
pg_vectorize
The simplest way to build AI workloads on Postgres
Stars: 768
pg_vectorize is a Postgres extension that automates text to embeddings transformation, enabling vector search and LLM applications with minimal function calls. It integrates with popular LLMs, provides workflows for vector search and RAG, and automates Postgres triggers for updating embeddings. The tool is part of the VectorDB Stack on Tembo Cloud, offering high-level APIs for easy initialization and search.
README:
A Postgres extension that automates the transformation and orchestration of text to embeddings and provides hooks into the most popular LLMs. This allows you to do vector search and build LLM applications on existing data with as little as two function calls.
This project relies heavily on the work by pgvector for vector similarity search, pgmq for orchestration in background workers, and SentenceTransformers.
pg_vectorize powers the VectorDB Stack on Tembo Cloud and is available in all hobby tier instances.
API Documentation: https://tembo.io/pg_vectorize/
Source: https://github.com/tembo-io/pg_vectorize
- Workflows for both vector search and RAG
- Integrations with OpenAI's embeddings and Text-Generation endpoints and a self-hosted container for running Hugging Face Sentence-Transformers
- Automated creation of Postgres triggers to keep your embeddings up to date
- High level API - one function to initialize embeddings transformations, and another function to search
- Features
- Table of Contents
- Installation
- Vector Search Example
- RAG Example
- Updating Embeddings
- Directly Interact with LLMs
- Importing Pre-existing Embeddings
- Creating a Table from Existing Embeddings
The fastest way to get started is by running the Tembo docker container and the vector server with docker compose:
docker compose up -dThen connect to Postgres:
docker compose exec -it postgres psql
Enable the extension and its dependencies
CREATE EXTENSION vectorize CASCADE;Install into an existing Postgres instance
If you're installing in an existing Postgres instance, you will need the following dependencies:
Rust:
Postgres Extensions:
Then set the following either in postgresql.conf or as a configuration parameter:
-- requires restart of Postgres
alter system set shared_preload_libraries = 'vectorize,pg_cron';
alter system set cron.database_name = 'postgres';And if you're running the vector-serve container, set the following url as a configuration parameter in Postgres.
The host may need to change from localhost to something else depending on where you are running the container.
alter system set vectorize.embedding_service_url = 'http://localhost:3000/v1';
SELECT pg_reload_conf();Text-to-embedding transformation can be done with either Hugging Face's Sentence-Transformers or OpenAI's embeddings. The following examples use Hugging Face's Sentence-Transformers. See the project documentation for OpenAI examples.
Follow the installation steps if you haven't already.
Setup a products table. Copy from the example data provided by the extension.
CREATE TABLE products (LIKE vectorize.example_products INCLUDING ALL);
INSERT INTO products SELECT * FROM vectorize.example_products;SELECT * FROM products limit 2; product_id | product_name | description | last_updated_at
------------+--------------+--------------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------
1 | Pencil | Utensil used for writing and often works best on paper | 2023-07-26 17:20:43.639351-05
2 | Laptop Stand | Elevated platform for laptops, enhancing ergonomics | 2023-07-26 17:20:43.639351-05
Create a job to vectorize the products table. We'll specify the tables primary key (product_id) and the columns that we want to search (product_name and description).
SELECT vectorize.table(
job_name => 'product_search_hf',
relation => 'products',
primary_key => 'product_id',
columns => ARRAY['product_name', 'description'],
transformer => 'sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2',
schedule => 'realtime'
);This adds a new column to your table, in our case it is named product_search_embeddings, then populates that data with the transformed embeddings from the product_name and description columns.
Then search,
SELECT * FROM vectorize.search(
job_name => 'product_search_hf',
query => 'accessories for mobile devices',
return_columns => ARRAY['product_id', 'product_name'],
num_results => 3
); search_results
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{"product_id": 13, "product_name": "Phone Charger", "similarity_score": 0.8147814132322894}
{"product_id": 6, "product_name": "Backpack", "similarity_score": 0.7743061352550308}
{"product_id": 11, "product_name": "Stylus Pen", "similarity_score": 0.7709902653575383}
Ask raw text questions of the example products dataset and get chat responses from an OpenAI LLM.
Follow the installation steps if you haven't already.
Set the OpenAI API key, this is required to for use with OpenAI's chat-completion models.
ALTER SYSTEM SET vectorize.openai_key TO '<your api key>';
SELECT pg_reload_conf();Create an example table if it does not already exist.
CREATE TABLE products (LIKE vectorize.example_products INCLUDING ALL);
INSERT INTO products SELECT * FROM vectorize.example_products;Initialize a table for RAG. We'll use an open source Sentence Transformer to generate embeddings.
Create a new column that we want to use as the context. In this case, we'll concatenate both product_name and description.
ALTER TABLE products
ADD COLUMN context TEXT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (product_name || ': ' || description) STORED;Initialize the RAG project.
We'll use the openai/text-embedding-3-small model to generate embeddings on our source documents.
SELECT vectorize.table(
job_name => 'product_chat',
relation => 'products',
primary_key => 'product_id',
columns => ARRAY['context'],
transformer => 'openai/text-embedding-3-small',
schedule => 'realtime'
);Now we can ask questions of the products table and get responses from the product_chat agent using the openai/gpt-3.5-turbo generative model.
SELECT vectorize.rag(
job_name => 'product_chat',
query => 'What is a pencil?',
chat_model => 'openai/gpt-3.5-turbo'
) -> 'chat_response';"A pencil is an item that is commonly used for writing and is known to be most effective on paper."
And to use a locally hosted Ollama service, change the chat_model parameter:
SELECT vectorize.rag(
job_name => 'product_chat',
query => 'What is a pencil?',
chat_model => 'ollama/wizardlm2:7b'
) -> 'chat_response';" A pencil is a writing instrument that consists of a solid or gelignola wood core, known as the \"lead,\" encased in a cylindrical piece of breakable material (traditionally wood or plastic), which serves as the body of the pencil. The tip of the body is tapered to a point for writing, and it can mark paper with the imprint of the lead. When used on a sheet of paper, the combination of the pencil's lead and the paper creates a visible mark that is distinct from unmarked areas of the paper. Pencils are particularly well-suited for writing on paper, as they allow for precise control over the marks made."
💡 Note that the -> 'chat_response' addition selects for that field of the JSON object output. Removing it will show the full JSON object, including information on which documents were included in the contextual prompt.
When the source text data is updated, how and when the embeddings are updated is determined by the value set to the schedule parameter in vectorize.table.
The default behavior is schedule => '* * * * *', which means the background worker process checks for changes every minute, and updates the embeddings accordingly. This method requires setting the updated_at_col value to point to a colum on the table indicating the time that the input text columns were last changed. schedule can be set to any cron-like value.
Alternatively, schedule => 'realtime creates triggers on the source table and updates embeddings anytime new records are inserted to the source table or existing records are updated.
Statements below would will result in new embeddings being generated either immediately (schedule => 'realtime') or within the cron schedule set in the schedule parameter.
INSERT INTO products (product_id, product_name, description, product_category, price)
VALUES (12345, 'pizza', 'dish of Italian origin consisting of a flattened disk of bread', 'food', 5.99);
UPDATE products
SET description = 'sling made of fabric, rope, or netting, suspended between two or more points, used for swinging, sleeping, or resting'
WHERE product_name = 'Hammock';Sometimes you want more control over the handling of embeddings. For those situations you can directly call various LLM providers using SQL:
For text generation:
select vectorize.generate(
input => 'Tell me the difference between a cat and a dog in 1 sentence',
model => 'openai/gpt-4o'
); generate
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cats are generally more independent and solitary, while dogs tend to be more social and loyal companions.
(1 row)
And for embedding generation:
select vectorize.encode(
input => 'Tell me the difference between a cat and a dog in 1 sentence',
model => 'openai/text-embedding-3-large'
);{0.0028769304,-0.005826319,-0.0035932811, ...}
If you have already computed embeddings using a compatible model (e.g., using Sentence-Transformers directly), you can import these into pg_vectorize without recomputation:
-- First create the vectorize project
SELECT vectorize.table(
job_name => 'my_search',
relation => 'my_table',
primary_key => 'id',
columns => ARRAY['content'],
transformer => 'sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2'
);
-- Then import your pre-computed embeddings
SELECT vectorize.import_embeddings(
job_name => 'my_search',
src_table => 'my_embeddings_table',
src_primary_key => 'id',
src_embeddings_col => 'embedding'
);The embeddings must match the dimensions of the specified transformer model. For example, 'sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2' expects 384-dimensional vectors.
If you have already computed embeddings using a compatible model, you can create a new vectorize table directly from them:
-- Create a vectorize table from existing embeddings
SELECT vectorize.table_from(
relation => 'my_table',
columns => ARRAY['content'],
job_name => 'my_search',
primary_key => 'id',
src_table => 'my_embeddings_table',
src_primary_key => 'id',
src_embeddings_col => 'embedding',
transformer => 'sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2'
);The embeddings must match the dimensions of the specified transformer model. This approach ensures your pre-computed embeddings are properly imported before any automatic updates are enabled.
We welcome contributions from the community! If you're interested in contributing to pg_vectorize, please check out our Contributing Guide. Your contributions help make this project better for everyone.
If you encounter any issues or have any questions, feel free to join our Tembo Community Slack. We're here to help!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for pg_vectorize
Similar Open Source Tools

pg_vectorize
pg_vectorize is a Postgres extension that automates text to embeddings transformation, enabling vector search and LLM applications with minimal function calls. It integrates with popular LLMs, provides workflows for vector search and RAG, and automates Postgres triggers for updating embeddings. The tool is part of the VectorDB Stack on Tembo Cloud, offering high-level APIs for easy initialization and search.
vinagent
Vinagent is a lightweight and flexible library designed for building smart agent assistants across various industries. It provides a simple yet powerful foundation for creating AI-powered customer service bots, data analysis assistants, or domain-specific automation agents. With its modular tool system, users can easily extend their agent's capabilities by integrating a wide range of tools that are self-contained, well-documented, and can be registered dynamically. Vinagent allows users to scale and adapt their agents to new tasks or environments effortlessly.
npcsh
`npcsh` is a python-based command-line tool designed to integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) and Agents into one's daily workflow by making them available and easily configurable through the command line shell. It leverages the power of LLMs to understand natural language commands and questions, execute tasks, answer queries, and provide relevant information from local files and the web. Users can also build their own tools and call them like macros from the shell. `npcsh` allows users to take advantage of agents (i.e. NPCs) through a managed system, tailoring NPCs to specific tasks and workflows. The tool is extensible with Python, providing useful functions for interacting with LLMs, including explicit coverage for popular providers like ollama, anthropic, openai, gemini, deepseek, and openai-like providers. Users can set up a flask server to expose their NPC team for use as a backend service, run SQL models defined in their project, execute assembly lines, and verify the integrity of their NPC team's interrelations. Users can execute bash commands directly, use favorite command-line tools like VIM, Emacs, ipython, sqlite3, git, pipe the output of these commands to LLMs, or pass LLM results to bash commands.
extractor
Extractor is an AI-powered data extraction library for Laravel that leverages OpenAI's capabilities to effortlessly extract structured data from various sources, including images, PDFs, and emails. It features a convenient wrapper around OpenAI Chat and Completion endpoints, supports multiple input formats, includes a flexible Field Extractor for arbitrary data extraction, and integrates with Textract for OCR functionality. Extractor utilizes JSON Mode from the latest GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models, providing accurate and efficient data extraction.
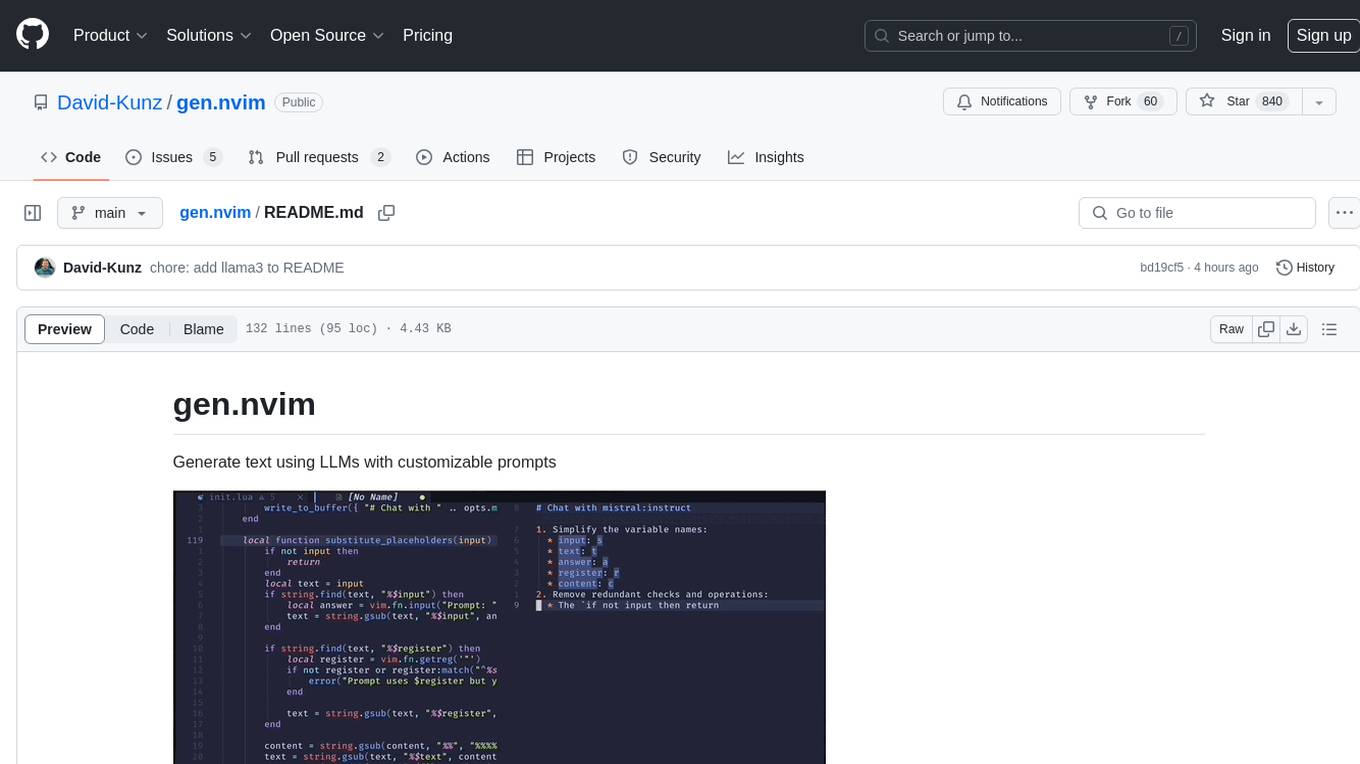
gen.nvim
gen.nvim is a tool that allows users to generate text using Language Models (LLMs) with customizable prompts. It requires Ollama with models like `llama3`, `mistral`, or `zephyr`, along with Curl for installation. Users can use the `Gen` command to generate text based on predefined or custom prompts. The tool provides key maps for easy invocation and allows for follow-up questions during conversations. Additionally, users can select a model from a list of installed models and customize prompts as needed.
magentic
Easily integrate Large Language Models into your Python code. Simply use the `@prompt` and `@chatprompt` decorators to create functions that return structured output from the LLM. Mix LLM queries and function calling with regular Python code to create complex logic.

Toolio
Toolio is an OpenAI-like HTTP server API implementation that supports structured LLM response generation, making it conform to a JSON schema. It is useful for reliable tool calling and agentic workflows based on schema-driven output. Toolio is based on the MLX framework for Apple Silicon, specifically M1/M2/M3/M4 Macs. It allows users to host MLX-format LLMs for structured output queries and provides a command line client for easier usage of tools. The tool also supports multiple tool calls and the creation of custom tools for specific tasks.
vectorflow
VectorFlow is an open source, high throughput, fault tolerant vector embedding pipeline. It provides a simple API endpoint for ingesting large volumes of raw data, processing, and storing or returning the vectors quickly and reliably. The tool supports text-based files like TXT, PDF, HTML, and DOCX, and can be run locally with Kubernetes in production. VectorFlow offers functionalities like embedding documents, running chunking schemas, custom chunking, and integrating with vector databases like Pinecone, Qdrant, and Weaviate. It enforces a standardized schema for uploading data to a vector store and supports features like raw embeddings webhook, chunk validation webhook, S3 endpoint, and telemetry. The tool can be used with the Python client and provides detailed instructions for running and testing the functionalities.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.

ActionWeaver
ActionWeaver is an AI application framework designed for simplicity, relying on OpenAI and Pydantic. It supports both OpenAI API and Azure OpenAI service. The framework allows for function calling as a core feature, extensibility to integrate any Python code, function orchestration for building complex call hierarchies, and telemetry and observability integration. Users can easily install ActionWeaver using pip and leverage its capabilities to create, invoke, and orchestrate actions with the language model. The framework also provides structured extraction using Pydantic models and allows for exception handling customization. Contributions to the project are welcome, and users are encouraged to cite ActionWeaver if found useful.
godot-llm
Godot LLM is a plugin that enables the utilization of large language models (LLM) for generating content in games. It provides functionality for text generation, text embedding, multimodal text generation, and vector database management within the Godot game engine. The plugin supports features like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and integrates llama.cpp-based functionalities for text generation, embedding, and multimodal capabilities. It offers support for various platforms and allows users to experiment with LLM models in their game development projects.
Hurley-AI
Hurley AI is a next-gen framework for developing intelligent agents through Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents, supports various agent types, and includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal. Hurley AI integrates with LLM inference services and provides observability with Arize Phoenix. Users can create Hurley RAG tools with a single line of code and customize agents with specific instructions. The tool also offers various helper functions to connect with Hurley RAG and search tools, along with pre-built tools for tasks like summarizing text, rephrasing text, understanding memecoins, and querying databases.
simpleAI
SimpleAI is a self-hosted alternative to the not-so-open AI API, focused on replicating main endpoints for LLM such as text completion, chat, edits, and embeddings. It allows quick experimentation with different models, creating benchmarks, and handling specific use cases without relying on external services. Users can integrate and declare models through gRPC, query endpoints using Swagger UI or API, and resolve common issues like CORS with FastAPI middleware. The project is open for contributions and welcomes PRs, issues, documentation, and more.
VMind
VMind is an open-source solution for intelligent visualization, providing an intelligent chart component based on LLM by VisActor. It allows users to create chart narrative works with natural language interaction, edit charts through dialogue, and export narratives as videos or GIFs. The tool is easy to use, scalable, supports various chart types, and offers one-click export functionality. Users can customize chart styles, specify themes, and aggregate data using LLM models. VMind aims to enhance efficiency in creating data visualization works through dialogue-based editing and natural language interaction.
laragenie
Laragenie is an AI chatbot designed to understand and assist developers with their codebases. It runs on the command line from a Laravel app, helping developers onboard to new projects, understand codebases, and provide daily support. Laragenie accelerates workflow and collaboration by indexing files and directories, allowing users to ask questions and receive AI-generated responses. It supports OpenAI and Pinecone for processing and indexing data, making it a versatile tool for any repo in any language.
py-vectara-agentic
The `vectara-agentic` Python library is designed for developing powerful AI assistants using Vectara and Agentic-RAG. It supports various agent types, includes pre-built tools for domains like finance and legal, and enables easy creation of custom AI assistants and agents. The library provides tools for summarizing text, rephrasing text, legal tasks like summarizing legal text and critiquing as a judge, financial tasks like analyzing balance sheets and income statements, and database tools for inspecting and querying databases. It also supports observability via LlamaIndex and Arize Phoenix integration.
For similar tasks
LLaMa2lang
This repository contains convenience scripts to finetune LLaMa3-8B (or any other foundation model) for chat towards any language (that isn't English). The rationale behind this is that LLaMa3 is trained on primarily English data and while it works to some extent for other languages, its performance is poor compared to English.
SiriLLama
Siri LLama is an Apple shortcut that allows users to access locally running LLMs through Siri or the shortcut UI on any Apple device connected to the same network as the host machine. It utilizes Langchain and supports open source models from Ollama or Fireworks AI. Users can easily set up and configure the tool to interact with various language models for chat and multimodal tasks. The tool provides a convenient way to leverage the power of language models through Siri or the shortcut interface, enhancing user experience and productivity.
text-generation-webui-telegram_bot
The text-generation-webui-telegram_bot is a wrapper and extension for llama.cpp, exllama, or transformers, providing additional functionality for the oobabooga/text-generation-webui tool. It enhances Telegram chat with features like buttons, prefixes, and voice/image generation. Users can easily install and run the tool as a standalone app or in extension mode, enabling seamless integration with the text-generation-webui tool. The tool offers various features such as chat templates, session history, character loading, model switching during conversation, voice generation, auto-translate, and more. It supports different bot modes for personalized interactions and includes configurations for running in different environments like Google Colab. Additionally, users can customize settings, manage permissions, and utilize various prefixes to enhance the chat experience.
rust-genai
genai is a multi-AI providers library for Rust that aims to provide a common and ergonomic single API to various generative AI providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Cohere, Ollama, and Gemini. It focuses on standardizing chat completion APIs across major AI services, prioritizing ergonomics and commonality. The library initially focuses on text chat APIs and plans to expand to support images, function calling, and more in the future versions. Version 0.1.x will have breaking changes in patches, while version 0.2.x will follow semver more strictly. genai does not provide a full representation of a given AI provider but aims to simplify the differences at a lower layer for ease of use.
whetstone.chatgpt
Whetstone.ChatGPT is a simple light-weight library that wraps the Open AI API with support for dependency injection. It supports features like GPT 4, GPT 3.5 Turbo, chat completions, audio transcription and translation, vision completions, files, fine tunes, images, embeddings, moderations, and response streaming. The library provides a video walkthrough of a Blazor web app built on it and includes examples such as a command line bot. It offers quickstarts for dependency injection, chat completions, completions, file handling, fine tuning, image generation, and audio transcription.

pg_vectorize
pg_vectorize is a Postgres extension that automates text to embeddings transformation, enabling vector search and LLM applications with minimal function calls. It integrates with popular LLMs, provides workflows for vector search and RAG, and automates Postgres triggers for updating embeddings. The tool is part of the VectorDB Stack on Tembo Cloud, offering high-level APIs for easy initialization and search.
gemini-api-quickstart
This repository contains a simple Python Flask App utilizing the Google AI Gemini API to explore multi-modal capabilities. It provides a basic UI and Flask backend for easy integration and testing. The app allows users to interact with the AI model through chat messages, making it a great starting point for developers interested in AI-powered applications.
ai21-python
The AI21 Labs Python SDK is a comprehensive tool for interacting with the AI21 API. It provides functionalities for chat completions, conversational RAG, token counting, error handling, and support for various cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Vertex. The SDK offers both synchronous and asynchronous usage, along with detailed examples and documentation. Users can quickly get started with the SDK to leverage AI21's powerful models for various natural language processing tasks.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
