
MachineSoM
[ACL 2024] Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View
Stars: 74
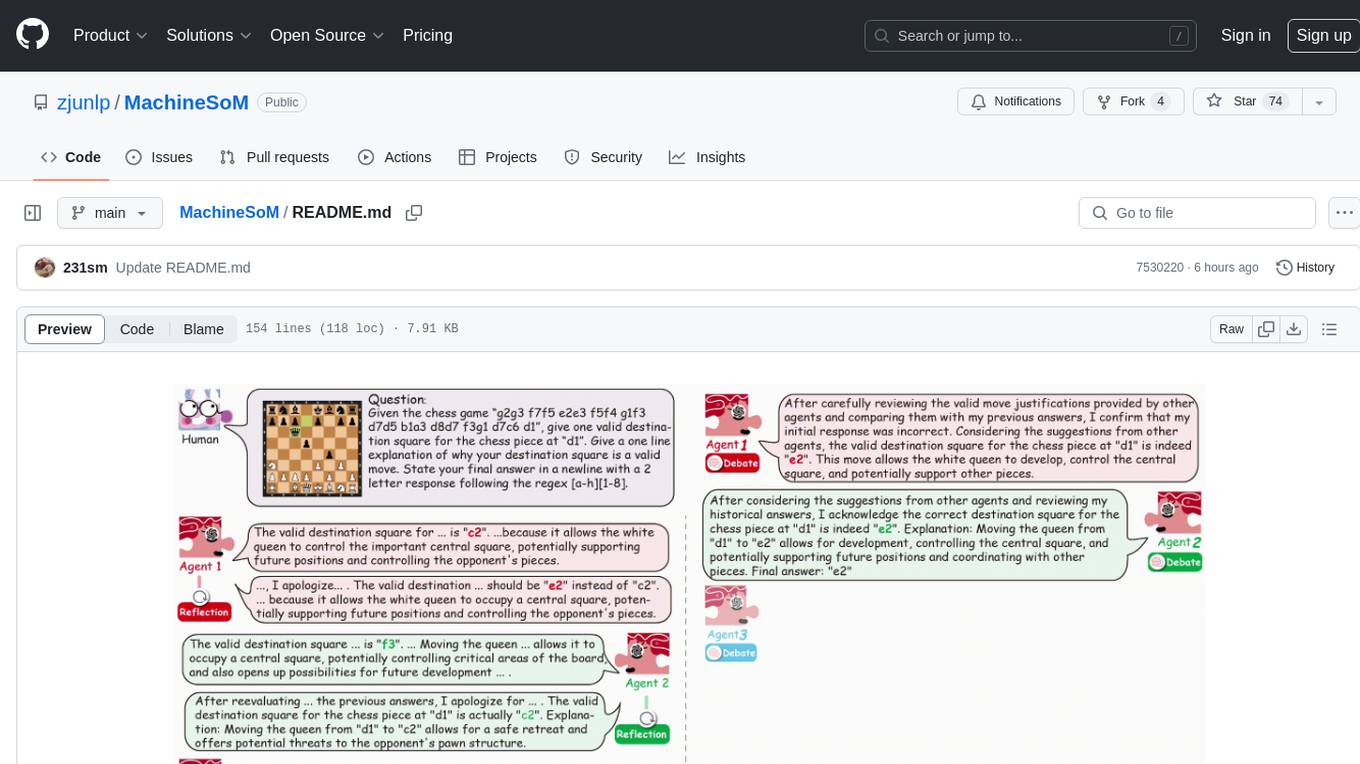
MachineSoM is a code repository for the paper 'Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View'. It focuses on the emergence of intelligence from collaborative and communicative computational modules, enabling effective completion of complex tasks. The repository includes code for societies of LLM agents with different traits, collaboration processes such as debate and self-reflection, and interaction strategies for determining when and with whom to interact. It provides a coding framework compatible with various inference services like Replicate, OpenAI, Dashscope, and Anyscale, supporting models like Qwen and GPT. Users can run experiments, evaluate results, and draw figures based on the paper's content, with available datasets for MMLU, Math, and Chess Move Validity.
README:
Code for the paper "Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View".
- The Society of Mind (SoM): the emergence of intelligence from collaborative and communicative computational modules, enabling humans to collaborate and complete complex tasks effectively
- Societies of LLM agents with different traits: easy-going and overconfident
- Collaboration Processes: debate and self-reflection
- Interaction Strategies: when to interact, interact with whom
- [2023.05.16] The paper "Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View" is accepted by ACL 2024 main conference.
- [2024.03.11] The paper "Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View" is accepted by Workshop on LLM Agents, ICLR 2024.
- [2023.10.03] The paper "Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View" is released.
- [2023.07.13] MachineSoM code is released!
Configure the environment using the following command:
conda create -n masom python=3.9
pip install -r requirements.txtThe data we sampled and used for the experiment is in the folder eval_data. You can download the raw datasets for MMLU, Math and Chess Move Validity separately.
Here is a brief overview of each file in the folder src:
# Core Code
|- api.py # API for storing the experiments
|- dataloader.py # Load datasets for experiments
|- evaluate.py # Evaluate the results of the experiment
|- prompt.py # Stores all the prompts involved in the experiment.
|- utils.py # The management center of the agents.
|- run_main.py # Simulate a society of agents using different collaborative strategies to solve problems (main experiment)
|- run_agent.py # Exploring the Impact of Agent Quantity
|- run_strategy.py # All agents can adopt different thinking patterns for collaboration
# Other Code
|- run_main.sh # Main experiment running script
|- run_agent.sh # The running script of the experiment on the number of agents
|- run_strategy.sh # The running script of the experiment on the strategies
|- run_turn.sh # The running script of the experiment on the number of collaboration rounds
|- conformity_and_consistency.py # Process and draw figures such as Figure 6 and Figure 7 in the paper
|- draw # Include the drawing code for all the figures in the paper
|- draw_10_agent.py
|- draw_conformity
|- ...-
Edit
src/api.pyto add your api-key.openai_api = { "replicate":[ "api_1", "api_2", ], "dashscope": [ "api_1" ], "openai": [ "api_1" ], "anyscale":[ "api_1", "api_2", "api_3" ] }
Our coding framework offers compatibility with a variety of inference services across multiple platforms, such as Replicate, OpenAI, Dashscope, and Anyscale. Specifically, Dashscope facilitates the deployment of the
Qwenmodel, whereas OpenAI provides support for theGPTmodel integration. -
Execute the scripts
run_main.sh,run_agent.sh,run_turn.sh, andrun_strategy.shhoused in thesrcdirectory. These scripts are designed to initiate a variety of experiments: the main experiment (corresponding to Table 2 in the paper), variations in agent numbers (Figure 3 in the paper), differing collaboration round counts (Figure 4 in the paper), and trials involving alternative collaboration strategies (Figure 5 in the paper). You can adjust the parameters within the scripts to accommodate different experimental settings.All the data in the paper is available for download on Google Drive.
-
Execute the
evaluate.pyin thesrcdirectory.a. For the main experiment results, you can execute the following command:
python evaluate.py main_table --experiment_type gpt-1106-main --dataset mmlu
This code will be output in LaTeX code format. The argument
--experimentshould be the name of a folder. To replicate the results presented in the paper, after downloading and uncompressing it into thesrcroot directory, rename theuploadtoresults. At this point, the available options for the--experimentparameter aregpt-1106-main,llama13-main,llama70-main,qwen-main, andmixtral-main. The optional values for argument--datasetaremmlu,math, andchess.b. For the siginificant test, you can execute the following commands:
python evaluate.py anova --types main --dataset chess --experiment_type "['llama13-main','gpt-1106-main']" python evaluate.py anova --types turn --dataset chess --experiment_type "['llama13-turn-4','llama70-turn-4']" python evaluate.py anova --types 10-turn --dataset chess --experiment_type "['gpt-1106-turn-10', 'qwen-turn-10', 'mixtral-turn-10']" python evaluate.py anova --types agent --dataset chess --experiment_type "['llama13-main','llama70-main']" python evaluate.py anova --types 10-agent --dataset chess --experiment_type "['gpt-1106-main','qwen-main']" python evaluate.py anova --types strategy --dataset chess --experiment_type "['gpt-1106-main','qwen-main']"
You can change the
--datasetand--experiment_typeto get the original result (e.g., Table 6 in the paper).c. We also provide code for drawing figures in the paper. For the vast majority of figures, the following code can be executed:
python evaluate.py draw --types distribute --experiment_type gpt-1106-main python evaluate.py draw --types agent --experiment_type llama13-main python evaluate.py draw --types turn --experiment_type llama70-main python evaluate.py draw --types strategy --experiment_type gpt-1106-main python evaluate.py draw --types 10-agent --experiment_type gpt-1106-main python evaluate.py draw --types 10-turn --experiment_type gpt-1106-main --dataset chess python evaluate.py draw --types radar --experiment_type gpt-1106-main python evaluate.py draw --types 10-agent-consistent --experiment_type gpt-1106-main python evaluate.py draw --types word --experiment_type gpt-1106-main
d. It should be noted that in order to obtain the results of Figures 6 and 7, you need to execute the following code:
python conformity_and_consistency.py --experiment_type 'mixtral-main' --type 'consistent' python conformity_and_consistency.py --experiment_type 'mixtral-main' --type 'conformity'
There are stylistic differences between the figures in the paper and those generated by the code, such as legend, color, layout, etc. But the data has not changed at all.
📋 Thank you very much for your interest in our work. If you use or extend our work, please cite the following paper:
@inproceedings{ACL2024_MachineSoM,
author = {Jintian Zhang and
Xin Xu and
Ningyu Zhang and
Ruibo Liu and
Bryan Hooi and
Shumin Deng},
title = {Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for {LLM} Agents: {A} Social Psychology View},
booktitle = {{ACL}},
pages = {},
publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2024},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.02124}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for MachineSoM
Similar Open Source Tools

MachineSoM
MachineSoM is a code repository for the paper 'Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View'. It focuses on the emergence of intelligence from collaborative and communicative computational modules, enabling effective completion of complex tasks. The repository includes code for societies of LLM agents with different traits, collaboration processes such as debate and self-reflection, and interaction strategies for determining when and with whom to interact. It provides a coding framework compatible with various inference services like Replicate, OpenAI, Dashscope, and Anyscale, supporting models like Qwen and GPT. Users can run experiments, evaluate results, and draw figures based on the paper's content, with available datasets for MMLU, Math, and Chess Move Validity.

ActionWeaver
ActionWeaver is an AI application framework designed for simplicity, relying on OpenAI and Pydantic. It supports both OpenAI API and Azure OpenAI service. The framework allows for function calling as a core feature, extensibility to integrate any Python code, function orchestration for building complex call hierarchies, and telemetry and observability integration. Users can easily install ActionWeaver using pip and leverage its capabilities to create, invoke, and orchestrate actions with the language model. The framework also provides structured extraction using Pydantic models and allows for exception handling customization. Contributions to the project are welcome, and users are encouraged to cite ActionWeaver if found useful.
ai2-scholarqa-lib
Ai2 Scholar QA is a system for answering scientific queries and literature review by gathering evidence from multiple documents across a corpus and synthesizing an organized report with evidence for each claim. It consists of a retrieval component and a three-step generator pipeline. The retrieval component fetches relevant evidence passages using the Semantic Scholar public API and reranks them. The generator pipeline includes quote extraction, planning and clustering, and summary generation. The system is powered by the ScholarQA class, which includes components like PaperFinder and MultiStepQAPipeline. It requires environment variables for Semantic Scholar API and LLMs, and can be run as local docker containers or embedded into another application as a Python package.
CogAgent
CogAgent is an advanced intelligent agent model designed for automating operations on graphical interfaces across various computing devices. It supports platforms like Windows, macOS, and Android, enabling users to issue commands, capture device screenshots, and perform automated operations. The model requires a minimum of 29GB of GPU memory for inference at BF16 precision and offers capabilities for executing tasks like sending Christmas greetings and sending emails. Users can interact with the model by providing task descriptions, platform specifications, and desired output formats.
gfm-rag
The GFM-RAG is a graph foundation model-powered pipeline that combines graph neural networks to reason over knowledge graphs and retrieve relevant documents for question answering. It features a knowledge graph index, efficiency in multi-hop reasoning, generalizability to unseen datasets, transferability for fine-tuning, compatibility with agent-based frameworks, and interpretability of reasoning paths. The tool can be used for conducting retrieval and question answering tasks using pre-trained models or fine-tuning on custom datasets.
llm-consortium
LLM Consortium is a plugin for the `llm` package that implements a model consortium system with iterative refinement and response synthesis. It orchestrates multiple learned language models to collaboratively solve complex problems through structured dialogue, evaluation, and arbitration. The tool supports multi-model orchestration, iterative refinement, advanced arbitration, database logging, configurable parameters, hundreds of models, and the ability to save and load consortium configurations.
allms
allms is a versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying Large Language Models (LLMs). Developed by Allegro engineers, it simplifies working with LLM applications by providing a user-friendly interface, asynchronous querying, automatic retrying mechanism, error handling, and output parsing. It supports various LLM families hosted on different platforms like OpenAI, Google, Azure, and GCP. The library offers features for configuring endpoint credentials, batch querying with symbolic variables, and forcing structured output format. It also provides documentation, quickstart guides, and instructions for local development, testing, updating documentation, and making new releases.
cortex
Cortex is a tool that simplifies and accelerates the process of creating applications utilizing modern AI models like chatGPT and GPT-4. It provides a structured interface (GraphQL or REST) to a prompt execution environment, enabling complex augmented prompting and abstracting away model connection complexities like input chunking, rate limiting, output formatting, caching, and error handling. Cortex offers a solution to challenges faced when using AI models, providing a simple package for interacting with NL AI models.
invariant
Invariant Analyzer is an open-source scanner designed for LLM-based AI agents to find bugs, vulnerabilities, and security threats. It scans agent execution traces to identify issues like looping behavior, data leaks, prompt injections, and unsafe code execution. The tool offers a library of built-in checkers, an expressive policy language, data flow analysis, real-time monitoring, and extensible architecture for custom checkers. It helps developers debug AI agents, scan for security violations, and prevent security issues and data breaches during runtime. The analyzer leverages deep contextual understanding and a purpose-built rule matching engine for security policy enforcement.
oasis
OASIS is a scalable, open-source social media simulator that integrates large language models with rule-based agents to realistically mimic the behavior of up to one million users on platforms like Twitter and Reddit. It facilitates the study of complex social phenomena such as information spread, group polarization, and herd behavior, offering a versatile tool for exploring diverse social dynamics and user interactions in digital environments. With features like scalability, dynamic environments, diverse action spaces, and integrated recommendation systems, OASIS provides a comprehensive platform for simulating social media interactions at a large scale.

marqo
Marqo is more than a vector database, it's an end-to-end vector search engine for both text and images. Vector generation, storage and retrieval are handled out of the box through a single API. No need to bring your own embeddings.
neo4j-graphrag-python
The Neo4j GraphRAG package for Python is an official repository that provides features for creating and managing vector indexes in Neo4j databases. It aims to offer developers a reliable package with long-term commitment, maintenance, and fast feature updates. The package supports various Python versions and includes functionalities for creating vector indexes, populating them, and performing similarity searches. It also provides guidelines for installation, examples, and development processes such as installing dependencies, making changes, and running tests.
VMind
VMind is an open-source solution for intelligent visualization, providing an intelligent chart component based on LLM by VisActor. It allows users to create chart narrative works with natural language interaction, edit charts through dialogue, and export narratives as videos or GIFs. The tool is easy to use, scalable, supports various chart types, and offers one-click export functionality. Users can customize chart styles, specify themes, and aggregate data using LLM models. VMind aims to enhance efficiency in creating data visualization works through dialogue-based editing and natural language interaction.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration, command line interface, push to Hugging Face Hub, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration files or programmatically using Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM for LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub. The library is not responsible for the content generated by models and advises users to review the data before using it in production environments.

AirGym
AirGym is an open source Python quadrotor simulator based on IsaacGym, providing a high-fidelity dynamics and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) framework for quadrotor robot learning research. It offers a lightweight and customizable platform with strict alignment with PX4 logic, multiple control modes, and Sim-to-Real toolkits. Users can perform tasks such as Hovering, Balloon, Tracking, Avoid, and Planning, with the ability to create customized environments and tasks. The tool also supports training from scratch, visual encoding approaches, playing and testing of trained models, and customization of new tasks and assets.
raid
RAID is the largest and most comprehensive dataset for evaluating AI-generated text detectors. It contains over 10 million documents spanning 11 LLMs, 11 genres, 4 decoding strategies, and 12 adversarial attacks. RAID is designed to be the go-to location for trustworthy third-party evaluation of popular detectors. The dataset covers diverse models, domains, sampling strategies, and attacks, making it a valuable resource for training detectors, evaluating generalization, protecting against adversaries, and comparing to state-of-the-art models from academia and industry.
For similar tasks
trickPrompt-engine
This repository contains a vulnerability mining engine based on GPT technology. The engine is designed to identify logic vulnerabilities in code by utilizing task-driven prompts. It does not require prior knowledge or fine-tuning and focuses on prompt design rather than model design. The tool is effective in real-world projects and should not be used for academic vulnerability testing. It supports scanning projects in various languages, with current support for Solidity. The engine is configured through prompts and environment settings, enabling users to scan for vulnerabilities in their codebase. Future updates aim to optimize code structure, add more language support, and enhance usability through command line mode. The tool has received a significant audit bounty of $50,000+ as of May 2024.

MachineSoM
MachineSoM is a code repository for the paper 'Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View'. It focuses on the emergence of intelligence from collaborative and communicative computational modules, enabling effective completion of complex tasks. The repository includes code for societies of LLM agents with different traits, collaboration processes such as debate and self-reflection, and interaction strategies for determining when and with whom to interact. It provides a coding framework compatible with various inference services like Replicate, OpenAI, Dashscope, and Anyscale, supporting models like Qwen and GPT. Users can run experiments, evaluate results, and draw figures based on the paper's content, with available datasets for MMLU, Math, and Chess Move Validity.
comfyui
ComfyUI is a highly-configurable, cloud-first AI-Dock container that allows users to run ComfyUI without bundled models or third-party configurations. Users can configure the container using provisioning scripts. The Docker image supports NVIDIA CUDA, AMD ROCm, and CPU platforms, with version tags for different configurations. Additional environment variables and Python environments are provided for customization. ComfyUI service runs on port 8188 and can be managed using supervisorctl. The tool also includes an API wrapper service and pre-configured templates for Vast.ai. The author may receive compensation for services linked in the documentation.

pyrfuniverse
pyrfuniverse is a python package used to interact with RFUniverse simulation environment. It is developed with reference to ML-Agents and produce new features. The package allows users to work with RFUniverse for simulation purposes, providing tools and functionalities to interact with the environment and create new features.
intentkit
IntentKit is an autonomous agent framework that enables the creation and management of AI agents with capabilities including blockchain interactions, social media management, and custom skill integration. It supports multiple agents, autonomous agent management, blockchain integration, social media integration, extensible skill system, and plugin system. The project is in alpha stage and not recommended for production use. It provides quick start guides for Docker and local development, integrations with Twitter and Coinbase, configuration options using environment variables or AWS Secrets Manager, project structure with core application code, entry points, configuration management, database models, skills, skill sets, and utility functions. Developers can add new skills by creating, implementing, and registering them in the skill directory.
pear-landing-page
PearAI Landing Page is an open-source AI-powered code editor managed by Nang and Pan. It is built with Next.js, Vercel, Tailwind CSS, and TypeScript. The project requires setting up environment variables for proper configuration. Users can run the project locally by starting the development server and visiting the specified URL in the browser. Recommended extensions include Prettier, ESLint, and JavaScript and TypeScript Nightly. Contributions to the project are welcomed and appreciated.
webapp-starter
webapp-starter is a modern full-stack application template built with Turborepo, featuring a Hono + Bun API backend and Next.js frontend. It provides an easy way to build a SaaS product. The backend utilizes technologies like Bun, Drizzle ORM, and Supabase, while the frontend is built with Next.js, Tailwind CSS, Shadcn/ui, and Clerk. Deployment can be done using Vercel and Render. The project structure includes separate directories for API backend and Next.js frontend, along with shared packages for the main database. Setup involves installing dependencies, configuring environment variables, and setting up services like Bun, Supabase, and Clerk. Development can be done using 'turbo dev' command, and deployment instructions are provided for Vercel and Render. Contributions are welcome through pull requests.
hayhooks
Hayhooks is a tool that simplifies the deployment and serving of Haystack pipelines as REST APIs. It allows users to wrap their pipelines with custom logic and expose them via HTTP endpoints, including OpenAI-compatible chat completion endpoints. With Hayhooks, users can easily convert their Haystack pipelines into API services with minimal boilerplate code.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

