Best AI tools for< Reproduce Results >
9 - AI tool Sites
Union.ai
Union.ai is an infrastructure platform designed for AI, ML, and data workloads. It offers a scalable MLOps platform that optimizes resources, reduces costs, and fosters collaboration among team members. Union.ai provides features such as declarative infrastructure, data lineage tracking, accelerated datasets, and more to streamline AI orchestration on Kubernetes. It aims to simplify the management of AI, ML, and data workflows in production environments by addressing complexities and offering cost-effective strategies.
Sacred
Sacred is a tool to configure, organize, log and reproduce computational experiments. It is designed to introduce only minimal overhead, while encouraging modularity and configurability of experiments. The ability to conveniently make experiments configurable is at the heart of Sacred. If the parameters of an experiment are exposed in this way, it will help you to: keep track of all the parameters of your experiment easily run your experiment for different settings save configurations for individual runs in files or a database reproduce your results In Sacred we achieve this through the following main mechanisms: Config Scopes are functions with a @ex.config decorator, that turn all local variables into configuration entries. This helps to set up your configuration really easily. Those entries can then be used in captured functions via dependency injection. That way the system takes care of passing parameters around for you, which makes using your config values really easy. The command-line interface can be used to change the parameters, which makes it really easy to run your experiment with modified parameters. Observers log every information about your experiment and the configuration you used, and saves them for example to a Database. This helps to keep track of all your experiments. Automatic seeding helps controlling the randomness in your experiments, such that they stay reproducible.
Comet ML
Comet ML is a machine learning platform that integrates with your existing infrastructure and tools so you can manage, visualize, and optimize models—from training runs to production monitoring.
Comet ML
Comet ML is a machine learning platform that integrates with your existing infrastructure and tools so you can manage, visualize, and optimize models—from training runs to production monitoring.
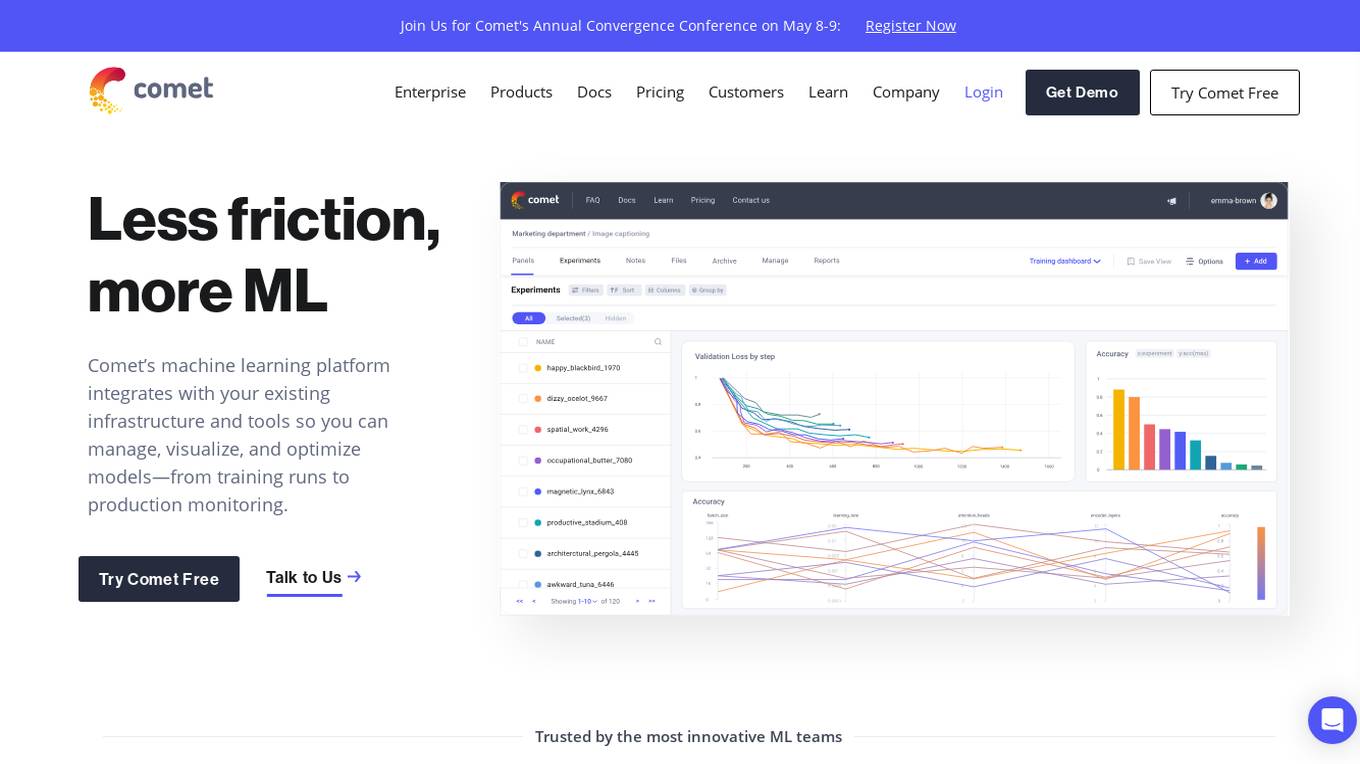
Comet ML
Comet ML is an extensible, fully customizable machine learning platform that aims to move ML forward by supporting productivity, reproducibility, and collaboration. It integrates with existing infrastructure and tools to manage, visualize, and optimize models from training runs to production monitoring. Users can track and compare training runs, create a model registry, and monitor models in production all in one platform. Comet's platform can be run on any infrastructure, enabling users to reshape their ML workflow and bring their existing software and data stack.
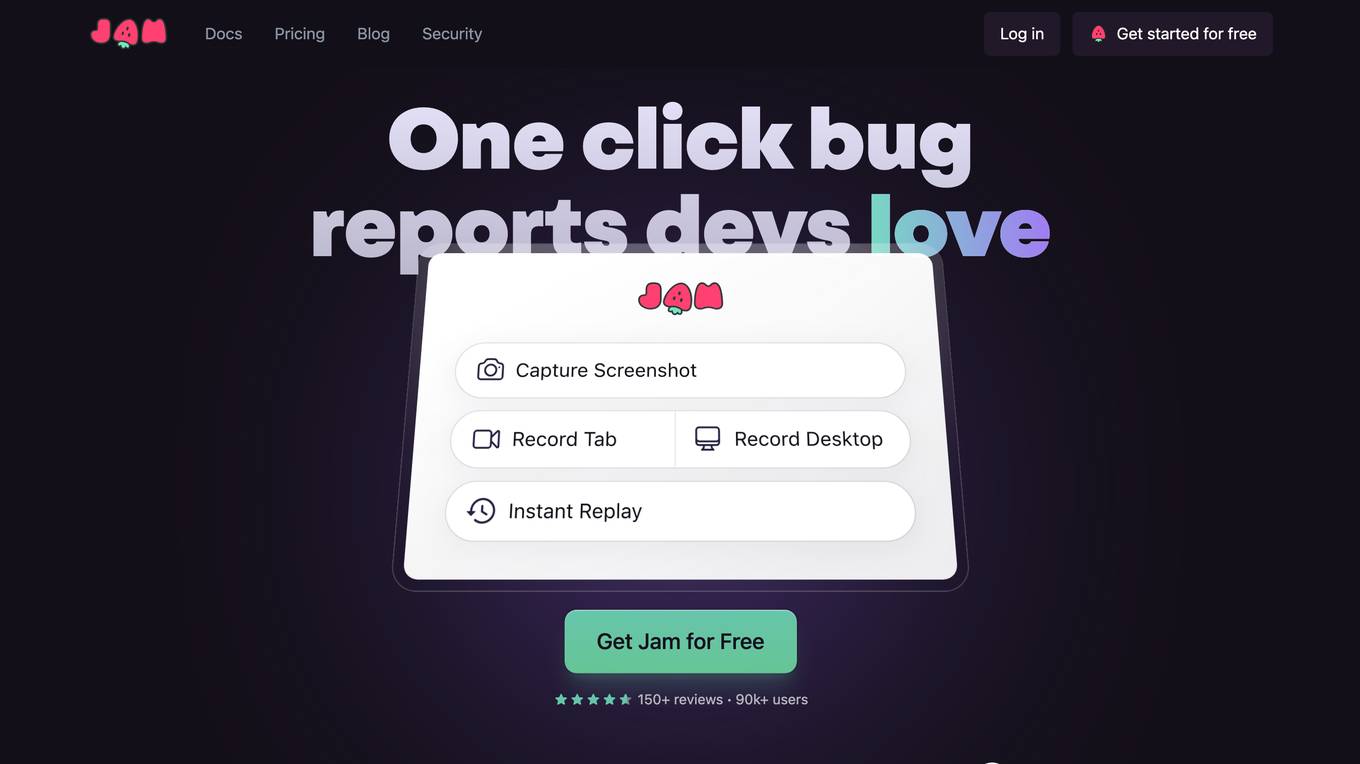
Jam
Jam is a bug-tracking tool that helps developers reproduce and debug issues quickly and easily. It automatically captures all the information engineers need to debug, including device and browser information, console logs, network logs, repro steps, and backend tracing. Jam also integrates with popular tools like GitHub, Jira, Linear, Slack, ClickUp, Asana, Sentry, Figma, Datadog, Gitlab, Notion, and Airtable. With Jam, developers can save time and effort by eliminating the need to write repro steps and manually collect information. Jam is used by over 90,000 developers and has received over 150 positive reviews.
ForgeFluencer
ForgeFluencer is an AI application that serves as an essential toolkit for crafting AI influencers and generating consistent and compelling content. It offers a user-friendly platform optimized for desktop and mobile, allowing users to create models, control various aspects of content generation, edit images with AI, and more. With features like Virtual Wardrobe, Pose Controller, and Photo Studio, ForgeFluencer empowers users to elevate their projects with AI-generated content effortlessly.
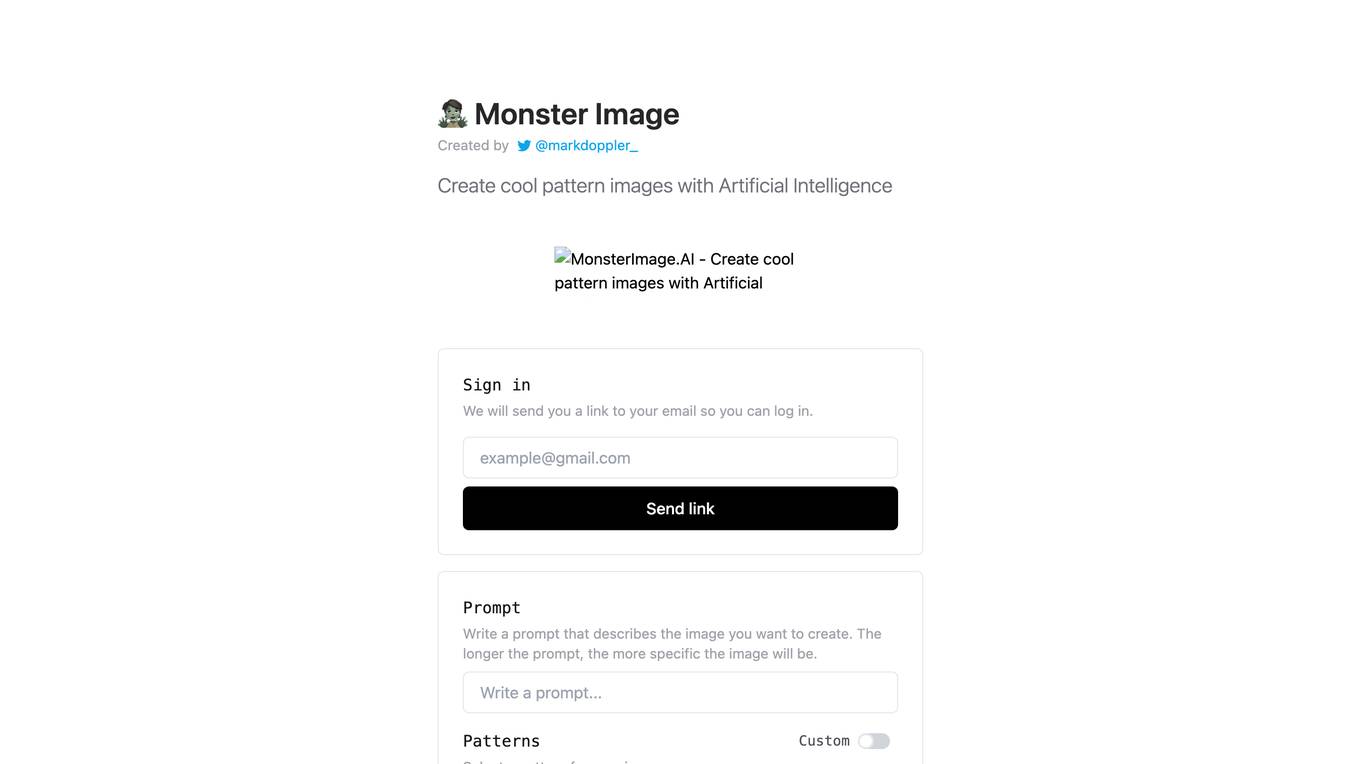
MonsterImage.AI
MonsterImage.AI is an AI-powered tool that allows users to create cool pattern images using Artificial Intelligence. Users can sign in to the platform and receive a link via email to log in. They can write a prompt to describe the image they want to create, select a pattern, specify negative prompts, use a seed for reproduction, adjust guidance scale, controlnet conditioning scale, and inference steps. The tool offers advanced options for creating images and allows users to save their creations in a public collection.

Fabfab.ai
Fabfab.ai is a website domain that is currently registered but potentially available for acquisition. The site does not provide any specific information or functionality as it is not developed or operational. Users visiting the domain will find a message indicating its registration status and the option to acquire the domain. Fabfab.ai does not offer any AI tools or applications at this time.
8 - Open Source AI Tools
RPG-DiffusionMaster
This repository contains the official implementation of RPG, a powerful training-free paradigm for text-to-image generation and editing. RPG utilizes proprietary or open-source MLLMs as prompt recaptioner and region planner with complementary regional diffusion. It achieves state-of-the-art results and can generate high-resolution images. The codebase supports diffusers and various diffusion backbones, including SDXL and SD v1.4/1.5. Users can reproduce results with GPT-4, Gemini-Pro, or local MLLMs like miniGPT-4. The repository provides tools for quick start, regional diffusion with GPT-4, and regional diffusion with local LLMs.
Atom
Atom is an accurate low-bit weight-activation quantization algorithm that combines mixed-precision, fine-grained group quantization, dynamic activation quantization, KV-cache quantization, and efficient CUDA kernels co-design. It introduces a low-bit quantization method, Atom, to maximize Large Language Models (LLMs) serving throughput with negligible accuracy loss. The codebase includes evaluation of perplexity and zero-shot accuracy, kernel benchmarking, and end-to-end evaluation. Atom significantly boosts serving throughput by using low-bit operators and reduces memory consumption via low-bit quantization.
sarathi-serve
Sarathi-Serve is the official OSDI'24 artifact submission for paper #444, focusing on 'Taming Throughput-Latency Tradeoff in LLM Inference'. It is a research prototype built on top of CUDA 12.1, designed to optimize throughput-latency tradeoff in Large Language Models (LLM) inference. The tool provides a Python environment for users to install and reproduce results from the associated experiments. Users can refer to specific folders for individual figures and are encouraged to cite the paper if they use the tool in their work.
rtdl-num-embeddings
This repository provides the official implementation of the paper 'On Embeddings for Numerical Features in Tabular Deep Learning'. It focuses on transforming scalar continuous features into vectors before integrating them into the main backbone of tabular neural networks, showcasing improved performance. The embeddings for continuous features are shown to enhance the performance of tabular DL models and are applicable to various conventional backbones, offering efficiency comparable to Transformer-based models. The repository includes Python packages for practical usage, exploration of metrics and hyperparameters, and reproducing reported results for different algorithms and datasets.
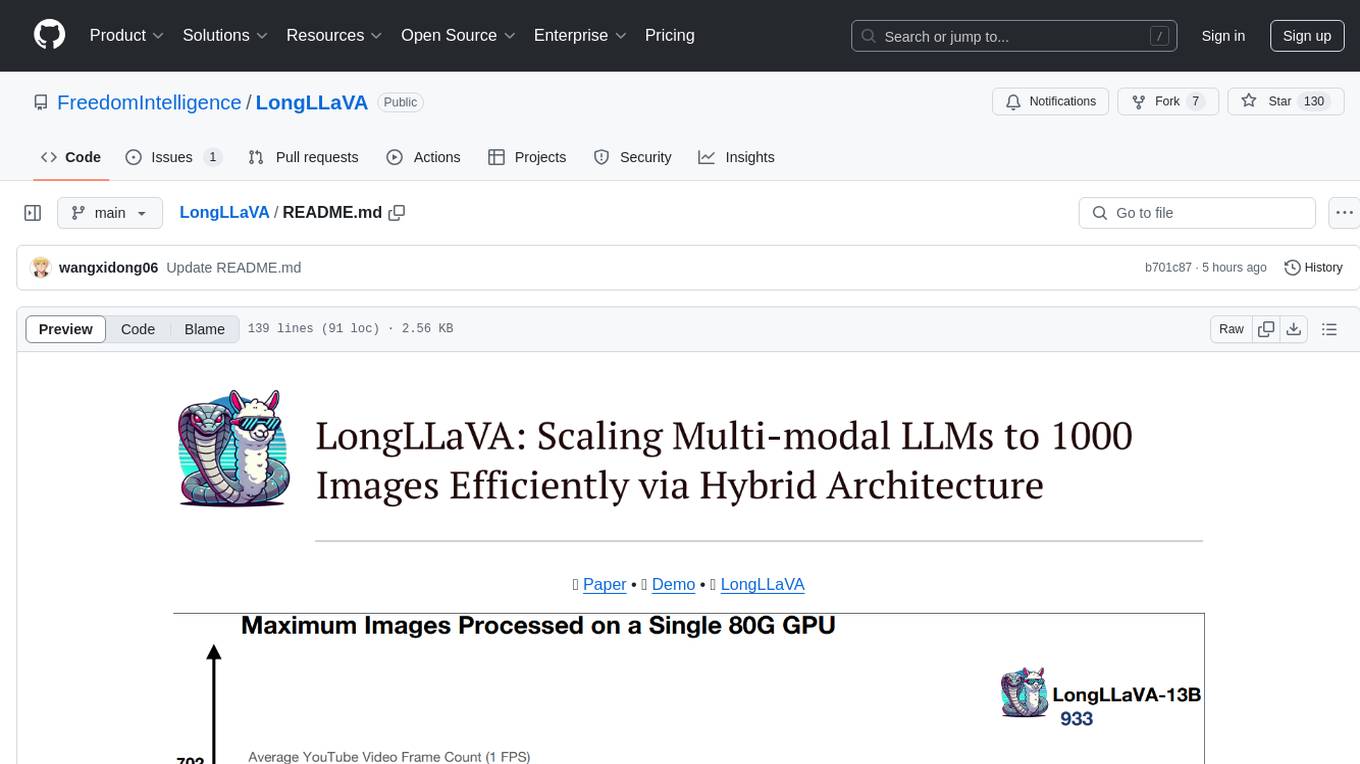
LongLLaVA
LongLLaVA is a tool for scaling multi-modal LLMs to 1000 images efficiently via hybrid architecture. It includes stages for single-image alignment, instruction-tuning, and multi-image instruction-tuning, with evaluation through a command line interface and model inference. The tool aims to achieve GPT-4V level capabilities and beyond, providing reproducibility of results and benchmarks for efficiency and performance.
KG-LLM-MDQA
This repository contains code and demo for Knowledge Graph Prompting for Multi-Document Question Answering. It includes modules for data collection, training DPR and MDR models, fine-tuning T5 and LLaMA, and reproducing KGP-LLM algorithm. The workflow involves document collection, knowledge graph construction, fine-tuning models, and reproducing main table results. The repository provides instructions for environment setup, folder architecture, and running different modules.
AReaL
AReaL (Ant Reasoning RL) is an open-source reinforcement learning system developed at the RL Lab, Ant Research. It is designed for training Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) in a fully open and inclusive manner. AReaL provides reproducible experiments for 1.5B and 7B LRMs, showcasing its scalability and performance across diverse computational budgets. The system follows an iterative training process to enhance model performance, with a focus on mathematical reasoning tasks. AReaL is equipped to adapt to different computational resource settings, enabling users to easily configure and launch training trials. Future plans include support for advanced models, optimizations for distributed training, and exploring research topics to enhance LRMs' reasoning capabilities.
WaferLLM
WaferLLM is the first wafer-scale Large Language Model (LLM) inference system designed to optimize the utilization of hundreds of thousands of on-chip cores in wafer-scale accelerators. It introduces MeshGEMM and MeshGEMV implementations for effective scaling on wafer-scale architectures, achieving significantly higher accelerator utilization and speedups compared to state-of-the-art methods. Users need the Cerebras SDK to reproduce the results, and the project provides detailed documentation and scripts for running simulations on both simulator and actual hardware.
1 - OpenAI Gpts

Infinite Image Creator
キーワードやコンテクストに基づいて、詳細な画像プロンプトを時間軸、文化軸、感情軸、現実と虚構軸など、多角的な視点を取り入れて、あなたのビジョンを忠実に再現します。