
chess_llm_interpretability
Visualizing the internal board state of a GPT trained on chess PGN strings, and performing interventions on its internal board state and representation of player Elo.
Stars: 162
This repository evaluates Large Language Models (LLMs) trained on PGN format chess games using linear probes. It assesses the LLMs' internal understanding of board state and their ability to estimate player skill levels. The repo provides tools to train, evaluate, and visualize linear probes on LLMs trained to play chess with PGN strings. Users can visualize the model's predictions, perform interventions on the model's internal board state, and analyze board state and player skill level accuracy across different LLMs. The experiments in the repo can be conducted with less than 1 GB of VRAM, and training probes on the 8 layer model takes about 10 minutes on an RTX 3050. The repo also includes scripts for performing board state interventions and skill interventions, along with useful links to open-source code, models, datasets, and pretrained models.
README:
This evaluates LLMs trained on PGN format chess games through the use of linear probes. We can check the LLMs internal understanding of board state and ability to estimate the skill level of the players involved. We can also perform interventions on the model's internal board state by deleting pieces from its internal world model.
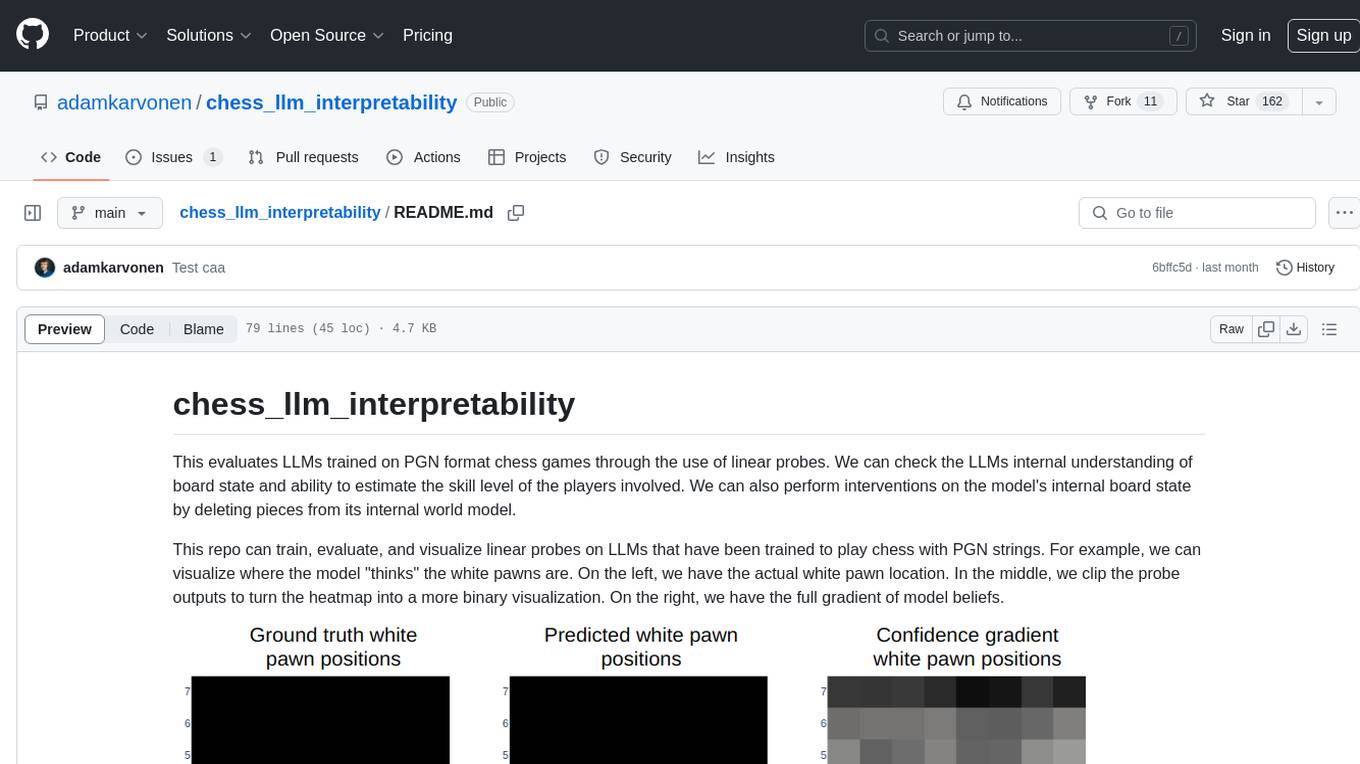
This repo can train, evaluate, and visualize linear probes on LLMs that have been trained to play chess with PGN strings. For example, we can visualize where the model "thinks" the white pawns are. On the left, we have the actual white pawn location. In the middle, we clip the probe outputs to turn the heatmap into a more binary visualization. On the right, we have the full gradient of model beliefs.
I trained linear probes on both the model's ability to compute board state and estimate player ELO as it's predicting the next character. Here we can see a per layer graph of board state and elo classification accuracy across a range of LLMs.
For more information, refer to this post.
Create a Python environment with Python 3.10 or 3.11 (I'm using 3.11).
pip install -r requirements.txt
python model_setup.py
Then click "Run All" on lichess_data_filtering.ipynb (I'm filtering data in a notebook instead of a script because I use a series of graphs to illustrate what the data filtering is doing).
To visualise probe outputs or better understand my work, check out probe_output_visualization.ipynb. It has commentary and many print statements to walk you through using a single probe and performing a single intervention.
The train_test_chess.py script can be used to either train new linear probes or test a saved probe on the test set.
Command line arguments:
--mode: Specifies train or test. Optional, defaults to train.
--probe: Determines the type of probe to be used. piece probes for the piece type on each square, skill probes the skill level of the White player. Optional, defaults to piece.
Examples:
Train piece board state probes:
python train_test_chess.py
Test skill probe:
python train_test_chess.py --mode test --probe skill
See all options: python train_test_chess.py -h
All experiments in this repo can be done with less than 1 GB of VRAM. Training probes on the 8 layer model takes about 10 minutes on my RTX 3050.
To perform board state interventions on one layer, run python board_state_interventions.py. It will record JSON results in intervention_logs/. To get better results, train a set of 8 (one per layer) board state probes using train_test_chess.py and rerun.
To perform skill interventions, you can train a set of 8 skill probes using train_test_chess.py or generate a set of 8 contrastive activations using caa.py. Note that contrastive activations tend to work a little better. If you want to use probe derived interventions, use this script to create activation files from the probes: utils/create_skill_intervention_from_skill_probe.ipynb.
Then, follow these directions to use them to perform skill interventions: https://github.com/adamkarvonen/chess_gpt_eval/tree/master/nanogpt
All code, models, and datasets are open source.
To play the nanoGPT model against Stockfish, please visit: https://github.com/adamkarvonen/chess_gpt_eval/tree/master/nanogpt
To train a Chess-GPT from scratch, please visit: https://github.com/adamkarvonen/nanoGPT
All pretrained models are available here: https://huggingface.co/adamkarvonen/chess_llms
All datasets are available here: https://huggingface.co/datasets/adamkarvonen/chess_games
Wandb training loss curves and model configs can be viewed here: https://api.wandb.ai/links/adam-karvonen/u783xspb
To run the end to end test suite, run pytest -s from the root directory. This will first train and test probes end to end on the 8 layer model, including comparing expected accuracy to actual accuracy within some tolerance. Then it will test out board state interventions and caa creation. It takes around 14 minutes. The -s flag is so you can see the training updates and gauge progress.
Much of my linear probing was developed using Neel Nanda's linear probing code as a reference. Here are the main references I used:
https://colab.research.google.com/github/neelnanda-io/TransformerLens/blob/main/demos/Othello_GPT.ipynb https://colab.research.google.com/github/likenneth/othello_world/blob/master/Othello_GPT_Circuits.ipynb https://www.neelnanda.io/mechanistic-interpretability/othello https://github.com/likenneth/othello_world/tree/master/mechanistic_interpretability
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for chess_llm_interpretability
Similar Open Source Tools

chess_llm_interpretability
This repository evaluates Large Language Models (LLMs) trained on PGN format chess games using linear probes. It assesses the LLMs' internal understanding of board state and their ability to estimate player skill levels. The repo provides tools to train, evaluate, and visualize linear probes on LLMs trained to play chess with PGN strings. Users can visualize the model's predictions, perform interventions on the model's internal board state, and analyze board state and player skill level accuracy across different LLMs. The experiments in the repo can be conducted with less than 1 GB of VRAM, and training probes on the 8 layer model takes about 10 minutes on an RTX 3050. The repo also includes scripts for performing board state interventions and skill interventions, along with useful links to open-source code, models, datasets, and pretrained models.

eureka-ml-insights
The Eureka ML Insights Framework is a repository containing code designed to help researchers and practitioners run reproducible evaluations of generative models efficiently. Users can define custom pipelines for data processing, inference, and evaluation, as well as utilize pre-defined evaluation pipelines for key benchmarks. The framework provides a structured approach to conducting experiments and analyzing model performance across various tasks and modalities.
ShieldLM
ShieldLM is a bilingual safety detector designed to detect safety issues in LLMs' generations. It aligns with human safety standards, supports customizable detection rules, and provides explanations for decisions. Outperforming strong baselines, ShieldLM is impressive across 4 test sets.
Winter
Winter is a UCI chess engine that has competed at top invite-only computer chess events. It is the top-rated chess engine from Switzerland and has a level of play that is super human but below the state of the art reached by large, distributed, and resource-intensive open-source projects like Stockfish and Leela Chess Zero. Winter has relied on many machine learning algorithms and techniques over the course of its development, including certain clustering methods not used in any other chess programs, such as Gaussian Mixture Models and Soft K-Means. As of Winter 0.6.2, the evaluation function relies on a small neural network for more precise evaluations.
llama3_interpretability_sae
This project focuses on implementing Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) for mechanistic interpretability in Large Language Models (LLMs) like Llama 3.2-3B. The SAEs aim to untangle superimposed representations in LLMs into separate, interpretable features for each neuron activation. The project provides an end-to-end pipeline for capturing training data, training the SAEs, analyzing learned features, and verifying results experimentally. It includes comprehensive logging, visualization, and checkpointing of SAE training, interpretability analysis tools, and a pure PyTorch implementation of Llama 3.1/3.2 chat and text completion. The project is designed for scalability, efficiency, and maintainability.
llm_steer
LLM Steer is a Python module designed to steer Large Language Models (LLMs) towards specific topics or subjects by adding steer vectors to different layers of the model. It enhances the model's capabilities, such as providing correct responses to logical puzzles. The tool should be used in conjunction with the transformers library. Users can add steering vectors to specific layers of the model with coefficients and text, retrieve applied steering vectors, and reset all steering vectors to the initial model. Advanced usage involves changing default parameters, but it may lead to the model outputting gibberish in most cases. The tool is meant for experimentation and can be used to enhance role-play characteristics in LLMs.

qlora-pipe
qlora-pipe is a pipeline parallel training script designed for efficiently training large language models that cannot fit on one GPU. It supports QLoRA, LoRA, and full fine-tuning, with efficient model loading and the ability to load any dataset that Axolotl can handle. The script allows for raw text training, resuming training from a checkpoint, logging metrics to Tensorboard, specifying a separate evaluation dataset, training on multiple datasets simultaneously, and supports various models like Llama, Mistral, Mixtral, Qwen-1.5, and Cohere (Command R). It handles pipeline- and data-parallelism using Deepspeed, enabling users to set the number of GPUs, pipeline stages, and gradient accumulation steps for optimal utilization.
SciMLBenchmarks.jl
SciMLBenchmarks.jl holds webpages, pdfs, and notebooks showing the benchmarks for the SciML Scientific Machine Learning Software ecosystem, including: * Benchmarks of equation solver implementations * Speed and robustness comparisons of methods for parameter estimation / inverse problems * Training universal differential equations (and subsets like neural ODEs) * Training of physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) * Surrogate comparisons, including radial basis functions, neural operators (DeepONets, Fourier Neural Operators), and more The SciML Bench suite is made to be a comprehensive open source benchmark from the ground up, covering the methods of computational science and scientific computing all the way to AI for science.
PromptAgent
PromptAgent is a repository for a novel automatic prompt optimization method that crafts expert-level prompts using language models. It provides a principled framework for prompt optimization by unifying prompt sampling and rewarding using MCTS algorithm. The tool supports different models like openai, palm, and huggingface models. Users can run PromptAgent to optimize prompts for specific tasks by strategically sampling model errors, generating error feedbacks, simulating future rewards, and searching for high-reward paths leading to expert prompts.
LLM-RGB
LLM-RGB is a repository containing a collection of detailed test cases designed to evaluate the reasoning and generation capabilities of Language Learning Models (LLMs) in complex scenarios. The benchmark assesses LLMs' performance in understanding context, complying with instructions, and handling challenges like long context lengths, multi-step reasoning, and specific response formats. Each test case evaluates an LLM's output based on context length difficulty, reasoning depth difficulty, and instruction compliance difficulty, with a final score calculated for each test case. The repository provides a score table, evaluation details, and quick start guide for running evaluations using promptfoo testing tools.
chronon
Chronon is a platform that simplifies and improves ML workflows by providing a central place to define features, ensuring point-in-time correctness for backfills, simplifying orchestration for batch and streaming pipelines, offering easy endpoints for feature fetching, and guaranteeing and measuring consistency. It offers benefits over other approaches by enabling the use of a broad set of data for training, handling large aggregations and other computationally intensive transformations, and abstracting away the infrastructure complexity of data plumbing.
LLMs-World-Models-for-Planning
This repository provides a Python implementation of a method that leverages pre-trained large language models to construct and utilize world models for model-based task planning. It includes scripts to generate domain models using natural language descriptions, correct domain models based on feedback, and support plan generation for tasks in different domains. The code has been refactored for better readability and includes tools for validating PDDL syntax and handling corrective feedback.
raft
RAFT (Retrieval-Augmented Fine-Tuning) is a method for creating conversational agents that realistically emulate specific human targets. It involves a dual-phase process of fine-tuning and retrieval-based augmentation to generate nuanced and personalized dialogue. The tool is designed to combine interview transcripts with memories from past writings to enhance language model responses. RAFT has the potential to advance the field of personalized, context-sensitive conversational agents.
deep-seek
DeepSeek is a new experimental architecture for a large language model (LLM) powered internet-scale retrieval engine. Unlike current research agents designed as answer engines, DeepSeek aims to process a vast amount of sources to collect a comprehensive list of entities and enrich them with additional relevant data. The end result is a table with retrieved entities and enriched columns, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic. DeepSeek utilizes both standard keyword search and neural search to find relevant content, and employs an LLM to extract specific entities and their associated contents. It also includes a smaller answer agent to enrich the retrieved data, ensuring thoroughness. DeepSeek has the potential to revolutionize research and information gathering by providing a comprehensive and structured way to access information from the vastness of the internet.
AIlice
AIlice is a fully autonomous, general-purpose AI agent that aims to create a standalone artificial intelligence assistant, similar to JARVIS, based on the open-source LLM. AIlice achieves this goal by building a "text computer" that uses a Large Language Model (LLM) as its core processor. Currently, AIlice demonstrates proficiency in a range of tasks, including thematic research, coding, system management, literature reviews, and complex hybrid tasks that go beyond these basic capabilities. AIlice has reached near-perfect performance in everyday tasks using GPT-4 and is making strides towards practical application with the latest open-source models. We will ultimately achieve self-evolution of AI agents. That is, AI agents will autonomously build their own feature expansions and new types of agents, unleashing LLM's knowledge and reasoning capabilities into the real world seamlessly.
textcoder
Textcoder is a proof-of-concept tool for steganographically encoding secret messages into ordinary text using arithmetic coding based on a statistical model derived from an LLM. It encrypts the secret message to produce a pseudorandom bit stream, which is then decompressed to generate text that appears randomly sampled from the LLM while encoding the secret message in specific token choices.
For similar tasks

chess_llm_interpretability
This repository evaluates Large Language Models (LLMs) trained on PGN format chess games using linear probes. It assesses the LLMs' internal understanding of board state and their ability to estimate player skill levels. The repo provides tools to train, evaluate, and visualize linear probes on LLMs trained to play chess with PGN strings. Users can visualize the model's predictions, perform interventions on the model's internal board state, and analyze board state and player skill level accuracy across different LLMs. The experiments in the repo can be conducted with less than 1 GB of VRAM, and training probes on the 8 layer model takes about 10 minutes on an RTX 3050. The repo also includes scripts for performing board state interventions and skill interventions, along with useful links to open-source code, models, datasets, and pretrained models.
LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
LESS
This repository contains the code for the paper 'LESS: Selecting Influential Data for Targeted Instruction Tuning'. The work proposes a data selection method to choose influential data for inducing a target capability. It includes steps for warmup training, building the gradient datastore, selecting data for a task, and training with the selected data. The repository provides tools for data preparation, data selection pipeline, and evaluation of the model trained on the selected data.
tiny-llm-zh
Tiny LLM zh is a project aimed at building a small-parameter Chinese language large model for quick entry into learning large model-related knowledge. The project implements a two-stage training process for large models and subsequent human alignment, including tokenization, pre-training, instruction fine-tuning, human alignment, evaluation, and deployment. It is deployed on ModeScope Tiny LLM website and features open access to all data and code, including pre-training data and tokenizer. The project trains a tokenizer using 10GB of Chinese encyclopedia text to build a Tiny LLM vocabulary. It supports training with Transformers deepspeed, multiple machine and card support, and Zero optimization techniques. The project has three main branches: llama2_torch, main tiny_llm, and tiny_llm_moe, each with specific modifications and features.
AI-Bootcamp
The AI Bootcamp is a comprehensive training program focusing on real-world applications to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to excel as AI engineers. The bootcamp covers topics such as Real-World PyTorch, Machine Learning Projects, Fine-tuning Tiny LLM, Deployment of LLM to Production, AI Agents with GPT-4 Turbo, CrewAI, Llama 3, and more. Participants will learn foundational skills in Python for AI, ML Pipelines, Large Language Models (LLMs), AI Agents, and work on projects like RagBase for private document chat.
torchchat
torchchat is a codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. It allows running LLMs using Python in various environments such as desktop, server, iOS, and Android. The tool supports running models via PyTorch, chatting, generating text, running chat in the browser, and running models on desktop/server without Python. It also provides features like AOT Inductor for faster execution, running in C++ using the runner, and deploying and running on iOS and Android. The tool supports popular hardware and OS including Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS, with various data types and execution modes available.
VulBench
This repository contains materials for the paper 'How Far Have We Gone in Vulnerability Detection Using Large Language Model'. It provides a tool for evaluating vulnerability detection models using datasets such as d2a, ctf, magma, big-vul, and devign. Users can query the model 'Llama-2-7b-chat-hf' and store results in a SQLite database for analysis. The tool supports binary and multiple classification tasks with concurrency settings. Additionally, users can evaluate the results and generate a CSV file with metrics for each dataset and prompt type.
HuaTuoAI
HuaTuoAI is an artificial intelligence image classification system specifically designed for traditional Chinese medicine. It utilizes deep learning techniques, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), to accurately classify Chinese herbs and ingredients based on input images. The project aims to unlock the secrets of plants, depict the unknown realm of Chinese medicine using technology and intelligence, and perpetuate ancient cultural heritage.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

