
WebRL
Building Open LLM Web Agents with Self-Evolving Online Curriculum RL
Stars: 270
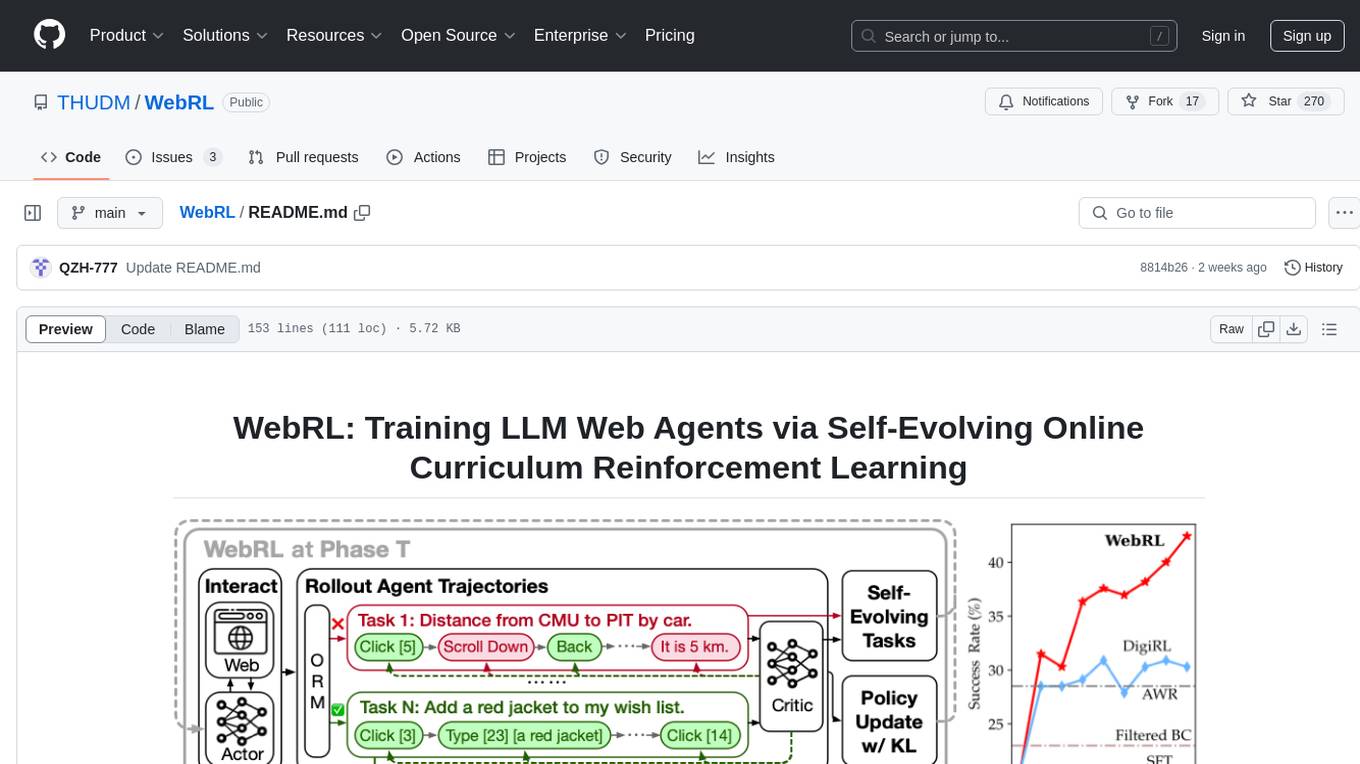
WebRL is a self-evolving online curriculum learning framework designed for training web agents in the WebArena environment. It provides model checkpoints, training instructions, and evaluation processes for training the actor and critic models. The tool enables users to generate new instructions and interact with WebArena to configure tasks for training and evaluation.
README:
Technique adopted in AutoGLM, a series of Phone Use and Web Browser Use Foundation Agents
📃 Paper | 🤗 WebRL-GLM-4-9B | WebRL-LLaMA-3.1-8B | ModelScope
WebRL, a self-evolving online curriculum learning framework designed for training web agents, targeting the WebArena environment.
First, create a conda environment and install all pip package requirements.
conda create -n webrl python==3.10
conda activate webrl
cd WebRL
pip install -e .The WebRL-GLM-4-9B checkpoint was released here and we use it:
The checkpoint for Outcome-supervised Reward Model (ORM) is as follow:
We use LLaMA-Factory to train the SFT baseline, which is the starting model for WebRL. We release the code and data used for training. You can train the SFT baseline with the following commands:
cd LLaMA-Factory
bash run.sh examples/train_full/llama3_full_policy_web.yamlAfter training the SFT baseline, you should use it as the initial model of the actor and critic. You can train WebRL with the following commands:
bash run_multinode.shThis command is used to train the actor and critic in each phase.
You can generate new instructions with the following commands:
python scripts/gen_task.pyThe instruction and script for interaction with WebArena is provided in VAB-WebArena-Lite.
You can implement the interaction process of WebRL according to the Evaluating in WebRL Setting (Text Modal) section of VAB-WebArena-Lite.
To enable interaction with WebArena, you need to configure each task in the same format as the sample test case provided in the test_webarena_lite.raw.json file in VAB-WebArena-Lite. Below is the template for a task configuration:
{
"sites": [
<site> # possible choices: "shopping_admin", "map", "shopping", "reddit", "gitlab"
],
"task_id": <Your task id>
"require_login": true,
"storage_state": "./.auth/shopping_admin_state.json",
"start_url": <start url of site>, # possible choices: "__SHOPPING_ADMIN__", "__SHOPPING__", "__GITLAB__", "__MAP__", "__REDDIT__"
"geolocation": null,
"intent_template": "",
"instantiation_dict": {},
"intent": <Task>,
"require_reset": false,
"eval": {
"eval_types": [
"string_match"
],
"reference_answers": {
"exact_match": "N/A"
},
"reference_url": "",
"program_html": [],
"string_note": "",
"reference_answer_raw_annotation": ""
},
"intent_template_id": 0
}After configuring the tasks, use the script scripts/generate_test_data.py to generate the configuration files. Make sure to modify the data path in the script to point to the JSON file containing your configured interaction cases.
After interaction finished, run scripts/process_data.py to process the interaction trajectories.
python scripts/process_data.py \
--stage 1 2 \
--add_reward \
--rollout_path <directory_of_interaction_trajectories> \
--experience_paths "path1", "path2" \
--orm_path <path_to_ORM_model> \
--actor_path <path_to_actor_model_for_computing_perplexity> \
--output_path <path_to_output_file>-
stage: Specifies the processing method for the data- 1: Convert rollout trajectories into the required format.
- 2: Incorporate historical experiences filtered by perplexity.
-
add_reward: Apply ORM to label each trajectory. -
output_path: The file containing processed interaction trajectories, ready for direct use in training.- stage 1: Processed interaction trajectories will be saved in this file. Contains data without historical experiences.
- stage 2: An additional file, output_path + '_filter', will also be generated.
- output_path: Contain data without historical experiences.
- output_path + '_filter': Contain data with historical experiences.
-
rollout_path: Path to thetracessubfolder containing initial interaction trajectories, typically generated after running Webarena-Lite. -
experience_paths: List of file paths to processed interaction data (output_path) from previous phases.
Both output_path and output_path + '_filter' are formatted for direct use in subsequent training.
@artical{qi2024webrl,
title={WebRL: Training LLM Web Agents via Self-Evolving Online Curriculum Reinforcement Learning},
author={Qi, Zehan and Liu, Xiao and Iong, Iat Long and Lai, Hanyu and Sun, Xueqiao and Yang, Xinyue and Sun, Jiadai and Yang, Yu and Yao, Shuntian and Zhang, Tianjie and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.02337},
year={2024},
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for WebRL
Similar Open Source Tools

WebRL
WebRL is a self-evolving online curriculum learning framework designed for training web agents in the WebArena environment. It provides model checkpoints, training instructions, and evaluation processes for training the actor and critic models. The tool enables users to generate new instructions and interact with WebArena to configure tasks for training and evaluation.
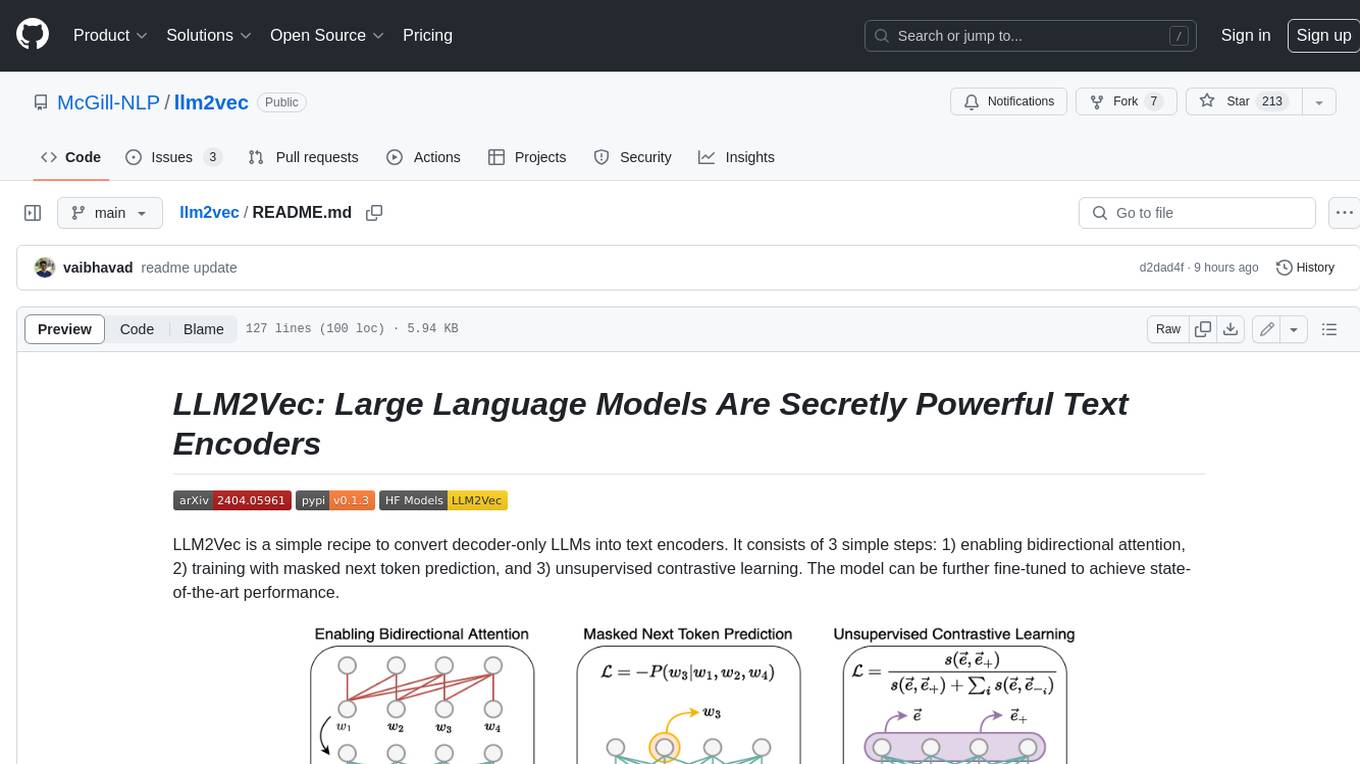
llm2vec
LLM2Vec is a simple recipe to convert decoder-only LLMs into text encoders. It consists of 3 simple steps: 1) enabling bidirectional attention, 2) training with masked next token prediction, and 3) unsupervised contrastive learning. The model can be further fine-tuned to achieve state-of-the-art performance.
empower-functions
Empower Functions is a family of large language models (LLMs) that provide GPT-4 level capabilities for real-world 'tool using' use cases. These models offer compatibility support to be used as drop-in replacements, enabling interactions with external APIs by recognizing when a function needs to be called and generating JSON containing necessary arguments based on user inputs. This capability is crucial for building conversational agents and applications that convert natural language into API calls, facilitating tasks such as weather inquiries, data extraction, and interactions with knowledge bases. The models can handle multi-turn conversations, choose between tools or standard dialogue, ask for clarification on missing parameters, integrate responses with tool outputs in a streaming fashion, and efficiently execute multiple functions either in parallel or sequentially with dependencies.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration, command line interface, push to Hugging Face Hub, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration files or programmatically using Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM for LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub. The library is not responsible for the content generated by models and advises users to review the data before using it in production environments.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using a local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration for tasks, command line interface for running tasks, push to Hugging Face Hub for dataset upload, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration or Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM to interface with LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub.
CoPilot
TigerGraph CoPilot is an AI assistant that combines graph databases and generative AI to enhance productivity across various business functions. It includes three core component services: InquiryAI for natural language assistance, SupportAI for knowledge Q&A, and QueryAI for GSQL code generation. Users can interact with CoPilot through a chat interface on TigerGraph Cloud and APIs. CoPilot requires LLM services for beta but will support TigerGraph's LLM in future releases. It aims to improve contextual relevance and accuracy of answers to natural-language questions by building knowledge graphs and using RAG. CoPilot is extensible and can be configured with different LLM providers, graph schemas, and LangChain tools.
LightAgent
LightAgent is a lightweight, open-source Agentic AI development framework with memory, tools, and a tree of thought. It supports multi-agent collaboration, autonomous learning, tool integration, complex task handling, and multi-model support. It also features a streaming API, tool generator, agent self-learning, adaptive tool mechanism, and more. LightAgent is designed for intelligent customer service, data analysis, automated tools, and educational assistance.
flow-prompt
Flow Prompt is a dynamic library for managing and optimizing prompts for large language models. It facilitates budget-aware operations, dynamic data integration, and efficient load distribution. Features include CI/CD testing, dynamic prompt development, multi-model support, real-time insights, and prompt testing and evolution.

AirGym
AirGym is an open source Python quadrotor simulator based on IsaacGym, providing a high-fidelity dynamics and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) framework for quadrotor robot learning research. It offers a lightweight and customizable platform with strict alignment with PX4 logic, multiple control modes, and Sim-to-Real toolkits. Users can perform tasks such as Hovering, Balloon, Tracking, Avoid, and Planning, with the ability to create customized environments and tasks. The tool also supports training from scratch, visual encoding approaches, playing and testing of trained models, and customization of new tasks and assets.
pipelex
Pipelex is an open-source devtool designed to transform how users build repeatable AI workflows. It acts as a Docker or SQL for AI operations, allowing users to create modular 'pipes' using different LLMs for structured outputs. These pipes can be connected sequentially, in parallel, or conditionally to build complex knowledge transformations from reusable components. With Pipelex, users can share and scale proven methods instantly, saving time and effort in AI workflow development.
awadb
AwaDB is an AI native database designed for embedding vectors. It simplifies database usage by eliminating the need for schema definition and manual indexing. The system ensures real-time search capabilities with millisecond-level latency. Built on 5 years of production experience with Vearch, AwaDB incorporates best practices from the community to offer stability and efficiency. Users can easily add and search for embedded sentences using the provided client libraries or RESTful API.

memobase
Memobase is a user profile-based memory system designed to enhance Generative AI applications by enabling them to remember, understand, and evolve with users. It provides structured user profiles, scalable profiling, easy integration with existing LLM stacks, batch processing for speed, and is production-ready. Users can manage users, insert data, get memory profiles, and track user preferences and behaviors. Memobase is ideal for applications that require user analysis, tracking, and personalized interactions.
tuui
TUUI is a desktop MCP client designed for accelerating AI adoption through the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and enabling cross-vendor LLM API orchestration. It is an LLM chat desktop application based on MCP, created using AI-generated components with strict syntax checks and naming conventions. The tool integrates AI tools via MCP, orchestrates LLM APIs, supports automated application testing, TypeScript, multilingual, layout management, global state management, and offers quick support through the GitHub community and official documentation.
agentpress
AgentPress is a collection of simple but powerful utilities that serve as building blocks for creating AI agents. It includes core components for managing threads, registering tools, processing responses, state management, and utilizing LLMs. The tool provides a modular architecture for handling messages, LLM API calls, response processing, tool execution, and results management. Users can easily set up the environment, create custom tools with OpenAPI or XML schema, and manage conversation threads with real-time interaction. AgentPress aims to be agnostic, simple, and flexible, allowing users to customize and extend functionalities as needed.
deep-searcher
DeepSearcher is a tool that combines reasoning LLMs and Vector Databases to perform search, evaluation, and reasoning based on private data. It is suitable for enterprise knowledge management, intelligent Q&A systems, and information retrieval scenarios. The tool maximizes the utilization of enterprise internal data while ensuring data security, supports multiple embedding models, and provides support for multiple LLMs for intelligent Q&A and content generation. It also includes features like private data search, vector database management, and document loading with web crawling capabilities under development.

chat-mcp
A Cross-Platform Interface for Large Language Models (LLMs) utilizing the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to connect and interact with various LLMs. The desktop app, built on Electron, ensures compatibility across Linux, macOS, and Windows. It simplifies understanding MCP principles, facilitates testing of multiple servers and LLMs, and supports dynamic LLM configuration and multi-client management. The UI can be extracted for web use, ensuring consistency across web and desktop versions.
For similar tasks

WebRL
WebRL is a self-evolving online curriculum learning framework designed for training web agents in the WebArena environment. It provides model checkpoints, training instructions, and evaluation processes for training the actor and critic models. The tool enables users to generate new instructions and interact with WebArena to configure tasks for training and evaluation.
MicroLens
MicroLens is a content-driven micro-video recommendation dataset at scale. It provides a large dataset with multimodal data, including raw text, images, audio, video, and video comments, for tasks such as multi-modal recommendation, foundation model building, and fairness recommendation. The dataset is available in two versions: MicroLens-50K and MicroLens-100K, with extracted features for multimodal recommendation tasks. Researchers can access the dataset through provided links and reach out to the corresponding author for the complete dataset. The repository also includes codes for various algorithms like VideoRec, IDRec, and VIDRec, each implementing different video models and baselines.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
