
CAG
Cache-Augmented Generation: A Simple, Efficient Alternative to RAG
Stars: 836
Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG) is an alternative paradigm to Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that eliminates real-time retrieval delays and errors by preloading all relevant resources into the model's context. CAG leverages extended context windows of large language models (LLMs) to generate responses directly, providing reduced latency, improved reliability, and simplified design. While CAG has limitations in knowledge size and context length, advancements in LLMs are addressing these issues, making CAG a practical and scalable alternative for complex applications.
README:
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful approach for enhancing language models by integrating external knowledge sources. However, RAG also introduces several challenges, including:
- Retrieval Latency – Delays caused by real-time retrieval steps.
- Retrieval Errors – Inaccuracies in selecting relevant documents.
- System Complexity – Increased architectural and maintenance overhead.
To address these limitations, we propose Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG)—an alternative paradigm that bypasses real-time retrieval. CAG leverages the extended context windows of modern large language models (LLMs) by preloading all relevant resources into the model’s context and caching its runtime parameters. During inference, the preloaded KV-cache enables the model to generate responses directly, eliminating the need for retrieval.
Advantages of CAG
- Reduced Latency – Eliminates real-time retrieval, enabling faster inference.
- Improved Reliability – Minimizes retrieval errors while maintaining context relevance.
- Simplified Design – Provides a streamlined, retrieval-free alternative to RAG, achieving comparable or superior results with lower complexity.
Limitations of CAG
- Limited Knowledge Size – CAG requires the entire knowledge source to fit within the context window, making it less suitable for tasks involving extremely large datasets.
- Context Length Constraints – The performance of LLMs may degrade with very long contexts (reference).
Our paper investigates the relationship between model performance and context length, providing insights into scenarios where CAG excels.
The limitations of CAG are rapidly being addressed by advancements in LLMs with longer context windows and improved capabilities for extracting relevant information from extended inputs. As these models continue to evolve, CAG is expected to handle increasingly complex applications, making it a practical and scalable alternative to traditional RAG.
pip install -r ./requirements.txt[!IMPORTANT]
download the requiredsquadandhotpotqadatasets by curl scriptsh ./downloads.sh
[!IMPORTANT] create
.envfile by.env.templateand input the keys requiredcp ./.env.template ./.env
-
rag.pyis for RAG Experiment -
kvcache.pyis for CAG Experiment
-
--kvcache: "file" -
--dataset: "hotpotqa-train" or "squad-train" -
--similarity"bertscore" -
--modelname: "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" -
--maxKnowledge: "", int, select how many document in dataset, explanation in Note -
--maxParagraph: 100 -
--maxQuestionint, max question number, explanation in Note -
--randomSeed: "", int, a random seed number -
--output: "", str, output filepath string -
--usePrompt, add this parameter if not using CAG knowledge cache acceleration
python ./kvcache.py --kvcache file --dataset "squad-train" --similarity bertscore \
--maxKnowledge 5 --maxParagraph 100 --maxQuestion 1000 \
--modelname "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --randomSeed 0 \
--output "./result_kvcache.txt"-
--index: "openai" or "bm25" -
--dataset: "hotpotqa-train" or "squad-train" -
--similarity"bertscore" -
--maxKnowledge: "", int, select how many document in dataset, explanation in Note -
--maxParagraph: 100 -
--maxQuestionint, max question number, explanation in Note -
--topk: int, the similarity topk of retrieval -
--modelname: "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" -
--randomSeed: "", int, a random seed number -
--output: "", str, output filepath string
python ./rag.py --index "bm25" --dataset "hotpotqa-train" --similarity bertscore \
--maxKnowledge 80 --maxParagraph 100 --maxQuestion 80 --topk 3 \
--modelname "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --randomSeed 0 \
--output "./rag_results.txt"[!NOTE] Approximate Tokens count corresponding to knowledge document size of "squad-train" and "hotpotqa-train" dataset.
datasets=("squad-train")
- when k = 3, tokens = 21,000
- when k = 4, tokens = 32,000
- when k = 7, tokens = 50,000
datasets=("hotpotqa-train")
- all k = 7405 article, tokens = 10,038,084
- when k = 1, tokens = 1,400
- when k = 16, tokens = 22,400
- when k = 24, tokens = 33,667
- when k = 32, tokens = 44,800
- when k = 48, tokens = 64,000
- when k = 64, tokens = 85,000
- when k = 80, tokens = 106,000
- when using "squad-train" dataset, 1 knowledge has average 150 questions
- when using "hotpotqa-train" dataset, 1 knowledge has 1 question
[!TIP] Since 1 document in "hotpoqa-train" dataset has only 1 question, it may not satisfy large-scale evaluation. Multiple evaluation could be a relatively better approach.
To build the docker image, run
docker build -t my-cag-app .and to run the container, run this for GPU users
docker run --gpus all -it --rm my-cag-appOR
docker run -it --rm my-cag-appfor CPU users.
if the .env file details were empty while building you will get error similar to this below
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/app/./kvcache.py", line 35, in <module>
env = validate_env_variables()
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "/app/./kvcache.py", line 31, in validate_env_variables
raise ValueError(f"Missing required environment variable: {key}")
ValueError: Missing required environment variable: HF_TOKENso ensure you populate the .env file before building the docker image
Note that the he CMD directive in the Dockerfile runs the kvcache.py script by default. You can override this in the docker run command if you'd like to execute other scripts like rag.py. For example:
docker run --gpus all -it --rm my-cag-app python ./rag.py --index "bm25" --dataset "hotpotqa-train" --similarity bertscore --maxKnowledge 80 --maxParagraph 100 --maxQuestion 80 --topk 3 --modelname "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct" --randomSeed 0 --output "./rag_results.txt"@misc{chan2024dontragcacheaugmentedgeneration,
title={Don't Do RAG: When Cache-Augmented Generation is All You Need for Knowledge Tasks},
author={Brian J Chan and Chao-Ting Chen and Jui-Hung Cheng and Hen-Hsen Huang},
year={2024},
eprint={2412.15605},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.15605},
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for CAG
Similar Open Source Tools

CAG
Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG) is an alternative paradigm to Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that eliminates real-time retrieval delays and errors by preloading all relevant resources into the model's context. CAG leverages extended context windows of large language models (LLMs) to generate responses directly, providing reduced latency, improved reliability, and simplified design. While CAG has limitations in knowledge size and context length, advancements in LLMs are addressing these issues, making CAG a practical and scalable alternative for complex applications.
hf-waitress
HF-Waitress is a powerful server application for deploying and interacting with HuggingFace Transformer models. It simplifies running open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) locally on-device, providing on-the-fly quantization via BitsAndBytes, HQQ, and Quanto. It requires no manual model downloads, offers concurrency, streaming responses, and supports various hardware and platforms. The server uses a `config.json` file for easy configuration management and provides detailed error handling and logging.
lionagi
LionAGI is a robust framework for orchestrating multi-step AI operations with precise control. It allows users to bring together multiple models, advanced reasoning, tool integrations, and custom validations in a single coherent pipeline. The framework is structured, expandable, controlled, and transparent, offering features like real-time logging, message introspection, and tool usage tracking. LionAGI supports advanced multi-step reasoning with ReAct, integrates with Anthropic's Model Context Protocol, and provides observability and debugging tools. Users can seamlessly orchestrate multiple models, integrate with Claude Code CLI SDK, and leverage a fan-out fan-in pattern for orchestration. The framework also offers optional dependencies for additional functionalities like reader tools, local inference support, rich output formatting, database support, and graph visualization.
effective_llm_alignment
This is a super customizable, concise, user-friendly, and efficient toolkit for training and aligning LLMs. It provides support for various methods such as SFT, Distillation, DPO, ORPO, CPO, SimPO, SMPO, Non-pair Reward Modeling, Special prompts basket format, Rejection Sampling, Scoring using RM, Effective FAISS Map-Reduce Deduplication, LLM scoring using RM, NER, CLIP, Classification, and STS. The toolkit offers key libraries like PyTorch, Transformers, TRL, Accelerate, FSDP, DeepSpeed, and tools for result logging with wandb or clearml. It allows mixing datasets, generation and logging in wandb/clearml, vLLM batched generation, and aligns models using the SMPO method.
LLM-Blender
LLM-Blender is a framework for ensembling large language models (LLMs) to achieve superior performance. It consists of two modules: PairRanker and GenFuser. PairRanker uses pairwise comparisons to distinguish between candidate outputs, while GenFuser merges the top-ranked candidates to create an improved output. LLM-Blender has been shown to significantly surpass the best LLMs and baseline ensembling methods across various metrics on the MixInstruct benchmark dataset.
stark
STaRK is a large-scale semi-structure retrieval benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases. It provides natural-sounding and practical queries crafted to incorporate rich relational information and complex textual properties, closely mirroring real-life scenarios. The benchmark aims to assess how effectively large language models can handle the interplay between textual and relational requirements in queries, using three diverse knowledge bases constructed from public sources.

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.

AirGym
AirGym is an open source Python quadrotor simulator based on IsaacGym, providing a high-fidelity dynamics and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) framework for quadrotor robot learning research. It offers a lightweight and customizable platform with strict alignment with PX4 logic, multiple control modes, and Sim-to-Real toolkits. Users can perform tasks such as Hovering, Balloon, Tracking, Avoid, and Planning, with the ability to create customized environments and tasks. The tool also supports training from scratch, visual encoding approaches, playing and testing of trained models, and customization of new tasks and assets.
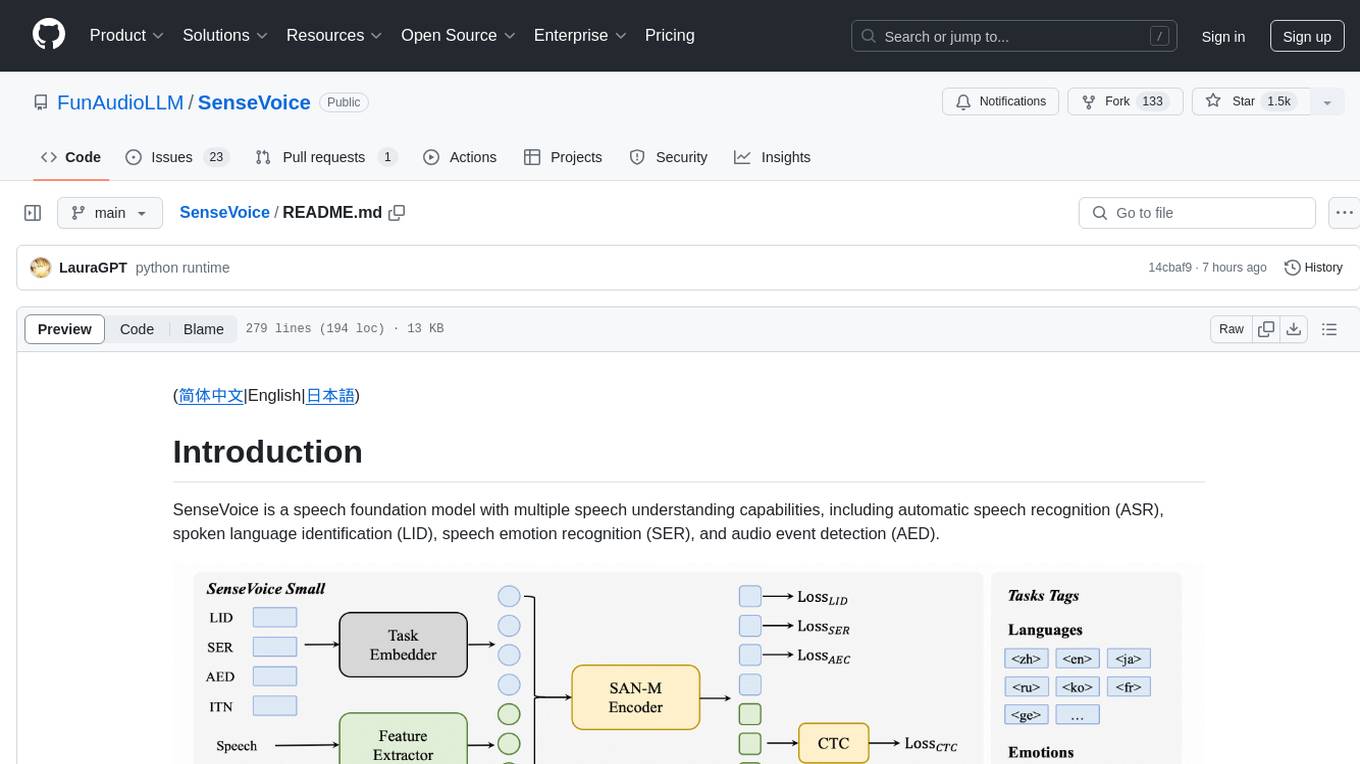
SenseVoice
SenseVoice is a speech foundation model focusing on high-accuracy multilingual speech recognition, speech emotion recognition, and audio event detection. Trained with over 400,000 hours of data, it supports more than 50 languages and excels in emotion recognition and sound event detection. The model offers efficient inference with low latency and convenient finetuning scripts. It can be deployed for service with support for multiple client-side languages. SenseVoice-Small model is open-sourced and provides capabilities for Mandarin, Cantonese, English, Japanese, and Korean. The tool also includes features for natural speech generation and fundamental speech recognition tasks.
consult-llm-mcp
Consult LLM MCP is an MCP server that enables users to consult powerful AI models like GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and DeepSeek Reasoner for complex problem-solving. It supports multi-turn conversations, direct queries with optional file context, git changes inclusion for code review, comprehensive logging with cost estimation, and various CLI modes for Gemini and Codex. The tool is designed to simplify the process of querying AI models for assistance in resolving coding issues and improving code quality.
semantic-cache
Semantic Cache is a tool for caching natural text based on semantic similarity. It allows for classifying text into categories, caching AI responses, and reducing API latency by responding to similar queries with cached values. The tool stores cache entries by meaning, handles synonyms, supports multiple languages, understands complex queries, and offers easy integration with Node.js applications. Users can set a custom proximity threshold for filtering results. The tool is ideal for tasks involving querying or retrieving information based on meaning, such as natural language classification or caching AI responses.

memobase
Memobase is a user profile-based memory system designed to enhance Generative AI applications by enabling them to remember, understand, and evolve with users. It provides structured user profiles, scalable profiling, easy integration with existing LLM stacks, batch processing for speed, and is production-ready. Users can manage users, insert data, get memory profiles, and track user preferences and behaviors. Memobase is ideal for applications that require user analysis, tracking, and personalized interactions.
KVCache-Factory
KVCache-Factory is a unified framework for KV Cache compression of diverse models. It supports multi-GPUs inference with big LLMs and various attention implementations. The tool enables KV cache compression without Flash Attention v2, multi-GPU inference, and specific models like Mistral. It also provides functions for KV cache budget allocation and batch inference. The visualization tools help in understanding the attention patterns of models.
pipelex
Pipelex is an open-source devtool designed to transform how users build repeatable AI workflows. It acts as a Docker or SQL for AI operations, allowing users to create modular 'pipes' using different LLMs for structured outputs. These pipes can be connected sequentially, in parallel, or conditionally to build complex knowledge transformations from reusable components. With Pipelex, users can share and scale proven methods instantly, saving time and effort in AI workflow development.
chatgpt-subtitle-translator
This tool utilizes the OpenAI ChatGPT API to translate text, with a focus on line-based translation, particularly for SRT subtitles. It optimizes token usage by removing SRT overhead and grouping text into batches, allowing for arbitrary length translations without excessive token consumption while maintaining a one-to-one match between line input and output.
langgraph4j
Langgraph4j is a Java library for language processing tasks such as text classification, sentiment analysis, and named entity recognition. It provides a set of tools and algorithms for analyzing text data and extracting useful information. The library is designed to be efficient and easy to use, making it suitable for both research and production applications.
For similar tasks
semantic-router
Semantic Router is a superfast decision-making layer for your LLMs and agents. Rather than waiting for slow LLM generations to make tool-use decisions, we use the magic of semantic vector space to make those decisions — _routing_ our requests using _semantic_ meaning.
hass-ollama-conversation
The Ollama Conversation integration adds a conversation agent powered by Ollama in Home Assistant. This agent can be used in automations to query information provided by Home Assistant about your house, including areas, devices, and their states. Users can install the integration via HACS and configure settings such as API timeout, model selection, context size, maximum tokens, and other parameters to fine-tune the responses generated by the AI language model. Contributions to the project are welcome, and discussions can be held on the Home Assistant Community platform.
luna-ai
Luna AI is a virtual streamer driven by a 'brain' composed of ChatterBot, GPT, Claude, langchain, chatglm, text-generation-webui, 讯飞星火, 智谱AI. It can interact with viewers in real-time during live streams on platforms like Bilibili, Douyin, Kuaishou, Douyu, or chat with you locally. Luna AI uses natural language processing and text-to-speech technologies like Edge-TTS, VITS-Fast, elevenlabs, bark-gui, VALL-E-X to generate responses to viewer questions and can change voice using so-vits-svc, DDSP-SVC. It can also collaborate with Stable Diffusion for drawing displays and loop custom texts. This project is completely free, and any identical copycat selling programs are pirated, please stop them promptly.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.

cria
Cria is a Python library designed for running Large Language Models with minimal configuration. It provides an easy and concise way to interact with LLMs, offering advanced features such as custom models, streams, message history management, and running multiple models in parallel. Cria simplifies the process of using LLMs by providing a straightforward API that requires only a few lines of code to get started. It also handles model installation automatically, making it efficient and user-friendly for various natural language processing tasks.
beyondllm
Beyond LLM offers an all-in-one toolkit for experimentation, evaluation, and deployment of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It simplifies the process with automated integration, customizable evaluation metrics, and support for various Large Language Models (LLMs) tailored to specific needs. The aim is to reduce LLM hallucination risks and enhance reliability.
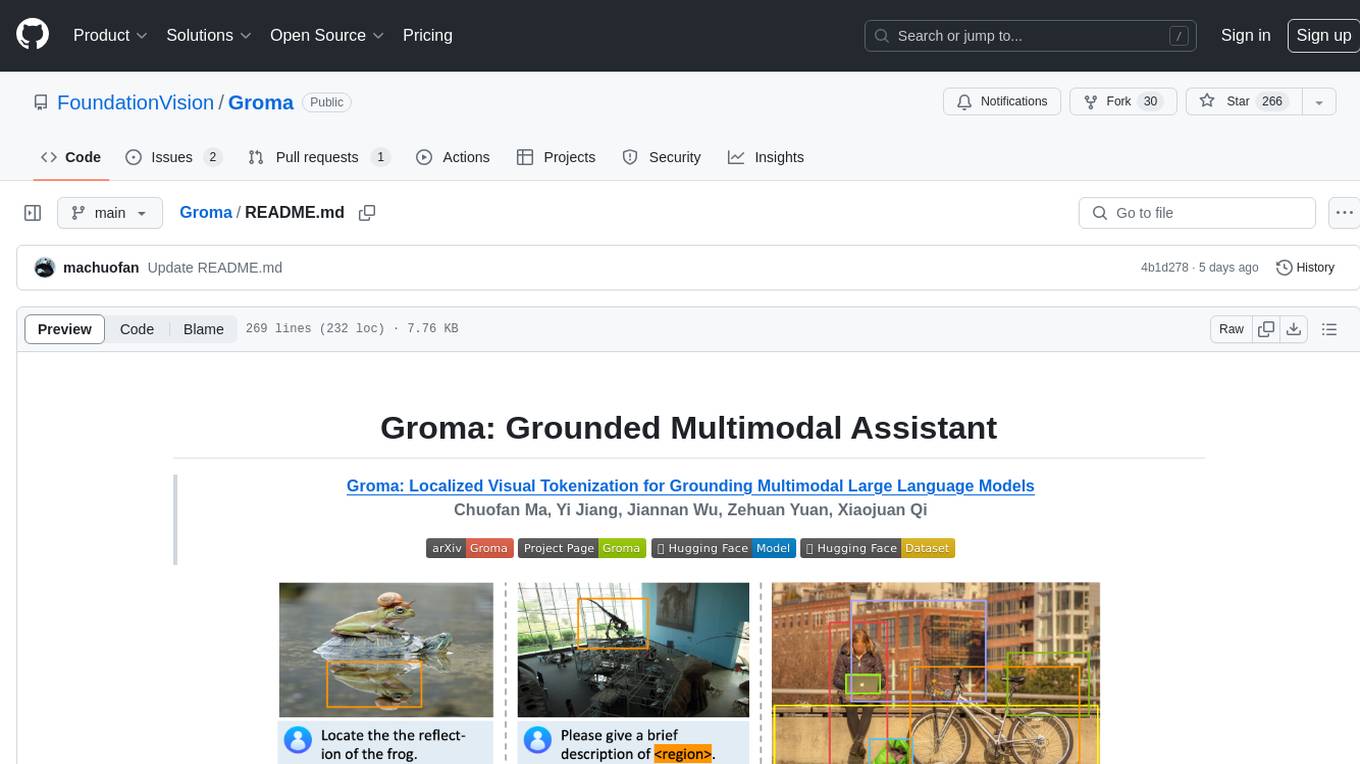
Groma
Groma is a grounded multimodal assistant that excels in region understanding and visual grounding. It can process user-defined region inputs and generate contextually grounded long-form responses. The tool presents a unique paradigm for multimodal large language models, focusing on visual tokenization for localization. Groma achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension benchmarks. The tool provides pretrained model weights and instructions for data preparation, training, inference, and evaluation. Users can customize training by starting from intermediate checkpoints. Groma is designed to handle tasks related to detection pretraining, alignment pretraining, instruction finetuning, instruction following, and more.
local-rag
Local RAG is an offline, open-source tool that allows users to ingest files for retrieval augmented generation (RAG) using large language models (LLMs) without relying on third parties or exposing sensitive data. It supports offline embeddings and LLMs, multiple sources including local files, GitHub repos, and websites, streaming responses, conversational memory, and chat export. Users can set up and deploy the app, learn how to use Local RAG, explore the RAG pipeline, check planned features, known bugs and issues, access additional resources, and contribute to the project.
For similar jobs
llmops-promptflow-template
LLMOps with Prompt flow is a template and guidance for building LLM-infused apps using Prompt flow. It provides centralized code hosting, lifecycle management, variant and hyperparameter experimentation, A/B deployment, many-to-many dataset/flow relationships, multiple deployment targets, comprehensive reporting, BYOF capabilities, configuration-based development, local prompt experimentation and evaluation, endpoint testing, and optional Human-in-loop validation. The tool is customizable to suit various application needs.
azure-search-vector-samples
This repository provides code samples in Python, C#, REST, and JavaScript for vector support in Azure AI Search. It includes demos for various languages showcasing vectorization of data, creating indexes, and querying vector data. Additionally, it offers tools like Azure AI Search Lab for experimenting with AI-enabled search scenarios in Azure and templates for deploying custom chat-with-your-data solutions. The repository also features documentation on vector search, hybrid search, creating and querying vector indexes, and REST API references for Azure AI Search and Azure OpenAI Service.
geti-sdk
The Intel® Geti™ SDK is a python package that enables teams to rapidly develop AI models by easing the complexities of model development and enhancing collaboration between teams. It provides tools to interact with an Intel® Geti™ server via the REST API, allowing for project creation, downloading, uploading, deploying for local inference with OpenVINO, setting project and model configuration, launching and monitoring training jobs, and media upload and prediction. The SDK also includes tutorial-style Jupyter notebooks demonstrating its usage.

booster
Booster is a powerful inference accelerator designed for scaling large language models within production environments or for experimental purposes. It is built with performance and scaling in mind, supporting various CPUs and GPUs, including Nvidia CUDA, Apple Metal, and OpenCL cards. The tool can split large models across multiple GPUs, offering fast inference on machines with beefy GPUs. It supports both regular FP16/FP32 models and quantised versions, along with popular LLM architectures. Additionally, Booster features proprietary Janus Sampling for code generation and non-English languages.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
amazon-transcribe-live-call-analytics
The Amazon Transcribe Live Call Analytics (LCA) with Agent Assist Sample Solution is designed to help contact centers assess and optimize caller experiences in real time. It leverages Amazon machine learning services like Amazon Transcribe, Amazon Comprehend, and Amazon SageMaker to transcribe and extract insights from contact center audio. The solution provides real-time supervisor and agent assist features, integrates with existing contact centers, and offers a scalable, cost-effective approach to improve customer interactions. The end-to-end architecture includes features like live call transcription, call summarization, AI-powered agent assistance, and real-time analytics. The solution is event-driven, ensuring low latency and seamless processing flow from ingested speech to live webpage updates.
ai-lab-recipes
This repository contains recipes for building and running containerized AI and LLM applications with Podman. It provides model servers that serve machine-learning models via an API, allowing developers to quickly prototype new AI applications locally. The recipes include components like model servers and AI applications for tasks such as chat, summarization, object detection, etc. Images for sample applications and models are available in `quay.io`, and bootable containers for AI training on Linux OS are enabled.
XLearning
XLearning is a scheduling platform for big data and artificial intelligence, supporting various machine learning and deep learning frameworks. It runs on Hadoop Yarn and integrates frameworks like TensorFlow, MXNet, Caffe, Theano, PyTorch, Keras, XGBoost. XLearning offers scalability, compatibility, multiple deep learning framework support, unified data management based on HDFS, visualization display, and compatibility with code at native frameworks. It provides functions for data input/output strategies, container management, TensorBoard service, and resource usage metrics display. XLearning requires JDK >= 1.7 and Maven >= 3.3 for compilation, and deployment on CentOS 7.2 with Java >= 1.7 and Hadoop 2.6, 2.7, 2.8.