=Prompts.A)
for i, dv1 in enumerate(doc_vecs):
for dv2 in doc_vecs[i+1:]:
print(cosine_similarity(dv1, dv2))Specify apply_billm and billm_model_class to load and infer billm models
import os
# set an environment variable for billm start index
os.environ['BiLLM_START_INDEX'] = '31'
import torch
from angle_emb import AnglE, Prompts
from angle_emb.utils import cosine_similarity
# specify `apply_billm` and `billm_model_class` to load billm models
angle = AnglE.from_pretrained('NousResearch/Llama-2-7b-hf',
pretrained_lora_path='SeanLee97/bellm-llama-7b-nli',
pooling_strategy='last',
is_llm=True,
apply_billm=True,
billm_model_class='LlamaForCausalLM',
torch_dtype=torch.float16).cuda()
doc_vecs = angle.encode([
{'text': 'The weather is great!'},
{'text': 'The weather is very good!'},
{'text': 'i am going to bed'}
], prompt='The representative word for sentence {text} is:"')
for i, dv1 in enumerate(doc_vecs):
for dv2 in doc_vecs[i+1:]:
print(cosine_similarity(dv1, dv2))Specify layer_index and embedding_size to truncate embeddings.
from angle_emb import AnglE
from angle_emb.utils import cosine_similarity
angle = AnglE.from_pretrained('mixedbread-ai/mxbai-embed-2d-large-v1', pooling_strategy='cls').cuda()
# truncate layer
angle = angle.truncate_layer(layer_index=22)
# specify embedding size to truncate embeddings
doc_vecs = angle.encode([
'The weather is great!',
'The weather is very good!',
'i am going to bed'
], embedding_size=768)
for i, dv1 in enumerate(doc_vecs):
for dv2 in doc_vecs[i+1:]:
print(cosine_similarity(dv1, dv2))You can load any transformer-based third-party models such as mixedbread-ai/mxbai-embed-large-v1, sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2, and BAAI/bge-large-en-v1.5 using angle_emb.
Here is an example:
from angle_emb import AnglE
model = AnglE.from_pretrained('mixedbread-ai/mxbai-embed-large-v1', pooling_strategy='cls').cuda()
vec = model.encode('hello world', to_numpy=True)
print(vec)It is recommended to use Mixedbread's batched library to speed up the inference process.
python -m pip install batchedimport batched
from angle_emb import AnglE
model = AnglE.from_pretrained("WhereIsAI/UAE-Large-V1", pooling_strategy='cls').cuda()
model.encode = batched.dynamically(model.encode, batch_size=64)
vecs = model.encode([
'The weather is great!',
'The weather is very good!',
'i am going to bed'
] * 50)💡 For more details, please refer to the training and fintuning.
We currently support three dataset formats:
-
DatasetFormats.A: it is a pair format with three columns:text1,text2, andlabel(0/1). -
DatasetFormats.B: it is a triple format with three columns:text,positive, andnegative.positiveandnegativestore the positive and negative samples oftext. -
DatasetFormats.C: it is a pair format with two columns:text,positive.positivestore the positive sample oftext.
You need to prepare your data into huggingface datasets.Dataset in one of the formats in terms of your supervised data.
Use angle-trainer to train your AnglE model in cli mode.
- Single gpu training:
Usage:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 angle-trainer --help- Multi-gpu training:
Usage:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 torchrun --nproc_per_node=2 --master_port=1234 -m angle_emb.angle_trainer --helpfrom datasets import load_dataset
from angle_emb import AnglE, AngleDataTokenizer
# 1. load pretrained model
angle = AnglE.from_pretrained('SeanLee97/angle-bert-base-uncased-nli-en-v1', max_length=128, pooling_strategy='cls').cuda()
# 2. load dataset
# `text1`, `text2`, and `label` are three required columns.
ds = load_dataset('mteb/stsbenchmark-sts')
ds = ds.map(lambda obj: {"text1": str(obj["sentence1"]), "text2": str(obj['sentence2']), "label": obj['score']})
ds = ds.select_columns(["text1", "text2", "label"])
# 3. transform data
train_ds = ds['train'].shuffle().map(AngleDataTokenizer(angle.tokenizer, angle.max_length), num_proc=8)
valid_ds = ds['validation'].map(AngleDataTokenizer(angle.tokenizer, angle.max_length), num_proc=8)
# 4. fit
angle.fit(
train_ds=train_ds,
valid_ds=valid_ds,
output_dir='ckpts/sts-b',
batch_size=32,
epochs=5,
learning_rate=2e-5,
save_steps=100,
eval_steps=1000,
warmup_steps=0,
gradient_accumulation_steps=1,
loss_kwargs={
'cosine_w': 1.0,
'ibn_w': 1.0,
'cln_w': 1.0,
'angle_w': 0.02,
'cosine_tau': 20,
'ibn_tau': 20,
'angle_tau': 20
},
fp16=True,
logging_steps=100
)
# 5. evaluate
corrcoef = angle.evaluate(ds['test'])
print('Spearman\'s corrcoef:', corrcoef)- To enable
llmtraining, please specify--is_llm 1and configure appropriate LoRA hyperparameters. - To enable
billmtraining, please specify--apply_billm 1and configure appropriatebillm_model_classsuch asLLamaForCausalLM(refer to: https://github.com/WhereIsAI/BiLLM?tab=readme-ov-file#usage). - To enable espresso sentence embeddings (ESE), please specify
--apply_ese 1and configure appropriate ESE hyperparameters via--ese_kl_temperature floatand--ese_compression_size integer. - To convert the trained AnglE models to
sentence-transformers, please runpython scripts/convert_to_sentence_transformers.py --helpfor more details.
For more details, please refer to the documentation.
1️⃣ If your dataset format is DatasetFormats.A, it is recommended to slightly increase the weight for cosine_w or slightly decrease the weight for ibn_w.
2️⃣ If your dataset format is DatasetFormats.B, it is recommended to set cosine_w to 0, and set angle_w to a small value like 0.02. Be sure to set cln_w and ibn_w.
3️⃣ If your dataset format is DatasetFormats.C, only ibn_w and ibn_tau are effective. You don't need to tune other parameters.
4️⃣ To alleviate information forgetting in fine-tuning, it is better to specify the teacher_name_or_path. If the teacher_name_or_path equals model_name_or_path, it will conduct self-distillation. It is worth to note that teacher_name_or_path has to have the same tokenizer as model_name_or_path. Or it will lead to unexpected results.
-
Training: SentenceTransformers also provides a implementation of AnglE loss. But it is partially implemented and may not work well as the official code. We recommend to use the official
angle_embfor fine-tuning AnglE model. -
Infering: If your model is trained with
angle_emb, and you want to use it withsentence-transformers. You can convert it tosentence-transformersmodel using the scriptexamples/convert_to_sentence_transformers.py.
You are welcome to use our code and pre-trained models. If you use our code and pre-trained models, please support us by citing our work as follows:
@article{li2023angle,
title={AnglE-optimized Text Embeddings},
author={Li, Xianming and Li, Jing},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.12871},
year={2023}
}| 📅 | Description |
|---|---|
| 2024 May 21 | support Espresso Sentence Embeddings |
| 2024 Feb 7 | support training with only positive pairs (DatasetFormats.C) |
| 2023 Dec 4 | Release a universal English sentence embedding model: WhereIsAI/UAE-Large-V1 |
| 2023 Nov 2 | Release an English pretrained model: SeanLee97/angle-llama-13b-nli
|
| 2023 Oct 28 | Release two chinese pretrained models: SeanLee97/angle-roberta-wwm-base-zhnli-v1 and SeanLee97/angle-llama-7b-zhnli-v1; Add chinese README.md |
If you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to contact us via email: [email protected]
This project is licensed under the MIT License. For the pretrained models, please refer to the corresponding license of the models.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AnglE
Similar Open Source Tools

AnglE
AnglE is a library for training state-of-the-art BERT/LLM-based sentence embeddings with just a few lines of code. It also serves as a general sentence embedding inference framework, allowing for inferring a variety of transformer-based sentence embeddings. The library supports various loss functions such as AnglE loss, Contrastive loss, CoSENT loss, and Espresso loss. It provides backbones like BERT-based models, LLM-based models, and Bi-directional LLM-based models for training on single or multi-GPU setups. AnglE has achieved significant performance on various benchmarks and offers official pretrained models for both BERT-based and LLM-based models.
candle-vllm
Candle-vllm is an efficient and easy-to-use platform designed for inference and serving local LLMs, featuring an OpenAI compatible API server. It offers a highly extensible trait-based system for rapid implementation of new module pipelines, streaming support in generation, efficient management of key-value cache with PagedAttention, and continuous batching. The tool supports chat serving for various models and provides a seamless experience for users to interact with LLMs through different interfaces.

hezar
Hezar is an all-in-one AI library designed specifically for the Persian community. It brings together various AI models and tools, making it easy to use AI with just a few lines of code. The library seamlessly integrates with Hugging Face Hub, offering a developer-friendly interface and task-based model interface. In addition to models, Hezar provides tools like word embeddings, tokenizers, feature extractors, and more. It also includes supplementary ML tools for deployment, benchmarking, and optimization.
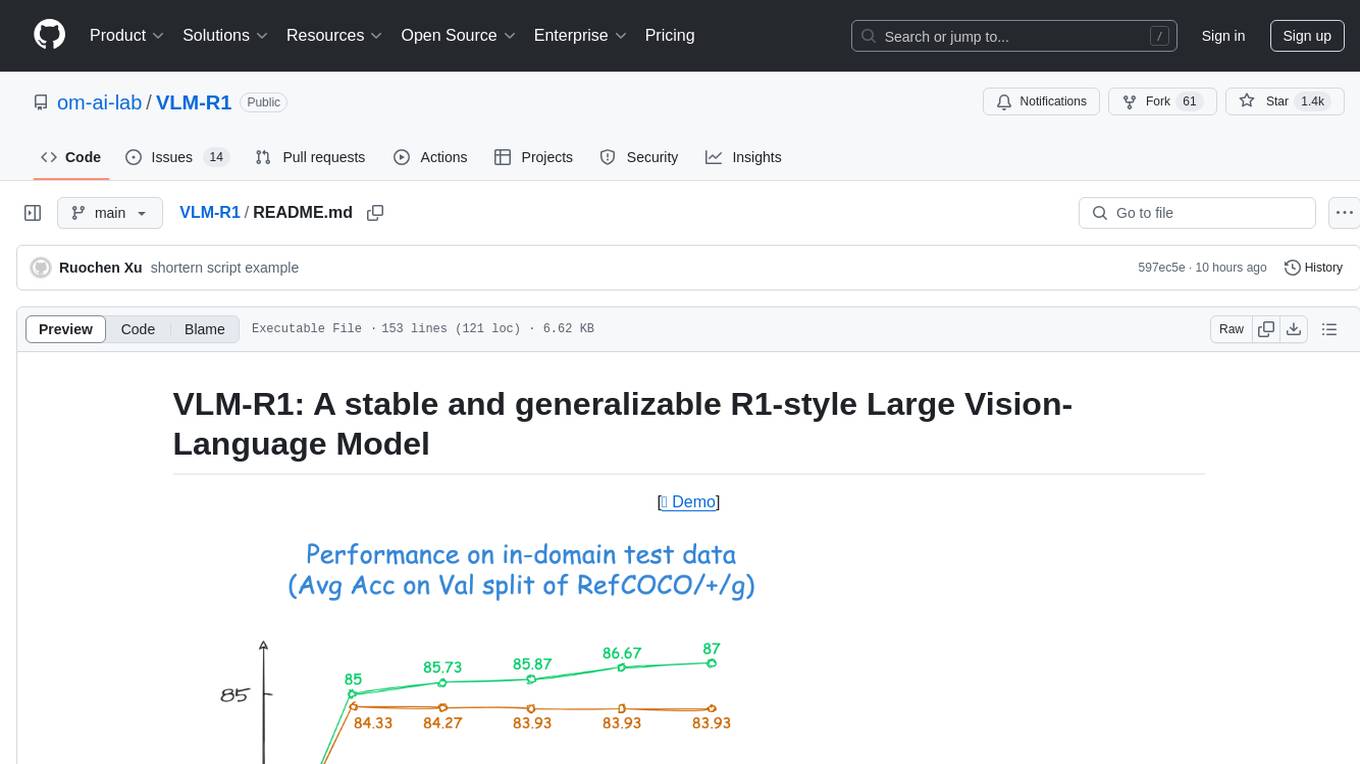
VLM-R1
VLM-R1 is a stable and generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model proposed for Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) task. It compares R1 and SFT approaches, showing R1 model's steady improvement on out-of-domain test data. The project includes setup instructions, training steps for GRPO and SFT models, support for user data loading, and evaluation process. Acknowledgements to various open-source projects and resources are mentioned. The project aims to provide a reliable and versatile solution for vision-language tasks.
ai00_server
AI00 RWKV Server is an inference API server for the RWKV language model based upon the web-rwkv inference engine. It supports VULKAN parallel and concurrent batched inference and can run on all GPUs that support VULKAN. No need for Nvidia cards!!! AMD cards and even integrated graphics can be accelerated!!! No need for bulky pytorch, CUDA and other runtime environments, it's compact and ready to use out of the box! Compatible with OpenAI's ChatGPT API interface. 100% open source and commercially usable, under the MIT license. If you are looking for a fast, efficient, and easy-to-use LLM API server, then AI00 RWKV Server is your best choice. It can be used for various tasks, including chatbots, text generation, translation, and Q&A.
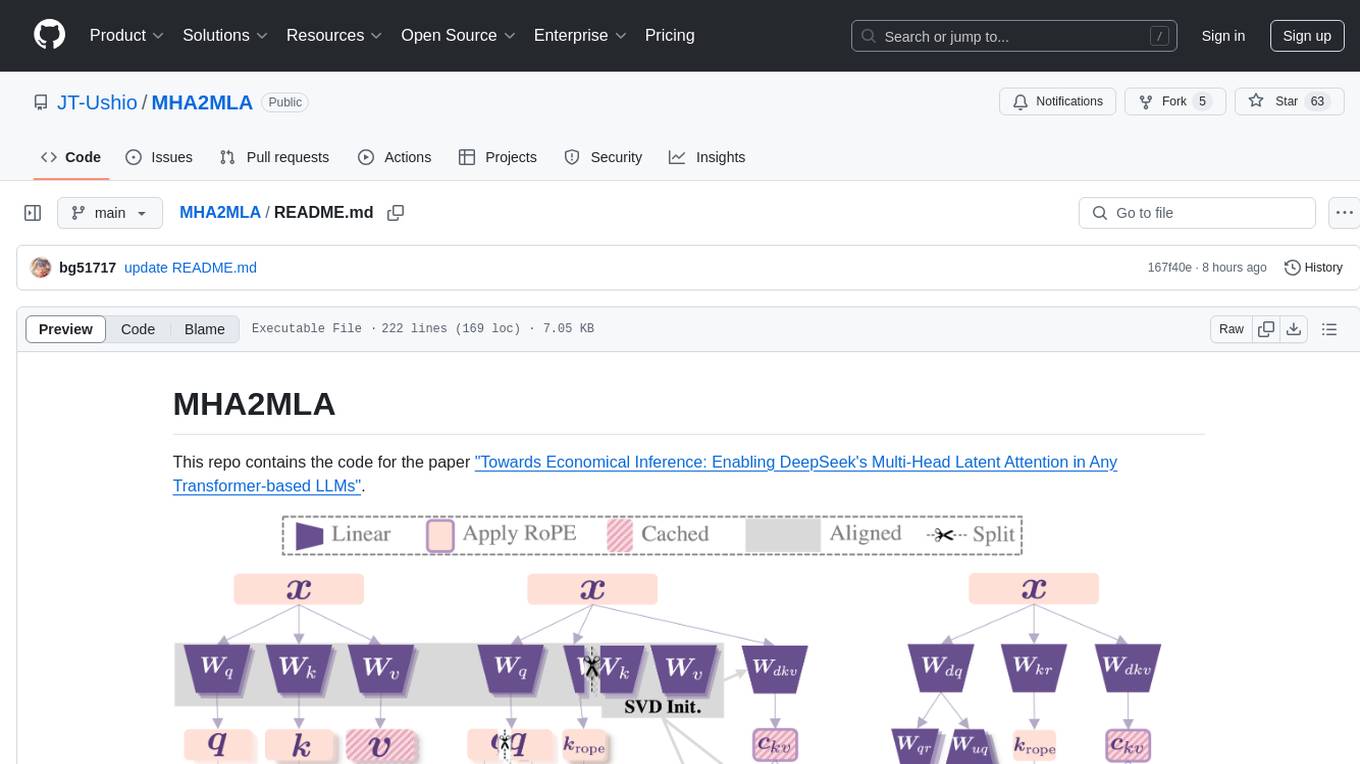
MHA2MLA
This repository contains the code for the paper 'Towards Economical Inference: Enabling DeepSeek's Multi-Head Latent Attention in Any Transformer-based LLMs'. It provides tools for fine-tuning and evaluating Llama models, converting models between different frameworks, processing datasets, and performing specific model training tasks like Partial-RoPE Fine-Tuning and Multiple-Head Latent Attention Fine-Tuning. The repository also includes commands for model evaluation using Lighteval and LongBench, along with necessary environment setup instructions.
rank_llm
RankLLM is a suite of prompt-decoders compatible with open source LLMs like Vicuna and Zephyr. It allows users to create custom ranking models for various NLP tasks, such as document reranking, question answering, and summarization. The tool offers a variety of features, including the ability to fine-tune models on custom datasets, use different retrieval methods, and control the context size and variable passages. RankLLM is easy to use and can be integrated into existing NLP pipelines.

CodeTF
CodeTF is a Python transformer-based library for code large language models (Code LLMs) and code intelligence. It provides an interface for training and inferencing on tasks like code summarization, translation, and generation. The library offers utilities for code manipulation across various languages, including easy extraction of code attributes. Using tree-sitter as its core AST parser, CodeTF enables parsing of function names, comments, and variable names. It supports fast model serving, fine-tuning of LLMs, various code intelligence tasks, preprocessed datasets, model evaluation, pretrained and fine-tuned models, and utilities to manipulate source code. CodeTF aims to facilitate the integration of state-of-the-art Code LLMs into real-world applications, ensuring a user-friendly environment for code intelligence tasks.
infinity
Infinity is a high-throughput, low-latency REST API for serving vector embeddings, supporting all sentence-transformer models and frameworks. It is developed under the MIT License and powers inference behind Gradient.ai. The API allows users to deploy models from SentenceTransformers, offers fast inference backends utilizing various accelerators, dynamic batching for efficient processing, correct and tested implementation, and easy-to-use API built on FastAPI with Swagger documentation. Users can embed text, rerank documents, and perform text classification tasks using the tool. Infinity supports various models from Huggingface and provides flexibility in deployment via CLI, Docker, Python API, and cloud services like dstack. The tool is suitable for tasks like embedding, reranking, and text classification.
cellseg_models.pytorch
cellseg-models.pytorch is a Python library built upon PyTorch for 2D cell/nuclei instance segmentation models. It provides multi-task encoder-decoder architectures and post-processing methods for segmenting cell/nuclei instances. The library offers high-level API to define segmentation models, open-source datasets for training, flexibility to modify model components, sliding window inference, multi-GPU inference, benchmarking utilities, regularization techniques, and example notebooks for training and finetuning models with different backbones.
langcheck
LangCheck is a Python library that provides a suite of metrics and tools for evaluating the quality of text generated by large language models (LLMs). It includes metrics for evaluating text fluency, sentiment, toxicity, factual consistency, and more. LangCheck also provides tools for visualizing metrics, augmenting data, and writing unit tests for LLM applications. With LangCheck, you can quickly and easily assess the quality of LLM-generated text and identify areas for improvement.
volga
Volga is a general purpose real-time data processing engine in Python for modern AI/ML systems. It aims to be a Python-native alternative to Flink/Spark Streaming with extended functionality for real-time AI/ML workloads. It provides a hybrid push+pull architecture, Entity API for defining data entities and feature pipelines, DataStream API for general data processing, and customizable data connectors. Volga can run on a laptop or a distributed cluster, making it suitable for building custom real-time AI/ML feature platforms or general data pipelines without relying on third-party platforms.
ax
Ax is a Typescript library that allows users to build intelligent agents inspired by agentic workflows and the Stanford DSP paper. It seamlessly integrates with multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) and VectorDBs to create RAG pipelines or collaborative agents capable of solving complex problems. The library offers advanced features such as streaming validation, multi-modal DSP, and automatic prompt tuning using optimizers. Users can easily convert documents of any format to text, perform smart chunking, embedding, and querying, and ensure output validation while streaming. Ax is production-ready, written in Typescript, and has zero dependencies.
LLMTSCS
LLMLight is a novel framework that employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as decision-making agents for Traffic Signal Control (TSC). The framework leverages the advanced generalization capabilities of LLMs to engage in a reasoning and decision-making process akin to human intuition for effective traffic control. LLMLight has been demonstrated to be remarkably effective, generalizable, and interpretable against various transportation-based and RL-based baselines on nine real-world and synthetic datasets.
avante.nvim
avante.nvim is a Neovim plugin that emulates the behavior of the Cursor AI IDE, providing AI-driven code suggestions and enabling users to apply recommendations to their source files effortlessly. It offers AI-powered code assistance and one-click application of suggested changes, streamlining the editing process and saving time. The plugin is still in early development, with functionalities like setting API keys, querying AI about code, reviewing suggestions, and applying changes. Key bindings are available for various actions, and the roadmap includes enhancing AI interactions, stability improvements, and introducing new features for coding tasks.
LongLoRA
LongLoRA is a tool for efficient fine-tuning of long-context large language models. It includes LongAlpaca data with long QA data collected and short QA sampled, models from 7B to 70B with context length from 8k to 100k, and support for GPTNeoX models. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning, context extension, and improved LoRA fine-tuning. It provides pre-trained weights, fine-tuning instructions, evaluation methods, local and online demos, streaming inference, and data generation via Pdf2text. LongLoRA is licensed under Apache License 2.0, while data and weights are under CC-BY-NC 4.0 License for research use only.
For similar tasks

AnglE
AnglE is a library for training state-of-the-art BERT/LLM-based sentence embeddings with just a few lines of code. It also serves as a general sentence embedding inference framework, allowing for inferring a variety of transformer-based sentence embeddings. The library supports various loss functions such as AnglE loss, Contrastive loss, CoSENT loss, and Espresso loss. It provides backbones like BERT-based models, LLM-based models, and Bi-directional LLM-based models for training on single or multi-GPU setups. AnglE has achieved significant performance on various benchmarks and offers official pretrained models for both BERT-based and LLM-based models.
lighteval
LightEval is a lightweight LLM evaluation suite that Hugging Face has been using internally with the recently released LLM data processing library datatrove and LLM training library nanotron. We're releasing it with the community in the spirit of building in the open. Note that it is still very much early so don't expect 100% stability ^^' In case of problems or question, feel free to open an issue!
Firefly
Firefly is an open-source large model training project that supports pre-training, fine-tuning, and DPO of mainstream large models. It includes models like Llama3, Gemma, Qwen1.5, MiniCPM, Llama, InternLM, Baichuan, ChatGLM, Yi, Deepseek, Qwen, Orion, Ziya, Xverse, Mistral, Mixtral-8x7B, Zephyr, Vicuna, Bloom, etc. The project supports full-parameter training, LoRA, QLoRA efficient training, and various tasks such as pre-training, SFT, and DPO. Suitable for users with limited training resources, QLoRA is recommended for fine-tuning instructions. The project has achieved good results on the Open LLM Leaderboard with QLoRA training process validation. The latest version has significant updates and adaptations for different chat model templates.
Awesome-Text2SQL
Awesome Text2SQL is a curated repository containing tutorials and resources for Large Language Models, Text2SQL, Text2DSL, Text2API, Text2Vis, and more. It provides guidelines on converting natural language questions into structured SQL queries, with a focus on NL2SQL. The repository includes information on various models, datasets, evaluation metrics, fine-tuning methods, libraries, and practice projects related to Text2SQL. It serves as a comprehensive resource for individuals interested in working with Text2SQL and related technologies.
create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch
The 'create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch' repository provides a detailed guide on creating a Large Language Model (LLM) with 2.3 million parameters from scratch. The blog replicates the LLaMA approach, incorporating concepts like RMSNorm for pre-normalization, SwiGLU activation function, and Rotary Embeddings. The model is trained on a basic dataset to demonstrate the ease of creating a million-parameter LLM without the need for a high-end GPU.
StableToolBench
StableToolBench is a new benchmark developed to address the instability of Tool Learning benchmarks. It aims to balance stability and reality by introducing features such as a Virtual API System with caching and API simulators, a new set of solvable queries determined by LLMs, and a Stable Evaluation System using GPT-4. The Virtual API Server can be set up either by building from source or using a prebuilt Docker image. Users can test the server using provided scripts and evaluate models with Solvable Pass Rate and Solvable Win Rate metrics. The tool also includes model experiments results comparing different models' performance.
BetaML.jl
The Beta Machine Learning Toolkit is a package containing various algorithms and utilities for implementing machine learning workflows in multiple languages, including Julia, Python, and R. It offers a range of supervised and unsupervised models, data transformers, and assessment tools. The models are implemented entirely in Julia and are not wrappers for third-party models. Users can easily contribute new models or request implementations. The focus is on user-friendliness rather than computational efficiency, making it suitable for educational and research purposes.
AI-TOD
AI-TOD is a dataset for tiny object detection in aerial images, containing 700,621 object instances across 28,036 images. Objects in AI-TOD are smaller with a mean size of 12.8 pixels compared to other aerial image datasets. To use AI-TOD, download xView training set and AI-TOD_wo_xview, then generate the complete dataset using the provided synthesis tool. The dataset is publicly available for academic and research purposes under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.







