
mlflow
The open source developer platform to build AI agents and models with confidence. Enhance your AI applications with end-to-end tracking, observability, and evaluations, all in one integrated platform.
Stars: 24154

MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking
README:
MLflow is an open-source developer platform to build AI/LLM applications and models with confidence. Enhance your AI applications with end-to-end experiment tracking, observability, and evaluations, all in one integrated platform.
To install the MLflow Python package, run the following command:
pip install mlflow
MLflow is the only platform that provides a unified solution for all your AI/ML needs, including LLMs, Agents, Deep Learning, and traditional machine learning.

🔍 Tracing / Observability Trace the internal states of your LLM/agentic applications for debugging quality issues and monitoring performance with ease.
Getting Started → |

📊 LLM Evaluation A suite of automated model evaluation tools, seamlessly integrated with experiment tracking to compare across multiple versions.
Getting Started → |

🤖 Prompt Management Version, track, and reuse prompts across your organization, helping maintain consistency and improve collaboration in prompt development.
Getting Started → |

📦 App Version Tracking MLflow keeps track of many moving parts in your AI applications, such as models, prompts, tools, and code, with end-to-end lineage.
Getting Started → |

📝 Experiment Tracking Track your models, parameters, metrics, and evaluation results in ML experiments and compare them using an interactive UI.
Getting Started → |
|

💾 Model Registry A centralized model store designed to collaboratively manage the full lifecycle and deployment of machine learning models.
Getting Started → |
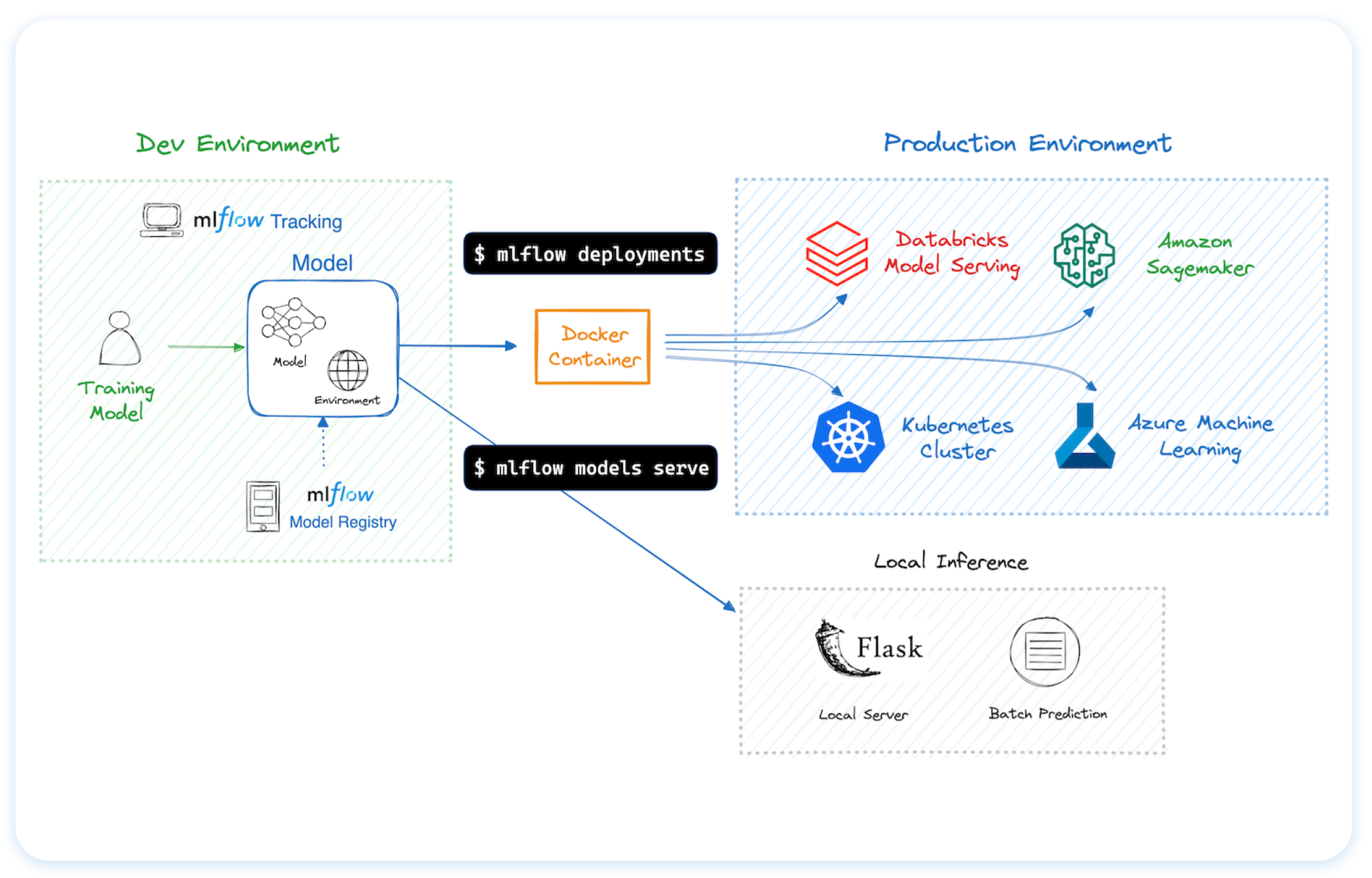
🚀 Deployment Tools for seamless model deployment to batch and real-time scoring on platforms like Docker, Kubernetes, Azure ML, and AWS SageMaker.
Getting Started → |
You can run MLflow in many different environments, including local machines, on-premise servers, and cloud infrastructure.
Trusted by thousands of organizations, MLflow is now offered as a managed service by most major cloud providers:
For hosting MLflow on your own infrastructure, please refer to this guidance.
MLflow is natively integrated with many popular machine learning frameworks and GenAI libraries.
Tracing (Observability) (Doc)
MLflow Tracing provides LLM observability for various GenAI libraries such as OpenAI, LangChain, LlamaIndex, DSPy, AutoGen, and more. To enable auto-tracing, call mlflow.xyz.autolog() before running your models. Refer to the documentation for customization and manual instrumentation.
import mlflow
from openai import OpenAI
# Enable tracing for OpenAI
mlflow.openai.autolog()
# Query OpenAI LLM normally
response = OpenAI().chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hi!"}],
temperature=0.1,
)Then navigate to the "Traces" tab in the MLflow UI to find the trace records for the OpenAI query.
Evaluating LLMs, Prompts, and Agents (Doc)
The following example runs automatic evaluation for question-answering tasks with several built-in metrics.
import os
import openai
import mlflow
from mlflow.genai.scorers import Correctness, Guidelines
client = openai.OpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"))
# 1. Define a simple QA dataset
dataset = [
{
"inputs": {"question": "Can MLflow manage prompts?"},
"expectations": {"expected_response": "Yes!"},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "Can MLflow create a taco for my lunch?"},
"expectations": {
"expected_response": "No, unfortunately, MLflow is not a taco maker."
},
},
]
# 2. Define a prediction function to generate responses
def predict_fn(question: str) -> str:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini", messages=[{"role": "user", "content": question}]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
# 3. Run the evaluation
results = mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=dataset,
predict_fn=predict_fn,
scorers=[
# Built-in LLM judge
Correctness(),
# Custom criteria using LLM judge
Guidelines(name="is_english", guidelines="The answer must be in English"),
],
)Navigate to the "Evaluations" tab in the MLflow UI to find the evaluation results.
Tracking Model Training (Doc)
The following example trains a simple regression model with scikit-learn, while enabling MLflow's autologging feature for experiment tracking.
import mlflow
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
# Enable MLflow's automatic experiment tracking for scikit-learn
mlflow.sklearn.autolog()
# Load the training dataset
db = load_diabetes()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(db.data, db.target)
rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, max_depth=6, max_features=3)
# MLflow triggers logging automatically upon model fitting
rf.fit(X_train, y_train)Once the above code finishes, run the following command in a separate terminal and access the MLflow UI via the printed URL. An MLflow Run should be automatically created, which tracks the training dataset, hyperparameters, performance metrics, the trained model, dependencies, and even more.
mlflow server
- For help or questions about MLflow usage (e.g. "how do I do X?") visit the documentation.
- In the documentation, you can ask the question to our AI-powered chat bot. Click on the "Ask AI" button at the right bottom.
- Join the virtual events like office hours and meetups.
- To report a bug, file a documentation issue, or submit a feature request, please open a GitHub issue.
- For release announcements and other discussions, please subscribe to our mailing list ([email protected]) or join us on Slack.
We happily welcome contributions to MLflow!
- Submit bug reports and feature requests
- Contribute for good-first-issues and help-wanted
- Writing about MLflow and sharing your experience
Please see our contribution guide to learn more about contributing to MLflow.
If you use MLflow in your research, please cite it using the "Cite this repository" button at the top of the GitHub repository page, which will provide you with citation formats including APA and BibTeX.
MLflow is currently maintained by the following core members with significant contributions from hundreds of exceptionally talented community members.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mlflow
Similar Open Source Tools

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking

sdialog
SDialog is an MIT-licensed open-source toolkit for building, simulating, and evaluating LLM-based conversational agents end-to-end. It aims to bridge agent construction, user simulation, dialog generation, and evaluation in a single reproducible workflow, enabling the generation of reliable, controllable dialog systems or data at scale. The toolkit standardizes a Dialog schema, offers persona-driven multi-agent simulation with LLMs, provides composable orchestration for precise control over behavior and flow, includes built-in evaluation metrics, and offers mechanistic interpretability. It allows for easy creation of user-defined components and interoperability across various AI platforms.

clearml
ClearML is an auto-magical suite of tools designed to streamline AI workflows. It includes modules for experiment management, MLOps/LLMOps, data management, model serving, and more. ClearML offers features like experiment tracking, model serving, orchestration, and automation. It supports various ML/DL frameworks and integrates with Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm for remote debugging. ClearML aims to simplify collaboration, automate processes, and enhance visibility in AI projects.

clearml
ClearML is a suite of tools designed to streamline the machine learning workflow. It includes an experiment manager, MLOps/LLMOps, data management, and model serving capabilities. ClearML is open-source and offers a free tier hosting option. It supports various ML/DL frameworks and integrates with Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm. ClearML provides extensive logging capabilities, including source control info, execution environment, hyper-parameters, and experiment outputs. It also offers automation features, such as remote job execution and pipeline creation. ClearML is designed to be easy to integrate, requiring only two lines of code to add to existing scripts. It aims to improve collaboration, visibility, and data transparency within ML teams.

starwhale
Starwhale is an MLOps/LLMOps platform that brings efficiency and standardization to machine learning operations. It streamlines the model development lifecycle, enabling teams to optimize workflows around key areas like model building, evaluation, release, and fine-tuning. Starwhale abstracts Model, Runtime, and Dataset as first-class citizens, providing tailored capabilities for common workflow scenarios including Models Evaluation, Live Demo, and LLM Fine-tuning. It is an open-source platform designed for clarity and ease of use, empowering developers to build customized MLOps features tailored to their needs.

lerobot
LeRobot is a state-of-the-art AI library for real-world robotics in PyTorch. It aims to provide models, datasets, and tools to lower the barrier to entry to robotics, focusing on imitation learning and reinforcement learning. LeRobot offers pretrained models, datasets with human-collected demonstrations, and simulation environments. It plans to support real-world robotics on affordable and capable robots. The library hosts pretrained models and datasets on the Hugging Face community page.
deepchecks
Deepchecks is a holistic open-source solution for AI & ML validation needs, enabling thorough testing of data and models from research to production. It includes components for testing, CI & testing management, and monitoring. Users can install and use Deepchecks for testing and monitoring their AI models, with customizable checks and suites for tabular, NLP, and computer vision data. The tool provides visual reports, pythonic/json output for processing, and a dynamic UI for collaboration and monitoring. Deepchecks is open source, with premium features available under a commercial license for monitoring components.
Kiln
Kiln is an intuitive tool for fine-tuning LLM models, generating synthetic data, and collaborating on datasets. It offers desktop apps for Windows, MacOS, and Linux, zero-code fine-tuning for various models, interactive data generation, and Git-based version control. Users can easily collaborate with QA, PM, and subject matter experts, generate auto-prompts, and work with a wide range of models and providers. The tool is open-source, privacy-first, and supports structured data tasks in JSON format. Kiln is free to use and helps build high-quality AI products with datasets, facilitates collaboration between technical and non-technical teams, allows comparison of models and techniques without code, ensures structured data integrity, and prioritizes user privacy.
MetaGPT
MetaGPT is a multi-agent framework that enables GPT to work in a software company, collaborating to tackle more complex tasks. It assigns different roles to GPTs to form a collaborative entity for complex tasks. MetaGPT takes a one-line requirement as input and outputs user stories, competitive analysis, requirements, data structures, APIs, documents, etc. Internally, MetaGPT includes product managers, architects, project managers, and engineers. It provides the entire process of a software company along with carefully orchestrated SOPs. MetaGPT's core philosophy is "Code = SOP(Team)", materializing SOP and applying it to teams composed of LLMs.
anything-llm
AnythingLLM is a full-stack application that enables you to turn any document, resource, or piece of content into context that any LLM can use as references during chatting. This application allows you to pick and choose which LLM or Vector Database you want to use as well as supporting multi-user management and permissions.
mobius
Mobius is an AI infra platform including realtime computing and training. It is built on Ray, a distributed computing framework, and provides a number of features that make it well-suited for online machine learning tasks. These features include: * **Cross Language**: Mobius can run in multiple languages (only Python and Java are supported currently) with high efficiency. You can implement your operator in different languages and run them in one job. * **Single Node Failover**: Mobius has a special failover mechanism that only needs to rollback the failed node itself, in most cases, to recover the job. This is a huge benefit if your job is sensitive about failure recovery time. * **AutoScaling**: Mobius can generate a new graph with different configurations in runtime without stopping the job. * **Fusion Training**: Mobius can combine TensorFlow/Pytorch and streaming, then building an e2e online machine learning pipeline. Mobius is still under development, but it has already been used to power a number of real-world applications, including: * A real-time recommendation system for a major e-commerce company * A fraud detection system for a large financial institution * A personalized news feed for a major news organization If you are interested in using Mobius for your own online machine learning projects, you can find more information in the documentation.

openlit
OpenLIT is an OpenTelemetry-native GenAI and LLM Application Observability tool. It's designed to make the integration process of observability into GenAI projects as easy as pie – literally, with just **a single line of code**. Whether you're working with popular LLM Libraries such as OpenAI and HuggingFace or leveraging vector databases like ChromaDB, OpenLIT ensures your applications are monitored seamlessly, providing critical insights to improve performance and reliability.
ChatDev
ChatDev is a virtual software company powered by intelligent agents like CEO, CPO, CTO, programmer, reviewer, tester, and art designer. These agents collaborate to revolutionize the digital world through programming. The platform offers an easy-to-use, highly customizable, and extendable framework based on large language models, ideal for studying collective intelligence. ChatDev introduces innovative methods like Iterative Experience Refinement and Experiential Co-Learning to enhance software development efficiency. It supports features like incremental development, Docker integration, Git mode, and Human-Agent-Interaction mode. Users can customize ChatChain, Phase, and Role settings, and share their software creations easily. The project is open-source under the Apache 2.0 License and utilizes data licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0.

lanarky
Lanarky is a Python web framework designed for building microservices using Large Language Models (LLMs). It is LLM-first, fast, modern, supports streaming over HTTP and WebSockets, and is open-source. The framework provides an abstraction layer for developers to easily create LLM microservices. Lanarky guarantees zero vendor lock-in and is free to use. It is built on top of FastAPI and offers features familiar to FastAPI users. The project is now in maintenance mode, with no active development planned, but community contributions are encouraged.
vocode-core
Vocode is an open source library that enables users to build voice-based LLM (Large Language Model) applications quickly and easily. With Vocode, users can create real-time streaming conversations with LLMs and deploy them for phone calls, Zoom meetings, and more. The library offers abstractions and integrations for transcription services, LLMs, and synthesis services, making it a comprehensive tool for voice-based app development. Vocode also provides out-of-the-box integrations with various services like AssemblyAI, OpenAI, Microsoft Azure, and more, allowing users to leverage these services seamlessly in their applications.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
For similar tasks

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

ray
Ray is a unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications. It consists of a core distributed runtime and a set of AI libraries for simplifying ML compute, including Data, Train, Tune, RLlib, and Serve. Ray runs on any machine, cluster, cloud provider, and Kubernetes, and features a growing ecosystem of community integrations. With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster, making it easy to meet the compute-intensive demands of modern ML workloads.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.

djl
Deep Java Library (DJL) is an open-source, high-level, engine-agnostic Java framework for deep learning. It is designed to be easy to get started with and simple to use for Java developers. DJL provides a native Java development experience and allows users to integrate machine learning and deep learning models with their Java applications. The framework is deep learning engine agnostic, enabling users to switch engines at any point for optimal performance. DJL's ergonomic API interface guides users with best practices to accomplish deep learning tasks, such as running inference and training neural networks.

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking
tt-metal
TT-NN is a python & C++ Neural Network OP library. It provides a low-level programming model, TT-Metalium, enabling kernel development for Tenstorrent hardware.
burn
Burn is a new comprehensive dynamic Deep Learning Framework built using Rust with extreme flexibility, compute efficiency and portability as its primary goals.
awsome-distributed-training
This repository contains reference architectures and test cases for distributed model training with Amazon SageMaker Hyperpod, AWS ParallelCluster, AWS Batch, and Amazon EKS. The test cases cover different types and sizes of models as well as different frameworks and parallel optimizations (Pytorch DDP/FSDP, MegatronLM, NemoMegatron...).
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.





