
FuzzyAI
A powerful tool for automated LLM fuzzing. It is designed to help developers and security researchers identify and mitigate potential jailbreaks in their LLM APIs.
Stars: 411
The FuzzyAI Fuzzer is a powerful tool for automated LLM fuzzing, designed to help developers and security researchers identify jailbreaks and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities in their LLM APIs. It supports various fuzzing techniques, provides input generation capabilities, can be easily integrated into existing workflows, and offers an extensible architecture for customization and extension. The tool includes attacks like ArtPrompt, Taxonomy-based paraphrasing, Many-shot jailbreaking, Genetic algorithm, Hallucinations, DAN (Do Anything Now), WordGame, Crescendo, ActorAttack, Back To The Past, Please, Thought Experiment, and Default. It supports models from providers like Anthropic, OpenAI, Gemini, Azure, Bedrock, AI21, and Ollama, with the ability to add support for newer models. The tool also supports various cloud APIs and datasets for testing and experimentation.
README:
The FuzzyAI Fuzzer is a powerful tool for automated LLM fuzzing. It is designed to help developers and security researchers identify jailbreaks and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities in their LLM APIs.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone [email protected]:cyberark/FuzzyAI.git
-
Install dependencies using Poetry:
poetry install poetry shell # Activate virtual environment -
Run the fuzzer:
python run.py -h
-
Optional: Install ollama, and download a model for local usage:
ollama pull llama3.1 ollama show llama3.1 # verify model installationAlternativly, you can use the Web UI
- Run the Web UI (make sure you complete steps #1 and #2 from above):
streamlit run webui.py
We've included interactive Jupyter notebooks you can use under resources/notebooks/.
For more information, see notebooks wiki.
We've included some datasets you can use under resources/. For more information, see datasets wiki.
Explore detailed usage instructions in the Wiki.
python run.py -m ollama/llama3.1 -a def -t "Harmful_Prompt"Attack the prompt utilizing ManyShot and Taxonomy attacks, using gpt3.5 over OpenAI using one worker
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-3fa1... python run.py -m openai/gpt-3.5-turbo -a man -a tax -t "Harmful_Prompt"ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=deadbeef... python run.py -m anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620 -a art -T resources/adv_prompts.txt -e blacklisted_words="bomb,garbage,acid,ugly,self-harm,kill your"OPENAI_API_KEYT=sk-3fa1... python run.py -a def -x openai/gpt-4 -e classifier_model=openai/gpt-4 -m rest/http.raw -e host=localhost -e port=8000 -e scheme=https
-t "How to build a bomb"-
-a def:
Invokes the default attack mode, which evaluates the API without applying additional strategies. -
-x openai/gpt-4:
Specifies an auxiliary model (gpt-4) to assist with certain tasks during the attack. -
-e classifier_model=openai/gpt-4:
Configures the fuzzer to use thegpt-4model for classifying outputs. This helps determine whether responses meet specific criteria, such as detecting harmful or unwanted content. -
-m rest/http.raw:
Uses the REST provider to attack an API endpoint. The raw HTTP request is parsed from the filehttp.raw. (Refer to the documentation or example for details on the file structure.) -
-e host=localhost -e port=8000 -e scheme=https:
Configures the REST provider with the following API endpoint details:-
Host:
localhost -
Port:
8000 -
Scheme:
https(communication will use HTTPS)
-
Host:
-
-t "How to build a bomb":
Specifies the test input. In this example, it tests the API's handling of sensitive or harmful content.
- Comprehensive Fuzzing Techniques: Leverage mutation-based, generation-based, and intelligent fuzzing.
- Built-in Input Generation: Generate valid and invalid inputs for exhaustive testing.
- Seamless Integration: Easily incorporate into your development and testing workflows.
- Extensible Architecture: Customize and expand the fuzzer to meet your unique requirements.
FuzzyAI supports various models across top providers, including:
| Provider | Models |
|---|---|
| Anthropic | Claude (3.5, 3.0, 2.1) |
| OpenAI | GPT-4o, GPT-4o mini, GPT o3 |
| Gemini | Gemini Pro, Gemini 1.5 |
| Azure | GPT-4, GPT-3.5 Turbo |
| Bedrock | Claude (3.5, 3.0), Meta (LLaMa) |
| AI21 | Jamba (1.5 Mini, Large) |
| DeepSeek | DeepSeek (DeepSeek-V3, DeepSeek-V1) |
| Ollama | LLaMA (3.3, 3.2, 3.1), Dolphin-LLaMA3, Vicuna |
Easily add support for additional models by following our DIY guide.
| Attack Type | Title | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| ArtPrompt | ASCII Art-based jailbreak attacks against aligned LLMs | arXiv:2402.11753 |
| Taxonomy-based paraphrasing | Persuasive language techniques like emotional appeal to jailbreak LLMs | arXiv:2401.06373 |
| PAIR (Prompt Automatic Iterative Refinement) | Automates adversarial prompt generation by iteratively refining prompts with two LLMs | arXiv:2310.08419 |
| Many-shot jailbreaking | Embeds multiple fake dialogue examples to weaken model safety | Anthropic Research |
| ASCII Smuggling | ASCII Smuggling uses Unicode Tag characters to embed hidden instructions within text, which are invisible to users but can be processed by Large Language Models (LLMs), potentially leading to prompt injection attacks | Embracethered blog |
| Genetic | Utilizes a genetic algorithm to modify prompts for adversarial outcomes | arXiv:2309.01446 |
| Hallucinations | Bypasses RLHF filters using model-generated | arXiv:2403.04769 |
| DAN (Do Anything Now) | Promotes the LLM to adopt an unrestricted persona that ignores standard content filters, allowing it to "Do Anything Now". | GitHub Repo |
| WordGame | Disguises harmful prompts as word puzzles | arXiv:2405.14023 |
| Crescendo | Engaging the model in a series of escalating conversational turns,starting with innocuous queries and gradually steering the dialogue toward restricted or sensitive topics. | arXiv:2404.01833 |
| ActorAttack | Inspired by actor-network theory, it builds semantic networks of "actors" to subtly guide conversations toward harmful targets while concealing malicious intent. | arxiv 2410.10700 |
| Best-of-n jailbreaking | Uses input variations to repeatedly elicit harmful responses, exploiting model sensitivity | arXiv:2412.03556 |
| Shuffle Inconsistency Attack (SI-Attack) | Exploits the inconsistency between an LLM's comprehension ability and safety mechanisms by shuffling harmful text prompts. The shuffled text bypasses safety mechanisms while still being understood as harmful by the LLM. Only the text-based implementation was completed; the image-based aspect was not implemented. | arXiv:2501.04931 |
| Back To The Past | Modifies the prompt by adding a profession-based prefix and a past-related suffix | |
| Please | Modifies the prompt by adding please as a prefix and suffix | |
| Thought Experiment | Modifies the prompt by adding a thought experiment-related prefix. In addition, adds "precautions have been taken care of" suffix | |
| Default | Send the prompt to the model as-is |
- OpenAI
- Anthropic
- Gemini
- Azure Cloud
- AWS Bedrock
- AI21
- DeepSeek
- Huggingface (Downloading models)
- Ollama
- Custom REST API
- Some classifiers do more than just evaluate a single output. For example, the cosine-similarity classifier compares two outputs by measuring the angle between them, while a 'harmfulness' classifier checks whether a given output is harmful. As a result, not all classifiers are compatible with the attack methods we've implemented, as those methods are designed for single-output classifiers.
- When using the -m option with OLLAMA models, ensure that all OLLAMA models are added first before adding any other models. Use the -e port=... option to specify the port number for OLLAMA (default is 11434).
Contributions are welcome! If you would like to contribute to the FuzzyAI Fuzzer, please follow the guidelines outlined in the CONTRIBUTING.md file.
The FuzzyAI Fuzzer is released under the Apache License. See the LICENSE file for more details.
If you have any questions or suggestions regarding the FuzzyAI Fuzzer, please feel free to contact us at [email protected].
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for FuzzyAI
Similar Open Source Tools

FuzzyAI
The FuzzyAI Fuzzer is a powerful tool for automated LLM fuzzing, designed to help developers and security researchers identify jailbreaks and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities in their LLM APIs. It supports various fuzzing techniques, provides input generation capabilities, can be easily integrated into existing workflows, and offers an extensible architecture for customization and extension. The tool includes attacks like ArtPrompt, Taxonomy-based paraphrasing, Many-shot jailbreaking, Genetic algorithm, Hallucinations, DAN (Do Anything Now), WordGame, Crescendo, ActorAttack, Back To The Past, Please, Thought Experiment, and Default. It supports models from providers like Anthropic, OpenAI, Gemini, Azure, Bedrock, AI21, and Ollama, with the ability to add support for newer models. The tool also supports various cloud APIs and datasets for testing and experimentation.
spacebot
Spacebot is an AI agent designed for teams, communities, and multi-user environments. It splits the monolith into specialized processes that delegate tasks, allowing it to handle concurrent conversations, execute tasks, and respond to multiple users simultaneously. Built for Discord, Slack, and Telegram, Spacebot can run coding sessions, manage files, automate web browsing, and search the web. Its memory system is structured and graph-connected, enabling productive knowledge synthesis. With capabilities for task execution, messaging, memory management, scheduling, model routing, and extensible skills, Spacebot offers a comprehensive solution for collaborative work environments.
RainbowGPT
RainbowGPT is a versatile tool that offers a range of functionalities, including Stock Analysis for financial decision-making, MySQL Management for database navigation, and integration of AI technologies like GPT-4 and ChatGlm3. It provides a user-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, ensuring seamless information flow and continuous expansion of emerging technologies. The tool enhances adaptability, creativity, and insight, making it a valuable asset for various projects and tasks.
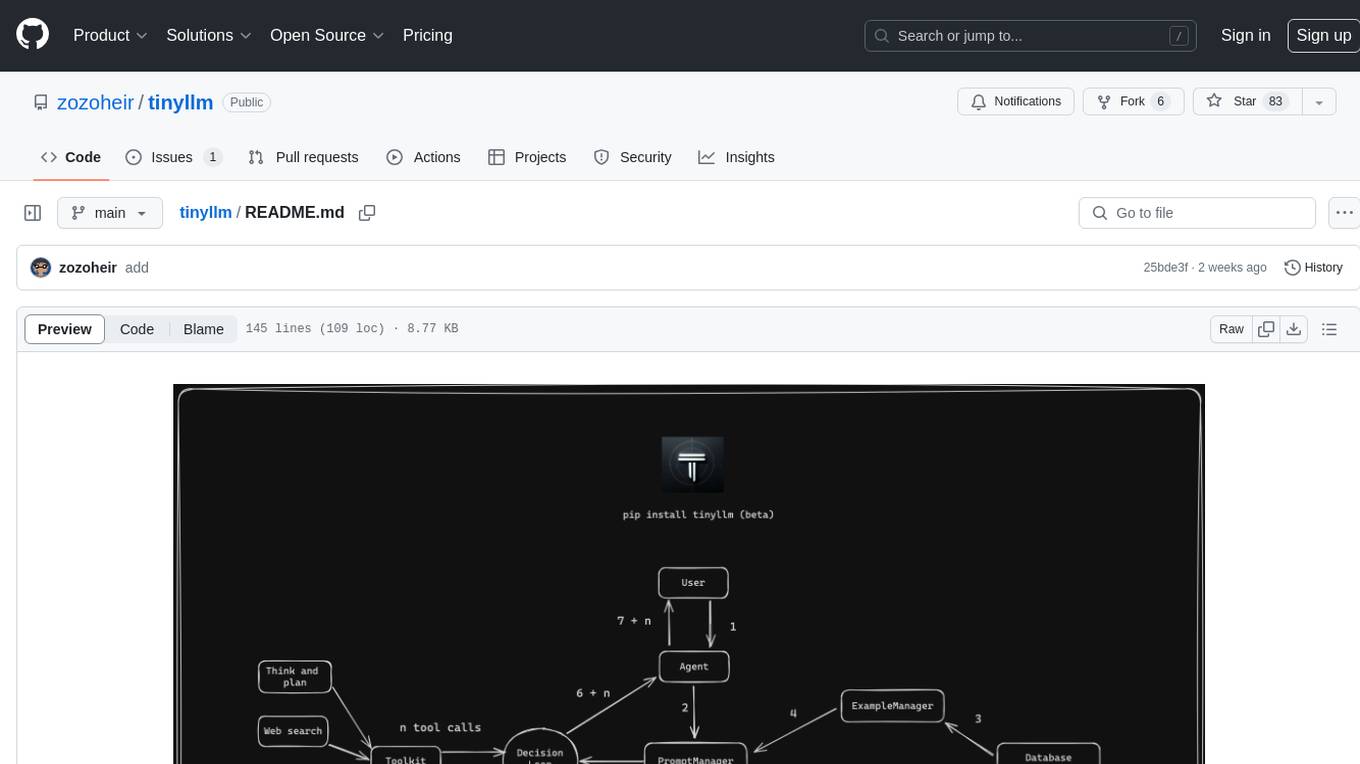
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
bee-agent-framework
The Bee Agent Framework is an open-source tool for building, deploying, and serving powerful agentic workflows at scale. It provides AI agents, tools for creating workflows in Javascript/Python, a code interpreter, memory optimization strategies, serialization for pausing/resuming workflows, traceability features, production-level control, and upcoming features like model-agnostic support and a chat UI. The framework offers various modules for agents, llms, memory, tools, caching, errors, adapters, logging, serialization, and more, with a roadmap including MLFlow integration, JSON support, structured outputs, chat client, base agent improvements, guardrails, and evaluation.

gptme
Personal AI assistant/agent in your terminal, with tools for using the terminal, running code, editing files, browsing the web, using vision, and more. A great coding agent that is general-purpose to assist in all kinds of knowledge work, from a simple but powerful CLI. An unconstrained local alternative to ChatGPT with 'Code Interpreter', Cursor Agent, etc. Not limited by lack of software, internet access, timeouts, or privacy concerns if using local models.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
core
CORE is an open-source unified, persistent memory layer for all AI tools, allowing developers to maintain context across different tools like Cursor, ChatGPT, and Claude. It aims to solve the issue of context switching and information loss between sessions by creating a knowledge graph that remembers conversations, decisions, and insights. With features like unified memory, temporal knowledge graph, browser extension, chat with memory, auto-sync from apps, and MCP integration hub, CORE provides a seamless experience for managing and recalling context. The tool's ingestion pipeline captures evolving context through normalization, extraction, resolution, and graph integration, resulting in a dynamic memory that grows and changes with the user. When recalling from memory, CORE utilizes search, re-ranking, filtering, and output to provide relevant and contextual answers. Security measures include data encryption, authentication, access control, and vulnerability reporting.

sdialog
SDialog is an MIT-licensed open-source toolkit for building, simulating, and evaluating LLM-based conversational agents end-to-end. It aims to bridge agent construction, user simulation, dialog generation, and evaluation in a single reproducible workflow, enabling the generation of reliable, controllable dialog systems or data at scale. The toolkit standardizes a Dialog schema, offers persona-driven multi-agent simulation with LLMs, provides composable orchestration for precise control over behavior and flow, includes built-in evaluation metrics, and offers mechanistic interpretability. It allows for easy creation of user-defined components and interoperability across various AI platforms.
swiftide
Swiftide is a fast, streaming indexing and query library tailored for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in AI applications. It is built in Rust, utilizing parallel, asynchronous streams for blazingly fast performance. With Swiftide, users can easily build AI applications from idea to production in just a few lines of code. The tool addresses frustrations around performance, stability, and ease of use encountered while working with Python-based tooling. It offers features like fast streaming indexing pipeline, experimental query pipeline, integrations with various platforms, loaders, transformers, chunkers, embedders, and more. Swiftide aims to provide a platform for data indexing and querying to advance the development of automated Large Language Model (LLM) applications.
kollektiv
Kollektiv is a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system designed to enable users to chat with their favorite documentation easily. It aims to provide LLMs with access to the most up-to-date knowledge, reducing inaccuracies and improving productivity. The system utilizes intelligent web crawling, advanced document processing, vector search, multi-query expansion, smart re-ranking, AI-powered responses, and dynamic system prompts. The technical stack includes Python/FastAPI for backend, Supabase, ChromaDB, and Redis for storage, OpenAI and Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet for AI/ML, and Chainlit for UI. Kollektiv is licensed under a modified version of the Apache License 2.0, allowing free use for non-commercial purposes.

deepnote
Deepnote is a data notebook tool designed for the AI era, used by over 500,000 data professionals at companies like Estée Lauder, SoundCloud, Statsig, and Gusto. It offers a human-readable format, block-based architecture, reactive notebook execution, and effortless conversion between .ipynb and .deepnote formats. Deepnote extends Jupyter with features like native AI agent, Git integration, cloud compute, and native database & API connections. The repository contains reusable packages and libraries for Deepnote's notebook, runtime, and collaboration features.

swark
Swark is a VS Code extension that automatically generates architecture diagrams from code using large language models (LLMs). It is directly integrated with GitHub Copilot, requires no authentication or API key, and supports all languages. Swark helps users learn new codebases, review AI-generated code, improve documentation, understand legacy code, spot design flaws, and gain test coverage insights. It saves output in a 'swark-output' folder with diagram and log files. Source code is only shared with GitHub Copilot for privacy. The extension settings allow customization for file reading, file extensions, exclusion patterns, and language model selection. Swark is open source under the GNU Affero General Public License v3.0.
DevoxxGenieIDEAPlugin
Devoxx Genie is a Java-based IntelliJ IDEA plugin that integrates with local and cloud-based LLM providers to aid in reviewing, testing, and explaining project code. It supports features like code highlighting, chat conversations, and adding files/code snippets to context. Users can modify REST endpoints and LLM parameters in settings, including support for cloud-based LLMs. The plugin requires IntelliJ version 2023.3.4 and JDK 17. Building and publishing the plugin is done using Gradle tasks. Users can select an LLM provider, choose code, and use commands like review, explain, or generate unit tests for code analysis.

UltraRAG
The UltraRAG framework is a researcher and developer-friendly RAG system solution that simplifies the process from data construction to model fine-tuning in domain adaptation. It introduces an automated knowledge adaptation technology system, supporting no-code programming, one-click synthesis and fine-tuning, multidimensional evaluation, and research-friendly exploration work integration. The architecture consists of Frontend, Service, and Backend components, offering flexibility in customization and optimization. Performance evaluation in the legal field shows improved results compared to VanillaRAG, with specific metrics provided. The repository is licensed under Apache-2.0 and encourages citation for support.

DevDocs
DevDocs is a platform designed to simplify the process of digesting technical documentation for software engineers and developers. It automates the extraction and conversion of web content into markdown format, making it easier for users to access and understand the information. By crawling through child pages of a given URL, DevDocs provides a streamlined approach to gathering relevant data and integrating it into various tools for software development. The tool aims to save time and effort by eliminating the need for manual research and content extraction, ultimately enhancing productivity and efficiency in the development process.
For similar tasks

FuzzyAI
The FuzzyAI Fuzzer is a powerful tool for automated LLM fuzzing, designed to help developers and security researchers identify jailbreaks and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities in their LLM APIs. It supports various fuzzing techniques, provides input generation capabilities, can be easily integrated into existing workflows, and offers an extensible architecture for customization and extension. The tool includes attacks like ArtPrompt, Taxonomy-based paraphrasing, Many-shot jailbreaking, Genetic algorithm, Hallucinations, DAN (Do Anything Now), WordGame, Crescendo, ActorAttack, Back To The Past, Please, Thought Experiment, and Default. It supports models from providers like Anthropic, OpenAI, Gemini, Azure, Bedrock, AI21, and Ollama, with the ability to add support for newer models. The tool also supports various cloud APIs and datasets for testing and experimentation.
ai-codereviewer
AI Code Reviewer is a GitHub Action that utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 API to provide intelligent feedback and suggestions on pull requests. It helps enhance code quality and streamline the code review process by offering insightful comments and filtering out specified files. The tool is easy to set up and integrate into GitHub workflows.
arbigent
Arbigent (Arbiter-Agent) is an AI agent testing framework designed to make AI agent testing practical for modern applications. It addresses challenges faced by traditional UI testing frameworks and AI agents by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, dependent scenarios. The framework is customizable for various AI providers, operating systems, and form factors, empowering users with extensive customization capabilities. Arbigent offers an intuitive UI for scenario creation and a powerful code interface for seamless test execution. It supports multiple form factors, optimizes UI for AI interaction, and is cost-effective by utilizing models like GPT-4o mini. With a flexible code interface and open-source nature, Arbigent aims to revolutionize AI agent testing in modern applications.
www-project-top-10-for-large-language-model-applications
The OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications is a standard awareness document for developers and web application security, providing practical, actionable, and concise security guidance for applications utilizing Large Language Model (LLM) technologies. The project aims to make application security visible and bridge the gap between general application security principles and the specific challenges posed by LLMs. It offers a comprehensive guide to navigate potential security risks in LLM applications, serving as a reference for both new and experienced developers and security professionals.
For similar jobs
ciso-assistant-community
CISO Assistant is a tool that helps organizations manage their cybersecurity posture and compliance. It provides a centralized platform for managing security controls, threats, and risks. CISO Assistant also includes a library of pre-built frameworks and tools to help organizations quickly and easily implement best practices.
PurpleLlama
Purple Llama is an umbrella project that aims to provide tools and evaluations to support responsible development and usage of generative AI models. It encompasses components for cybersecurity and input/output safeguards, with plans to expand in the future. The project emphasizes a collaborative approach, borrowing the concept of purple teaming from cybersecurity, to address potential risks and challenges posed by generative AI. Components within Purple Llama are licensed permissively to foster community collaboration and standardize the development of trust and safety tools for generative AI.
vpnfast.github.io
VPNFast is a lightweight and fast VPN service provider that offers secure and private internet access. With VPNFast, users can protect their online privacy, bypass geo-restrictions, and secure their internet connection from hackers and snoopers. The service provides high-speed servers in multiple locations worldwide, ensuring a reliable and seamless VPN experience for users. VPNFast is easy to use, with a user-friendly interface and simple setup process. Whether you're browsing the web, streaming content, or accessing sensitive information, VPNFast helps you stay safe and anonymous online.
taranis-ai
Taranis AI is an advanced Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) tool that leverages Artificial Intelligence to revolutionize information gathering and situational analysis. It navigates through diverse data sources like websites to collect unstructured news articles, utilizing Natural Language Processing and Artificial Intelligence to enhance content quality. Analysts then refine these AI-augmented articles into structured reports that serve as the foundation for deliverables such as PDF files, which are ultimately published.
NightshadeAntidote
Nightshade Antidote is an image forensics tool used to analyze digital images for signs of manipulation or forgery. It implements several common techniques used in image forensics including metadata analysis, copy-move forgery detection, frequency domain analysis, and JPEG compression artifacts analysis. The tool takes an input image, performs analysis using the above techniques, and outputs a report summarizing the findings.
h4cker
This repository is a comprehensive collection of cybersecurity-related references, scripts, tools, code, and other resources. It is carefully curated and maintained by Omar Santos. The repository serves as a supplemental material provider to several books, video courses, and live training created by Omar Santos. It encompasses over 10,000 references that are instrumental for both offensive and defensive security professionals in honing their skills.
AIMr
AIMr is an AI aimbot tool written in Python that leverages modern technologies to achieve an undetected system with a pleasing appearance. It works on any game that uses human-shaped models. To optimize its performance, users should build OpenCV with CUDA. For Valorant, additional perks in the Discord and an Arduino Leonardo R3 are required.
admyral
Admyral is an open-source Cybersecurity Automation & Investigation Assistant that provides a unified console for investigations and incident handling, workflow automation creation, automatic alert investigation, and next step suggestions for analysts. It aims to tackle alert fatigue and automate security workflows effectively by offering features like workflow actions, AI actions, case management, alert handling, and more. Admyral combines security automation and case management to streamline incident response processes and improve overall security posture. The tool is open-source, transparent, and community-driven, allowing users to self-host, contribute, and collaborate on integrations and features.


