
SPAG
Self-playing Adversarial Language Game Enhances LLM Reasoning, NeurIPS 2024
Stars: 120
This repository contains the implementation of Self-Play of Adversarial Language Game (SPAG) as described in the paper 'Self-playing Adversarial Language Game Enhances LLM Reasoning'. The SPAG involves training Language Models (LLMs) in an adversarial language game called Adversarial Taboo. The repository provides tools for imitation learning, self-play episode collection, and reinforcement learning on game episodes to enhance LLM reasoning abilities. The process involves training models using GPUs, launching imitation learning, conducting self-play episodes, assigning rewards based on outcomes, and learning the SPAG model through reinforcement learning. Continuous improvements on reasoning benchmarks can be observed by repeating the episode-collection and SPAG-learning processes.
README:
This repo contains the implementation of NeurIPS 2024 paper:
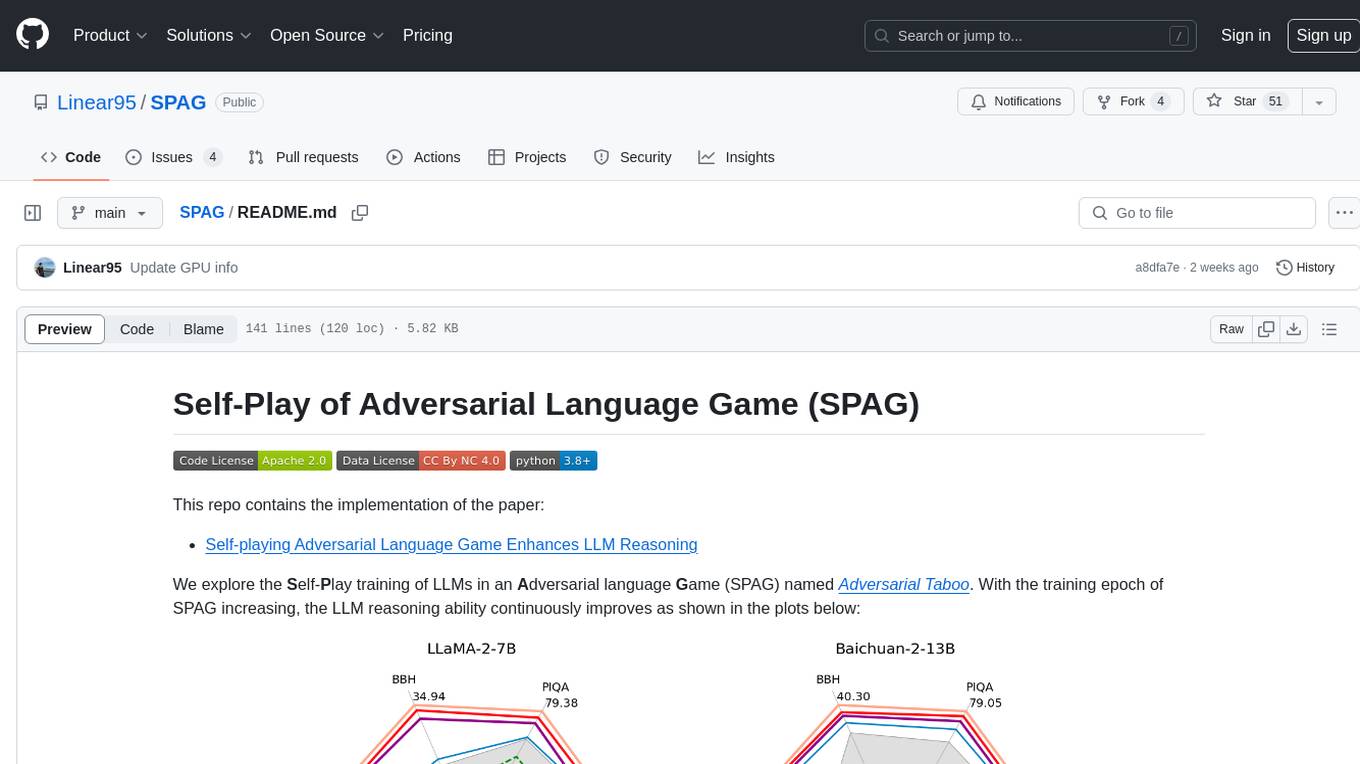
We explore the Self-Play training of LLMs in an Adversarial language Game (SPAG) named Adversarial Taboo. In the following game examples with the target word "conversation", the attacker wins left while the defender wins right:
With the training epoch of SPAG increasing, the LLM reasoning ability continuously improves as shown in the plots below:
Many thanks to @thwu1, who has reproduced the SPAG experiments and released model checkpoints (Imitation Model, SPAG-1, SPAG-2, SPAG-3) on Huggingface 🤗!
To build the running environment, use the following command:
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
We train models and sampling episodes using 32 40G A100 GPUs with CUDA 11.0. The commands below are also compatible with 8 A100 GPUs.
To ensure the instruction-following ability of LLMs to the game rules, we first let LLMs imitate the winning behaviors of GPT-4. To launch the imitation learning on LLaMA-2-7B-base, use the following command:
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 --master_port=6000 train.py \
--output_dir <path_to_save_your_imitation_checkpoint> \
--model_name_or_path "Llama-2-7b-hf" \
--ref_model_name_or_path "Llama-2-7b-hf" \
--lm_kl_coeff 0.1 \
--train_method "SFTwithKL" \
--train_data_path "./data/train_imitation_gpt4.json" \
--remove_unused_columns False \
--num_train_epochs 1 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 2 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 8 \
--evaluation_strategy no \
--padding_side "right" \
--truncation_side "left" \
--max_length 2048 \
--save_strategy epoch \
--learning_rate 5e-6 \
--lr_scheduler_type "cosine" \
--warmup_ratio 0.03 \
--logging_steps 1 \
--weight_decay 0. \
--deepspeed "./configs/default_offload_opt_param.json" \
--gradient_checkpointing True \
--tf32 True --bf16 TrueHere Llama-2-7b-hf can be replaced by Baichuan2-13B-Base to reproduce the Baichuan-2 results in our paper.
After the imitation learning, we can conduct the self-play with the imitation-learned model on all targets words:
export PYTHONPATH=.
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 --master_port=6000 tools/play_llm_game.py \
--taboo_max_turns 5 \
--attacker_model_name_or_path <path_to_imitation_learned_model> \
--defender_model_name_or_path <path_to_imitation_learned_model> \
--model_prefix "im_llama2" \
--data_path "./data/all_target_words.txt" \
--output_dir "./data/self_play_results" \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 1 \
--task_type "sampling" \
--data_suffix "all_words" \
--max_length 2048 \
--max_new_tokens 256 \
--logging_steps 5 \
--bf16 True --tf32 TrueWhen the self-play collection is finished, we can access all the game episodes in im_llama2_sampling_all_words_results.json at data/self_play_results/.
To conduct reinforcement learning on game episodes, we first calculate the outcomes by rule-based judgment and assign rewards to actions:
export PYTHONPATH=.
python3 tools/assign_rewards.py \
--input_data_path data/self_play_results/im_llama2_sampling_all_target_words_results.json \
--output_data_path data/train_spag_data_im_llama2.json \
--sft_data_path data/alpaca_train.jsonThe output file train_spag_data_im_llama2.json is already in an instruction-tuning format, with the following keywords:
-
query&target: the input and label for language modeling, -
reward: the reward assigned to the current utterance (target), -
weight: the re-weighting parameter to ensure that both attacker and defender have an equal learning coefficient 1/2 in expectation.
Then the SPAG model can be learned with the following command:
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 --master_port=6000 train.py \
--output_dir <path_to_save_your_SPAG_checkpoint> \
--model_name_or_path <path_to_your_imitation_checkpoint> \
--ref_model_name_or_path <path_to_your_imitation_checkpoint> \
--lm_kl_coeff 0.2 \
--lm_sft_coeff 0.5 \
--train_method "OfflinePO" \
--train_data_path "./data/train_spag_data_im_llama2.json" \
--remove_unused_columns False \
--num_train_epochs 1 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 2 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 8 \
--evaluation_strategy no \
--padding_side "right" \
--truncation_side "left" \
--max_length 2048 \
--save_strategy epoch \
--learning_rate 2e-6 \
--lr_scheduler_type "cosine" \
--warmup_ratio 0.03 \
--logging_steps 1 \
--weight_decay 0. \
--deepspeed "./configs/default_offload_opt_param.json" \
--gradient_checkpointing True \
--tf32 True --bf16 TrueBy repeating the episode-collection and SPAG-learning processes, we can observe continous improvements on reasoning benchmarks. For LLM reasoning evaluation, we use the lm-evaluation-harness repo with the setups described in our paper.
Please cite our paper if you find the code useful.
@inproceedings{cheng2024spag,
title = {Self-playing Adversarial Language Game Enhances LLM Reasoning},
author = {Cheng, Pengyu and Hu, Tianhao and Xu, Han and Zhang, Zhisong and Dai, Yong and Han, Lei and du, nan and Li, Xiaolong},
booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
pages = {126515--126543},
volume = {37},
year = {2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for SPAG
Similar Open Source Tools

SPAG
This repository contains the implementation of Self-Play of Adversarial Language Game (SPAG) as described in the paper 'Self-playing Adversarial Language Game Enhances LLM Reasoning'. The SPAG involves training Language Models (LLMs) in an adversarial language game called Adversarial Taboo. The repository provides tools for imitation learning, self-play episode collection, and reinforcement learning on game episodes to enhance LLM reasoning abilities. The process involves training models using GPUs, launching imitation learning, conducting self-play episodes, assigning rewards based on outcomes, and learning the SPAG model through reinforcement learning. Continuous improvements on reasoning benchmarks can be observed by repeating the episode-collection and SPAG-learning processes.
gfm-rag
The GFM-RAG is a graph foundation model-powered pipeline that combines graph neural networks to reason over knowledge graphs and retrieve relevant documents for question answering. It features a knowledge graph index, efficiency in multi-hop reasoning, generalizability to unseen datasets, transferability for fine-tuning, compatibility with agent-based frameworks, and interpretability of reasoning paths. The tool can be used for conducting retrieval and question answering tasks using pre-trained models or fine-tuning on custom datasets.
WebRL
WebRL is a self-evolving online curriculum learning framework designed for training web agents in the WebArena environment. It provides model checkpoints, training instructions, and evaluation processes for training the actor and critic models. The tool enables users to generate new instructions and interact with WebArena to configure tasks for training and evaluation.
vinagent
Vinagent is a lightweight and flexible library designed for building smart agent assistants across various industries. It provides a simple yet powerful foundation for creating AI-powered customer service bots, data analysis assistants, or domain-specific automation agents. With its modular tool system, users can easily extend their agent's capabilities by integrating a wide range of tools that are self-contained, well-documented, and can be registered dynamically. Vinagent allows users to scale and adapt their agents to new tasks or environments effortlessly.
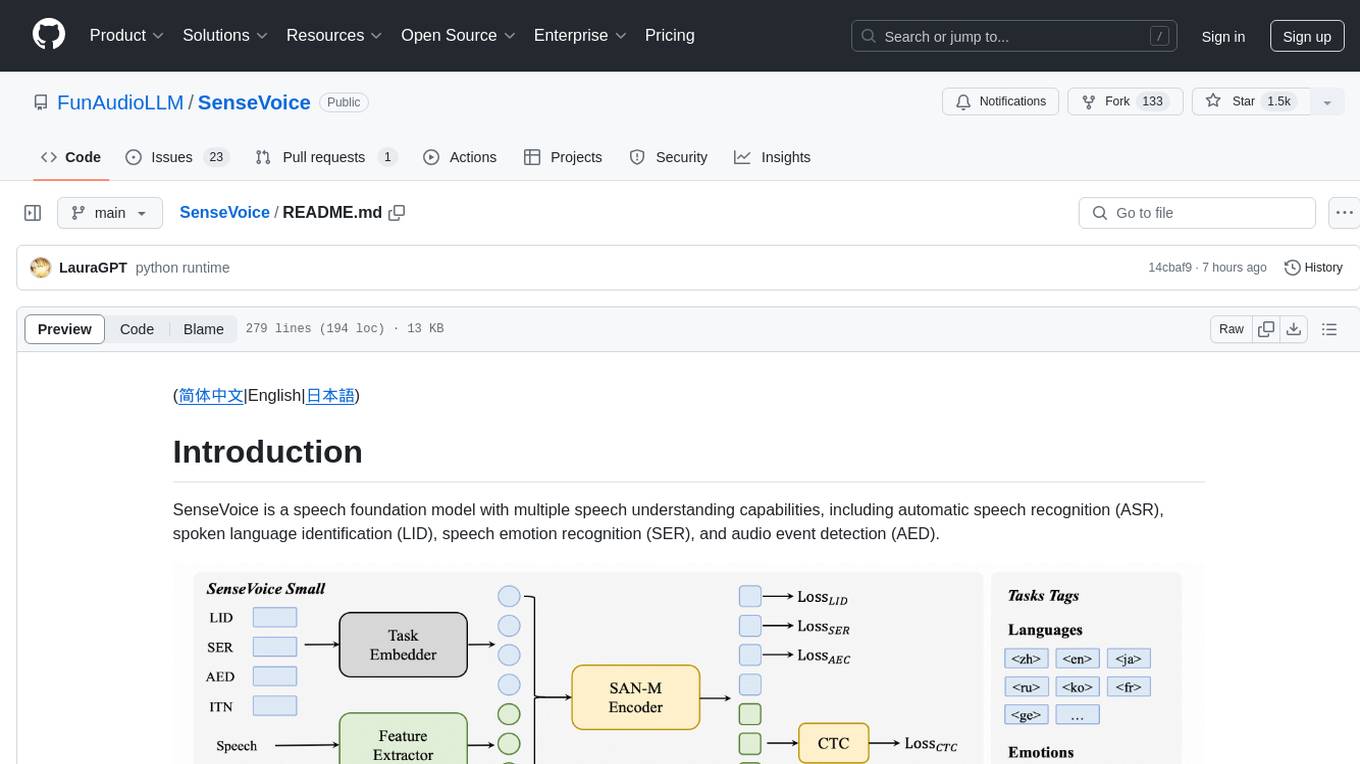
SenseVoice
SenseVoice is a speech foundation model focusing on high-accuracy multilingual speech recognition, speech emotion recognition, and audio event detection. Trained with over 400,000 hours of data, it supports more than 50 languages and excels in emotion recognition and sound event detection. The model offers efficient inference with low latency and convenient finetuning scripts. It can be deployed for service with support for multiple client-side languages. SenseVoice-Small model is open-sourced and provides capabilities for Mandarin, Cantonese, English, Japanese, and Korean. The tool also includes features for natural speech generation and fundamental speech recognition tasks.

CEO-Agentic-AI-Framework
CEO-Agentic-AI-Framework is an ultra-lightweight Agentic AI framework based on the ReAct paradigm. It supports mainstream LLMs and is stronger than Swarm. The framework allows users to build their own agents, assign tasks, and interact with them through a set of predefined abilities. Users can customize agent personalities, grant and deprive abilities, and assign queries for specific tasks. CEO also supports multi-agent collaboration scenarios, where different agents with distinct capabilities can work together to achieve complex tasks. The framework provides a quick start guide, examples, and detailed documentation for seamless integration into research projects.

AirGym
AirGym is an open source Python quadrotor simulator based on IsaacGym, providing a high-fidelity dynamics and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) framework for quadrotor robot learning research. It offers a lightweight and customizable platform with strict alignment with PX4 logic, multiple control modes, and Sim-to-Real toolkits. Users can perform tasks such as Hovering, Balloon, Tracking, Avoid, and Planning, with the ability to create customized environments and tasks. The tool also supports training from scratch, visual encoding approaches, playing and testing of trained models, and customization of new tasks and assets.
alignment-attribution-code
This repository provides an original implementation of Assessing the Brittleness of Safety Alignment via Pruning and Low-Rank Modifications. It includes tools for neuron-level pruning, pruning based on set difference, Wanda/SNIP score dumping, rank-level pruning, and rank removal with orthogonal projection. Users can specify parameters like prune method, datasets, sparsity ratio, model, and save location to evaluate and modify neural networks for safety alignment.
llm-rag-workshop
The LLM RAG Workshop repository provides a workshop on using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to generate and understand text in a human-like manner. It includes instructions on setting up the environment, indexing Zoomcamp FAQ documents, creating a Q&A system, and using OpenAI for generation based on retrieved information. The repository focuses on enhancing language model responses with retrieved information from external sources, such as document databases or search engines, to improve factual accuracy and relevance of generated text.
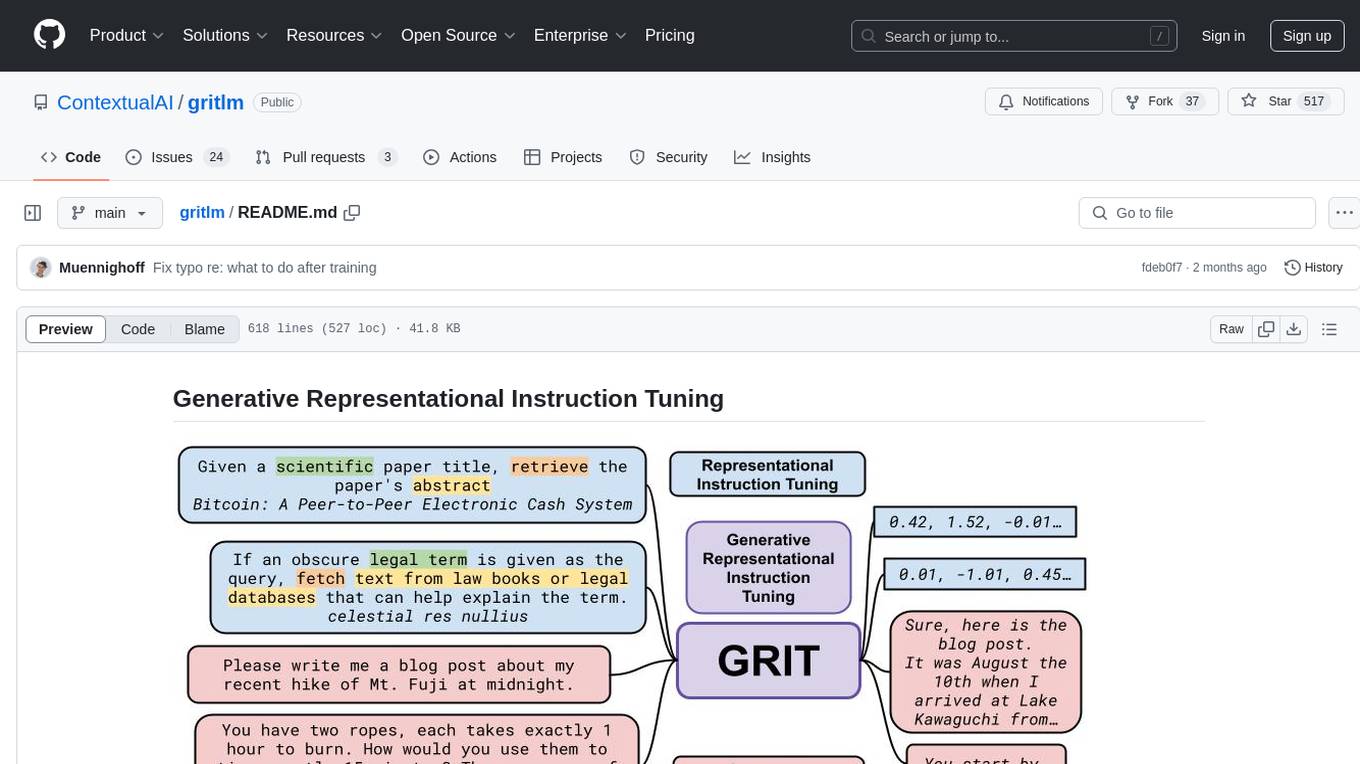
gritlm
The 'gritlm' repository provides all materials for the paper Generative Representational Instruction Tuning. It includes code for inference, training, evaluation, and known issues related to the GritLM model. The repository also offers models for embedding and generation tasks, along with instructions on how to train and evaluate the models. Additionally, it contains visualizations, acknowledgements, and a citation for referencing the work.
CAG
Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG) is an alternative paradigm to Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that eliminates real-time retrieval delays and errors by preloading all relevant resources into the model's context. CAG leverages extended context windows of large language models (LLMs) to generate responses directly, providing reduced latency, improved reliability, and simplified design. While CAG has limitations in knowledge size and context length, advancements in LLMs are addressing these issues, making CAG a practical and scalable alternative for complex applications.
MemoryLLM
MemoryLLM is a large language model designed for self-updating capabilities. It offers pretrained models with different memory capacities and features, such as chat models. The repository provides training code, evaluation scripts, and datasets for custom experiments. MemoryLLM aims to enhance knowledge retention and performance on various natural language processing tasks.
AnyGPT
AnyGPT is a unified multimodal language model that utilizes discrete representations for processing various modalities like speech, text, images, and music. It aligns the modalities for intermodal conversions and text processing. AnyInstruct dataset is constructed for generative models. The model proposes a generative training scheme using Next Token Prediction task for training on a Large Language Model (LLM). It aims to compress vast multimodal data on the internet into a single model for emerging capabilities. The tool supports tasks like text-to-image, image captioning, ASR, TTS, text-to-music, and music captioning.
Avalon-LLM
Avalon-LLM is a repository containing the official code for AvalonBench and the Avalon agent Strategist. AvalonBench evaluates Large Language Models (LLMs) playing The Resistance: Avalon, a board game requiring deductive reasoning, coordination, collaboration, and deception skills. Strategist utilizes LLMs to learn strategic skills through self-improvement, including high-level strategic evaluation and low-level execution guidance. The repository provides instructions for running AvalonBench, setting up Strategist, and conducting experiments with different agents in the game environment.

LightRAG
LightRAG is a PyTorch library designed for building and optimizing Retriever-Agent-Generator (RAG) pipelines. It follows principles of simplicity, quality, and optimization, offering developers maximum customizability with minimal abstraction. The library includes components for model interaction, output parsing, and structured data generation. LightRAG facilitates tasks like providing explanations and examples for concepts through a question-answering pipeline.
cheating-based-prompt-engine
This is a vulnerability mining engine purely based on GPT, requiring no prior knowledge base, no fine-tuning, yet its effectiveness can overwhelmingly surpass most of the current related research. The core idea revolves around being task-driven, not question-driven, driven by prompts, not by code, and focused on prompt design, not model design. The essence is encapsulated in one word: deception. It is a type of code understanding logic vulnerability mining that fully stimulates the capabilities of GPT, suitable for real actual projects.
For similar tasks

SPAG
This repository contains the implementation of Self-Play of Adversarial Language Game (SPAG) as described in the paper 'Self-playing Adversarial Language Game Enhances LLM Reasoning'. The SPAG involves training Language Models (LLMs) in an adversarial language game called Adversarial Taboo. The repository provides tools for imitation learning, self-play episode collection, and reinforcement learning on game episodes to enhance LLM reasoning abilities. The process involves training models using GPUs, launching imitation learning, conducting self-play episodes, assigning rewards based on outcomes, and learning the SPAG model through reinforcement learning. Continuous improvements on reasoning benchmarks can be observed by repeating the episode-collection and SPAG-learning processes.
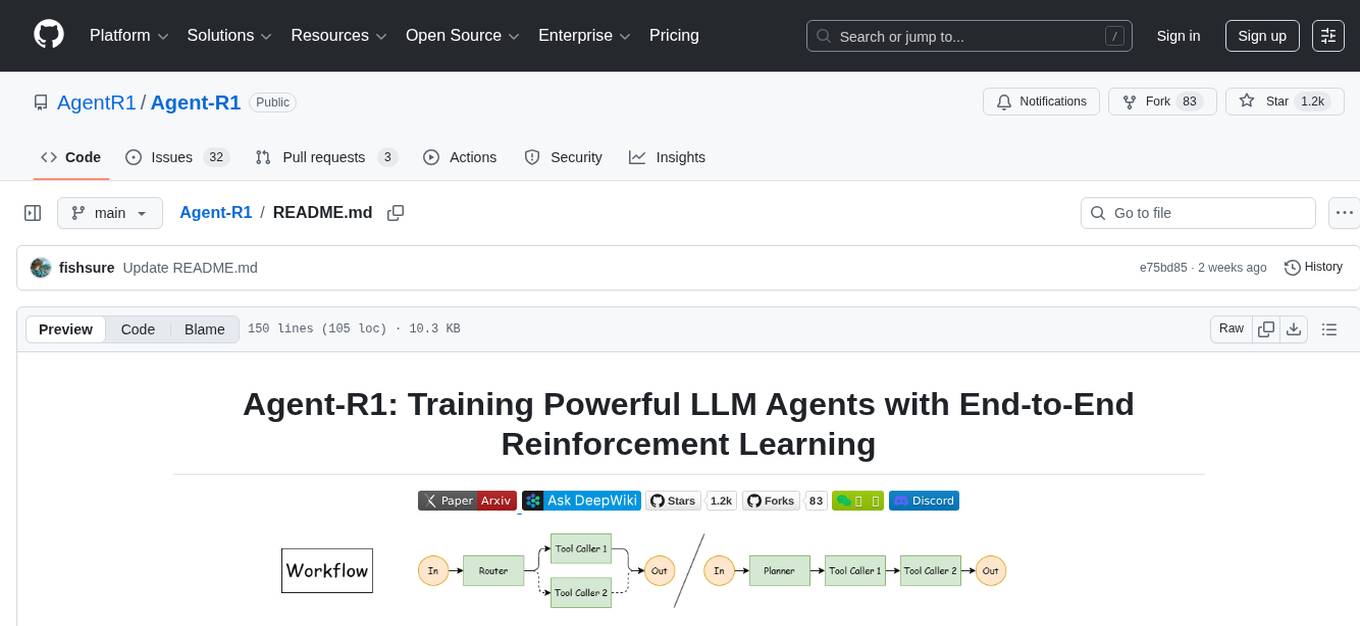
Agent-R1
Agent-R1 is an open-source framework designed to accelerate research and development at the critical intersection of RL and Agent. It employs End-to-End reinforcement learning to train agents in specific environments. Developers define domain-specific tools and reward functions to extend Agent-R1 to unique use cases, eliminating the need for complex workflow engineering. Key features include multi-turn tool calling, multi-tool coordination, process rewards, custom tools and environments, support for multiple RL algorithms, and multi-modal support. It aims to make it easier for researchers and developers to create and explore agents in their own domains, collectively advancing the development of autonomous agents.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

ray
Ray is a unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications. It consists of a core distributed runtime and a set of AI libraries for simplifying ML compute, including Data, Train, Tune, RLlib, and Serve. Ray runs on any machine, cluster, cloud provider, and Kubernetes, and features a growing ecosystem of community integrations. With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster, making it easy to meet the compute-intensive demands of modern ML workloads.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.

djl
Deep Java Library (DJL) is an open-source, high-level, engine-agnostic Java framework for deep learning. It is designed to be easy to get started with and simple to use for Java developers. DJL provides a native Java development experience and allows users to integrate machine learning and deep learning models with their Java applications. The framework is deep learning engine agnostic, enabling users to switch engines at any point for optimal performance. DJL's ergonomic API interface guides users with best practices to accomplish deep learning tasks, such as running inference and training neural networks.

mojo
Mojo is a new programming language that bridges the gap between research and production by combining Python syntax and ecosystem with systems programming and metaprogramming features. Mojo is still young, but it is designed to become a superset of Python over time.
tt-metal
TT-NN is a python & C++ Neural Network OP library. It provides a low-level programming model, TT-Metalium, enabling kernel development for Tenstorrent hardware.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.




