
allms
A versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying LLMs
Stars: 82
allms is a versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying Large Language Models (LLMs). Developed by Allegro engineers, it simplifies working with LLM applications by providing a user-friendly interface, asynchronous querying, automatic retrying mechanism, error handling, and output parsing. It supports various LLM families hosted on different platforms like OpenAI, Google, Azure, and GCP. The library offers features for configuring endpoint credentials, batch querying with symbolic variables, and forcing structured output format. It also provides documentation, quickstart guides, and instructions for local development, testing, updating documentation, and making new releases.
README:
allms is a versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying Large Language Models (LLMs) 🤖💬
Developed by the Allegro engineers, allms is based on popular libraries like transformers, pydantic, and langchain. It takes care of the boring boiler-plate code you write around your LLM applications, quickly enabling you to prototype ideas, and eventually helping you to scale up for production use-cases!
Among the allms most notable features, you will find:
-
😊 Simple and User-Friendly Interface: The module offers an intuitive and easy-to-use interface, making it straightforward to work with the model.
-
🔀 Asynchronous Querying: Requests to the model are processed asynchronously by default, ensuring efficient and non-blocking interactions.
-
🔄 Automatic Retrying Mechanism : The module includes an automatic retrying mechanism, which helps handle transient errors and ensures that queries to the model are robust.
-
🛠️ Error Handling and Management: Errors that may occur during interactions with the model are handled and managed gracefully, providing informative error messages and potential recovery options.
-
⚙️ Output Parsing: The module simplifies the process of defining the model's output format as well as parsing and working with it, allowing you to easily extract the information you need.
| LLM Family | Hosting | Supported LLMs |
|---|---|---|
| GPT(s) | OpenAI endpoint |
gpt-3.5-turbo, gpt-4, gpt-4-turbo, gpt4-o, gpt4-o mini
|
| Google LLMs | VertexAI deployment |
text-bison@001, Gemini family
|
| Llama2 | Azure deployment |
llama2-7b, llama2-13b, llama2-70b
|
| Mistral | Azure deployment |
Mistral-7b, Mixtral-7bx8
|
| Gemma | GCP deployment | gemma |
- Do you already have a subscription to a Cloud Provider for any the models above? Configure the model using your credentials and start querying!
- Are you interested in knowing how to self-deploy open-source models in Azure and GCP? Consult our guide
Full documentation available at allms.allegro.tech
Get familiar with allms 🚀: introductory jupyter notebook
Install the package via pip:
pip install allms
Configure endpoint credentials and start querying the model with any prompt:
from allms.models import AzureOpenAIModel
from allms.domain.configuration import AzureOpenAIConfiguration
configuration = AzureOpenAIConfiguration(
api_key="your-secret-api-key",
base_url="https://endpoint.openai.azure.com/",
api_version="2023-03-15-preview",
deployment="gpt-35-turbo",
model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo"
)
gpt_model = AzureOpenAIModel(config=configuration)
gpt_response = gpt_model.generate(prompt="Plan me a 3-day holiday trip to Italy")You can pass also a system prompt:
gpt_response = gpt_model.generate(
system_prompt="You are an AI assistant acting as a trip planner",
prompt="Plan me a 3-day holiday trip to Italy"
)If you want to generate responses for a batch of examples, you can achieve this by preparing a prompt with symbolic variables and providing input data that will be injected into the prompt. Symbolic variables can be more than one.
positive_review_0 = "Very good coffee, lightly roasted, with good aroma and taste. The taste of sourness is barely noticeable (which is good because I don't like sour coffees). After grinding, the aroma spreads throughout the room. I recommend it to all those who do not like strongly roasted and pitch-black coffees. A very good solution is to close the package with string, which allows you to preserve the aroma and freshness."
positive_review_1 = "Delicious coffee!! Delicate, just the way I like it, and the smell after opening is amazing. It smells freshly roasted. Faithful to Lavazza coffee for years, I decided to look for other flavors. Based on the reviews, I blindly bought it and it was a 10-shot, it outperformed Lavazze in taste. For me the best."
negative_review = "Marketing is doing its job and I was tempted too, but this coffee is nothing above the level of coffees from the supermarket. And the method of brewing or grinding does not help here. The coffee is simply weak - both in terms of strength and taste. I do not recommend."
prompt = "You'll be provided with a review of a coffe. Decide if the review is positive or negative. Review: {review}"
input_data = [
InputData(input_mappings={"review": positive_review_0}, id="0"),
InputData(input_mappings={"review": positive_review_1}, id="1"),
InputData(input_mappings={"review": negative_review}, id="2")
]
responses = model.generate(prompt=prompt, input_data=input_data)
# >>> {f"review_id={response.input_data.id}": response.response for response in responses}
# {
# 'review_id=0': 'The review is positive.',
# 'review_id=1': 'The review is positive.',
# 'review_id=2': 'The review is negative.'
# }Through pydantic integration, in allms you can pass an output dataclass and force the LLM to provide you the response in a structured way.
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class ReviewOutputDataModel(BaseModel):
summary: str = Field(description="Summary of a product description")
should_buy: bool = Field(description="Recommendation whether I should buy the product or not")
brand_name: str = Field(description="Brand of the coffee")
aroma:str = Field(description="Description of the coffee aroma")
cons: list[str] = Field(description="List of cons of the coffee")
review = "Marketing is doing its job and I was tempted too, but this Blue Orca coffee is nothing above the level of coffees from the supermarket. And the method of brewing or grinding does not help here. The coffee is simply weak - both in terms of strength and taste. I do not recommend."
prompt = "Summarize review of the coffee. Review: {review}"
input_data = [InputData(input_mappings={"review": review}, id="0")]
responses = model.generate(
prompt=prompt,
input_data=input_data,
output_data_model_class=ReviewOutputDataModel
)
response = responses[0].response
# >>> type(response)
# ReviewOutputDataModel
#
# >>> response.should_buy
# False
#
# >>> response.brand_name
# "Blue Orca"
#
# >>> response.aroma
# "Not mentioned in the review"
#
# >>> response.cons
# ['Weak in terms of strength', 'Weak in terms of taste']We assume that you have python 3.10.* installed on your machine.
You can set it up using pyenv
(How to install pyenv on MacOS). To install allms env locally:
- Activate your venv;
- Install Poetry via:
make install-poetry- Install allms dependencies with the command:
make install-envIn order to execute tests, run:
make testsRun mkdocs serve to serve a local instance of the documentation.
Modify the content of docs directory to update the documentation. The updated content will be deployed
via the github action .github/workflows/docs.yml
When a new version of allms is ready to be released, do the following operations:
-
Merge to master the dev branch in which the new version has been specified:
- In this branch,
versionunder[tool.poetry]section inpyproject.tomlshould be updated, e.g0.1.0; - Update the CHANGELOG, specifying the new release.
- In this branch,
-
Tag the new master with the name of the newest version:
- e.g
v0.1.0.
- e.g
-
Publish package to PyPI:
- Go to Actions → Manual Publish To PyPI;
- Select "master" as branch and click Run workflow;
- If successful, you will find the package under # TODO: open-source.
-
Make a GitHub release:
- Go to Releases → Draft a new release;
- Select the recently created tag in Choose a tag window;
- Copy/paste all the content present in the CHANGELOG under the version you are about to release;
- Upload
allms-<NEW-VERSION>.whlandallms-<NEW-VERSION>.tar.gzas assets; - Click
Publish release.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for allms
Similar Open Source Tools

allms
allms is a versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying Large Language Models (LLMs). Developed by Allegro engineers, it simplifies working with LLM applications by providing a user-friendly interface, asynchronous querying, automatic retrying mechanism, error handling, and output parsing. It supports various LLM families hosted on different platforms like OpenAI, Google, Azure, and GCP. The library offers features for configuring endpoint credentials, batch querying with symbolic variables, and forcing structured output format. It also provides documentation, quickstart guides, and instructions for local development, testing, updating documentation, and making new releases.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.
CogAgent
CogAgent is an advanced intelligent agent model designed for automating operations on graphical interfaces across various computing devices. It supports platforms like Windows, macOS, and Android, enabling users to issue commands, capture device screenshots, and perform automated operations. The model requires a minimum of 29GB of GPU memory for inference at BF16 precision and offers capabilities for executing tasks like sending Christmas greetings and sending emails. Users can interact with the model by providing task descriptions, platform specifications, and desired output formats.
web-llm
WebLLM is a modular and customizable javascript package that directly brings language model chats directly onto web browsers with hardware acceleration. Everything runs inside the browser with no server support and is accelerated with WebGPU. WebLLM is fully compatible with OpenAI API. That is, you can use the same OpenAI API on any open source models locally, with functionalities including json-mode, function-calling, streaming, etc. We can bring a lot of fun opportunities to build AI assistants for everyone and enable privacy while enjoying GPU acceleration.
giskard
Giskard is an open-source Python library that automatically detects performance, bias & security issues in AI applications. The library covers LLM-based applications such as RAG agents, all the way to traditional ML models for tabular data.
quivr
Quivr is a personal assistant powered by Generative AI, designed to be a second brain for users. It offers fast and efficient access to data, ensuring security and compatibility with various file formats. Quivr is open source and free to use, allowing users to share their brains publicly or keep them private. The marketplace feature enables users to share and utilize brains created by others, boosting productivity. Quivr's offline mode provides anytime, anywhere access to data. Key features include speed, security, OS compatibility, file compatibility, open source nature, public/private sharing options, a marketplace, and offline mode.
oasis
OASIS is a scalable, open-source social media simulator that integrates large language models with rule-based agents to realistically mimic the behavior of up to one million users on platforms like Twitter and Reddit. It facilitates the study of complex social phenomena such as information spread, group polarization, and herd behavior, offering a versatile tool for exploring diverse social dynamics and user interactions in digital environments. With features like scalability, dynamic environments, diverse action spaces, and integrated recommendation systems, OASIS provides a comprehensive platform for simulating social media interactions at a large scale.

axar
AXAR AI is a lightweight framework designed for building production-ready agentic applications using TypeScript. It aims to simplify the process of creating robust, production-grade LLM-powered apps by focusing on familiar coding practices without unnecessary abstractions or steep learning curves. The framework provides structured, typed inputs and outputs, familiar and intuitive patterns like dependency injection and decorators, explicit control over agent behavior, real-time logging and monitoring tools, minimalistic design with little overhead, model agnostic compatibility with various AI models, and streamed outputs for fast and accurate results. AXAR AI is ideal for developers working on real-world AI applications who want a tool that gets out of the way and allows them to focus on shipping reliable software.

marqo
Marqo is more than a vector database, it's an end-to-end vector search engine for both text and images. Vector generation, storage and retrieval are handled out of the box through a single API. No need to bring your own embeddings.

supallm
Supallm is a Python library for super resolution of images using deep learning techniques. It provides pre-trained models for enhancing image quality by increasing resolution. The library is easy to use and allows users to upscale images with high fidelity and detail. Supallm is suitable for tasks such as enhancing image quality, improving visual appearance, and increasing the resolution of low-quality images. It is a valuable tool for researchers, photographers, graphic designers, and anyone looking to enhance image quality using AI technology.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using a local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration for tasks, command line interface for running tasks, push to Hugging Face Hub for dataset upload, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration or Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM to interface with LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub.
otto-m8
otto-m8 is a flowchart based automation platform designed to run deep learning workloads with minimal to no code. It provides a user-friendly interface to spin up a wide range of AI models, including traditional deep learning models and large language models. The tool deploys Docker containers of workflows as APIs for integration with existing workflows, building AI chatbots, or standalone applications. Otto-m8 operates on an Input, Process, Output paradigm, simplifying the process of running AI models into a flowchart-like UI.
simpleAI
SimpleAI is a self-hosted alternative to the not-so-open AI API, focused on replicating main endpoints for LLM such as text completion, chat, edits, and embeddings. It allows quick experimentation with different models, creating benchmarks, and handling specific use cases without relying on external services. Users can integrate and declare models through gRPC, query endpoints using Swagger UI or API, and resolve common issues like CORS with FastAPI middleware. The project is open for contributions and welcomes PRs, issues, documentation, and more.
bedrock-claude-chat
This repository is a sample chatbot using the Anthropic company's LLM Claude, one of the foundational models provided by Amazon Bedrock for generative AI. It allows users to have basic conversations with the chatbot, personalize it with their own instructions and external knowledge, and analyze usage for each user/bot on the administrator dashboard. The chatbot supports various languages, including English, Japanese, Korean, Chinese, French, German, and Spanish. Deployment is straightforward and can be done via the command line or by using AWS CDK. The architecture is built on AWS managed services, eliminating the need for infrastructure management and ensuring scalability, reliability, and security.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration, command line interface, push to Hugging Face Hub, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration files or programmatically using Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM for LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub. The library is not responsible for the content generated by models and advises users to review the data before using it in production environments.
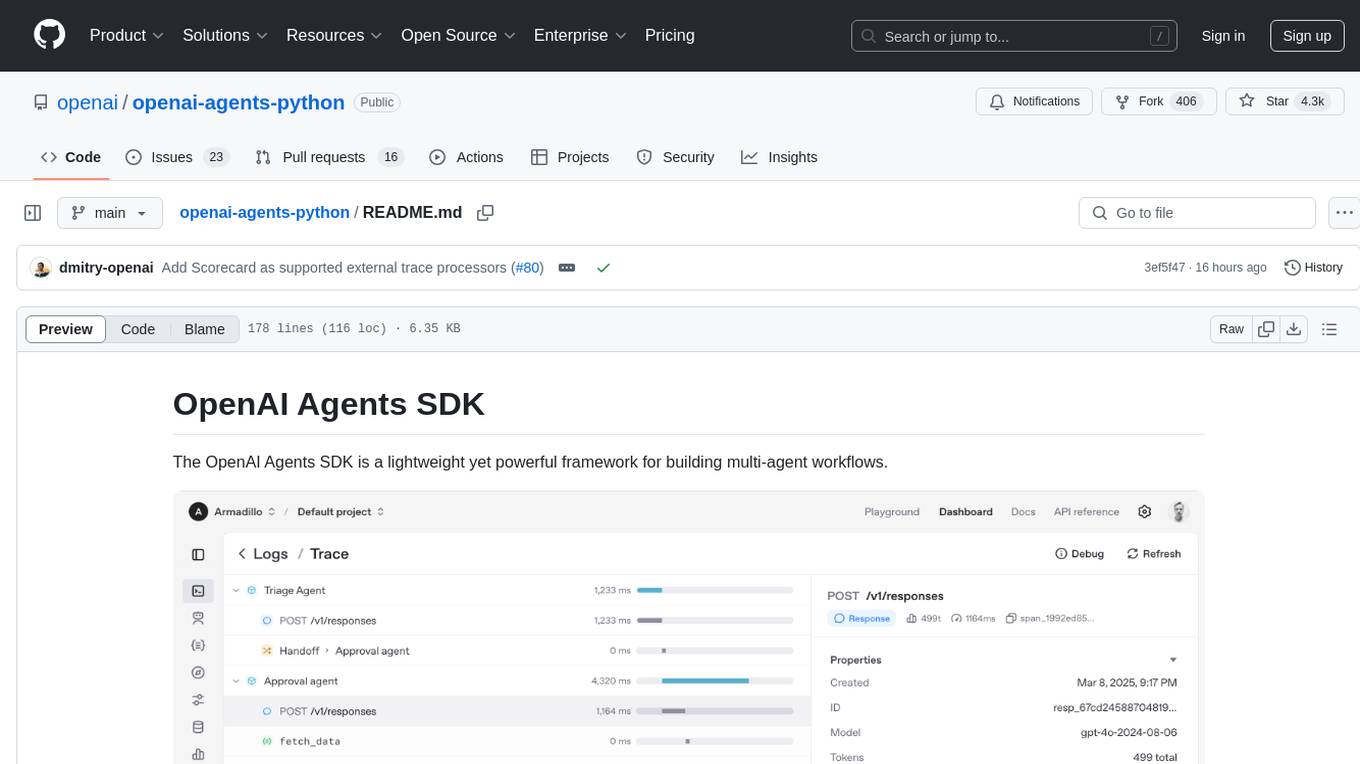
openai-agents-python
The OpenAI Agents SDK is a lightweight framework for building multi-agent workflows. It includes concepts like Agents, Handoffs, Guardrails, and Tracing to facilitate the creation and management of agents. The SDK is compatible with any model providers supporting the OpenAI Chat Completions API format. It offers flexibility in modeling various LLM workflows and provides automatic tracing for easy tracking and debugging of agent behavior. The SDK is designed for developers to create deterministic flows, iterative loops, and more complex workflows.
For similar tasks

allms
allms is a versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying Large Language Models (LLMs). Developed by Allegro engineers, it simplifies working with LLM applications by providing a user-friendly interface, asynchronous querying, automatic retrying mechanism, error handling, and output parsing. It supports various LLM families hosted on different platforms like OpenAI, Google, Azure, and GCP. The library offers features for configuring endpoint credentials, batch querying with symbolic variables, and forcing structured output format. It also provides documentation, quickstart guides, and instructions for local development, testing, updating documentation, and making new releases.
semantic-router
Semantic Router is a superfast decision-making layer for your LLMs and agents. Rather than waiting for slow LLM generations to make tool-use decisions, we use the magic of semantic vector space to make those decisions — _routing_ our requests using _semantic_ meaning.
hass-ollama-conversation
The Ollama Conversation integration adds a conversation agent powered by Ollama in Home Assistant. This agent can be used in automations to query information provided by Home Assistant about your house, including areas, devices, and their states. Users can install the integration via HACS and configure settings such as API timeout, model selection, context size, maximum tokens, and other parameters to fine-tune the responses generated by the AI language model. Contributions to the project are welcome, and discussions can be held on the Home Assistant Community platform.
luna-ai
Luna AI is a virtual streamer driven by a 'brain' composed of ChatterBot, GPT, Claude, langchain, chatglm, text-generation-webui, 讯飞星火, 智谱AI. It can interact with viewers in real-time during live streams on platforms like Bilibili, Douyin, Kuaishou, Douyu, or chat with you locally. Luna AI uses natural language processing and text-to-speech technologies like Edge-TTS, VITS-Fast, elevenlabs, bark-gui, VALL-E-X to generate responses to viewer questions and can change voice using so-vits-svc, DDSP-SVC. It can also collaborate with Stable Diffusion for drawing displays and loop custom texts. This project is completely free, and any identical copycat selling programs are pirated, please stop them promptly.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.

cria
Cria is a Python library designed for running Large Language Models with minimal configuration. It provides an easy and concise way to interact with LLMs, offering advanced features such as custom models, streams, message history management, and running multiple models in parallel. Cria simplifies the process of using LLMs by providing a straightforward API that requires only a few lines of code to get started. It also handles model installation automatically, making it efficient and user-friendly for various natural language processing tasks.
beyondllm
Beyond LLM offers an all-in-one toolkit for experimentation, evaluation, and deployment of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It simplifies the process with automated integration, customizable evaluation metrics, and support for various Large Language Models (LLMs) tailored to specific needs. The aim is to reduce LLM hallucination risks and enhance reliability.
Groma
Groma is a grounded multimodal assistant that excels in region understanding and visual grounding. It can process user-defined region inputs and generate contextually grounded long-form responses. The tool presents a unique paradigm for multimodal large language models, focusing on visual tokenization for localization. Groma achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension benchmarks. The tool provides pretrained model weights and instructions for data preparation, training, inference, and evaluation. Users can customize training by starting from intermediate checkpoints. Groma is designed to handle tasks related to detection pretraining, alignment pretraining, instruction finetuning, instruction following, and more.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.