
phidata
Build multi-modal Agents with memory, knowledge, tools and reasoning. Chat with them using a beautiful Agent UI.
Stars: 18266
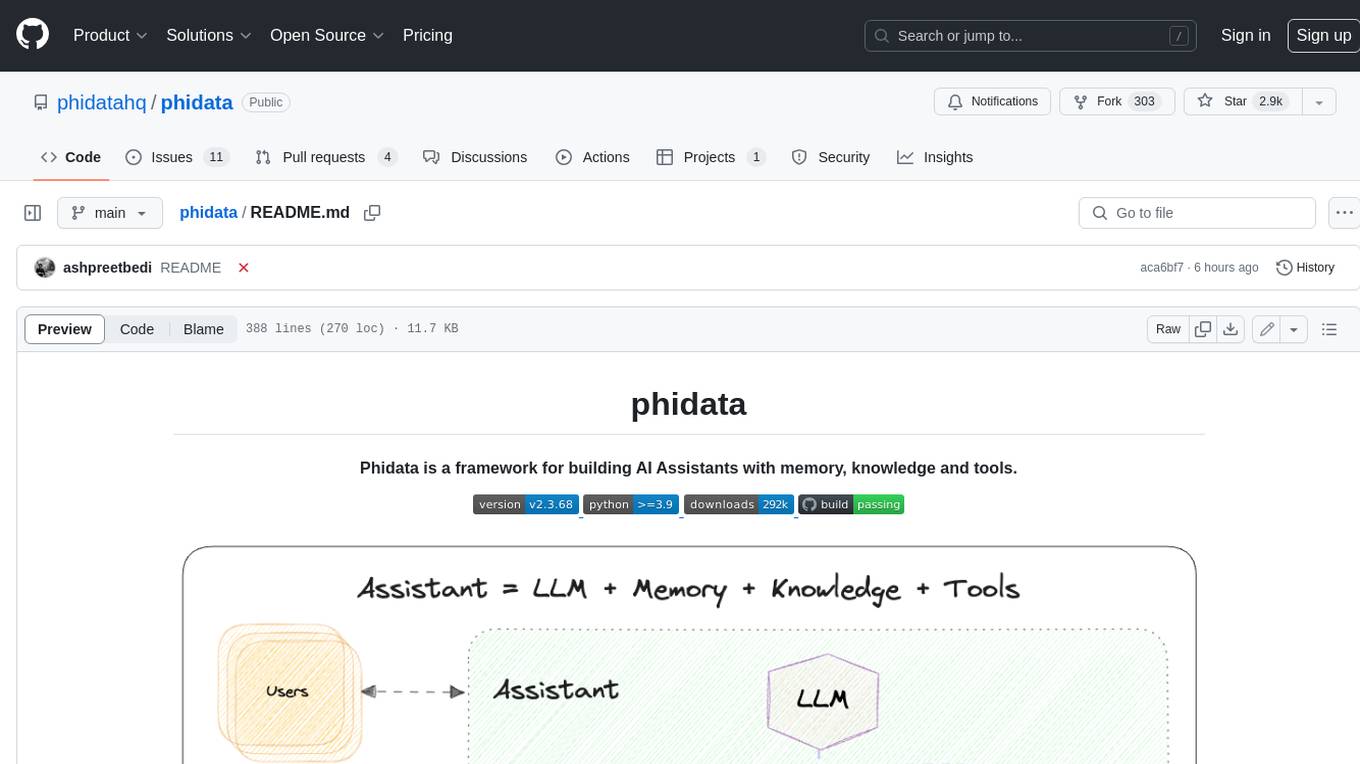
Phidata is a framework for building AI Assistants with memory, knowledge, and tools. It enables LLMs to have long-term conversations by storing chat history in a database, provides them with business context by storing information in a vector database, and enables them to take actions like pulling data from an API, sending emails, or querying a database. Memory and knowledge make LLMs smarter, while tools make them autonomous.
README:
Phidata is a framework for building multi-modal agents, use phidata to:
- Build multi-modal agents with memory, knowledge, tools and reasoning.
- Build teams of agents that can work together to solve problems.
- Chat with your agents using a beautiful Agent UI.
pip install -U phidata- Simple & Elegant
- Powerful & Flexible
- Multi-Modal by default
- Multi-Agent orchestration
- A beautiful Agent UI to chat with your agents
- Agentic RAG built-in
- Structured Outputs
- Reasoning Agents
- Monitoring & Debugging built-in
- Demo Agents
Phidata Agents are simple and elegant, resulting in minimal, beautiful code.
For example, you can create a web search agent in 10 lines of code, create a file web_search.py
from phi.agent import Agent
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
from phi.tools.duckduckgo import DuckDuckGo
web_agent = Agent(
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
tools=[DuckDuckGo()],
instructions=["Always include sources"],
show_tool_calls=True,
markdown=True,
)
web_agent.print_response("Tell me about OpenAI Sora?", stream=True)Install libraries, export your OPENAI_API_KEY and run the Agent:
pip install phidata openai duckduckgo-search
export OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-xxxx
python web_search.pyPhidata agents can use multiple tools and follow instructions to achieve complex tasks.
For example, you can create a finance agent with tools to query financial data, create a file finance_agent.py
from phi.agent import Agent
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
from phi.tools.yfinance import YFinanceTools
finance_agent = Agent(
name="Finance Agent",
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
tools=[YFinanceTools(stock_price=True, analyst_recommendations=True, company_info=True, company_news=True)],
instructions=["Use tables to display data"],
show_tool_calls=True,
markdown=True,
)
finance_agent.print_response("Summarize analyst recommendations for NVDA", stream=True)Install libraries and run the Agent:
pip install yfinance
python finance_agent.pyPhidata agents support text, images, audio and video.
For example, you can create an image agent that can understand images and make tool calls as needed, create a file image_agent.py
from phi.agent import Agent
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
from phi.tools.duckduckgo import DuckDuckGo
agent = Agent(
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
tools=[DuckDuckGo()],
markdown=True,
)
agent.print_response(
"Tell me about this image and give me the latest news about it.",
images=["https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/bf/Krakow_-_Kosciol_Mariacki.jpg"],
stream=True,
)Run the Agent:
python image_agent.pyPhidata agents can work together as a team to achieve complex tasks, create a file agent_team.py
from phi.agent import Agent
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
from phi.tools.duckduckgo import DuckDuckGo
from phi.tools.yfinance import YFinanceTools
web_agent = Agent(
name="Web Agent",
role="Search the web for information",
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
tools=[DuckDuckGo()],
instructions=["Always include sources"],
show_tool_calls=True,
markdown=True,
)
finance_agent = Agent(
name="Finance Agent",
role="Get financial data",
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
tools=[YFinanceTools(stock_price=True, analyst_recommendations=True, company_info=True)],
instructions=["Use tables to display data"],
show_tool_calls=True,
markdown=True,
)
agent_team = Agent(
team=[web_agent, finance_agent],
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
instructions=["Always include sources", "Use tables to display data"],
show_tool_calls=True,
markdown=True,
)
agent_team.print_response("Summarize analyst recommendations and share the latest news for NVDA", stream=True)Run the Agent team:
python agent_team.pyPhidata provides a beautiful UI for interacting with your agents. Let's take it for a spin, create a file playground.py
[!NOTE] Phidata does not store any data, all agent data is stored locally in a sqlite database.
from phi.agent import Agent
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
from phi.storage.agent.sqlite import SqlAgentStorage
from phi.tools.duckduckgo import DuckDuckGo
from phi.tools.yfinance import YFinanceTools
from phi.playground import Playground, serve_playground_app
web_agent = Agent(
name="Web Agent",
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
tools=[DuckDuckGo()],
instructions=["Always include sources"],
storage=SqlAgentStorage(table_name="web_agent", db_file="agents.db"),
add_history_to_messages=True,
markdown=True,
)
finance_agent = Agent(
name="Finance Agent",
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
tools=[YFinanceTools(stock_price=True, analyst_recommendations=True, company_info=True, company_news=True)],
instructions=["Use tables to display data"],
storage=SqlAgentStorage(table_name="finance_agent", db_file="agents.db"),
add_history_to_messages=True,
markdown=True,
)
app = Playground(agents=[finance_agent, web_agent]).get_app()
if __name__ == "__main__":
serve_playground_app("playground:app", reload=True)Authenticate with phidata by running the following command:
phi author by exporting the PHI_API_KEY for your workspace from phidata.app
export PHI_API_KEY=phi-***Install dependencies and run the Agent Playground:
pip install 'fastapi[standard]' sqlalchemy
python playground.py
- Open the link provided or navigate to
http://phidata.app/playground - Select the
localhost:7777endpoint and start chatting with your agents!
We were the first to pioneer Agentic RAG using our Auto-RAG paradigm. With Agentic RAG (or auto-rag), the Agent can search its knowledge base (vector db) for the specific information it needs to achieve its task, instead of always inserting the "context" into the prompt.
This saves tokens and improves response quality. Create a file rag_agent.py
from phi.agent import Agent
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
from phi.embedder.openai import OpenAIEmbedder
from phi.knowledge.pdf import PDFUrlKnowledgeBase
from phi.vectordb.lancedb import LanceDb, SearchType
# Create a knowledge base from a PDF
knowledge_base = PDFUrlKnowledgeBase(
urls=["https://phi-public.s3.amazonaws.com/recipes/ThaiRecipes.pdf"],
# Use LanceDB as the vector database
vector_db=LanceDb(
table_name="recipes",
uri="tmp/lancedb",
search_type=SearchType.vector,
embedder=OpenAIEmbedder(model="text-embedding-3-small"),
),
)
# Comment out after first run as the knowledge base is loaded
knowledge_base.load()
agent = Agent(
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
# Add the knowledge base to the agent
knowledge=knowledge_base,
show_tool_calls=True,
markdown=True,
)
agent.print_response("How do I make chicken and galangal in coconut milk soup", stream=True)Install libraries and run the Agent:
pip install lancedb tantivy pypdf sqlalchemy
python rag_agent.pyAgents can return their output in a structured format as a Pydantic model.
Create a file structured_output.py
from typing import List
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from phi.agent import Agent
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
# Define a Pydantic model to enforce the structure of the output
class MovieScript(BaseModel):
setting: str = Field(..., description="Provide a nice setting for a blockbuster movie.")
ending: str = Field(..., description="Ending of the movie. If not available, provide a happy ending.")
genre: str = Field(..., description="Genre of the movie. If not available, select action, thriller or romantic comedy.")
name: str = Field(..., description="Give a name to this movie")
characters: List[str] = Field(..., description="Name of characters for this movie.")
storyline: str = Field(..., description="3 sentence storyline for the movie. Make it exciting!")
# Agent that uses JSON mode
json_mode_agent = Agent(
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
description="You write movie scripts.",
response_model=MovieScript,
)
# Agent that uses structured outputs
structured_output_agent = Agent(
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
description="You write movie scripts.",
response_model=MovieScript,
structured_outputs=True,
)
json_mode_agent.print_response("New York")
structured_output_agent.print_response("New York")- Run the
structured_output.pyfile
python structured_output.py- The output is an object of the
MovieScriptclass, here's how it looks:
MovieScript(
│ setting='A bustling and vibrant New York City',
│ ending='The protagonist saves the city and reconciles with their estranged family.',
│ genre='action',
│ name='City Pulse',
│ characters=['Alex Mercer', 'Nina Castillo', 'Detective Mike Johnson'],
│ storyline='In the heart of New York City, a former cop turned vigilante, Alex Mercer, teams up with a street-smart activist, Nina Castillo, to take down a corrupt political figure who threatens to destroy the city. As they navigate through the intricate web of power and deception, they uncover shocking truths that push them to the brink of their abilities. With time running out, they must race against the clock to save New York and confront their own demons.'
)Reasoning helps agents work through a problem step-by-step, backtracking and correcting as needed. Create a file reasoning_agent.py.
from phi.agent import Agent
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
task = (
"Three missionaries and three cannibals need to cross a river. "
"They have a boat that can carry up to two people at a time. "
"If, at any time, the cannibals outnumber the missionaries on either side of the river, the cannibals will eat the missionaries. "
"How can all six people get across the river safely? Provide a step-by-step solution and show the solutions as an ascii diagram"
)
reasoning_agent = Agent(model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"), reasoning=True, markdown=True, structured_outputs=True)
reasoning_agent.print_response(task, stream=True, show_full_reasoning=True)Run the Reasoning Agent:
python reasoning_agent.py[!WARNING] Reasoning is an experimental feature and will break ~20% of the time. It is not a replacement for o1.
It is an experiment fueled by curiosity, combining COT and tool use. Set your expectations very low for this initial release. For example: It will not be able to count ‘r’s in ‘strawberry’.
The Agent Playground includes a few demo agents that you can test with. If you have recommendations for other demo agents, please let us know in our community forum.
Phidata comes with built-in monitoring. You can set monitoring=True on any agent to track sessions or set PHI_MONITORING=true in your environment.
[!NOTE] Run
phi authto authenticate your local account or export thePHI_API_KEY
from phi.agent import Agent
agent = Agent(markdown=True, monitoring=True)
agent.print_response("Share a 2 sentence horror story")Run the agent and monitor the results on phidata.app/sessions
# You can also set the environment variable
# export PHI_MONITORING=true
python monitoring.pyView the agent session on phidata.app/sessions
Phidata also includes a built-in debugger that will show debug logs in the terminal. You can set debug_mode=True on any agent to track sessions or set PHI_DEBUG=true in your environment.
from phi.agent import Agent
agent = Agent(markdown=True, debug_mode=True)
agent.print_response("Share a 2 sentence horror story")- Read the docs at docs.phidata.com
- Post your questions on the community forum
- Chat with us on discord
Show code
The PythonAgent can achieve tasks by writing and running python code.
- Create a file
python_agent.py
from phi.agent.python import PythonAgent
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
from phi.file.local.csv import CsvFile
python_agent = PythonAgent(
model=OpenAIChat(id="gpt-4o"),
files=[
CsvFile(
path="https://phidata-public.s3.amazonaws.com/demo_data/IMDB-Movie-Data.csv",
description="Contains information about movies from IMDB.",
)
],
markdown=True,
pip_install=True,
show_tool_calls=True,
)
python_agent.print_response("What is the average rating of movies?")- Run the
python_agent.py
python python_agent.pyShow code
The DuckDbAgent can perform data analysis using SQL.
- Create a file
data_analyst.py
import json
from phi.model.openai import OpenAIChat
from phi.agent.duckdb import DuckDbAgent
data_analyst = DuckDbAgent(
model=OpenAIChat(model="gpt-4o"),
markdown=True,
semantic_model=json.dumps(
{
"tables": [
{
"name": "movies",
"description": "Contains information about movies from IMDB.",
"path": "https://phidata-public.s3.amazonaws.com/demo_data/IMDB-Movie-Data.csv",
}
]
},
indent=2,
),
)
data_analyst.print_response(
"Show me a histogram of ratings. "
"Choose an appropriate bucket size but share how you chose it. "
"Show me the result as a pretty ascii diagram",
stream=True,
)- Install duckdb and run the
data_analyst.pyfile
pip install duckdb
python data_analyst.pyCheck out the cookbook for more examples.
We're an open-source project and welcome contributions, please read the contributing guide for more information.
- If you have a feature request, please open an issue or make a pull request.
- If you have ideas on how we can improve, please create a discussion.
Phidata logs which model an agent used so we can prioritize features for the most popular models.
You can disable this by setting PHI_TELEMETRY=false in your environment.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for phidata
Similar Open Source Tools

phidata
Phidata is a framework for building AI Assistants with memory, knowledge, and tools. It enables LLMs to have long-term conversations by storing chat history in a database, provides them with business context by storing information in a vector database, and enables them to take actions like pulling data from an API, sending emails, or querying a database. Memory and knowledge make LLMs smarter, while tools make them autonomous.
vinagent
Vinagent is a lightweight and flexible library designed for building smart agent assistants across various industries. It provides a simple yet powerful foundation for creating AI-powered customer service bots, data analysis assistants, or domain-specific automation agents. With its modular tool system, users can easily extend their agent's capabilities by integrating a wide range of tools that are self-contained, well-documented, and can be registered dynamically. Vinagent allows users to scale and adapt their agents to new tasks or environments effortlessly.
simpleAI
SimpleAI is a self-hosted alternative to the not-so-open AI API, focused on replicating main endpoints for LLM such as text completion, chat, edits, and embeddings. It allows quick experimentation with different models, creating benchmarks, and handling specific use cases without relying on external services. Users can integrate and declare models through gRPC, query endpoints using Swagger UI or API, and resolve common issues like CORS with FastAPI middleware. The project is open for contributions and welcomes PRs, issues, documentation, and more.
npcsh
`npcsh` is a python-based command-line tool designed to integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) and Agents into one's daily workflow by making them available and easily configurable through the command line shell. It leverages the power of LLMs to understand natural language commands and questions, execute tasks, answer queries, and provide relevant information from local files and the web. Users can also build their own tools and call them like macros from the shell. `npcsh` allows users to take advantage of agents (i.e. NPCs) through a managed system, tailoring NPCs to specific tasks and workflows. The tool is extensible with Python, providing useful functions for interacting with LLMs, including explicit coverage for popular providers like ollama, anthropic, openai, gemini, deepseek, and openai-like providers. Users can set up a flask server to expose their NPC team for use as a backend service, run SQL models defined in their project, execute assembly lines, and verify the integrity of their NPC team's interrelations. Users can execute bash commands directly, use favorite command-line tools like VIM, Emacs, ipython, sqlite3, git, pipe the output of these commands to LLMs, or pass LLM results to bash commands.

cria
Cria is a Python library designed for running Large Language Models with minimal configuration. It provides an easy and concise way to interact with LLMs, offering advanced features such as custom models, streams, message history management, and running multiple models in parallel. Cria simplifies the process of using LLMs by providing a straightforward API that requires only a few lines of code to get started. It also handles model installation automatically, making it efficient and user-friendly for various natural language processing tasks.
agentlang
AgentLang is an open-source programming language and framework designed for solving complex tasks with the help of AI agents. It allows users to build business applications rapidly from high-level specifications, making it more efficient than traditional programming languages. The language is data-oriented and declarative, with a syntax that is intuitive and closer to natural languages. AgentLang introduces innovative concepts such as first-class AI agents, graph-based hierarchical data model, zero-trust programming, declarative dataflow, resolvers, interceptors, and entity-graph-database mapping.
swarmzero
SwarmZero SDK is a library that simplifies the creation and execution of AI Agents and Swarms of Agents. It supports various LLM Providers such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Anthropic, MistralAI, Gemini, Nebius, and Ollama. Users can easily install the library using pip or poetry, set up the environment and configuration, create and run Agents, collaborate with Swarms, add tools for complex tasks, and utilize retriever tools for semantic information retrieval. Sample prompts are provided to help users explore the capabilities of the agents and swarms. The SDK also includes detailed examples and documentation for reference.
Hurley-AI
Hurley AI is a next-gen framework for developing intelligent agents through Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents, supports various agent types, and includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal. Hurley AI integrates with LLM inference services and provides observability with Arize Phoenix. Users can create Hurley RAG tools with a single line of code and customize agents with specific instructions. The tool also offers various helper functions to connect with Hurley RAG and search tools, along with pre-built tools for tasks like summarizing text, rephrasing text, understanding memecoins, and querying databases.
perplexity-ai
Perplexity is a module that utilizes emailnator to generate new accounts, providing users with 5 pro queries per account creation. It enables the creation of new Gmail accounts with emailnator, ensuring unlimited pro queries. The tool requires specific Python libraries for installation and offers both a web interface and an API for different usage scenarios. Users can interact with the tool to perform various tasks such as account creation, query searches, and utilizing different modes for research purposes. Perplexity also supports asynchronous operations and provides guidance on obtaining cookies for account usage and account generation from emailnator.

memobase
Memobase is a user profile-based memory system designed to enhance Generative AI applications by enabling them to remember, understand, and evolve with users. It provides structured user profiles, scalable profiling, easy integration with existing LLM stacks, batch processing for speed, and is production-ready. Users can manage users, insert data, get memory profiles, and track user preferences and behaviors. Memobase is ideal for applications that require user analysis, tracking, and personalized interactions.
magentic
Easily integrate Large Language Models into your Python code. Simply use the `@prompt` and `@chatprompt` decorators to create functions that return structured output from the LLM. Mix LLM queries and function calling with regular Python code to create complex logic.
MiniAgents
MiniAgents is an open-source Python framework designed to simplify the creation of multi-agent AI systems. It offers a parallelism and async-first design, allowing users to focus on building intelligent agents while handling concurrency challenges. The framework, built on asyncio, supports LLM-based applications with immutable messages and seamless asynchronous token and message streaming between agents.
invariant
Invariant Analyzer is an open-source scanner designed for LLM-based AI agents to find bugs, vulnerabilities, and security threats. It scans agent execution traces to identify issues like looping behavior, data leaks, prompt injections, and unsafe code execution. The tool offers a library of built-in checkers, an expressive policy language, data flow analysis, real-time monitoring, and extensible architecture for custom checkers. It helps developers debug AI agents, scan for security violations, and prevent security issues and data breaches during runtime. The analyzer leverages deep contextual understanding and a purpose-built rule matching engine for security policy enforcement.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
openai
An open-source client package that allows developers to easily integrate the power of OpenAI's state-of-the-art AI models into their Dart/Flutter applications. The library provides simple and intuitive methods for making requests to OpenAI's various APIs, including the GPT-3 language model, DALL-E image generation, and more. It is designed to be lightweight and easy to use, enabling developers to focus on building their applications without worrying about the complexities of dealing with HTTP requests. Note that this is an unofficial library as OpenAI does not have an official Dart library.
agent-mimir
Agent Mimir is a command line and Discord chat client 'agent' manager for LLM's like Chat-GPT that provides the models with access to tooling and a framework with which accomplish multi-step tasks. It is easy to configure your own agent with a custom personality or profession as well as enabling access to all tools that are compatible with LangchainJS. Agent Mimir is based on LangchainJS, every tool or LLM that works on Langchain should also work with Mimir. The tasking system is based on Auto-GPT and BabyAGI where the agent needs to come up with a plan, iterate over its steps and review as it completes the task.
For similar tasks

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.

jupyter-ai
Jupyter AI connects generative AI with Jupyter notebooks. It provides a user-friendly and powerful way to explore generative AI models in notebooks and improve your productivity in JupyterLab and the Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, Jupyter AI offers: * An `%%ai` magic that turns the Jupyter notebook into a reproducible generative AI playground. This works anywhere the IPython kernel runs (JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab, Kaggle, VSCode, etc.). * A native chat UI in JupyterLab that enables you to work with generative AI as a conversational assistant. * Support for a wide range of generative model providers, including AI21, Anthropic, AWS, Cohere, Gemini, Hugging Face, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. * Local model support through GPT4All, enabling use of generative AI models on consumer grade machines with ease and privacy.

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
