
1filellm
Specify a github or local repo, github pull request, arXiv or Sci-Hub paper, Youtube transcript or documentation URL on the web and scrape into a text file and clipboard for easier LLM ingestion
Stars: 292
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
README:
Data2LLM is a command-line tool designed to streamline the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models (LLMs). It aggregates and preprocesses data from a variety of sources, compiling them into a single text file that is automatically copied to your clipboard for quick use.
- Automatic source type detection based on provided path, URL, or identifier
- Support for local files and/or directories, GitHub repositories, GitHub pull requests, GitHub issues, academic papers from ArXiv, YouTube transcripts, web page documentation, Sci-Hub hosted papers via DOI or PMID
- Handling of multiple file formats, including Jupyter Notebooks (.ipynb), and PDFs
- Web crawling functionality to extract content from linked pages up to a specified depth
- Integration with Sci-Hub for automatic downloading of research papers using DOIs or PMIDs
- Text preprocessing, including compressed and uncompressed outputs, stopword removal, and lowercase conversion
- Automatic copying of uncompressed text to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs
- Token count reporting for both compressed and uncompressed outputs
- XML encapsulation of output for improved LLM performance
+--------------------------------+
| External Services |
|--------------------------------|
| GitHub API | YouTube API |
| Sci-Hub | ArXiv |
+--------------------------------+
|
|
v
+----------------------+ +---------------------+ +----------------------+
| | | | | |
| User | | Command Line Tool | | External Libraries |
|----------------------| |---------------------| |----------------------|
| - Provides input URL |--------->| - Handles user input| | - Requests |
| | | - Detects source |<--------| - BeautifulSoup |
| - Receives text | | type | | - PyPDF2 |
| in clipboard |<---------| - Calls appropriate | | - Tiktoken |
| | | processing modules| | - NLTK |
+----------------------+ | - Preprocesses text | | - Nbformat |
| - Generates output | | - Nbconvert |
| files | | - YouTube Transcript |
| - Copies text to | | API |
| clipboard | | - Pyperclip |
| - Reports token | | - Wget |
| count | | - Tqdm |
+---------------------+ | - Rich |
| +----------------------+
|
v
+---------------------+
| Source Type |
| Detection |
|---------------------|
| - Determines type |
| of source |
+---------------------+
|
v
+---------------------+
| Processing Modules |
|---------------------|
| - GitHub Repo Proc |
| - Local Dir Proc |
| - YouTube Transcript|
| Proc |
| - ArXiv PDF Proc |
| - Sci-Hub Paper Proc|
| - Webpage Crawling |
| Proc |
+---------------------+
|
v
+---------------------+
| Text Preprocessing |
|---------------------|
| - Stopword removal |
| - Lowercase |
| conversion |
| - Text cleaning |
+---------------------+
|
v
+---------------------+
| Output Generation |
|---------------------|
| - Compressed text |
| file output |
| - Uncompressed text |
| file output |
+---------------------+
|
v
+---------------------+
| Token Count |
| Reporting |
|---------------------|
| - Report token count|
| |
| - Copies text to |
| clipboard |
+---------------------+
-
2024-07-29:
- Updated output format to encapsulate content in XML tags. This change was implemented due to evaluations showing that LLMs perform better with prompts structured in XML.
- Added tests for GitHub issues and GitHub pull requests to improve robustness and reliability.
- Updated various processing functions to return formatted content instead of writing directly to files, improving consistency and testability.
- 2024-05-17: Added ability to pass path or URL as command line argument.
- 2024-05-16: Updated text colors.
-
2024-05-11:
- Updated requirements.txt.
- Added Rich library to
onefilellm.py.
-
2024-04-04:
- Added GitHub PR and issue tests.
- Added GitHub PR and issues.
- Added tests for GitHub PRs and issues.
- Added ability to concatenate specific GitHub issue and repo when GitHub issue URL is passed.
- Updated tests to include pull request changes.
- Added ability to concatenate pull request and repo when GitHub pull request URL is passed.
-
2024-04-03:
- Included the ability to pull a complete GitHub pull request given the GitHub pull request URL.
- Updated
onefilellm.pyto return an error when Sci-hub is inaccessible or no document is found.
Install the required dependencies:
pip install -U -r requirements.txtOptionally, create a virtual environment for isolation:
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install -U -r requirements.txtTo access private GitHub repositories, generate a personal access token as described in the 'Obtaining a GitHub Personal Access Token' section.
Clone the repository or download the source code.
Run the script using the following command:
python onefilellm.pyOr pass the URL or path in at the command line for the same behavior with less human interaction:
python onefilellm.py https://github.com/jimmc414/1filellmThe tool supports the following input options:
- Local file path (e.g., C:\documents\report.pdf)
- Local directory path (e.g., C:\projects\research) -> (files of selected filetypes segmented into one flat text file)
- GitHub repository URL (e.g., https://github.com/jimmc414/onefilellm) -> (Repo files of selected filetypes segmented into one flat text file)
- GitHub pull request URL (e.g., https://github.com/dear-github/dear-github/pull/102) -> (Pull request diff detail and comments and entire repository content concatenated into one flat text file)
- GitHub issue URL (e.g., https://github.com/isaacs/github/issues/1191) -> (Issue details, comments, and entire repository content concatenated into one flat text file)
- ArXiv paper URL (e.g., https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.14295) -> (Full paper PDF to text file)
- YouTube video URL (e.g., https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KZ_NlnmPQYk) -> (Video transcript to text file)
- Webpage URL (e.g., https://llm.datasette.io/en/stable/) -> (To scrape pages to x depth in segmented text file)
- Sci-Hub Paper DOI (Digital Object Identifier of Sci-Hub hosted paper) (e.g., 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.08.002) -> (Full Sci-Hub paper PDF to text file)
- Sci-Hub Paper PMID (PubMed Identifier of Sci-Hub hosted paper) (e.g., 29203127) -> (Full Sci-Hub paper PDF to text file)
The tool supports the following input options, with their corresponding output actions. Note that the input file extensions are selected based on the following section of code (Applicable to Repos only):
allowed_extensions = ['.xyz', '.pdq', '.example']The output for all options is encapsulated in LLM prompt-appropriate XML and automatically copied to the clipboard.
-
Local file path
-
Example Input:
C:\documents\report.pdf - Output: The contents of the PDF file are extracted and saved into a single text file.
-
Example Input:
-
Local directory path
-
Example Input:
C:\projects\research - Output: Files of selected file types within the directory are segmented and saved into a single flat text file.
-
Example Input:
-
GitHub repository URL
-
Example Input:
https://github.com/jimmc414/onefilellm - Output: Repository files of selected file types are segmented and saved into a single flat text file.
-
Example Input:
-
GitHub pull request URL
-
Example Input:
https://github.com/dear-github/dear-github/pull/102 - Output: Pull request diff details, comments, and the entire repository content are concatenated into a single flat text file.
-
Example Input:
-
GitHub issue URL
-
Example Input:
https://github.com/isaacs/github/issues/1191 - Output: Issue details, comments, and the entire repository content are concatenated into a single flat text file.
-
Example Input:
-
ArXiv paper URL
-
Example Input:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.14295 - Output: The full paper PDF is converted into a text file.
-
Example Input:
-
YouTube video URL
-
Example Input:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KZ_NlnmPQYk - Output: The video transcript is extracted and saved into a text file.
-
Example Input:
-
Webpage URL
-
Example Input:
https://llm.datasette.io/en/stable/ - Output: The webpage content and linked pages up to a specified depth are scraped and segmented into a text file.
-
Example Input:
-
Sci-Hub Paper DOI
-
Example Input:
10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.08.002 - Output: The full Sci-Hub paper PDF is converted into a text file.
-
Example Input:
-
Sci-Hub Paper PMID
-
Example Input:
29203127 - Output: The full Sci-Hub paper PDF is converted into a text file.
-
Example Input:
The script generates the following output files:
-
uncompressed_output.txt: The full text output, automatically copied to the clipboard. -
compressed_output.txt: Cleaned and compressed text. -
processed_urls.txt: A list of all processed URLs during web crawling.
- To modify the allowed file types for repository processing, update the
allowed_extensionslist in the code. - To change the depth of web crawling, adjust the
max_depthvariable in the code.
To access private GitHub repositories, you need a personal access token. Follow these steps:
- Log in to your GitHub account and go to Settings.
- Navigate to Developer settings > Personal access tokens.
- Click on "Generate new token" and provide a name.
- Select the necessary scopes (at least
repofor private repositories). - Click "Generate token" and copy the token value.
In the onefilellm.py script, replace GITHUB_TOKEN with your actual token or set it as an environment variable:
-
For Windows:
setx GITHUB_TOKEN "YourGitHubToken" -
For Linux:
echo 'export GITHUB_TOKEN="YourGitHubToken"' >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
All output is now encapsulated in XML tags. This change was implemented based on evaluations showing that LLMs perform better with prompts structured in XML. The general structure of the output is as follows:
<source type="[source_type]" [additional_attributes]>
<[content_type]>
[Extracted content]
</[content_type]>
</source>Where [source_type] could be one of: "github_repository", "github_pull_request", "github_issue", "arxiv_paper", "youtube_transcript", "web_documentation", "sci_hub_paper", or "local_directory".
This XML structure provides clear delineation of different content types and sources, potentially improving the LLM's understanding and processing of the input.
- For Repos, Modify this line of code to add or remove filetypes processed:
allowed_extensions = ['.py', '.txt', '.js', '.rst', '.sh', '.md', '.pyx', '.html', '.yaml','.json', '.jsonl', '.ipynb', '.h', '.c', '.sql', '.csv'] - For Web scraping, Modify this line of code to change how many links deep from the starting URL to include
max_depth = 2 - Token counts are displayed in the console for both output files.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for 1filellm
Similar Open Source Tools

1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
vision-parse
Vision Parse is a tool that leverages Vision Language Models to parse PDF documents into beautifully formatted markdown content. It offers smart content extraction, content formatting, multi-LLM support, PDF document support, and local model hosting using Ollama. Users can easily convert PDFs to markdown with high precision and preserve document hierarchy and styling. The tool supports multiple Vision LLM providers like OpenAI, LLama, and Gemini for accuracy and speed, making document processing efficient and effortless.
paperless-gpt
paperless-gpt is a tool designed to generate accurate and meaningful document titles and tags for paperless-ngx using Large Language Models (LLMs). It supports multiple LLM providers, including OpenAI and Ollama. With paperless-gpt, you can streamline your document management by automatically suggesting appropriate titles and tags based on the content of your scanned documents. The tool offers features like multiple LLM support, customizable prompts, easy integration with paperless-ngx, user-friendly interface for reviewing and applying suggestions, dockerized deployment, automatic document processing, and an experimental OCR feature.
kernel-memory
Kernel Memory (KM) is a multi-modal AI Service specialized in the efficient indexing of datasets through custom continuous data hybrid pipelines, with support for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), synthetic memory, prompt engineering, and custom semantic memory processing. KM is available as a Web Service, as a Docker container, a Plugin for ChatGPT/Copilot/Semantic Kernel, and as a .NET library for embedded applications. Utilizing advanced embeddings and LLMs, the system enables Natural Language querying for obtaining answers from the indexed data, complete with citations and links to the original sources. Designed for seamless integration as a Plugin with Semantic Kernel, Microsoft Copilot and ChatGPT, Kernel Memory enhances data-driven features in applications built for most popular AI platforms.
airunner
AI Runner is a multi-modal AI interface that allows users to run open-source large language models and AI image generators on their own hardware. The tool provides features such as voice-based chatbot conversations, text-to-speech, speech-to-text, vision-to-text, text generation with large language models, image generation capabilities, image manipulation tools, utility functions, and more. It aims to provide a stable and user-friendly experience with security updates, a new UI, and a streamlined installation process. The application is designed to run offline on users' hardware without relying on a web server, offering a smooth and responsive user experience.
pgvecto.rs
pgvecto.rs is a Postgres extension written in Rust that provides vector similarity search functions. It offers ultra-low-latency, high-precision vector search capabilities, including sparse vector search and full-text search. With complete SQL support, async indexing, and easy data management, it simplifies data handling. The extension supports various data types like FP16/INT8, binary vectors, and Matryoshka embeddings. It ensures system performance with production-ready features, high availability, and resource efficiency. Security and permissions are managed through easy access control. The tool allows users to create tables with vector columns, insert vector data, and calculate distances between vectors using different operators. It also supports half-precision floating-point numbers for better performance and memory usage optimization.
NExT-GPT
NExT-GPT is an end-to-end multimodal large language model that can process input and generate output in various combinations of text, image, video, and audio. It leverages existing pre-trained models and diffusion models with end-to-end instruction tuning. The repository contains code, data, and model weights for NExT-GPT, allowing users to work with different modalities and perform tasks like encoding, understanding, reasoning, and generating multimodal content.
LLM4Decompile
LLM4Decompile is an open-source large language model dedicated to decompilation of Linux x86_64 binaries, supporting GCC's O0 to O3 optimization levels. It focuses on assessing re-executability of decompiled code through HumanEval-Decompile benchmark. The tool includes models with sizes ranging from 1.3 billion to 33 billion parameters, available on Hugging Face. Users can preprocess C code into binary and assembly instructions, then decompile assembly instructions into C using LLM4Decompile. Ongoing efforts aim to expand capabilities to support more architectures and configurations, integrate with decompilation tools like Ghidra and Rizin, and enhance performance with larger training datasets.
auto-md
Auto-MD is a Python tool that converts various file types and GitHub repositories into Markdown documents optimized for quick indexing via large language models. It supports multiple file types, processes zip files/folders/individual files and GitHub repositories, generates single or multiple Markdown files, and creates a table of contents and metadata for each processed file.

evedel
Evedel is an Emacs package designed to streamline the interaction with LLMs during programming. It aims to reduce manual code writing by creating detailed instruction annotations in the source files for LLM models. The tool leverages overlays to track instructions, categorize references with tags, and provide a seamless workflow for managing and processing directives. Evedel offers features like saving instruction overlays, complex query expressions for directives, and easy navigation through instruction overlays across all buffers. It is versatile and can be used in various types of buffers beyond just programming buffers.
indexify
Indexify is an open-source engine for building fast data pipelines for unstructured data (video, audio, images, and documents) using reusable extractors for embedding, transformation, and feature extraction. LLM Applications can query transformed content friendly to LLMs by semantic search and SQL queries. Indexify keeps vector databases and structured databases (PostgreSQL) updated by automatically invoking the pipelines as new data is ingested into the system from external data sources. **Why use Indexify** * Makes Unstructured Data **Queryable** with **SQL** and **Semantic Search** * **Real-Time** Extraction Engine to keep indexes **automatically** updated as new data is ingested. * Create **Extraction Graph** to describe **data transformation** and extraction of **embedding** and **structured extraction**. * **Incremental Extraction** and **Selective Deletion** when content is deleted or updated. * **Extractor SDK** allows adding new extraction capabilities, and many readily available extractors for **PDF**, **Image**, and **Video** indexing and extraction. * Works with **any LLM Framework** including **Langchain**, **DSPy**, etc. * Runs on your laptop during **prototyping** and also scales to **1000s of machines** on the cloud. * Works with many **Blob Stores**, **Vector Stores**, and **Structured Databases** * We have even **Open Sourced Automation** to deploy to Kubernetes in production.
DB-GPT
DB-GPT is a personal database administrator that can solve database problems by reading documents, using various tools, and writing analysis reports. It is currently undergoing an upgrade. **Features:** * **Online Demo:** * Import documents into the knowledge base * Utilize the knowledge base for well-founded Q&A and diagnosis analysis of abnormal alarms * Send feedbacks to refine the intermediate diagnosis results * Edit the diagnosis result * Browse all historical diagnosis results, used metrics, and detailed diagnosis processes * **Language Support:** * English (default) * Chinese (add "language: zh" in config.yaml) * **New Frontend:** * Knowledgebase + Chat Q&A + Diagnosis + Report Replay * **Extreme Speed Version for localized llms:** * 4-bit quantized LLM (reducing inference time by 1/3) * vllm for fast inference (qwen) * Tiny LLM * **Multi-path extraction of document knowledge:** * Vector database (ChromaDB) * RESTful Search Engine (Elasticsearch) * **Expert prompt generation using document knowledge** * **Upgrade the LLM-based diagnosis mechanism:** * Task Dispatching -> Concurrent Diagnosis -> Cross Review -> Report Generation * Synchronous Concurrency Mechanism during LLM inference * **Support monitoring and optimization tools in multiple levels:** * Monitoring metrics (Prometheus) * Flame graph in code level * Diagnosis knowledge retrieval (dbmind) * Logical query transformations (Calcite) * Index optimization algorithms (for PostgreSQL) * Physical operator hints (for PostgreSQL) * Backup and Point-in-time Recovery (Pigsty) * **Continuously updated papers and experimental reports** This project is constantly evolving with new features. Don't forget to star ⭐ and watch 👀 to stay up to date.
lance
Lance is a modern columnar data format optimized for ML workflows and datasets. It offers high-performance random access, vector search, zero-copy automatic versioning, and ecosystem integrations with Apache Arrow, Pandas, Polars, and DuckDB. Lance is designed to address the challenges of the ML development cycle, providing a unified data format for collection, exploration, analytics, feature engineering, training, evaluation, deployment, and monitoring. It aims to reduce data silos and streamline the ML development process.
pocketpaw
PocketPaw is a lightweight and user-friendly tool designed for managing and organizing your digital assets. It provides a simple interface for users to easily categorize, tag, and search for files across different platforms. With PocketPaw, you can efficiently organize your photos, documents, and other files in a centralized location, making it easier to access and share them. Whether you are a student looking to organize your study materials, a professional managing project files, or a casual user wanting to declutter your digital space, PocketPaw is the perfect solution for all your file management needs.
logicstamp-context
LogicStamp Context is a static analyzer that extracts deterministic component contracts from TypeScript codebases, providing structured architectural context for AI coding assistants. It helps AI assistants understand architecture by extracting props, hooks, and dependencies without implementation noise. The tool works with React, Next.js, Vue, Express, and NestJS, and is compatible with various AI assistants like Claude, Cursor, and MCP agents. It offers features like watch mode for real-time updates, breaking change detection, and dependency graph creation. LogicStamp Context is a security-first tool that protects sensitive data, runs locally, and is non-opinionated about architectural decisions.
oxylabs-mcp
The Oxylabs MCP Server acts as a bridge between AI models and the web, providing clean, structured data from any site. It enables scraping of URLs, rendering JavaScript-heavy pages, content extraction for AI use, bypassing anti-scraping measures, and accessing geo-restricted web data from 195+ countries. The implementation utilizes the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to facilitate secure interactions between AI assistants and web content. Key features include scraping content from any site, automatic data cleaning and conversion, bypassing blocks and geo-restrictions, flexible setup with cross-platform support, and built-in error handling and request management.
For similar tasks
vespa
Vespa is a platform that performs operations such as selecting a subset of data in a large corpus, evaluating machine-learned models over the selected data, organizing and aggregating it, and returning it, typically in less than 100 milliseconds, all while the data corpus is continuously changing. It has been in development for many years and is used on a number of large internet services and apps which serve hundreds of thousands of queries from Vespa per second.

1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.

letsql
LETSQL is a data processing library built on top of Ibis and DataFusion to write multi-engine data workflows. It is currently in development and does not have a stable release. Users can install LETSQL from PyPI and use it to connect to data sources, read data, filter, group, and aggregate data for analysis. Contributions to the project are welcome, and the library is actively maintained with support available for any issues. LETSQL heavily relies on Ibis and DataFusion for its functionality.
onefilellm
OneFileLLM is a command-line tool that streamlines the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models (LLMs). It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources, compiling them into a single text file for quick use. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, token count reporting, and XML encapsulation of output for improved LLM performance. Users can easily access private GitHub repositories by generating a personal access token. The tool's output is encapsulated in XML tags to enhance LLM understanding and processing.
context7
Context7 is a powerful tool for analyzing and visualizing data in various formats. It provides a user-friendly interface for exploring datasets, generating insights, and creating interactive visualizations. With advanced features such as data filtering, aggregation, and customization, Context7 is suitable for both beginners and experienced data analysts. The tool supports a wide range of data sources and formats, making it versatile for different use cases. Whether you are working on exploratory data analysis, data visualization, or data storytelling, Context7 can help you uncover valuable insights and communicate your findings effectively.
RepoToText
RepoToText is a web app that scrapes a GitHub repository and converts its files into a single organized .txt. It allows users to enter the URL of a GitHub repository and an optional documentation URL, retrieves the contents of the repository and documentation, and saves them in a structured text file. The tool can be used to interact with the repository using chatbots like GPT-4 or Claude Opus. Users can run the application with Docker, set up environment variables, choose specific file types for scraping, and copy the generated text to the clipboard. Additionally, FolderToText.py script allows converting local folders or files into a .txt file with customizable options.
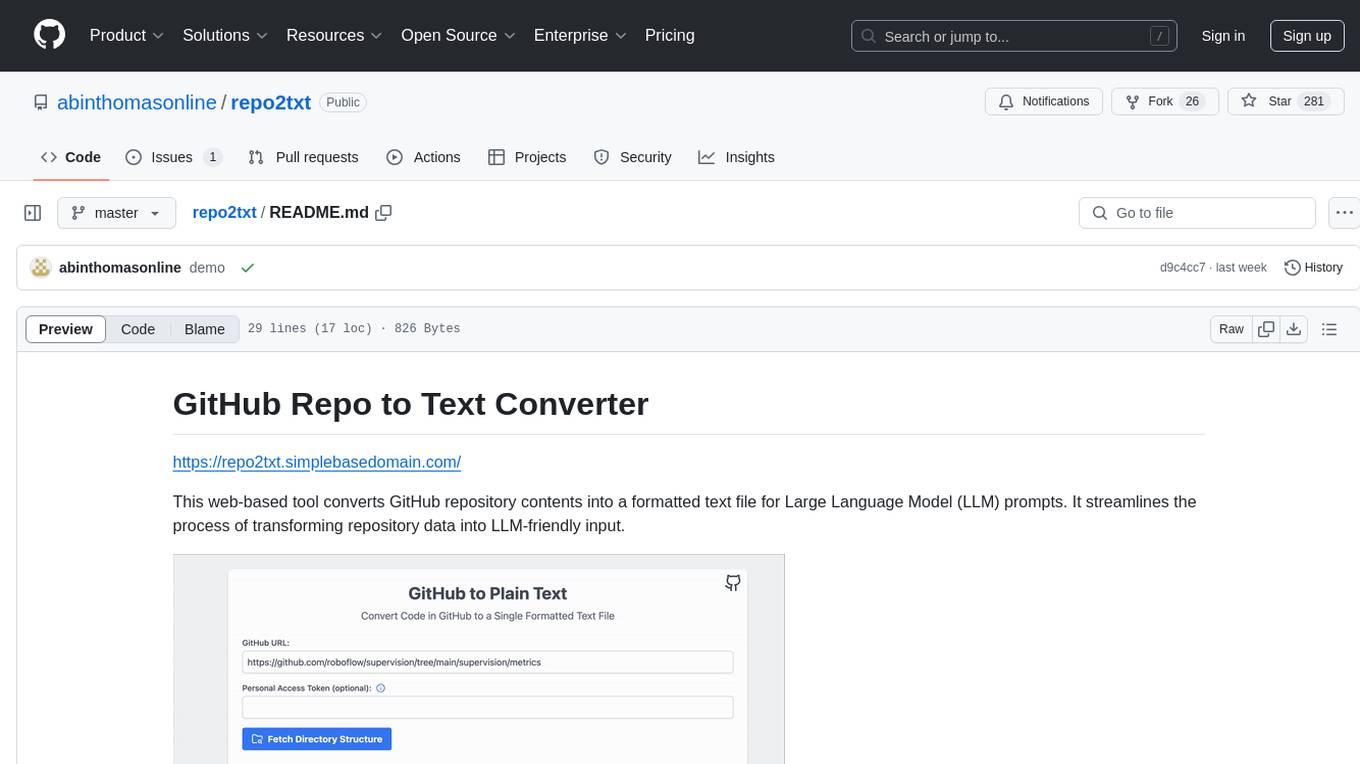
repo2txt
The GitHub Repo to Text Converter is a web-based tool that converts GitHub repository contents into a formatted text file for Large Language Model (LLM) prompts. It streamlines the process of transforming repository data into LLM-friendly input. The tool displays the GitHub repository structure, allows users to select files/directories to include, generates a formatted text file, enables copying text to clipboard, supports downloading generated text, and works with private repositories. It ensures data security by running entirely in the browser without server-side processing.
AudioNotes
AudioNotes is a system built on FunASR and Qwen2 that can quickly extract content from audio and video, and organize it using large models into structured markdown notes for easy reading. Users can interact with the audio and video content, install Ollama, pull models, and deploy services using Docker or locally with a PostgreSQL database. The system provides a seamless way to convert audio and video into structured notes for efficient consumption.
For similar jobs
Perplexica
Perplexica is an open-source AI-powered search engine that utilizes advanced machine learning algorithms to provide clear answers with sources cited. It offers various modes like Copilot Mode, Normal Mode, and Focus Modes for specific types of questions. Perplexica ensures up-to-date information by using SearxNG metasearch engine. It also features image and video search capabilities and upcoming features include finalizing Copilot Mode and adding Discover and History Saving features.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
MMMU
MMMU is a benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal models on college-level subject knowledge tasks, covering 30 subjects and 183 subfields with 11.5K questions. It focuses on advanced perception and reasoning with domain-specific knowledge, challenging models to perform tasks akin to those faced by experts. The evaluation of various models highlights substantial challenges, with room for improvement to stimulate the community towards expert artificial general intelligence (AGI).

1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
gpt-researcher
GPT Researcher is an autonomous agent designed for comprehensive online research on a variety of tasks. It can produce detailed, factual, and unbiased research reports with customization options. The tool addresses issues of speed, determinism, and reliability by leveraging parallelized agent work. The main idea involves running 'planner' and 'execution' agents to generate research questions, seek related information, and create research reports. GPT Researcher optimizes costs and completes tasks in around 3 minutes. Features include generating long research reports, aggregating web sources, an easy-to-use web interface, scraping web sources, and exporting reports to various formats.
ChatTTS
ChatTTS is a generative speech model optimized for dialogue scenarios, providing natural and expressive speech synthesis with fine-grained control over prosodic features. It supports multiple speakers and surpasses most open-source TTS models in terms of prosody. The model is trained with 100,000+ hours of Chinese and English audio data, and the open-source version on HuggingFace is a 40,000-hour pre-trained model without SFT. The roadmap includes open-sourcing additional features like VQ encoder, multi-emotion control, and streaming audio generation. The tool is intended for academic and research use only, with precautions taken to limit potential misuse.
HebTTS
HebTTS is a language modeling approach to diacritic-free Hebrew text-to-speech (TTS) system. It addresses the challenge of accurately mapping text to speech in Hebrew by proposing a language model that operates on discrete speech representations and is conditioned on a word-piece tokenizer. The system is optimized using weakly supervised recordings and outperforms diacritic-based Hebrew TTS systems in terms of content preservation and naturalness of generated speech.
do-research-in-AI
This repository is a collection of research lectures and experience sharing posts from frontline researchers in the field of AI. It aims to help individuals upgrade their research skills and knowledge through insightful talks and experiences shared by experts. The content covers various topics such as evaluating research papers, choosing research directions, research methodologies, and tips for writing high-quality scientific papers. The repository also includes discussions on academic career paths, research ethics, and the emotional aspects of research work. Overall, it serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in advancing their research capabilities in the field of AI.