
LLMBox
A comprehensive library for implementing LLMs, including a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation.
Stars: 755
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
README:
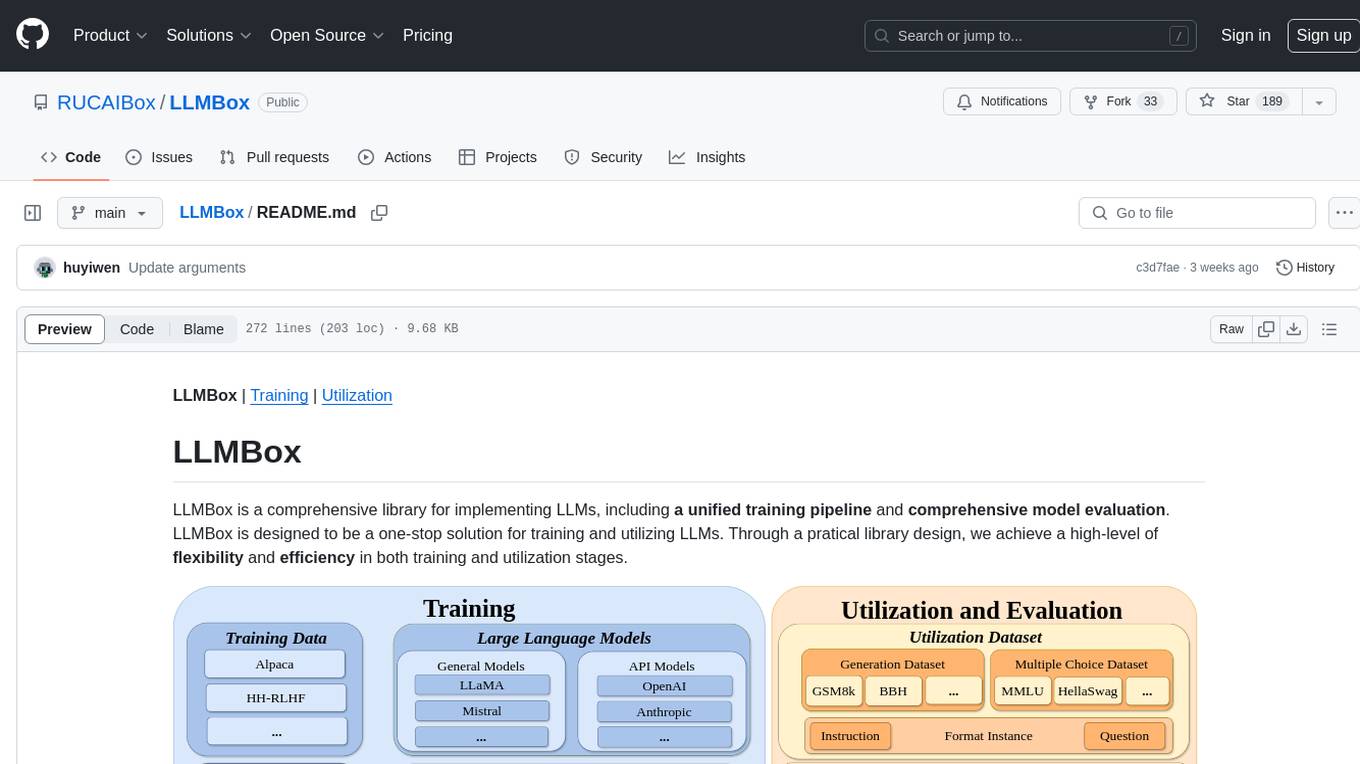
LLMBox | Training | Utilization
LLMBox is a comprehensive library for implementing LLMs, including a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. LLMBox is designed to be a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs. Through a practical library design, we achieve a high-level of flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages.
Training
-
Diverse training strategies: We support multiple training strategies, including Supervised Fine-tuning (
SFT), Pre-training (PT),PPOandDPO. - Comprehensive SFT datasets: We support 9 SFT datasets as the inputs for training.
- Tokenizer Vocabulary Merging: We support the tokenizer merging function to expand the vocabulary.
-
Data Construction Strategies: We currently support merging multiple datasets for training.
Self-InstructandEvol-Instructare also available to process the dataset. -
Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning:
LoRAandQLoRAare supported in SFT or PT. -
Efficient Training: We support
Flash AttentionandDeepspeedfor efficient training.
Utilization
-
Blazingly Fast: By managing the KV Cache of prefixes or using
vLLM, we can speed up local inference by up to 6x 🚀. - Comprehensive Evaluation: 59+ commonly used datasets and benchmarks in evaluating LLMs.
- Evaluation Methods: 📏 Accurately reproduce results from original papers of OpenAI, LLaMA, Mistral, and other models.
-
In-Context Learning: We support various ICL strategies, including
KATE,GlobalE, andAPE. -
Chain-of-Thought: For some datasets, we support three types of CoT evaluation:
base,least-to-most, andpal. - Quantization: BitsAndBytes and GPTQ quantization are supported.
- Easy To Use: Detailed results are provided for users to debug or integrate new models/datasets/cot.
See documentations for more details.
git clone https://github.com/RUCAIBox/LLMBox.git && cd LLMBox
pip install -r requirements.txtIf you are only evaluating the OpenAI (or OpenAI compatible like DeepSeek, Perplexity) models, you can install the minimal requirements requirements-openai.txt.
For installation problem, see trouble shooting.
Update LLMBox
Currently, you can simply pull the latest repository from GitHub to update LLMBox.
git pullIf you are facing a merge conflict, please try to drop, stash, or commit your local changes first.
git checkout local_changes && git add -p && git commit -m "local changes"
git checkout main
git pullThe above commands show how to commit your local changes to a new branch, and then update the LLMBox.
You can start with training a SFT model based on LLaMA-2 (7B) with deepspeed3:
cd training
bash download.sh
bash bash/run_ds3.shTo utilize your model, or evaluate an existing model, you can run the following command:
python inference.py -m gpt-3.5-turbo -d copa # --num_shot 0 --model_type chatThis is default to run the OpenAI GPT 3.5 turbo model on the CoPA dataset in a zero-shot manner.
LLMBox Training supports various training strategies and dataset construction strategies, along with some efficiency-improving modules. You can train your model with the following command:
python train.py \
--model_name_or_path meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf \
--data_path data/ \
--dataset alpaca_data_1k.json \
--output_dir $OUTPUT_DIR \
--num_train_epochs 2 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 2 \
--save_strategy "epoch" \
--save_steps 2 \
--save_total_limit 2 \
--learning_rate 1e-5 \
--lr_scheduler_type "constant"Alternatively, you can use the following preset bash scripts to train your model:
If you want to pre-train your models on corpora with languages or tokens not well-supported in original language mdoels(e.g., LLaMA), we provide the tokenizer merging function to expand the vocabulary based on the corpora by using sentencepiece. You can check merge_tokenizer.py for detailed information. Please follow the guide in Pre-train.
bash bash/run_7b_pt.shIf you want to train your models with a mix of multiple datasets, you can pass a list of dataset files or names to LLMBox. LLMBox will transfer each file or name into a PTDataset or SFTDataset, and merge them together to construct a combined dataset. You can also set the merging ratio of each dataset by passing a list of floats to LLMBox. Please follow the guide in Merge Dataset.
bash bash/run_7b_hybrid.shSince manually creating instruction data of high qualities to train the model is very time-consuming and labor-intensive, Self-Instruct and Evol-Instruct are proposed to create large amounts of instruction data with varying levels of complexity using LLM instead of humans. LLMBox support both Self-Instruct and Evol-Instruct to augment or enhance the input data files. Please follow the guide in Self-Insturct and Evol-Instruct
python self_instruct/self_instruct.py --seed_tasks_path=seed_tasks.jsonlFor more details, view the training documentation.
We provide a broad support on Huggingface models (e.g. LLaMA-3, Mistral, or the model you are building on), OpenAI, Anthropic, QWen and other OpenAI-compatible models for further utilization. Full list of model backends: here.
Currently a total of 59+ commonly used datasets are supported, including: HellaSwag, MMLU, GSM8K, GPQA, AGIEval, CEval, and CMMLU. Full list of datasets: here.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python inference.py \
-m llama-2-7b-hf \
-d mmlu agieval:[English] \
--model_type chat \
--num_shot 5 \
--ranking_type ppl_no_option-
🔥 Recently supported datasets:
imbue_code,imbue_public, andimbue_private. -
🔥 See benchmarking LLaMA3 for more examples.
| Performance | |||
| Model | get_ppl |
get_prob |
generation |
| Hellaswag (0-shot) | MMLU (5-shot) | GSM (8-shot) | |
| GPT-3.5 Turbo | 79.98 | 69.25 | 75.13 |
| LLaMA-2 (7B) | 76 | 45.95 | 14.63 |
We by default enable prefix caching for efficient evaluation. vLLM is also supported.
| Time | |||||
| Model | Efficient Method | get_ppl |
get_prob |
generation |
|
| Hellaswag (0-shot) | MMLU (5-shot) | GSM (8-shot) | |||
| LLaMA-2 (7B) | Vanilla | 0:05:32 | 0:18:30 | 2:10:27 | |
| vLLM | 0:06:37 | 0:14:55 | 0:03:36 | ||
| Prefix Caching | 0:05:48 | 0:05:51 | 0:17:13 | ||
You can also use the following command to use vllm:
python inference.py -m ../Llama-2-7b-hf -d mmlu:abstract_algebra,anatomy --vllm True # --prefix_caching False --flash_attention FalseTo evaluate with quantization, you can use the following command:
python inference.py -m model -d dataset --load_in_4bits # --load_in_8_bits or --gptqVarious types of evaluation methods are supported:
| Dataset | Evaluation Method | Instruction |
|
Generation |
Generate based on the source text Example: ARC-Challenge (extract choice characters like A, B, C, D from model generation), GSM8K, HumanEval Notes: |
|
|
MultipleChoice |
Calculate perplexity of the option text based on the source text (i.e. compute log-likelihood over the suffix) Example: WinoGrande, BoolQ Notes: Some datasets, such as ARC, OpenbookQA, and RACE use normalized accuracy when evaluated with the |
|
|
|
||
|
Get the probability of each option label (i.e. over choice characters) Example: MMLU, ARC-Challange |
|
You can find more evaluation details for each dataset at supported datasets.
You can use --instruction to pass a jinja template to override the default instruction.
By default, we use the get_ppl method with ppl_no_option ranking type for MultipleChoiceDataset and the generation method for GenerationDataset. You can also use the following command to use the get_prob method or ppl variant of get_ppl for MultipleChoiceDataset:
python inference.py -m model -d dataset --ranking_type prob # or pplWe also support In-Context Learning and Chain-of-Thought evaluation for some datasets:
python inference.py -m model -d dataset --kate # --globale or --ape
python inference.py -m model -d dataset --cot least_to_most # --base or --palFor a more detailed instruction on model utilization, view the utilization documentation.
For a full list of evaluation results, see our paper LLMBox: A Comprehensive Library for Large Language Models.
Please let us know if you encounter a bug or have any suggestions by filing an issue.
We welcome all contributions from bug fixes to new features and extensions.
We expect all contributions discussed in the issue tracker and going through PRs.
For more details, view the CONTRIBUTING documentation.
We thank the following contributors for their contributions to LLMBox:
- @xansar for fixing multiple complex issues like batch sampler and self-consistency.
LLMBox is developed and maintained by AI Box. See more details in change log
LLMBox uses MIT License.
If you find LLMBox useful for your research or development, please cite the following papers:
@inproceedings{tang2024llmbox,
title={LLMBox: A Comprehensive Library for Large Language Models},
author={Tang, Tianyi and Yiwen, Hu and Li, Bingqian and Luo, Wenyang and Qin, ZiJing and Sun, Haoxiang and Wang, Jiapeng and Xu, Shiyi and Cheng, Xiaoxue and Guo, Geyang and others},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 3: System Demonstrations)},
pages={388--399},
year={2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLMBox
Similar Open Source Tools

LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
distilabel
Distilabel is a framework for synthetic data and AI feedback for AI engineers that require high-quality outputs, full data ownership, and overall efficiency. It helps you synthesize data and provide AI feedback to improve the quality of your AI models. With Distilabel, you can: * **Synthesize data:** Generate synthetic data to train your AI models. This can help you to overcome the challenges of data scarcity and bias. * **Provide AI feedback:** Get feedback from AI models on your data. This can help you to identify errors and improve the quality of your data. * **Improve your AI output quality:** By using Distilabel to synthesize data and provide AI feedback, you can improve the quality of your AI models and get better results.
KnowAgent
KnowAgent is a tool designed for Knowledge-Augmented Planning for LLM-Based Agents. It involves creating an action knowledge base, converting action knowledge into text for model understanding, and a knowledgeable self-learning phase to continually improve the model's planning abilities. The tool aims to enhance agents' potential for application in complex situations by leveraging external reservoirs of information and iterative processes.
EasyInstruct
EasyInstruct is a Python package proposed as an easy-to-use instruction processing framework for Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, LLaMA, ChatGLM in your research experiments. EasyInstruct modularizes instruction generation, selection, and prompting, while also considering their combination and interaction.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.
RainbowGPT
RainbowGPT is a versatile tool that offers a range of functionalities, including Stock Analysis for financial decision-making, MySQL Management for database navigation, and integration of AI technologies like GPT-4 and ChatGlm3. It provides a user-friendly interface suitable for all skill levels, ensuring seamless information flow and continuous expansion of emerging technologies. The tool enhances adaptability, creativity, and insight, making it a valuable asset for various projects and tasks.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
bigcodebench
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for code generation with practical and challenging programming tasks. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls. BigCodeBench focuses on the evaluation of LLM4Code with diverse function calls and complex instructions, providing precise evaluation & ranking and pre-generated samples to accelerate code intelligence research. It inherits the design of the EvalPlus framework but differs in terms of execution environment and test evaluation.
generative-fusion-decoding
Generative Fusion Decoding (GFD) is a novel shallow fusion framework that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into multi-modal text recognition systems such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and optical character recognition (OCR). GFD operates across mismatched token spaces of different models by mapping text token space to byte token space, enabling seamless fusion during the decoding process. It simplifies the complexity of aligning different model sample spaces, allows LLMs to correct errors in tandem with the recognition model, increases robustness in long-form speech recognition, and enables fusing recognition models deficient in Chinese text recognition with LLMs extensively trained on Chinese. GFD significantly improves performance in ASR and OCR tasks, offering a unified solution for leveraging existing pre-trained models through step-by-step fusion.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
sec-parser
The `sec-parser` project simplifies extracting meaningful information from SEC EDGAR HTML documents by organizing them into semantic elements and a tree structure. It helps in parsing SEC filings for financial and regulatory analysis, analytics and data science, AI and machine learning, causal AI, and large language models. The tool is especially beneficial for AI, ML, and LLM applications by streamlining data pre-processing and feature extraction.
Easy-Translate
Easy-Translate is a script designed for translating large text files with a single command. It supports various models like M2M100, NLLB200, SeamlessM4T, LLaMA, and Bloom. The tool is beginner-friendly and offers seamless and customizable features for advanced users. It allows acceleration on CPU, multi-CPU, GPU, multi-GPU, and TPU, with support for different precisions and decoding strategies. Easy-Translate also provides an evaluation script for translations. Built on HuggingFace's Transformers and Accelerate library, it supports prompt usage and loading huge models efficiently.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.
For similar tasks

LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
chess_llm_interpretability
This repository evaluates Large Language Models (LLMs) trained on PGN format chess games using linear probes. It assesses the LLMs' internal understanding of board state and their ability to estimate player skill levels. The repo provides tools to train, evaluate, and visualize linear probes on LLMs trained to play chess with PGN strings. Users can visualize the model's predictions, perform interventions on the model's internal board state, and analyze board state and player skill level accuracy across different LLMs. The experiments in the repo can be conducted with less than 1 GB of VRAM, and training probes on the 8 layer model takes about 10 minutes on an RTX 3050. The repo also includes scripts for performing board state interventions and skill interventions, along with useful links to open-source code, models, datasets, and pretrained models.
LESS
This repository contains the code for the paper 'LESS: Selecting Influential Data for Targeted Instruction Tuning'. The work proposes a data selection method to choose influential data for inducing a target capability. It includes steps for warmup training, building the gradient datastore, selecting data for a task, and training with the selected data. The repository provides tools for data preparation, data selection pipeline, and evaluation of the model trained on the selected data.
tiny-llm-zh
Tiny LLM zh is a project aimed at building a small-parameter Chinese language large model for quick entry into learning large model-related knowledge. The project implements a two-stage training process for large models and subsequent human alignment, including tokenization, pre-training, instruction fine-tuning, human alignment, evaluation, and deployment. It is deployed on ModeScope Tiny LLM website and features open access to all data and code, including pre-training data and tokenizer. The project trains a tokenizer using 10GB of Chinese encyclopedia text to build a Tiny LLM vocabulary. It supports training with Transformers deepspeed, multiple machine and card support, and Zero optimization techniques. The project has three main branches: llama2_torch, main tiny_llm, and tiny_llm_moe, each with specific modifications and features.
AI-Bootcamp
The AI Bootcamp is a comprehensive training program focusing on real-world applications to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to excel as AI engineers. The bootcamp covers topics such as Real-World PyTorch, Machine Learning Projects, Fine-tuning Tiny LLM, Deployment of LLM to Production, AI Agents with GPT-4 Turbo, CrewAI, Llama 3, and more. Participants will learn foundational skills in Python for AI, ML Pipelines, Large Language Models (LLMs), AI Agents, and work on projects like RagBase for private document chat.
torchchat
torchchat is a codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. It allows running LLMs using Python in various environments such as desktop, server, iOS, and Android. The tool supports running models via PyTorch, chatting, generating text, running chat in the browser, and running models on desktop/server without Python. It also provides features like AOT Inductor for faster execution, running in C++ using the runner, and deploying and running on iOS and Android. The tool supports popular hardware and OS including Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS, with various data types and execution modes available.
VulBench
This repository contains materials for the paper 'How Far Have We Gone in Vulnerability Detection Using Large Language Model'. It provides a tool for evaluating vulnerability detection models using datasets such as d2a, ctf, magma, big-vul, and devign. Users can query the model 'Llama-2-7b-chat-hf' and store results in a SQLite database for analysis. The tool supports binary and multiple classification tasks with concurrency settings. Additionally, users can evaluate the results and generate a CSV file with metrics for each dataset and prompt type.
HuaTuoAI
HuaTuoAI is an artificial intelligence image classification system specifically designed for traditional Chinese medicine. It utilizes deep learning techniques, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), to accurately classify Chinese herbs and ingredients based on input images. The project aims to unlock the secrets of plants, depict the unknown realm of Chinese medicine using technology and intelligence, and perpetuate ancient cultural heritage.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
