
catalyst
🚀 Catalyst is a C# Natural Language Processing library built for speed. Inspired by spaCy's design, it brings pre-trained models, out-of-the box support for training word and document embeddings, and flexible entity recognition models.
Stars: 706

Catalyst is a C# Natural Language Processing library designed for speed, inspired by spaCy's design. It provides pre-trained models, support for training word and document embeddings, and flexible entity recognition models. The library is fast, modern, and pure-C#, supporting .NET standard 2.0. It is cross-platform, running on Windows, Linux, macOS, and ARM. Catalyst offers non-destructive tokenization, named entity recognition, part-of-speech tagging, language detection, and efficient binary serialization. It includes pre-built models for language packages and lemmatization. Users can store and load models using streams. Getting started with Catalyst involves installing its NuGet Package and setting the storage to use the online repository. The library supports lazy loading of models from disk or online. Users can take advantage of C# lazy evaluation and native multi-threading support to process documents in parallel. Training a new FastText word2vec embedding model is straightforward, and Catalyst also provides algorithms for fast embedding search and dimensionality reduction.
README:
catalyst is a C# Natural Language Processing library built for speed. Inspired by spaCy's design, it brings pre-trained models, out-of-the box support for training word and document embeddings, and flexible entity recognition models.
- Fast, modern pure-C# NLP library, supporting .NET standard 2.0
- Cross-platform, runs anywhere .NET core is supported - Windows, Linux, macOS and even ARM
- Non-destructive tokenization, >99.9% RegEx-free, >1M tokens/s on a modern CPU
- Named Entity Recognition (gazeteer, rule-based & perceptron-based)
- Pre-trained models based on Universal Dependencies project
- Custom models for learning Abbreviations & Senses
- Out-of-the-box support for training FastText and StarSpace embeddings (pre-trained models coming soon)
- Part-of-speech tagging
- Language detection using FastText or cld3
- Efficient binary serialization based on MessagePack
- Pre-built models for language packages ✨
- Lemmatization ✨ (using lookup tables ported from spaCy)
All language-specific data and models are provided as NuGet packages, you can find all packages here.
The new models are trained on the latest release of Universal Dependencies v2.7.
We've also added the option to store and load models using streams:
// Creates and stores the model
var isApattern = new PatternSpotter(Language.English, 0, tag: "is-a-pattern", captureTag: "IsA");
isApattern.NewPattern(
"Is+Noun",
mp => mp.Add(
new PatternUnit(P.Single().WithToken("is").WithPOS(PartOfSpeech.VERB)),
new PatternUnit(P.Multiple().WithPOS(PartOfSpeech.NOUN, PartOfSpeech.PROPN, PartOfSpeech.AUX, PartOfSpeech.DET, PartOfSpeech.ADJ))
));
using(var f = File.OpenWrite("my-pattern-spotter.bin"))
{
await isApattern.StoreAsync(f);
}
// Load the model back from disk
var isApattern2 = new PatternSpotter(Language.English, 0, tag: "is-a-pattern", captureTag: "IsA");
using(var f = File.OpenRead("my-pattern-spotter.bin"))
{
await isApattern2.LoadAsync(f);
}Using catalyst is as simple as installing its NuGet Package, and setting the storage to use our online repository. This way, models will be lazy loaded either from disk or downloaded from our online repository. Check out also some of the sample projects for more examples on how to use catalyst.
Catalyst.Models.English.Register(); //You need to pre-register each language (and install the respective NuGet Packages)
Storage.Current = new DiskStorage("catalyst-models");
var nlp = await Pipeline.ForAsync(Language.English);
var doc = new Document("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog", Language.English);
nlp.ProcessSingle(doc);
Console.WriteLine(doc.ToJson());You can also take advantage of C# lazy evaluation and native multi-threading support to process a large number of documents in parallel:
var docs = GetDocuments();
var parsed = nlp.Process(docs);
DoSomething(parsed);
IEnumerable<IDocument> GetDocuments()
{
//Generates a few documents, to demonstrate multi-threading & lazy evaluation
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
yield return new Document("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog", Language.English);
}
}
void DoSomething(IEnumerable<IDocument> docs)
{
foreach(var doc in docs)
{
Console.WriteLine(doc.ToJson());
}
}Training a new FastText word2vec embedding model is as simple as this:
var nlp = await Pipeline.ForAsync(Language.English);
var ft = new FastText(Language.English, 0, "wiki-word2vec");
ft.Data.Type = FastText.ModelType.CBow;
ft.Data.Loss = FastText.LossType.NegativeSampling;
ft.Train(nlp.Process(GetDocs()));
ft.StoreAsync();For fast embedding search, we have also released a C# version of the "Hierarchical Navigable Small World" (HNSW) algorithm on NuGet, based on our fork of Microsoft's HNSW.Net. We have also released a C# version of the "Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection" (UMAP) algorithm for dimensionality reduction on GitHub and on NuGet.
| Documentation | |
|---|---|
| Contribute | How to contribute to catalyst codebase. |
| Samples | Sample projects demonstrating catalyst capabilities |
| Join our gitter channel |
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for catalyst
Similar Open Source Tools

catalyst
Catalyst is a C# Natural Language Processing library designed for speed, inspired by spaCy's design. It provides pre-trained models, support for training word and document embeddings, and flexible entity recognition models. The library is fast, modern, and pure-C#, supporting .NET standard 2.0. It is cross-platform, running on Windows, Linux, macOS, and ARM. Catalyst offers non-destructive tokenization, named entity recognition, part-of-speech tagging, language detection, and efficient binary serialization. It includes pre-built models for language packages and lemmatization. Users can store and load models using streams. Getting started with Catalyst involves installing its NuGet Package and setting the storage to use the online repository. The library supports lazy loading of models from disk or online. Users can take advantage of C# lazy evaluation and native multi-threading support to process documents in parallel. Training a new FastText word2vec embedding model is straightforward, and Catalyst also provides algorithms for fast embedding search and dimensionality reduction.
FaceAiSharp
FaceAiSharp is a .NET library designed for face-related computer vision tasks. It offers functionalities such as face detection, face recognition, facial landmarks detection, and eye state detection. The library utilizes pretrained ONNX models for accurate and efficient results, enabling users to integrate these capabilities into their .NET applications easily. With a focus on simplicity and performance, FaceAiSharp provides a local processing solution without relying on cloud services, supporting image-based face processing using ImageSharp. It is cross-platform compatible, supporting Windows, Linux, Android, and more.
chromem-go
chromem-go is an embeddable vector database for Go with a Chroma-like interface and zero third-party dependencies. It enables retrieval augmented generation (RAG) and similar embeddings-based features in Go apps without the need for a separate database. The focus is on simplicity and performance for common use cases, allowing querying of documents with minimal memory allocations. The project is in beta and may introduce breaking changes before v1.0.0.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.

slideflow
Slideflow is a deep learning library for digital pathology, offering a user-friendly interface for model development. It is designed for medical researchers and AI enthusiasts, providing an accessible platform for developing state-of-the-art pathology models. Slideflow offers customizable training pipelines, robust slide processing and stain normalization toolkit, support for weakly-supervised or strongly-supervised labels, built-in foundation models, multiple-instance learning, self-supervised learning, generative adversarial networks, explainability tools, layer activation analysis tools, uncertainty quantification, interactive user interface for model deployment, and more. It supports both PyTorch and Tensorflow, with optional support for Libvips for slide reading. Slideflow can be installed via pip, Docker container, or from source, and includes non-commercial add-ons for additional tools and pretrained models. It allows users to create projects, extract tiles from slides, train models, and provides evaluation tools like heatmaps and mosaic maps.
FlashRank
FlashRank is an ultra-lite and super-fast Python library designed to add re-ranking capabilities to existing search and retrieval pipelines. It is based on state-of-the-art Language Models (LLMs) and cross-encoders, offering support for pairwise/pointwise rerankers and listwise LLM-based rerankers. The library boasts the tiniest reranking model in the world (~4MB) and runs on CPU without the need for Torch or Transformers. FlashRank is cost-conscious, with a focus on low cost per invocation and smaller package size for efficient serverless deployments. It supports various models like ms-marco-TinyBERT, ms-marco-MiniLM, rank-T5-flan, ms-marco-MultiBERT, and more, with plans for future model additions. The tool is ideal for enhancing search precision and speed in scenarios where lightweight models with competitive performance are preferred.
AgentFly
AgentFly is an extensible framework for building LLM agents with reinforcement learning. It supports multi-turn training by adapting traditional RL methods with token-level masking. It features a decorator-based interface for defining tools and reward functions, enabling seamless extension and ease of use. To support high-throughput training, it implemented asynchronous execution of tool calls and reward computations, and designed a centralized resource management system for scalable environment coordination. A suite of prebuilt tools and environments are provided.
transformers
Transformers is a state-of-the-art pretrained models library that acts as the model-definition framework for machine learning models in text, computer vision, audio, video, and multimodal tasks. It centralizes model definition for compatibility across various training frameworks, inference engines, and modeling libraries. The library simplifies the usage of new models by providing simple, customizable, and efficient model definitions. With over 1M+ Transformers model checkpoints available, users can easily find and utilize models for their tasks.

embodied-agents
Embodied Agents is a toolkit for integrating large multi-modal models into existing robot stacks with just a few lines of code. It provides consistency, reliability, scalability, and is configurable to any observation and action space. The toolkit is designed to reduce complexities involved in setting up inference endpoints, converting between different model formats, and collecting/storing datasets. It aims to facilitate data collection and sharing among roboticists by providing Python-first abstractions that are modular, extensible, and applicable to a wide range of tasks. The toolkit supports asynchronous and remote thread-safe agent execution for maximal responsiveness and scalability, and is compatible with various APIs like HuggingFace Spaces, Datasets, Gymnasium Spaces, Ollama, and OpenAI. It also offers automatic dataset recording and optional uploads to the HuggingFace hub.
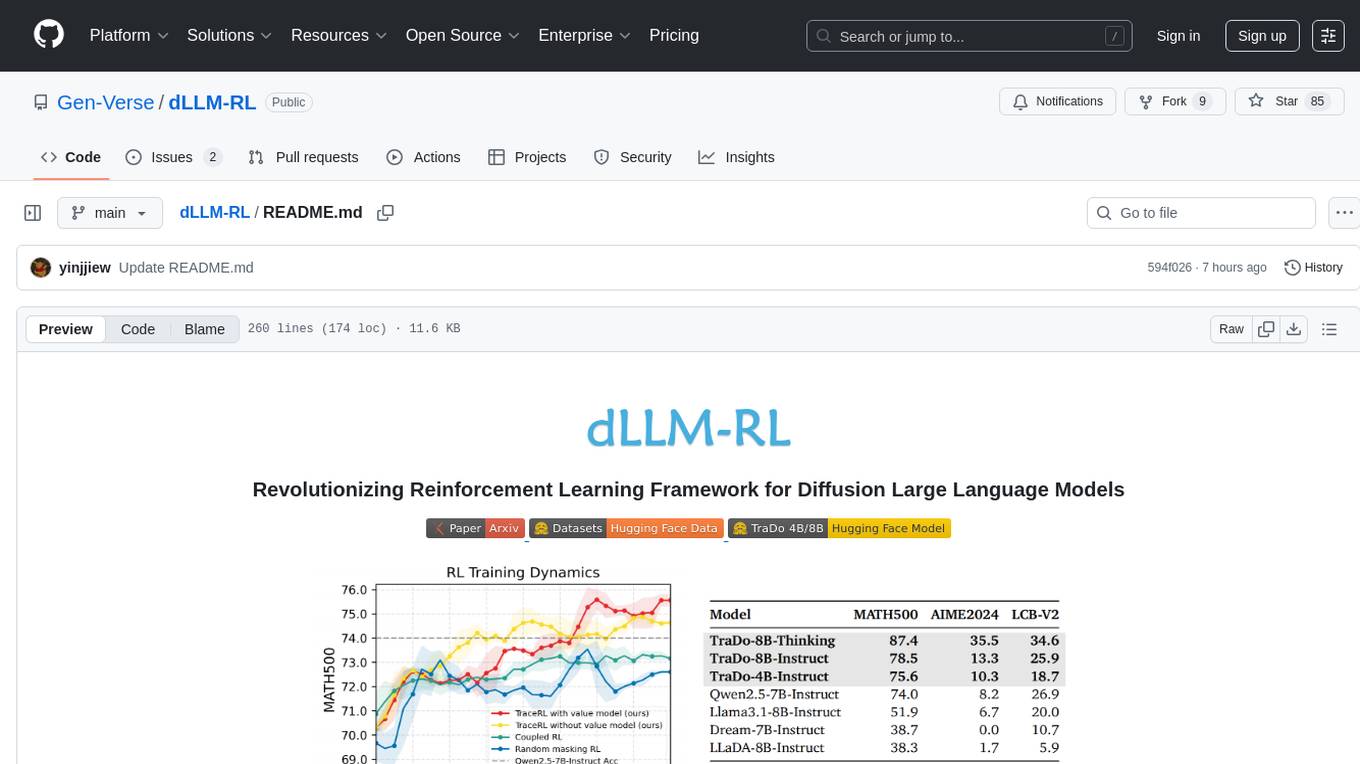
dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
dive
Dive is an AI toolkit for Go that enables the creation of specialized teams of AI agents and seamless integration with leading LLMs. It offers a CLI and APIs for easy integration, with features like creating specialized agents, hierarchical agent systems, declarative configuration, multiple LLM support, extended reasoning, model context protocol, advanced model settings, tools for agent capabilities, tool annotations, streaming, CLI functionalities, thread management, confirmation system, deep research, and semantic diff. Dive also provides semantic diff analysis, unified interface for LLM providers, tool system with annotations, custom tool creation, and support for various verified models. The toolkit is designed for developers to build AI-powered applications with rich agent capabilities and tool integrations.
langfun
Langfun is a Python library that aims to make language models (LM) fun to work with. It enables a programming model that flows naturally, resembling the human thought process. Langfun emphasizes the reuse and combination of language pieces to form prompts, thereby accelerating innovation. Unlike other LM frameworks, which feed program-generated data into the LM, langfun takes a distinct approach: It starts with natural language, allowing for seamless interactions between language and program logic, and concludes with natural language and optional structured output. Consequently, langfun can aptly be described as Language as functions, capturing the core of its methodology.
qa-mdt
This repository provides an implementation of QA-MDT, integrating state-of-the-art models for music generation. It offers a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for enhanced music generation. The code is based on various repositories like AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. The implementation allows for training and fine-tuning the model with different strategies and datasets. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets in LMDB format and provides a script for creating a toy LMDB dataset. The model can be used for music generation tasks, with a focus on quality injection to enhance the musicality of generated music.
Jlama
Jlama is a modern Java inference engine designed for large language models. It supports various model types such as Gemma, Llama, Mistral, GPT-2, BERT, and more. The tool implements features like Flash Attention, Mixture of Experts, and supports different model quantization formats. Built with Java 21 and utilizing the new Vector API for faster inference, Jlama allows users to add LLM inference directly to their Java applications. The tool includes a CLI for running models, a simple UI for chatting with LLMs, and examples for different model types.
RTL-Coder
RTL-Coder is a tool designed to outperform GPT-3.5 in RTL code generation by providing a fully open-source dataset and a lightweight solution. It targets Verilog code generation and offers an automated flow to generate a large labeled dataset with over 27,000 diverse Verilog design problems and answers. The tool addresses the data availability challenge in IC design-related tasks and can be used for various applications beyond LLMs. The tool includes four RTL code generation models available on the HuggingFace platform, each with specific features and performance characteristics. Additionally, RTL-Coder introduces a new LLM training scheme based on code quality feedback to further enhance model performance and reduce GPU memory consumption.
lance
Lance is a modern columnar data format optimized for ML workflows and datasets. It offers high-performance random access, vector search, zero-copy automatic versioning, and ecosystem integrations with Apache Arrow, Pandas, Polars, and DuckDB. Lance is designed to address the challenges of the ML development cycle, providing a unified data format for collection, exploration, analytics, feature engineering, training, evaluation, deployment, and monitoring. It aims to reduce data silos and streamline the ML development process.
For similar tasks
phospho
Phospho is a text analytics platform for LLM apps. It helps you detect issues and extract insights from text messages of your users or your app. You can gather user feedback, measure success, and iterate on your app to create the best conversational experience for your users.
OpenFactVerification
Loki is an open-source tool designed to automate the process of verifying the factuality of information. It provides a comprehensive pipeline for dissecting long texts into individual claims, assessing their worthiness for verification, generating queries for evidence search, crawling for evidence, and ultimately verifying the claims. This tool is especially useful for journalists, researchers, and anyone interested in the factuality of information.
open-parse
Open Parse is a Python library for visually discerning document layouts and chunking them effectively. It is designed to fill the gap in open-source libraries for handling complex documents. Unlike text splitting, which converts a file to raw text and slices it up, Open Parse visually analyzes documents for superior LLM input. It also supports basic markdown for parsing headings, bold, and italics, and has high-precision table support, extracting tables into clean Markdown formats with accuracy that surpasses traditional tools. Open Parse is extensible, allowing users to easily implement their own post-processing steps. It is also intuitive, with great editor support and completion everywhere, making it easy to use and learn.
spaCy
spaCy is an industrial-strength Natural Language Processing (NLP) library in Python and Cython. It incorporates the latest research and is designed for real-world applications. The library offers pretrained pipelines supporting 70+ languages, with advanced neural network models for tasks such as tagging, parsing, named entity recognition, and text classification. It also facilitates multi-task learning with pretrained transformers like BERT, along with a production-ready training system and streamlined model packaging, deployment, and workflow management. spaCy is commercial open-source software released under the MIT license.
NanoLLM
NanoLLM is a tool designed for optimized local inference for Large Language Models (LLMs) using HuggingFace-like APIs. It supports quantization, vision/language models, multimodal agents, speech, vector DB, and RAG. The tool aims to provide efficient and effective processing for LLMs on local devices, enhancing performance and usability for various AI applications.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.

lima
LIMA is a multilingual linguistic analyzer developed by the CEA LIST, LASTI laboratory. It is Free Software available under the MIT license. LIMA has state-of-the-art performance for more than 60 languages using deep learning modules. It also includes a powerful rules-based mechanism called ModEx for extracting information in new domains without annotated data.
liboai
liboai is a simple C++17 library for the OpenAI API, providing developers with access to OpenAI endpoints through a collection of methods and classes. It serves as a spiritual port of OpenAI's Python library, 'openai', with similar structure and features. The library supports various functionalities such as ChatGPT, Audio, Azure, Functions, Image DALL·E, Models, Completions, Edit, Embeddings, Files, Fine-tunes, Moderation, and Asynchronous Support. Users can easily integrate the library into their C++ projects to interact with OpenAI services.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.


