
mergekit
Tools for merging pretrained large language models.
Stars: 5461
Mergekit is a toolkit for merging pre-trained language models. It uses an out-of-core approach to perform unreasonably elaborate merges in resource-constrained situations. Merges can be run entirely on CPU or accelerated with as little as 8 GB of VRAM. Many merging algorithms are supported, with more coming as they catch my attention.
README:
mergekit is a toolkit for merging pre-trained language models. mergekit uses an out-of-core approach to perform unreasonably elaborate merges in resource-constrained situations. Merges can be run entirely on CPU or accelerated with as little as 8 GB of VRAM. Many merging algorithms are supported, with more coming as they catch my attention.
- Why Merge Models?
- Features
- Installation
- Usage
- Merge Configuration
- Merge Methods
- LoRA extraction
- Mixture of Experts merging
- Evolutionary merge methods
- Merge in the Cloud
- Citation
Model merging is a powerful technique that allows combining the strengths of different models without the computational overhead of ensembling or the need for additional training. By operating directly in the weight space of models, merging can:
- Combine multiple specialized models into a single versatile model
- Transfer capabilities between models without access to training data
- Find optimal trade-offs between different model behaviors
- Improve performance while maintaining inference costs
- Create new capabilities through creative model combinations
Unlike traditional ensembling which requires running multiple models, merged models maintain the same inference cost as a single model while often achieving comparable or superior performance.
Key features of mergekit include:
- Supports Llama, Mistral, GPT-NeoX, StableLM, and more
- Many merge methods
- GPU or CPU execution
- Lazy loading of tensors for low memory use
- Interpolated gradients for parameter values (inspired by Gryphe's BlockMerge_Gradient script)
- Piecewise assembly of language models from layers ("Frankenmerging")
- Mixture of Experts merging
- LORA extraction
- Evolutionary merge methods
🌐 GUI Launch Alert 🤗 - We are excited to announce the launch of a mega-GPU backed graphical user interface for mergekit in Arcee! This GUI simplifies the merging process, making it more accessible to a broader audience. Check it out and contribute at the Arcee App. There is also a Hugging Face Space with limited amounts of GPUs.
git clone https://github.com/arcee-ai/mergekit.git
cd mergekit
pip install -e . # install the package and make scripts availableIf the above fails with the error of:
ERROR: File "setup.py" or "setup.cfg" not found. Directory cannot be installed in editable mode:
(A "pyproject.toml" file was found, but editable mode currently requires a setuptools-based build.)
You may need to upgrade pip to > 21.3 with the command python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip
The script mergekit-yaml is the main entry point for mergekit. It takes a YAML configuration file and an output path, like so:
mergekit-yaml path/to/your/config.yml ./output-model-directory [--cuda] [--lazy-unpickle] [--allow-crimes] [... other options]This will run the merge and write your merged model to ./output-model-directory.
For more information on the arguments accepted by mergekit-yaml run the command mergekit-yaml --help.
When you have a merged model you're happy with, you may want to share it on the Hugging Face Hub. mergekit generates a README.md for your merge with some basic information for a model card. You can edit it to include more details about your merge, like giving it a good name or explaining what it's good at; rewrite it entirely; or use the generated README.md as-is. It is also possible to edit your README.md online once it has been uploaded to the Hub.
Once you're happy with your model card and merged model, you can upload it to the Hugging Face Hub using the huggingface_hub Python library.
# log in to huggingface with an access token (must have write permission)
huggingface-cli login
# upload your model
huggingface-cli upload your_hf_username/my-cool-model ./output-model-directory .The documentation for huggingface_hub goes into more detail about other options for uploading.
Merge configurations are YAML documents specifying the operations to perform in order to produce your merged model. Below are the primary elements of a configuration file:
-
merge_method: Specifies the method to use for merging models. See Merge Methods for a list. -
slices: Defines slices of layers from different models to be used. This field is mutually exclusive withmodels. -
models: Defines entire models to be used for merging. This field is mutually exclusive withslices. -
base_model: Specifies the base model used in some merging methods. -
parameters: Holds various parameters such as weights and densities, which can also be specified at different levels of the configuration. -
dtype: Specifies the data type used for the merging operation. -
tokenizerortokenizer_source: Determines how to construct a tokenizer for the merged model. -
chat_template: Specifies a chat template for the merged model.
Parameters are flexible and can be set with varying precedence. They can be specified conditionally using tensor name filters, which allows finer control such as differentiating between attention heads and fully connected layers.
Parameters can be specified as:
- Scalars: Single floating-point values.
- Gradients: List of floating-point values, specifying an interpolated gradient.
The parameters can be set at different levels, with decreasing precedence as follows:
-
slices.*.sources.parameters- applying to a specific input slice -
slices.*.parameters- applying to a specific output slice -
models.*.parametersorinput_model_parameters- applying to any tensors coming from specific input models -
parameters- catchall
The tokenizer behavior can be configured in two ways: using the new tokenizer field (recommended) or the legacy tokenizer_source field (maintained for backward compatibility). These fields are mutually exclusive - you should use one or the other, not both.
The tokenizer field provides fine-grained control over vocabulary and embeddings:
tokenizer:
source: "union" # or "base" or a specific model path
tokens: # Optional: configure specific tokens
<token_name>:
source: ... # Specify embedding source
force: false # Optional: force this embedding for all models
pad_to_multiple_of: null # Optional: pad vocabulary sizeThe source field determines the vocabulary of the output model:
-
union: Combine vocabularies from all input models (default) -
base: Use vocabulary from the base model -
"path/to/model": Use vocabulary from a specific model
When merging models with different vocabularies, mergekit uses smart defaults to handle token embeddings:
- If a token exists in the base model, its embedding is used as the default
- If only one model has the token, that model's embedding is used
- Otherwise, an average of all available embeddings is used
You can override these defaults for specific tokens:
tokenizer:
source: union
tokens:
# Use embedding from a specific model
<|im_start|>:
source: "path/to/chatml/model"
# Force a specific embedding for all models
<|special|>:
source: "path/to/model"
force: true
# Map a token to another model's token embedding
<|renamed_token|>:
source:
kind: "model_token"
model: "path/to/model"
token: "<|original_token|>" # or use token_id: 1234Here's how you might preserve both Llama 3 Instruct and ChatML prompt formats when merging models:
tokenizer:
source: union
tokens:
# ChatML tokens
<|im_start|>:
source: "chatml_model"
<|im_end|>:
source: "chatml_model"
# Llama 3 tokens - force original embeddings
<|start_header_id|>:
source: "llama3_model"
force: true
<|end_header_id|>:
source: "llama3_model"
force: true
<|eot_id|>:
source: "llama3_model"
force: trueFor backward compatibility, the tokenizer_source field is still supported:
tokenizer_source: "union" # or "base" or a model pathThis provides basic tokenizer selection but lacks the fine-grained control of the modern tokenizer field.
The optional chat_template field allows overriding the chat template used for the merged model.
chat_template: "auto" # or a template name or Jinja2 templateOptions include:
-
"auto": Automatically select the most common template among input models - Built-in templates:
"alpaca","chatml","llama3","mistral","exaone" - A Jinja2 template string for custom formatting
Several examples of merge configurations are available in examples/.
A quick overview of the currently supported merge methods:
| Method |
merge_method value |
Multi-Model | Uses base model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear (Model Soups) | linear |
✅ | ❌ |
| SLERP | slerp |
❌ | ✅ |
| Nearswap | nearswap |
❌ | ✅ |
| Task Arithmetic | task_arithmetic |
✅ | ✅ |
| TIES | ties |
✅ | ✅ |
| DARE TIES | dare_ties |
✅ | ✅ |
| DARE Task Arithmetic | dare_linear |
✅ | ✅ |
| Passthrough | passthrough |
❌ | ❌ |
| Model Breadcrumbs | breadcrumbs |
✅ | ✅ |
| Model Breadcrumbs + TIES | breadcrumbs_ties |
✅ | ✅ |
| Model Stock | model_stock |
✅ | ✅ |
| NuSLERP | nuslerp |
❌ | ✅ |
| DELLA | della |
✅ | ✅ |
| DELLA Task Arithmetic | della_linear |
✅ | ✅ |
| SCE | sce |
✅ | ✅ |
The classic merge method - a simple weighted average.
Parameters:
-
weight- relative (or absolute ifnormalize=False) weighting of a given tensor -
normalize- if true, the weights of all models contributing to a tensor will be normalized. Default behavior.
Spherically interpolate the parameters of two models. One must be set as base_model.
Parameters:
-
t- interpolation factor. Att=0will returnbase_model, att=1will return the other one.
Interpolates base model with secondary model if similarity is below t. Accepts two models.
Parameters:
-
t- similarity threshold
Computes "task vectors" for each model by subtracting a base model. Merges the task vectors linearly and adds back the base. Works great for models that were fine tuned from a common ancestor. Also a super useful mental framework for several of the more involved merge methods.
Parameters: same as Linear, plus:
-
lambda- scaling factor applied after weighted sum of task vectors
Builds on the task arithmetic framework. Resolves interference between models by sparsifying the task vectors and applying a sign consensus algorithm. Allows you to merge a larger number of models and retain more of their strengths.
Parameters: same as Task Arithmetic, plus:
-
density- fraction of weights in differences from the base model to retain
In the same vein as TIES, sparsifies task vectors to reduce interference. Differs in that DARE uses random pruning with a novel rescaling to better match performance of the original models. DARE can be used either with the sign consensus algorithm of TIES (dare_ties) or without (dare_linear).
Parameters: same as TIES for dare_ties, or Linear for dare_linear
passthrough is a no-op that simply passes input tensors through unmodified. It is meant to be used for layer-stacking type merges where you have only one input model. Useful for frankenmerging.
An extension of task arithmetic that discards both small and extremely large differences from the base model. As with DARE, the Model Breadcrumbs algorithm can be used with (breadcrumbs_ties) or without (breadcrumbs) the sign consensus algorithm of TIES.
Parameters: same as Task Arithmetic, plus:
-
density- fraction of weights in differences from the base model to retain -
gamma- fraction of largest magnitude differences to remove
Note that gamma corresponds with the parameter β described in the paper, while density is the final density of the sparsified tensors (related to γ and β by density = 1 - γ - β). For good default values, try density: 0.9 and gamma: 0.01.
Uses some neat geometric properties of fine tuned models to compute good weights for linear interpolation. Requires at least three models, including a base model.
Parameters:
-
filter_wise: if true, weight calculation will be per-row rather than per-tensor. Not recommended.
Spherically interpolate between parameters, but with more options and more sensical configuration! Does not require a base model, but can use one to do spherical interpolation of task vectors. Only works with either two models or two plus a base model.
Parameters:
-
weight: relative weighting of a given tensor -
nuslerp_flatten: set to false to do row-wise/column-wise interpolation instead of treating tensors as vectors -
nuslerp_row_wise: SLERP row vectors instead of column vectors
To replicate the behavior of the original slerp method, set weight to 1-t and t for your first and second model respectively.
Building upon DARE, DELLA uses adaptive pruning based on parameter magnitudes. DELLA first ranks parameters in each row of delta parameters and assigns drop probabilities inversely proportional to their magnitudes. This allows it to retain more important changes while reducing interference. After pruning, it rescales the remaining parameters similar to DARE. DELLA can be used with (della) or without (della_linear) the sign elect step of TIES
Parameters: same as Task Arithmetic, plus:
-
density- fraction of weights in differences from the base model to retain -
epsilon- maximum change in drop probability based on magnitude. Drop probabilities assigned will range fromdensity - epsilontodensity + epsilon. (When selecting values fordensityandepsilon, ensure that the range of probabilities falls within 0 to 1)
SCE introduces adaptive matrix-level merging weights based on parameter variances. SCE first selects the top-k% elements from each parameter matrix that exhibit high variance across all delta parameters. Following this selection, SCE calculates matrix-level merging weights based on the sum of squares of elements in the delta parameters. Finally, it erases minority elements, a step similar to the sign election process in TIES.
Parameters: same as TIES, plus:
-
select_topk- fraction of elements with the highest variance in the delta parameters to retain.
Mergekit allows extracting PEFT-compatible low-rank approximations of finetuned models.
mergekit-extract-lora --model finetuned_model_id_or_path --base-model base_model_id_or_path --out-path output_path [--no-lazy-unpickle] [--cuda] [--max-rank=desired_rank] [--sv-epsilon=tol]The mergekit-moe script supports merging multiple dense models into a mixture of experts, either for direct use or for further training. For more details see the mergekit-moe documentation.
See docs/evolve.md for details.
We host merging on Arcee's cloud GPUs - you can launch a cloud merge in the Arcee App. Or through python - grab an ARCEE_API_KEY:
export ARCEE_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
pip install -q arcee-py
import arcee
arcee.merge_yaml("bio-merge","./examples/bio-merge.yml")Check your merge status at the Arcee App
When complete, either deploy your merge:
arcee.start_deployment("bio-merge", merging="bio-merge")Or download your merge:
!arcee merging download bio-merge
If you find mergekit useful in your research, please consider citing the paper:
@inproceedings{goddard-etal-2024-arcees,
title = "Arcee{'}s {M}erge{K}it: A Toolkit for Merging Large Language Models",
author = "Goddard, Charles and
Siriwardhana, Shamane and
Ehghaghi, Malikeh and
Meyers, Luke and
Karpukhin, Vladimir and
Benedict, Brian and
McQuade, Mark and
Solawetz, Jacob",
editor = "Dernoncourt, Franck and
Preo{\c{t}}iuc-Pietro, Daniel and
Shimorina, Anastasia",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track",
month = nov,
year = "2024",
address = "Miami, Florida, US",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.emnlp-industry.36",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2024.emnlp-industry.36",
pages = "477--485",
abstract = "The rapid growth of open-source language models provides the opportunity to merge model checkpoints, combining their parameters to improve performance and versatility. Advances in transfer learning have led to numerous task-specific models, which model merging can integrate into powerful multitask models without additional training. MergeKit is an open-source library designed to support this process with an efficient and extensible framework suitable for any hardware. It has facilitated the merging of thousands of models, contributing to some of the world{'}s most powerful open-source model checkpoints. The library is accessible at: https://github.com/arcee-ai/mergekit.",
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mergekit
Similar Open Source Tools

mergekit
Mergekit is a toolkit for merging pre-trained language models. It uses an out-of-core approach to perform unreasonably elaborate merges in resource-constrained situations. Merges can be run entirely on CPU or accelerated with as little as 8 GB of VRAM. Many merging algorithms are supported, with more coming as they catch my attention.
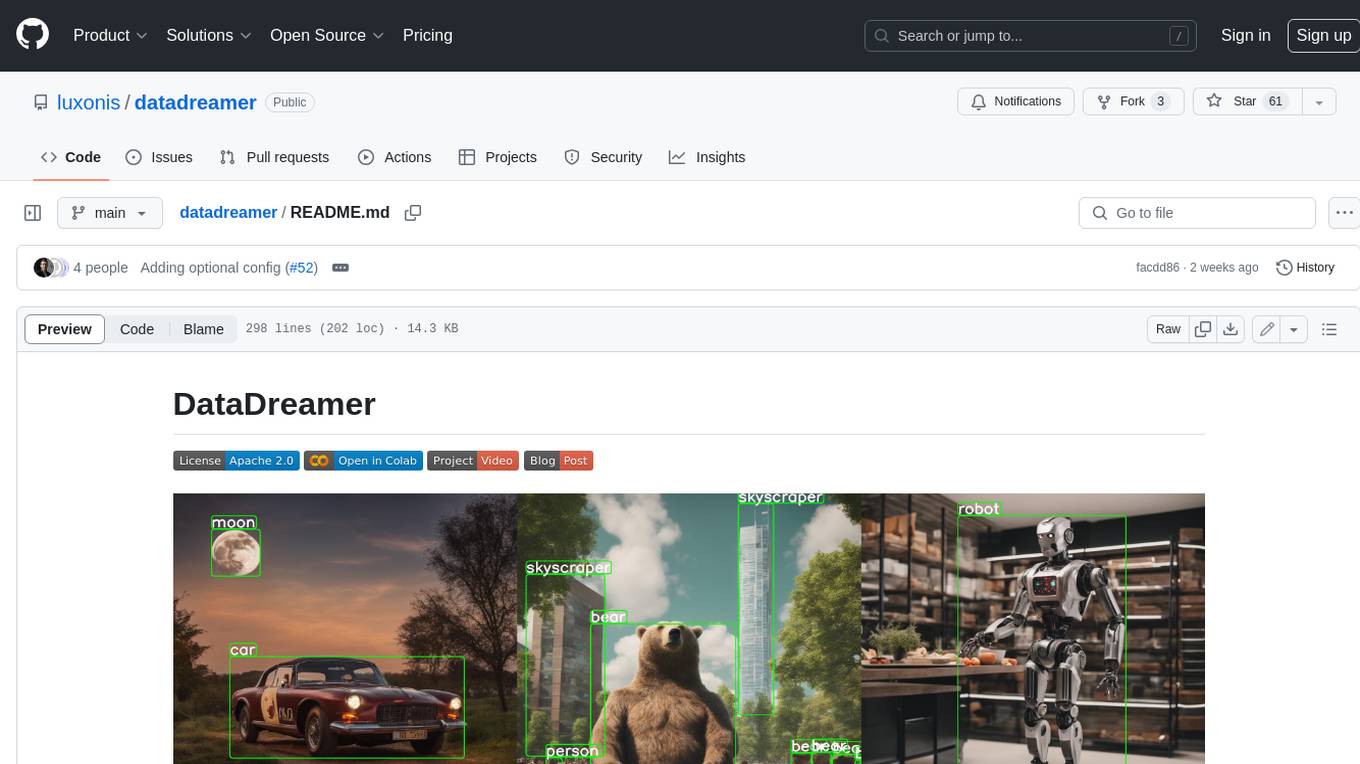
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.
garak
Garak is a free tool that checks if a Large Language Model (LLM) can be made to fail in a way that is undesirable. It probes for hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, jailbreaks, and many other weaknesses. Garak's a free tool. We love developing it and are always interested in adding functionality to support applications.
garak
Garak is a vulnerability scanner designed for LLMs (Large Language Models) that checks for various weaknesses such as hallucination, data leakage, prompt injection, misinformation, toxicity generation, and jailbreaks. It combines static, dynamic, and adaptive probes to explore vulnerabilities in LLMs. Garak is a free tool developed for red-teaming and assessment purposes, focusing on making LLMs or dialog systems fail. It supports various LLM models and can be used to assess their security and robustness.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
mflux
MFLUX is a line-by-line port of the FLUX implementation in the Huggingface Diffusers library to Apple MLX. It aims to run powerful FLUX models from Black Forest Labs locally on Mac machines. The codebase is minimal and explicit, prioritizing readability over generality and performance. Models are implemented from scratch in MLX, with tokenizers from the Huggingface Transformers library. Dependencies include Numpy and Pillow for image post-processing. Installation can be done using `uv tool` or classic virtual environment setup. Command-line arguments allow for image generation with specified models, prompts, and optional parameters. Quantization options for speed and memory reduction are available. LoRA adapters can be loaded for fine-tuning image generation. Controlnet support provides more control over image generation with reference images. Current limitations include generating images one by one, lack of support for negative prompts, and some LoRA adapters not working.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
mlx-lm
MLX LM is a Python package designed for generating text and fine-tuning large language models on Apple silicon using MLX. It offers integration with the Hugging Face Hub for easy access to thousands of LLMs, support for quantizing and uploading models to the Hub, low-rank and full model fine-tuning capabilities, and distributed inference and fine-tuning with `mx.distributed`. Users can interact with the package through command line options or the Python API, enabling tasks such as text generation, chatting with language models, model conversion, streaming generation, and sampling. MLX LM supports various Hugging Face models and provides tools for efficient scaling to long prompts and generations, including a rotating key-value cache and prompt caching. It requires macOS 15.0 or higher for optimal performance.
kvpress
This repository implements multiple key-value cache pruning methods and benchmarks using transformers, aiming to simplify the development of new methods for researchers and developers in the field of long-context language models. It provides a set of 'presses' that compress the cache during the pre-filling phase, with each press having a compression ratio attribute. The repository includes various training-free presses, special presses, and supports KV cache quantization. Users can contribute new presses and evaluate the performance of different presses on long-context datasets.
generative-models
Generative Models by Stability AI is a repository that provides various generative models for research purposes. It includes models like Stable Video 4D (SV4D) for video synthesis, Stable Video 3D (SV3D) for multi-view synthesis, SDXL-Turbo for text-to-image generation, and more. The repository focuses on modularity and implements a config-driven approach for building and combining submodules. It supports training with PyTorch Lightning and offers inference demos for different models. Users can access pre-trained models like SDXL-base-1.0 and SDXL-refiner-1.0 under a CreativeML Open RAIL++-M license. The codebase also includes tools for invisible watermark detection in generated images.
rtdl-num-embeddings
This repository provides the official implementation of the paper 'On Embeddings for Numerical Features in Tabular Deep Learning'. It focuses on transforming scalar continuous features into vectors before integrating them into the main backbone of tabular neural networks, showcasing improved performance. The embeddings for continuous features are shown to enhance the performance of tabular DL models and are applicable to various conventional backbones, offering efficiency comparable to Transformer-based models. The repository includes Python packages for practical usage, exploration of metrics and hyperparameters, and reproducing reported results for different algorithms and datasets.
llm-analysis
llm-analysis is a tool designed for Latency and Memory Analysis of Transformer Models for Training and Inference. It automates the calculation of training or inference latency and memory usage for Large Language Models (LLMs) or Transformers based on specified model, GPU, data type, and parallelism configurations. The tool helps users to experiment with different setups theoretically, understand system performance, and optimize training/inference scenarios. It supports various parallelism schemes, communication methods, activation recomputation options, data types, and fine-tuning strategies. Users can integrate llm-analysis in their code using the `LLMAnalysis` class or use the provided entry point functions for command line interface. The tool provides lower-bound estimations of memory usage and latency, and aims to assist in achieving feasible and optimal setups for training or inference.
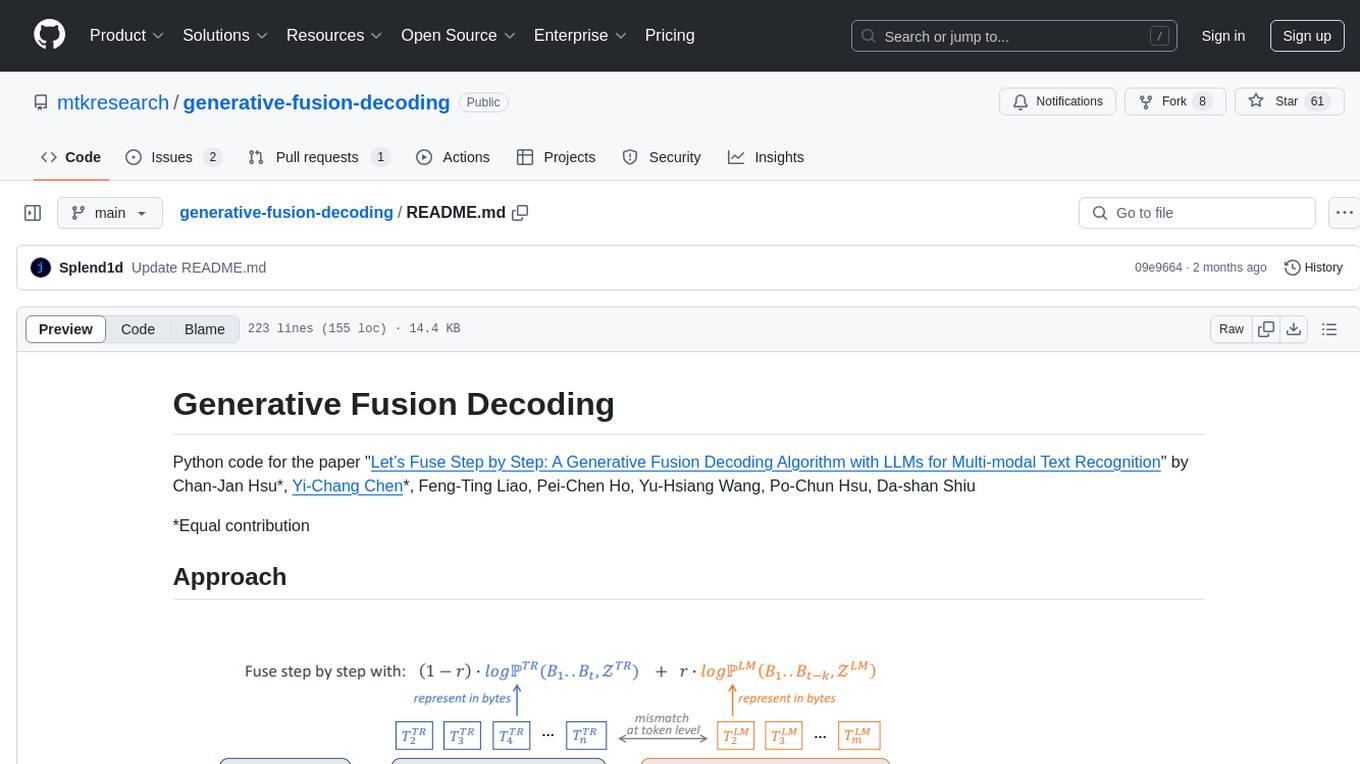
generative-fusion-decoding
Generative Fusion Decoding (GFD) is a novel shallow fusion framework that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into multi-modal text recognition systems such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and optical character recognition (OCR). GFD operates across mismatched token spaces of different models by mapping text token space to byte token space, enabling seamless fusion during the decoding process. It simplifies the complexity of aligning different model sample spaces, allows LLMs to correct errors in tandem with the recognition model, increases robustness in long-form speech recognition, and enables fusing recognition models deficient in Chinese text recognition with LLMs extensively trained on Chinese. GFD significantly improves performance in ASR and OCR tasks, offering a unified solution for leveraging existing pre-trained models through step-by-step fusion.
cortex
Cortex is a tool that simplifies and accelerates the process of creating applications utilizing modern AI models like chatGPT and GPT-4. It provides a structured interface (GraphQL or REST) to a prompt execution environment, enabling complex augmented prompting and abstracting away model connection complexities like input chunking, rate limiting, output formatting, caching, and error handling. Cortex offers a solution to challenges faced when using AI models, providing a simple package for interacting with NL AI models.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
For similar tasks

mergekit
Mergekit is a toolkit for merging pre-trained language models. It uses an out-of-core approach to perform unreasonably elaborate merges in resource-constrained situations. Merges can be run entirely on CPU or accelerated with as little as 8 GB of VRAM. Many merging algorithms are supported, with more coming as they catch my attention.
For similar jobs

mergekit
Mergekit is a toolkit for merging pre-trained language models. It uses an out-of-core approach to perform unreasonably elaborate merges in resource-constrained situations. Merges can be run entirely on CPU or accelerated with as little as 8 GB of VRAM. Many merging algorithms are supported, with more coming as they catch my attention.