
gfm-rag
[NeurIPS'25] Graph Foundation Model for Retrieval Augmented Generation
Stars: 123
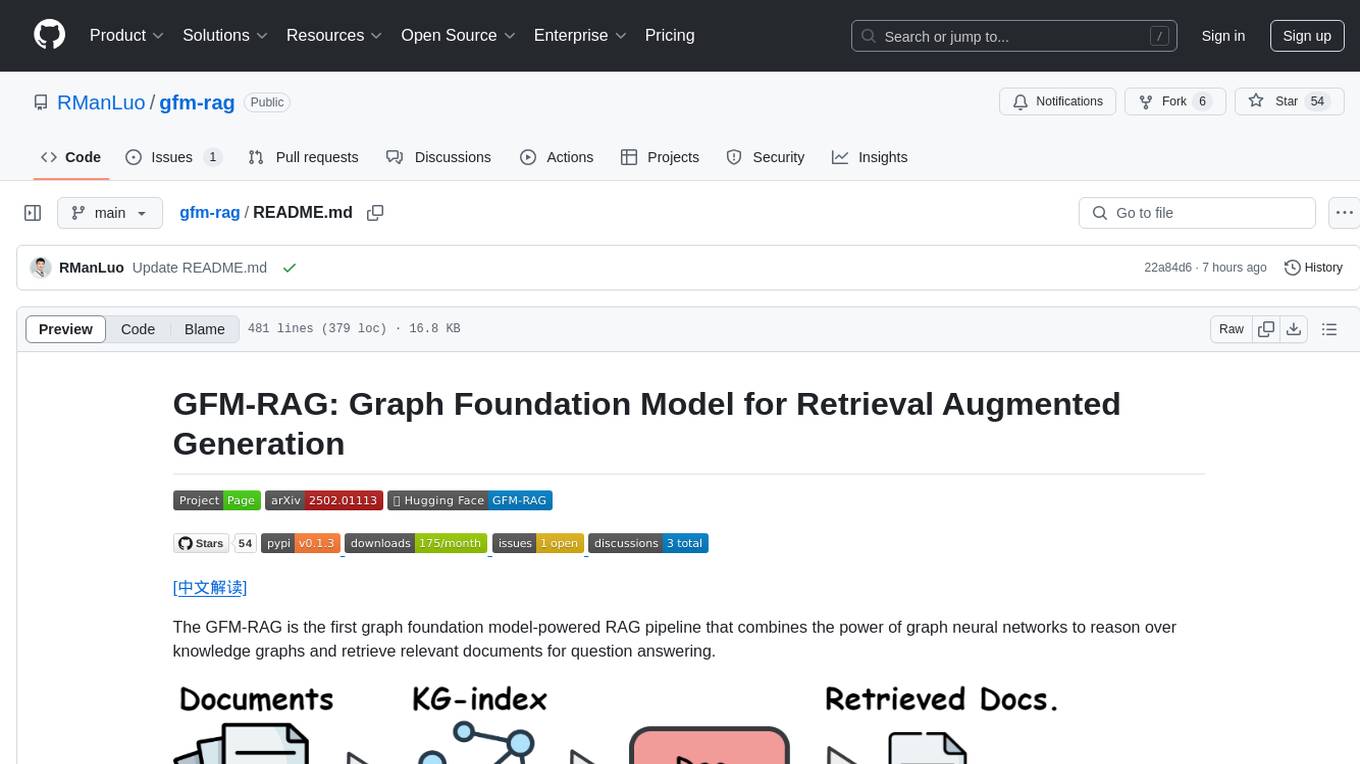
The GFM-RAG is a graph foundation model-powered pipeline that combines graph neural networks to reason over knowledge graphs and retrieve relevant documents for question answering. It features a knowledge graph index, efficiency in multi-hop reasoning, generalizability to unseen datasets, transferability for fine-tuning, compatibility with agent-based frameworks, and interpretability of reasoning paths. The tool can be used for conducting retrieval and question answering tasks using pre-trained models or fine-tuning on custom datasets.
README:
The GFM-RAG is the first graph foundation model-powered RAG pipeline that combines the power of graph neural networks to reason over knowledge graphs and retrieve relevant documents for question answering.
We first build a knowledge graph index (KG-index) from the documents to capture the relationships between knowledge. Then, we feed the query and constructed KG-index into the pre-trained graph foundation model (GFM) retriever to obtain relevant documents for LLM generation. The GFM retriever experiences large-scale training and can be directly applied to unseen datasets without fine-tuning.
For more details, please refer to our project page and paper.
- [2025-09-19] We excited to share that GFM-RAG has been accepted by NeurIPS 2025.
- [2025-06-03] We have released a new version of GFM-RAG (2025-06-03) which is pre-trained on 286 KGs. Performance comparison with the previous version can be found in CHANGELOG.
- [2025-02-06] We have released the GFM-RAG codebase and a 8M pre-trained model. 🚀
- Graph Foundation Model (GFM): A graph neural network-based retriever that can reason over the KG-index.
- Knowledge Graph Index: A knowledge graph index that captures the relationships between knowledge.
- Efficiency: The GFM-RAG pipeline is efficient in conducting multi-hop reasoning with single-step retrieval.
- Generalizability: The GFM-RAG can be directly applied to unseen datasets without fine-tuning.
- Transferability: The GFM-RAG can be fine-tuned on your own dataset to improve performance on specific domains.
- Compatibility: The GFM-RAG is compatible with arbitrary agent-based framework to conduct multi-step reasoning.
- Interpretability: The GFM-RAG can illustrate the captured reasoning paths for better understanding.
- Python 3.12
- CUDA 12 and above
Conda provides an easy way to install the CUDA development toolkit which is required by GFM-RAG
Install packages
conda create -n gfmrag python=3.12
conda activate gfmrag
conda install cuda-toolkit -c nvidia/label/cuda-12.4.1 # Replace with your desired CUDA version
pip install gfmrag[!NOTE] Read the full documentation at: https://rmanluo.github.io/gfm-rag/
We have provided the testing split and an example of the training data in here.
You need to prepare the following files:
-
dataset_corpus.json: A JSON file containing the entire document corpus. -
train.json(optional): A JSON file containing the training data. -
test.json(optional): A JSON file containing the test data.
Place your files in the following structure:
data_name/
├── raw/
│ ├── dataset_corpus.json
│ ├── train.json # (optional)
│ └── test.json # (optional)
└── processed/ # Output directory
The dataset_corpus.json is a dictionary where each key is the title or unique id of a document and the value is the text of the document.
{
"Fred Gehrke":
"Clarence Fred Gehrke (April 24, 1918 – February 9, 2002) was an American football player and executive. He played in the National Football League (NFL) for the Cleveland / Los Angeles Rams, San Francisco 49ers and Chicago Cardinals from 1940 through 1950. To boost team morale, Gehrke designed and painted the Los Angeles Rams logo in 1948, which was the first painted on the helmets of an NFL team. He later served as the general manager of the Denver Broncos from 1977 through 1981. He is the great-grandfather of Miami Marlin Christian Yelich"
,
"Manny Machado":
"Manuel Arturo Machado (] ; born July 6, 1992) is an American professional baseball third baseman and shortstop for the Baltimore Orioles of Major League Baseball (MLB). He attended Brito High School in Miami and was drafted by the Orioles with the third overall pick in the 2010 Major League Baseball draft. He bats and throws right-handed."
,
...
}If you want to train and evaluate the model, you need to provide training and testing data in the form of a JSON file. Each entry in the JSON file should contain the following fields:
-
id: A unique identifier for the example. -
question: The question or query. -
supporting_facts: A list of supporting facts relevant to the question. Each supporting fact is a list containing the title of the document that can be found in thedataset_corpus.jsonfile.
Each entry can also contain additional fields depending on the task. For example:
-
answer: The answer to the question.
The additional fields will be copied during the following steps of the pipeline.
Example:
[
{
"id": "5adf5e285542992d7e9f9323",
"question": "When was the judge born who made notable contributions to the trial of the man who tortured, raped, and murdered eight student nurses from South Chicago Community Hospital on the night of July 13-14, 1966?",
"answer": "June 4, 1931",
"supporting_facts": [
"Louis B. Garippo",
"Richard Speck"
]
},
{
"id": "5a7f7b365542992097ad2f80",
"question": "Did the Beaulieu Mine or the McIntyre Mines yield gold and copper?",
"answer": "The McIntyre also yielded a considerable amount of copper",
"supporting_facts": [
"Beaulieu Mine",
"McIntyre Mines"
]
}
...
]You need to create a KG-index configuration file.
Details of the configuration parameters are explained in the KG-index Configuration page.
python -m gfmrag.workflow.stage1_index_datasetThis method performs two main tasks:
- Create and save knowledge graph related files (
kg.txtanddocument2entities.json) from thedataset_corpus.jsonfile - Identify the query entities and supporting entities in training and testing data if available in the raw data directory.
Files created:
-
kg.txt: Contains knowledge graph triples -
document2entities.json: Maps documents to their entities -
train.json: Processed training data (if raw exists) -
test.json: Processed testing data (if raw exists)
Directory structure:
data_name/
├── raw/
│ ├── dataset_corpus.json
│ ├── train.json (optional)
│ └── test.json (optional)
└── processed/
└── stage1/
├── kg.txt
├── document2entities.json
├── train.json
└── test.json
You need to create a configuration file for inference.
[!NOTE] We have already released the pre-trained model here, which can be used directly for retrieval. The model will be automatically downloaded by specifying it in the configuration.
graph_retriever: model_path: rmanluo/GFM-RAG-8M
Details of the configuration parameters are explained in the GFM-RAG Configuration page.
You can initialize the GFMRetriever with the following code. It will load the pre-trained GFM-RAG model and the KG-index for retrieval.
import logging
import os
import hydra
from hydra.core.hydra_config import HydraConfig
from omegaconf import DictConfig, OmegaConf
from gfmrag import GFMRetriever
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@hydra.main(
config_path="config", config_name="stage3_qa_ircot_inference", version_base=None
)
def main(cfg: DictConfig) -> None:
output_dir = HydraConfig.get().runtime.output_dir
logger.info(f"Config:\n {OmegaConf.to_yaml(cfg)}")
logger.info(f"Current working directory: {os.getcwd()}")
logger.info(f"Output directory: {output_dir}")
gfmrag_retriever = GFMRetriever.from_config(cfg)You can use GFM-RAG retriever to reason over the KG-index and obtain documents for a given query.
docs = retriever.retrieve("Who is the president of France?", top_k=5)from hydra.utils import instantiate
from gfmrag.llms import BaseLanguageModel
from gfmrag.prompt_builder import QAPromptBuilder
llm = instantiate(cfg.llm)
qa_prompt_builder = QAPromptBuilder(cfg.qa_prompt)
message = qa_prompt_builder.build_input_prompt(current_query, retrieved_docs)
answer = llm.generate_sentence(message) # Answer: "Emmanuel Macron"During fine-tuning, the GFM model will be trained on the query-documents pairs train.json from the labeled dataset to learn complex relationships for retrieval.
It can be conducted on your own dataset to improve the performance of the model on your specific domain.
An example of the training data:
[
{
"id": "5abc553a554299700f9d7871",
"question": "Kyle Ezell is a professor at what School of Architecture building at Ohio State?",
"answer": "Knowlton Hall",
"supporting_facts": [
"Knowlton Hall",
"Kyle Ezell"
],
"question_entities": [
"kyle ezell",
"architectural association school of architecture",
"ohio state"
],
"supporting_entities": [
"10 million donation",
"2004",
"architecture",
"austin e knowlton",
"austin e knowlton school of architecture",
"bachelor s in architectural engineering",
"city and regional planning",
"columbus ohio united states",
"ives hall",
"july 2002",
"knowlton hall",
"ksa",
]
},
...
]You need to create a configuration file for fine-tuning.
[!NOTE] We have already released the pre-trained model checkpoint here, which can be used for further finetuning. The model will be automatically downloaded by specifying it in the configuration.
checkpoint: rmanluo/GFM-RAG-8M
Details of the configuration parameters are explained in the GFM-RAG Fine-tuning Configuration page.
You can fine-tune the pre-trained GFM-RAG model on your dataset using the following command:
python -m gfmrag.workflow.stage2_qa_finetune
# Multi-GPU training
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 -m gfmrag.workflow.stage2_qa_finetune
# Multi-node Multi-GPU training
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 --nnodes=2 -m gfmrag.workflow.stage2_qa_finetuneWe are working on releasing the full training datasets.
We have provided the testing split and an example of the training data in here.
Download the datasets and put them under the data directory.
data/
├── 2wikimultihopqa_test
│ ├── processed
│ └── raw
├── hotpotqa_test
│ ├── processed
│ └── raw
├── hotpotqa_train_example
│ ├── processed
│ └── raw
└── musique_test
├── processed
└── raw
We have provided the indexed testing datasets in the data/*/processed/stage1 directory. You can build the index for the testing dataset with the following command:
# Build the index for testing dataset
N_GPU=1
DATA_ROOT="data"
DATA_NAME_LIST="hotpotqa_test 2wikimultihopqa_test musique_test"
for DATA_NAME in ${DATA_NAME_LIST}; do
python -m gfmrag.workflow.stage1_index_dataset \
dataset.root=${DATA_ROOT} \
dataset.data_name=${DATA_NAME}
doneFull script is available at scripts/stage1_data_index.sh.
Unsupervised training on the constructed KG.
python -m gfmrag.workflow.stage2_kg_pretrain
# Multi-GPU training
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 -m gfmrag.workflow.stage2_kg_pretrainFull script is available at scripts/stage2_pretrain.sh.
Supervised training on the QA dataset.
python -m gfmrag.workflow.stage2_qa_finetune
# Multi-GPU training
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 -m gfmrag.workflow.stage2_qa_finetuneFull script is available at scripts/stage2_finetune.sh.
N_GPU=4
DATA_ROOT="data"
checkpoints=rmanluo/GFM-RAG-8M # Or the path to your checkpoints
torchrun --nproc_per_node=${N_GPU} -m gfmrag.workflow.stage2_qa_finetune \
train.checkpoint=${checkpoints} \
datasets.cfgs.root=${DATA_ROOT} \
datasets.train_names=[] \
train.num_epoch=0# Batch inference for QA on the test set.
N_GPU=4
DATA_ROOT="data"
DATA_NAME="hotpotqa" # hotpotqa musique 2wikimultihopqa
LLM="gpt-4o-mini"
DOC_TOP_K=5
N_THREAD=10
torchrun --nproc_per_node=${N_GPU} -m gfmrag.workflow.stage3_qa_inference \
dataset.root=${DATA_ROOT} \
qa_prompt=${DATA_NAME} \
qa_evaluator=${DATA_NAME} \
llm.model_name_or_path=${LLM} \
test.n_threads=${N_THREAD} \
test.top_k=${DOC_TOP_K} \
dataset.data_name=${DATA_NAME}_testhotpotqa
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 -m gfmrag.workflow.stage3_qa_inference dataset.data_name=hotpotqa_test qa_prompt=hotpotqa qa_evaluator=hotpotqamusique
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 -m gfmrag.workflow.stage3_qa_inference dataset.data_name=musique_test qa_prompt=musique qa_evaluator=musique2Wikimultihopqa
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 -m gfmrag.workflow.stage3_qa_inference dataset.data_name=2wikimultihopqa_test qa_prompt=2wikimultihopqa qa_evaluator=2wikimultihopqa# IRCoT + GFM-RAG inference on QA tasks
N_GPU=1
DATA_ROOT="data"
DATA_NAME="hotpotqa" # hotpotqa musique 2wikimultihopqa
LLM="gpt-4o-mini"
MAX_STEPS=3
MAX_SAMPLE=10
python -m gfmrag.workflow.stage3_qa_ircot_inference \
dataset.root=${DATA_ROOT} \
llm.model_name_or_path=${LLM} \
qa_prompt=${DATA_NAME} \
qa_evaluator=${DATA_NAME} \
agent_prompt=${DATA_NAME}_ircot \
test.max_steps=${MAX_STEPS} \
test.max_test_samples=${MAX_SAMPLE} \
dataset.data_name=${DATA_NAME}_testhotpotqa
python -m gfmrag.workflow.stage3_qa_ircot_inference qa_prompt=hotpotqa qa_evaluator=hotpotqa agent_prompt=hotpotqa_ircot dataset.data_name=hotpotqa_test test.max_steps=2musique
python -m gfmrag.workflow.stage3_qa_ircot_inference qa_prompt=musique qa_evaluator=musique agent_prompt=musique_ircot dataset.data_name=musique_test test.max_steps=42Wikimultihopqa
python -m gfmrag.workflow.stage3_qa_ircot_inference qa_prompt=2wikimultihopqa qa_evaluator=2wikimultihopqa agent_prompt=2wikimultihopqa_ircot dataset.data_name=2wikimultihopqa_test test.max_steps=2python -m gfmrag.workflow.experiments.visualize_path dataset.data_name=hotpotqa_testWe greatly appreciate the following repositories for their help to this project:
- DeepGraphLearning/ULTRA: The ULTRA model is used as the base GNN model for the GFM retriever.
- OSU-NLP-Group/HippoRAG: We get great inspiration from the KG construction process of HippoRAG.
- microsoft/graphrag: We get great inspiration from the project design of GraphRAG.
If you find this repository helpful, please consider citing our paper:
@article{luo2025gfmrag,
title={GFM-RAG: Graph Foundation Model for Retrieval Augmented Generation},
author={Luo, Linhao and Zhao, Zicheng and Haffari, Gholamreza and Phung, Dinh and Gong, Chen and Pan, Shirui},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.01113},
year={2025}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for gfm-rag
Similar Open Source Tools

gfm-rag
The GFM-RAG is a graph foundation model-powered pipeline that combines graph neural networks to reason over knowledge graphs and retrieve relevant documents for question answering. It features a knowledge graph index, efficiency in multi-hop reasoning, generalizability to unseen datasets, transferability for fine-tuning, compatibility with agent-based frameworks, and interpretability of reasoning paths. The tool can be used for conducting retrieval and question answering tasks using pre-trained models or fine-tuning on custom datasets.
HippoRAG
HippoRAG is a novel retrieval augmented generation (RAG) framework inspired by the neurobiology of human long-term memory that enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to continuously integrate knowledge across external documents. It provides RAG systems with capabilities that usually require a costly and high-latency iterative LLM pipeline for only a fraction of the computational cost. The tool facilitates setting up retrieval corpus, indexing, and retrieval processes for LLMs, offering flexibility in choosing different online LLM APIs or offline LLM deployments through LangChain integration. Users can run retrieval on pre-defined queries or integrate directly with the HippoRAG API. The tool also supports reproducibility of experiments and provides data, baselines, and hyperparameter tuning scripts for research purposes.
swe-rl
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.

AirGym
AirGym is an open source Python quadrotor simulator based on IsaacGym, providing a high-fidelity dynamics and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) framework for quadrotor robot learning research. It offers a lightweight and customizable platform with strict alignment with PX4 logic, multiple control modes, and Sim-to-Real toolkits. Users can perform tasks such as Hovering, Balloon, Tracking, Avoid, and Planning, with the ability to create customized environments and tasks. The tool also supports training from scratch, visual encoding approaches, playing and testing of trained models, and customization of new tasks and assets.
stark
STaRK is a large-scale semi-structure retrieval benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases. It provides natural-sounding and practical queries crafted to incorporate rich relational information and complex textual properties, closely mirroring real-life scenarios. The benchmark aims to assess how effectively large language models can handle the interplay between textual and relational requirements in queries, using three diverse knowledge bases constructed from public sources.

shellChatGPT
ShellChatGPT is a shell wrapper for OpenAI's ChatGPT, DALL-E, Whisper, and TTS, featuring integration with LocalAI, Ollama, Gemini, Mistral, Groq, and GitHub Models. It provides text and chat completions, vision, reasoning, and audio models, voice-in and voice-out chatting mode, text editor interface, markdown rendering support, session management, instruction prompt manager, integration with various service providers, command line completion, file picker dialogs, color scheme personalization, stdin and text file input support, and compatibility with Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and Termux for a responsive experience.
plexe
Plexe is a tool that allows users to create machine learning models by describing them in plain language. Users can explain their requirements, provide a dataset, and the AI-powered system will build a fully functional model through an automated agentic approach. It supports multiple AI agents and model building frameworks like XGBoost, CatBoost, and Keras. Plexe also provides Docker images with pre-configured environments, YAML configuration for customization, and support for multiple LiteLLM providers. Users can visualize experiment results using the built-in Streamlit dashboard and extend Plexe's functionality through custom integrations.
friendly-stable-audio-tools
This repository is a refactored and updated version of `stable-audio-tools`, an open-source code for audio/music generative models originally by Stability AI. It contains refactored codes for improved readability and usability, useful scripts for evaluating and playing with trained models, and instructions on how to train models such as `Stable Audio 2.0`. The repository does not contain any pretrained checkpoints. Requirements include PyTorch 2.0 or later for Flash Attention support and Python 3.8.10 or later for development. The repository provides guidance on installing, building a training environment using Docker or Singularity, logging with Weights & Biases, training configurations, and stages for VAE-GAN and Diffusion Transformer (DiT) training.
mLoRA
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.
langgraph4j
Langgraph4j is a Java library for language processing tasks such as text classification, sentiment analysis, and named entity recognition. It provides a set of tools and algorithms for analyzing text data and extracting useful information. The library is designed to be efficient and easy to use, making it suitable for both research and production applications.
cheating-based-prompt-engine
This is a vulnerability mining engine purely based on GPT, requiring no prior knowledge base, no fine-tuning, yet its effectiveness can overwhelmingly surpass most of the current related research. The core idea revolves around being task-driven, not question-driven, driven by prompts, not by code, and focused on prompt design, not model design. The essence is encapsulated in one word: deception. It is a type of code understanding logic vulnerability mining that fully stimulates the capabilities of GPT, suitable for real actual projects.
nano-graphrag
nano-GraphRAG is a simple, easy-to-hack implementation of GraphRAG that provides a smaller, faster, and cleaner version of the official implementation. It is about 800 lines of code, small yet scalable, asynchronous, and fully typed. The tool supports incremental insert, async methods, and various parameters for customization. Users can replace storage components and LLM functions as needed. It also allows for embedding function replacement and comes with pre-defined prompts for entity extraction and community reports. However, some features like covariates and global search implementation differ from the original GraphRAG. Future versions aim to address issues related to data source ID, community description truncation, and add new components.
llm-vscode
llm-vscode is an extension designed for all things LLM, utilizing llm-ls as its backend. It offers features such as code completion with 'ghost-text' suggestions, the ability to choose models for code generation via HTTP requests, ensuring prompt size fits within the context window, and code attribution checks. Users can configure the backend, suggestion behavior, keybindings, llm-ls settings, and tokenization options. Additionally, the extension supports testing models like Code Llama 13B, Phind/Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2, and WizardLM/WizardCoder-Python-34B-V1.0. Development involves cloning llm-ls, building it, and setting up the llm-vscode extension for use.
trickPrompt-engine
This repository contains a vulnerability mining engine based on GPT technology. The engine is designed to identify logic vulnerabilities in code by utilizing task-driven prompts. It does not require prior knowledge or fine-tuning and focuses on prompt design rather than model design. The tool is effective in real-world projects and should not be used for academic vulnerability testing. It supports scanning projects in various languages, with current support for Solidity. The engine is configured through prompts and environment settings, enabling users to scan for vulnerabilities in their codebase. Future updates aim to optimize code structure, add more language support, and enhance usability through command line mode. The tool has received a significant audit bounty of $50,000+ as of May 2024.
KVCache-Factory
KVCache-Factory is a unified framework for KV Cache compression of diverse models. It supports multi-GPUs inference with big LLMs and various attention implementations. The tool enables KV cache compression without Flash Attention v2, multi-GPU inference, and specific models like Mistral. It also provides functions for KV cache budget allocation and batch inference. The visualization tools help in understanding the attention patterns of models.
Phi-3-Vision-MLX
Phi-3-MLX is a versatile AI framework that leverages both the Phi-3-Vision multimodal model and the Phi-3-Mini-128K language model optimized for Apple Silicon using the MLX framework. It provides an easy-to-use interface for a wide range of AI tasks, from advanced text generation to visual question answering and code execution. The project features support for batched generation, flexible agent system, custom toolchains, model quantization, LoRA fine-tuning capabilities, and API integration for extended functionality.
For similar tasks

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.

jupyter-ai
Jupyter AI connects generative AI with Jupyter notebooks. It provides a user-friendly and powerful way to explore generative AI models in notebooks and improve your productivity in JupyterLab and the Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, Jupyter AI offers: * An `%%ai` magic that turns the Jupyter notebook into a reproducible generative AI playground. This works anywhere the IPython kernel runs (JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab, Kaggle, VSCode, etc.). * A native chat UI in JupyterLab that enables you to work with generative AI as a conversational assistant. * Support for a wide range of generative model providers, including AI21, Anthropic, AWS, Cohere, Gemini, Hugging Face, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. * Local model support through GPT4All, enabling use of generative AI models on consumer grade machines with ease and privacy.

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.








