swiftide
Fast, streaming indexing, query, and agentic LLM applications in Rust
Stars: 572
Swiftide is a fast, streaming indexing and query library tailored for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in AI applications. It is built in Rust, utilizing parallel, asynchronous streams for blazingly fast performance. With Swiftide, users can easily build AI applications from idea to production in just a few lines of code. The tool addresses frustrations around performance, stability, and ease of use encountered while working with Python-based tooling. It offers features like fast streaming indexing pipeline, experimental query pipeline, integrations with various platforms, loaders, transformers, chunkers, embedders, and more. Swiftide aims to provide a platform for data indexing and querying to advance the development of automated Large Language Model (LLM) applications.
README:

Fast, streaming indexing, query, and agentic LLM applications in Rust
Read more on swiftide.rs »
API Docs
·
Report Bug
·
Request Feature
·
Discord
Swiftide is a Rust library for building LLM applications. From performing a simple prompt completion, to building fast, streaming indexing and querying pipelines, to building agents that can use tools and call other agents.
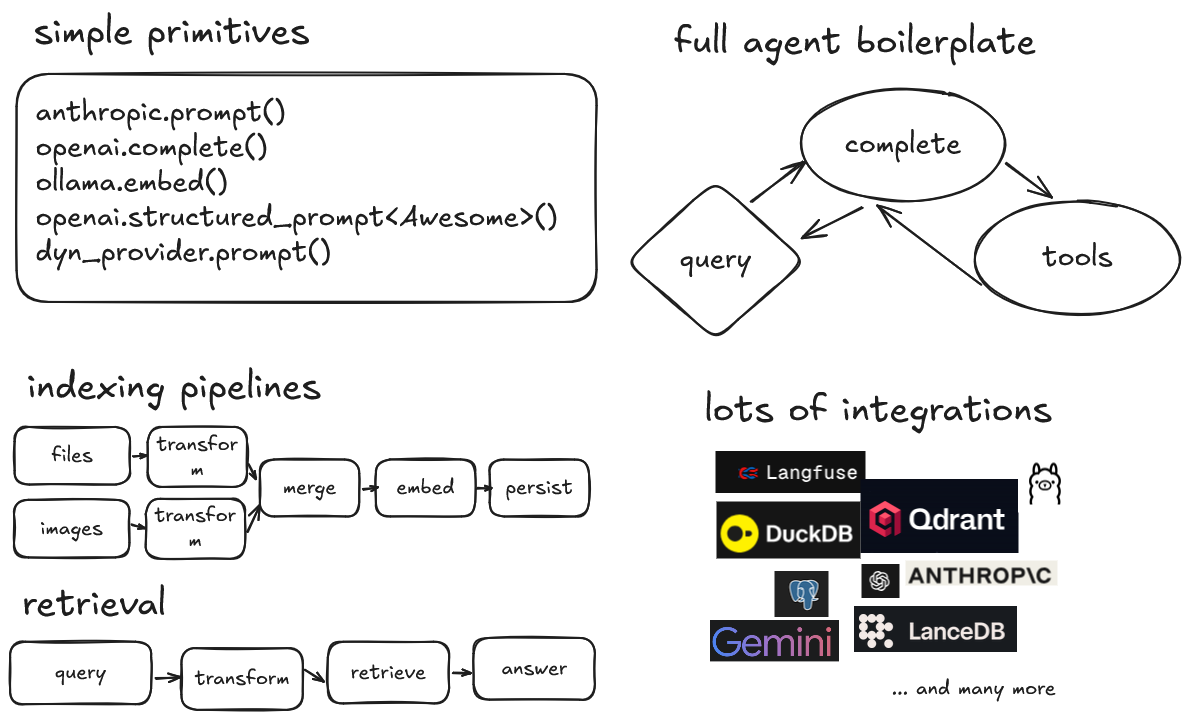
- Simple primitives for common LLM tasks
- Build fast, streaming indexing and querying pipelines
- Easily build agents, mix and match with previously built pipelines
- A modular and extendable API, with minimal abstractions
- Integrations with popular LLMs and storage providers
- Ready to use pipeline transformations or bring your own
- Build graph like workflows with Tasks
- Langfuse support
Part of the bosun.ai project. An upcoming platform for autonomous code improvement.
We <3 feedback: project ideas, suggestions, and complaints are very welcome. Feel free to open an issue or contact us on discord.
[!CAUTION] Swiftide is under heavy development and can have breaking changes. Documentation might fall short of all features, and despite our efforts be slightly outdated. We recommend to always keep an eye on our github and api documentation. If you found an issue or have any kind of feedback we'd love to hear from you.
- Swiftide 0.31 - Tasks, Langfuse, Multi-Modal, and more
- Swiftide 0.27 - Easy human-in-the-loop flows for agentic AI
- Swiftide 0.26 - Streaming agents
- Releasing kwaak with kwaak
- Swiftide 0.16 - AI Agents in Rust
- Rust in LLM based tools for performance
- Evaluate Swiftide pipelines with Ragas (2024-09-15)
- Release - Swiftide 0.12 (2024-09-13)
- Local code intel with Ollama, FastEmbed and OpenTelemetry (2024-09-04)
More on our blog
Indexing a local code project, chunking into smaller pieces, enriching the nodes with metadata, and persisting into Qdrant:
indexing::Pipeline::from_loader(FileLoader::new(".").with_extensions(&["rs"]))
.with_default_llm_client(openai_client.clone())
.filter_cached(Redis::try_from_url(
redis_url,
"swiftide-examples",
)?)
.then_chunk(ChunkCode::try_for_language_and_chunk_size(
"rust",
10..2048,
)?)
.then(MetadataQACode::default())
.then(move |node| my_own_thing(node))
.then_in_batch(Embed::new(openai_client.clone()))
.then_store_with(
Qdrant::builder()
.batch_size(50)
.vector_size(1536)
.build()?,
)
.run()
.await?;Querying for an example on how to use the query pipeline:
query::Pipeline::default()
.then_transform_query(GenerateSubquestions::from_client(
openai_client.clone(),
))
.then_transform_query(Embed::from_client(
openai_client.clone(),
))
.then_retrieve(qdrant.clone())
.then_answer(Simple::from_client(openai_client.clone()))
.query("How can I use the query pipeline in Swiftide?")
.await?;Running an agent that can search code:
#[swiftide::tool(
description = "Searches code",
param(name = "code_query", description = "The code query")
)]
async fn search_code(
context: &dyn AgentContext,
code_query: &str,
) -> Result<ToolOutput, ToolError> {
let command_output = context
.executor()
.exec_cmd(&Command::shell(format!("rg '{code_query}'")))
.await?;
Ok(command_output.into())
}
agents::Agent::builder()
.llm(&openai)
.tools(vec![search_code()])
.build()?
.query("In what file can I find an example of a swiftide agent?")
.await?;Agents loop over LLM calls, tool calls, and lifecycle hooks until a final answer is reached.
You can find more detailed examples in /examples
Our goal is to create a fast, extendable platform for building LLM applications in Rust, to further the development of automated AI applications, with an easy-to-use and easy-to-extend api.
- Simple primitives for common LLM tasks
- Fast, modular streaming indexing pipeline with async, parallel processing
- Experimental query pipeline
- Experimental agent framework
- A variety of loaders, transformers, semantic chunkers, embedders, and more
- Bring your own transformers by extending straightforward traits or use a closure
- Splitting and merging pipelines
- Jinja-like templating for prompts
- Store into multiple backends
- Integrations with OpenAI, Groq, Gemini, Anthropic, Redis, Qdrant, Ollama, FastEmbed-rs, Fluvio, LanceDB, and Treesitter
- Evaluate pipelines with RAGAS
- Sparse vector support for hybrid search
-
tracingsupported for logging and tracing, see /examples and thetracingcrate for more information. - Tracing layer for exporting to Langfuse
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Supported Large Language Model providers | OpenAI (and Azure) Anthropic Gemini OpenRouter AWS Bedrock - Anthropic and Titan Groq - All models Ollama - All models |
| Agents | All the boiler plate for autonomous agents so you don't have to |
| Tasks | Build graph like workflows with tasks, combining all the above to build complex applications |
| Loading data | Files Scraping Fluvio Parquet Kafka Other pipelines and streams |
| Example and pre-build transformers and metadata generation | Generate Question and answerers for both text and code (Hyde) Summaries, titles and queries via an LLM Extract definitions and references with tree-sitter |
| Splitting and chunking | Markdown Text (text_splitter) Code (with tree-sitter) |
| Storage | Qdrant Redis LanceDB Postgres Duckdb |
| Query pipeline | Similarity and hybrid search, query and response transformations, and evaluation |
Make sure you have the rust toolchain installed. rustup Is the recommended approach.
To use OpenAI, an API key is required. Note that by default async_openai uses the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variables.
Other integrations might have their own requirements.
-
Set up a new Rust project
-
Add swiftide
cargo add swiftide
-
Enable the features of integrations you would like to use in your
Cargo.toml -
Write a pipeline (see our examples and documentation)
Before building your streams, you need to enable and configure any integrations required. See /examples.
We have a lot of examples, please refer to /examples and the Documentation
[!NOTE] No integrations are enabled by default as some are code heavy. We recommend you to cherry-pick the integrations you need. By convention flags have the same name as the integration they represent.
An indexing stream starts with a Loader that emits Nodes. For instance, with the Fileloader each file is a Node.
You can then slice and dice, augment, and filter nodes. Each different kind of step in the pipeline requires different traits. This enables extension.
Nodes are generic over their inner type. This is a transition in progress, but when you BYO, feel free to slice and dice. The inner type can change midway through the pipeline.
-
from_loader
(impl Loader)starting point of the stream, creates and emits Nodes -
filter_cached
(impl NodeCache)filters cached nodes -
then
(impl Transformer)transforms the node and puts it on the stream -
then_in_batch
(impl BatchTransformer)transforms multiple nodes and puts them on the stream -
then_chunk
(impl ChunkerTransformer)transforms a single node and emits multiple nodes -
then_store_with
(impl Storage)stores the nodes in a storage backend, this can be chained
Additionally, several generic transformers are implemented. They take implementers of SimplePrompt and EmbedModel to do their things.
[!WARNING] Due to the performance, chunking before adding metadata gives rate limit errors on OpenAI very fast, especially with faster models like gpt-5-nano. Be aware. The
async-openaicrate provides an exmponential backoff strategy. If that is still a problem, there is also a decorator that supports streaming inswiftide_core/indexing_decorators.
A query stream starts with a search strategy. In the query pipeline a Query goes through several stages. Transformers and retrievers work together to get the right context into a prompt, before generating an answer. Transformers and Retrievers operate on different stages of the Query via a generic statemachine. Additionally, the search strategy is generic over the pipeline and Retrievers need to implement specifically for each strategy.
That sounds like a lot but, tl&dr; the query pipeline is fully and strongly typed.
- Pending The query has not been executed, and can be further transformed with transformers
- Retrieved Documents have been retrieved, and can be further transformed to provide context for an answer
- Answered The query is done
Additionally, query pipelines can also be evaluated. I.e. by Ragas.
Similar to the indexing pipeline each step is governed by simple Traits and closures implement these traits as well.
Swiftide is in a very early stage and we are aware that we lack features for the wider community. Contributions are very welcome. 🎉
If you have a great idea, please fork the repo and create a pull request. You can also simply open an issue with the tag "enhancement". Don't forget to give the project a star! Thanks again!
If you just want to contribute (bless you!), see our issues or join us on Discord.
- Fork the Project
- Create your Feature Branch (
git checkout -b feature/AmazingFeature) - Commit your Changes (
git commit -m 'feat: Add some AmazingFeature') - Push to the Branch (
git push origin feature/AmazingFeature) - Open a Pull Request
See CONTRIBUTING for more
|
timonv open for swiftide consulting |
tinco |
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for more information.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for swiftide
Similar Open Source Tools

swiftide
Swiftide is a fast, streaming indexing and query library tailored for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in AI applications. It is built in Rust, utilizing parallel, asynchronous streams for blazingly fast performance. With Swiftide, users can easily build AI applications from idea to production in just a few lines of code. The tool addresses frustrations around performance, stability, and ease of use encountered while working with Python-based tooling. It offers features like fast streaming indexing pipeline, experimental query pipeline, integrations with various platforms, loaders, transformers, chunkers, embedders, and more. Swiftide aims to provide a platform for data indexing and querying to advance the development of automated Large Language Model (LLM) applications.

AIL-framework
AIL framework is a modular framework to analyze potential information leaks from unstructured data sources like pastes from Pastebin or similar services or unstructured data streams. AIL framework is flexible and can be extended to support other functionalities to mine or process sensitive information (e.g. data leak prevention).

ail-framework
AIL framework is a modular framework to analyze potential information leaks from unstructured data sources like pastes from Pastebin or similar services or unstructured data streams. AIL framework is flexible and can be extended to support other functionalities to mine or process sensitive information (e.g. data leak prevention).
unify
The Unify Python Package provides access to the Unify REST API, allowing users to query Large Language Models (LLMs) from any Python 3.7.1+ application. It includes Synchronous and Asynchronous clients with Streaming responses support. Users can easily use any endpoint with a single key, route to the best endpoint for optimal throughput, cost, or latency, and customize prompts to interact with the models. The package also supports dynamic routing to automatically direct requests to the top-performing provider. Additionally, users can enable streaming responses and interact with the models asynchronously for handling multiple user requests simultaneously.

DocsGPT
DocsGPT is an open-source documentation assistant powered by GPT models. It simplifies the process of searching for information in project documentation by allowing developers to ask questions and receive accurate answers. With DocsGPT, users can say goodbye to manual searches and quickly find the information they need. The tool aims to revolutionize project documentation experiences and offers features like live previews, Discord community, guides, and contribution opportunities. It consists of a Flask app, Chrome extension, similarity search index creation script, and a frontend built with Vite and React. Users can quickly get started with DocsGPT by following the provided setup instructions and can contribute to its development by following the guidelines in the CONTRIBUTING.md file. The project follows a Code of Conduct to ensure a harassment-free community environment for all participants. DocsGPT is licensed under MIT and is built with LangChain.
bee-agent-framework
The Bee Agent Framework is an open-source tool for building, deploying, and serving powerful agentic workflows at scale. It provides AI agents, tools for creating workflows in Javascript/Python, a code interpreter, memory optimization strategies, serialization for pausing/resuming workflows, traceability features, production-level control, and upcoming features like model-agnostic support and a chat UI. The framework offers various modules for agents, llms, memory, tools, caching, errors, adapters, logging, serialization, and more, with a roadmap including MLFlow integration, JSON support, structured outputs, chat client, base agent improvements, guardrails, and evaluation.
DataDreamer
DataDreamer is a powerful open-source Python library designed for prompting, synthetic data generation, and training workflows. It is simple, efficient, and research-grade, allowing users to create prompting workflows, generate synthetic datasets, and train models with ease. The library is built for researchers, by researchers, focusing on correctness, best practices, and reproducibility. It offers features like aggressive caching, resumability, support for bleeding-edge techniques, and easy sharing of datasets and models. DataDreamer enables users to run multi-step prompting workflows, generate synthetic datasets for various tasks, and train models by aligning, fine-tuning, instruction-tuning, and distilling them using existing or synthetic data.
workflows-py
LlamaIndex Workflows is a framework for orchestrating and chaining together complex systems of steps and events. It shines in orchestrating complex, multi-step processes involving AI models, APIs, and decision-making. The async-first, event-driven architecture allows building workflows that can route between different capabilities, implement parallel processing patterns, loop over complex sequences, and maintain state across multiple steps. Key features include async-first design, event-driven structure, state management, and observability through tools like Arize Phoenix and OpenTelemetry.

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking
eino
Eino is an ultimate LLM application development framework in Golang, emphasizing simplicity, scalability, reliability, and effectiveness. It provides a curated list of component abstractions, a powerful composition framework, meticulously designed APIs, best practices, and tools covering the entire development cycle. Eino standardizes and improves efficiency in AI application development by offering rich components, powerful orchestration, complete stream processing, highly extensible aspects, and a comprehensive framework structure.
AIOS
AIOS, a Large Language Model (LLM) Agent operating system, embeds large language model into Operating Systems (OS) as the brain of the OS, enabling an operating system "with soul" -- an important step towards AGI. AIOS is designed to optimize resource allocation, facilitate context switch across agents, enable concurrent execution of agents, provide tool service for agents, maintain access control for agents, and provide a rich set of toolkits for LLM Agent developers.
Mindolph
Mindolph is an open source personal knowledge management software for all desktop platforms. It allows users to create and manage their own files in separate workspaces with saving in their local storage, organize their files as a tree in their workspaces, and have multiple tabs for opening files instead of a single file window. Mindolph supports Mind Map, Markdown, PlantUML, CSV sheet, and plain text file formats. It also has features such as quickly navigating to files and searching text in files under a specific folder, editing mind maps easily and quickly with key shortcuts, supporting themes and providing some pre-defined themes, importing from other mind map formats, and exporting to other file formats.
mobius
Mobius is an AI infra platform including realtime computing and training. It is built on Ray, a distributed computing framework, and provides a number of features that make it well-suited for online machine learning tasks. These features include: * **Cross Language**: Mobius can run in multiple languages (only Python and Java are supported currently) with high efficiency. You can implement your operator in different languages and run them in one job. * **Single Node Failover**: Mobius has a special failover mechanism that only needs to rollback the failed node itself, in most cases, to recover the job. This is a huge benefit if your job is sensitive about failure recovery time. * **AutoScaling**: Mobius can generate a new graph with different configurations in runtime without stopping the job. * **Fusion Training**: Mobius can combine TensorFlow/Pytorch and streaming, then building an e2e online machine learning pipeline. Mobius is still under development, but it has already been used to power a number of real-world applications, including: * A real-time recommendation system for a major e-commerce company * A fraud detection system for a large financial institution * A personalized news feed for a major news organization If you are interested in using Mobius for your own online machine learning projects, you can find more information in the documentation.

aigne-framework
AIGNE Framework is a functional AI application development framework designed to simplify and accelerate the process of building modern applications. It combines functional programming features, powerful artificial intelligence capabilities, and modular design principles to help developers easily create scalable solutions. With key features like modular design, TypeScript support, multiple AI model support, flexible workflow patterns, MCP protocol integration, code execution capabilities, and Blocklet ecosystem integration, AIGNE Framework offers a comprehensive solution for developers. The framework provides various workflow patterns such as Workflow Router, Workflow Sequential, Workflow Concurrency, Workflow Handoff, Workflow Reflection, Workflow Orchestration, Workflow Code Execution, and Workflow Group Chat to address different application scenarios efficiently. It also includes built-in MCP support for running MCP servers and integrating with external MCP servers, along with packages for core functionality, agent library, CLI, and various models like OpenAI, Gemini, Claude, and Nova.

clearml
ClearML is a suite of tools designed to streamline the machine learning workflow. It includes an experiment manager, MLOps/LLMOps, data management, and model serving capabilities. ClearML is open-source and offers a free tier hosting option. It supports various ML/DL frameworks and integrates with Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm. ClearML provides extensive logging capabilities, including source control info, execution environment, hyper-parameters, and experiment outputs. It also offers automation features, such as remote job execution and pipeline creation. ClearML is designed to be easy to integrate, requiring only two lines of code to add to existing scripts. It aims to improve collaboration, visibility, and data transparency within ML teams.
langgraph-mcp-agents
LangGraph Agent with MCP is a toolkit provided by LangChain AI that enables AI agents to interact with external tools and data sources through the Model Context Protocol (MCP). It offers a user-friendly interface for deploying ReAct agents to access various data sources and APIs through MCP tools. The toolkit includes features such as a Streamlit Interface for interaction, Tool Management for adding and configuring MCP tools dynamically, Streaming Responses in real-time, and Conversation History tracking.
For similar tasks

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
AI-in-a-Box
AI-in-a-Box is a curated collection of solution accelerators that can help engineers establish their AI/ML environments and solutions rapidly and with minimal friction, while maintaining the highest standards of quality and efficiency. It provides essential guidance on the responsible use of AI and LLM technologies, specific security guidance for Generative AI (GenAI) applications, and best practices for scaling OpenAI applications within Azure. The available accelerators include: Azure ML Operationalization in-a-box, Edge AI in-a-box, Doc Intelligence in-a-box, Image and Video Analysis in-a-box, Cognitive Services Landing Zone in-a-box, Semantic Kernel Bot in-a-box, NLP to SQL in-a-box, Assistants API in-a-box, and Assistants API Bot in-a-box.
spring-ai
The Spring AI project provides a Spring-friendly API and abstractions for developing AI applications. It offers a portable client API for interacting with generative AI models, enabling developers to easily swap out implementations and access various models like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and HuggingFace. Spring AI also supports prompt engineering, providing classes and interfaces for creating and parsing prompts, as well as incorporating proprietary data into generative AI without retraining the model. This is achieved through Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), which involves extracting, transforming, and loading data into a vector database for use by AI models. Spring AI's VectorStore abstraction allows for seamless transitions between different vector database implementations.
ragstack-ai
RAGStack is an out-of-the-box solution simplifying Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in GenAI apps. RAGStack includes the best open-source for implementing RAG, giving developers a comprehensive Gen AI Stack leveraging LangChain, CassIO, and more. RAGStack leverages the LangChain ecosystem and is fully compatible with LangSmith for monitoring your AI deployments.
breadboard
Breadboard is a library for prototyping generative AI applications. It is inspired by the hardware maker community and their boundless creativity. Breadboard makes it easy to wire prototypes and share, remix, reuse, and compose them. The library emphasizes ease and flexibility of wiring, as well as modularity and composability.
cloudflare-ai-web
Cloudflare-ai-web is a lightweight and easy-to-use tool that allows you to quickly deploy a multi-modal AI platform using Cloudflare Workers AI. It supports serverless deployment, password protection, and local storage of chat logs. With a size of only ~638 kB gzip, it is a great option for building AI-powered applications without the need for a dedicated server.
app-builder
AppBuilder SDK is a one-stop development tool for AI native applications, providing basic cloud resources, AI capability engine, Qianfan large model, and related capability components to improve the development efficiency of AI native applications.
cookbook
This repository contains community-driven practical examples of building AI applications and solving various tasks with AI using open-source tools and models. Everyone is welcome to contribute, and we value everybody's contribution! There are several ways you can contribute to the Open-Source AI Cookbook: Submit an idea for a desired example/guide via GitHub Issues. Contribute a new notebook with a practical example. Improve existing examples by fixing issues/typos. Before contributing, check currently open issues and pull requests to avoid working on something that someone else is already working on.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.