bedrock-claude-chat
AWS-native chatbot using Bedrock + Claude (+Nova and Mistral)
Stars: 1067
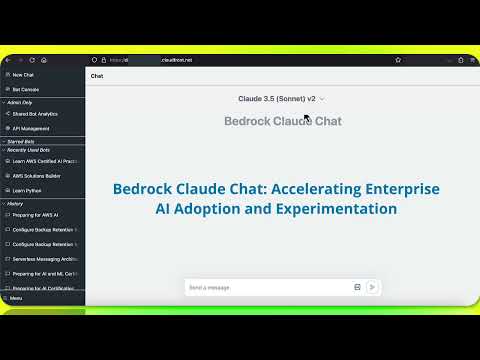
This repository is a sample chatbot using the Anthropic company's LLM Claude, one of the foundational models provided by Amazon Bedrock for generative AI. It allows users to have basic conversations with the chatbot, personalize it with their own instructions and external knowledge, and analyze usage for each user/bot on the administrator dashboard. The chatbot supports various languages, including English, Japanese, Korean, Chinese, French, German, and Spanish. Deployment is straightforward and can be done via the command line or by using AWS CDK. The architecture is built on AWS managed services, eliminating the need for infrastructure management and ensuring scalability, reliability, and security.
README:
English | 日本語 | 한국어 | 中文 | Français | Deutsch | Español | Italian | Norsk | ไทย | Bahasa Indonesia | Bahasa Melayu | Tiếng Việt | Polski
[!Warning]
V2 released. To update, please carefully review the migration guide. Without any care, BOTS FROM V1 WILL BECOME UNUSABLE.
A multilingual chatbot using LLM models provided by Amazon Bedrock for generative AI.
Add your own instruction and give external knowledge as URL or files (a.k.a RAG. The bot can be shared among application users. The customized bot also can be published as stand-alone API (See the detail).
[!Important] For governance reasons, only allowed users are able to create customized bots. To allow the creation of customized bots, the user must be a member of group called
CreatingBotAllowed, which can be set up via the management console > Amazon Cognito User pools or aws cli. Note that the user pool id can be referred by accessing CloudFormation > BedrockChatStack > Outputs >AuthUserPoolIdxxxx.
LLM-powered Agent
By using the Agent functionality, your chatbot can automatically handle more complex tasks. For example, to answer a user's question, the Agent can retrieve necessary information from external tools or break down the task into multiple steps for processing.
- In the us-east-1 region, open Bedrock Model access >
Manage model access> Check all ofAnthropic / Claude 3, all ofAmazon / Nova,Amazon / Titan Text Embeddings V2andCohere / Embed MultilingualthenSave changes.
- Open CloudShell at the region where you want to deploy
- Run deployment via following commands. If you want to specify the version to deploy or need to apply security policies, please specify the appropriate parameters from Optional Parameters.
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/bedrock-claude-chat.git
cd bedrock-claude-chat
chmod +x bin.sh
./bin.sh- You will be asked if a new user or using v2. If you are not a continuing user from v0, please enter
y.
You can specify the following parameters during deployment to enhance security and customization:
- --disable-self-register: Disable self-registration (default: enabled). If this flag is set, you will need to create all users on cognito and it will not allow users to self register their accounts.
- --enable-lambda-snapstart: Enable Lambda SnapStart (default: disabled). If this flag is set, improves cold start times for Lambda functions, providing faster response times for better user experience.
- --ipv4-ranges: Comma-separated list of allowed IPv4 ranges. (default: allow all ipv4 addresses)
- --ipv6-ranges: Comma-separated list of allowed IPv6 ranges. (default: allow all ipv6 addresses)
- --disable-ipv6: Disable connections over IPv6. (default: enabled)
- --allowed-signup-email-domains: Comma-separated list of allowed email domains for sign-up. (default: no domain restriction)
- --bedrock-region: Define the region where bedrock is available. (default: us-east-1)
- --repo-url: The custom repo of Bedrock Claude Chat to deploy, if forked or custom source control. (default: https://github.com/aws-samples/bedrock-claude-chat.git)
- --version: The version of Bedrock Claude Chat to deploy. (default: latest version in development)
- --cdk-json-override: You can override any CDK context values during deployment using the override JSON block. This allows you to modify the configuration without editing the cdk.json file directly.
Example usage:
./bin.sh --cdk-json-override '{
"context": {
"selfSignUpEnabled": false,
"enableLambdaSnapStart": true,
"allowedIpV4AddressRanges": ["192.168.1.0/24"],
"allowedSignUpEmailDomains": ["example.com"]
}
}'The override JSON must follow the same structure as cdk.json. You can override any context values including:
selfSignUpEnabledenableLambdaSnapStartallowedIpV4AddressRangesallowedIpV6AddressRangesallowedSignUpEmailDomainsbedrockRegionenableRagReplicasenableBedrockCrossRegionInference- And other context values defined in cdk.json
[!Note] The override values will be merged with the existing cdk.json configuration during the deployment time in the AWS code build. Values specified in the override will take precedence over the values in cdk.json.
./bin.sh --disable-self-register --ipv4-ranges "192.0.2.0/25,192.0.2.128/25" --ipv6-ranges "2001:db8:1:2::/64,2001:db8:1:3::/64" --allowed-signup-email-domains "example.com,anotherexample.com" --bedrock-region "us-west-2" --version "v1.2.6"- After about 35 minutes, you will get the following output, which you can access from your browser
Frontend URL: https://xxxxxxxxx.cloudfront.net
The sign-up screen will appear as shown above, where you can register your email and log in.
[!Important] Without setting the optional parameter, this deployment method allows anyone who knows the URL to sign up. For production use, it is strongly recommended to add IP address restrictions and disable self-signup to mitigate security risks (you can define allowed-signup-email-domains to restrict users so that only email addresses from your company’s domain can sign up). Use both ipv4-ranges and ipv6-ranges for IP address restrictions, and disable self-signup by using disable-self-register when executing ./bin.
[!TIP] If the
Frontend URLdoes not appear or Bedrock Claude Chat does not work properly, it may be a problem with the latest version. In this case, please add--version "v1.2.6"to the parameters and try deployment again.
It's an architecture built on AWS managed services, eliminating the need for infrastructure management. Utilizing Amazon Bedrock, there's no need to communicate with APIs outside of AWS. This enables deploying scalable, reliable, and secure applications.
- Amazon DynamoDB: NoSQL database for conversation history storage
- Amazon API Gateway + AWS Lambda: Backend API endpoint (AWS Lambda Web Adapter, FastAPI)
- Amazon CloudFront + S3: Frontend application delivery (React, Tailwind CSS)
- AWS WAF: IP address restriction
- Amazon Cognito: User authentication
- Amazon Bedrock: Managed service to utilize foundational models via APIs
- Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases: Provides a managed interface for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), offering services for embedding and parsing documents
- Amazon EventBridge Pipes: Receiving event from DynamoDB stream and launching Step Functions to embed external knowledge
- AWS Step Functions: Orchestrating ingestion pipeline to embed external knowledge into Bedrock Knowledge Bases
- Amazon OpenSearch Serverless: Serves as the backend database for Bedrock Knowledge Bases, providing full-text search and vector search capabilities, enabling accurate retrieval of relevant information
- Amazon Athena: Query service to analyze S3 bucket
Super-easy Deployment uses AWS CodeBuild to perform deployment by CDK internally. This section describes the procedure for deploying directly with CDK.
- Please have UNIX, Docker and a Node.js runtime environment. If not, you can also use Cloud9
[!Important] If there is insufficient storage space in the local environment during deployment, CDK bootstrapping may result in an error. If you are running in Cloud9 etc., we recommend expanding the volume size of the instance before deploying.
- Clone this repository
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/bedrock-claude-chat
- Install npm packages
cd bedrock-claude-chat
cd cdk
npm ci
-
If necessary, edit the following entries in cdk.json if necessary.
-
bedrockRegion: Region where Bedrock is available. NOTE: Bedrock does NOT support all regions for now. -
allowedIpV4AddressRanges,allowedIpV6AddressRanges: Allowed IP Address range. -
enableLambdaSnapStart: Defaults to true. Set to false if deploying to a region that doesn't support Lambda SnapStart for Python functions.
-
-
Before deploying the CDK, you will need to work with Bootstrap once for the region you are deploying to.
npx cdk bootstrap
- Deploy this sample project
npx cdk deploy --require-approval never --all
- You will get output similar to the following. The URL of the web app will be output in
BedrockChatStack.FrontendURL, so please access it from your browser.
✅ BedrockChatStack
✨ Deployment time: 78.57s
Outputs:
BedrockChatStack.AuthUserPoolClientIdXXXXX = xxxxxxx
BedrockChatStack.AuthUserPoolIdXXXXXX = ap-northeast-1_XXXX
BedrockChatStack.BackendApiBackendApiUrlXXXXX = https://xxxxx.execute-api.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com
BedrockChatStack.FrontendURL = https://xxxxx.cloudfront.netYou can define parameters for your deployment in two ways: using cdk.json or using the type-safe parameter.ts file.
The traditional way to configure parameters is by editing the cdk.json file. This approach is simple but lacks type checking:
{
"app": "npx ts-node --prefer-ts-exts bin/bedrock-chat.ts",
"context": {
"bedrockRegion": "us-east-1",
"allowedIpV4AddressRanges": ["0.0.0.0/1", "128.0.0.0/1"],
"enableMistral": false,
"selfSignUpEnabled": true
}
}For better type safety and developer experience, you can use the parameter.ts file to define your parameters:
// Define parameters for the default environment
bedrockChatParams.set("default", {
bedrockRegion: "us-east-1",
allowedIpV4AddressRanges: ["192.168.0.0/16"],
enableMistral: false,
selfSignUpEnabled: true,
});
// Define parameters for additional environments
bedrockChatParams.set("dev", {
bedrockRegion: "us-west-2",
allowedIpV4AddressRanges: ["10.0.0.0/8"],
enableRagReplicas: false, // Cost-saving for dev environment
});
bedrockChatParams.set("prod", {
bedrockRegion: "us-east-1",
allowedIpV4AddressRanges: ["172.16.0.0/12"],
enableLambdaSnapStart: true,
enableRagReplicas: true, // Enhanced availability for production
});[!Note] Existing users can continue using
cdk.jsonwithout any changes. Theparameter.tsapproach is recommended for new deployments or when you need to manage multiple environments.
You can deploy multiple environments from the same codebase using the parameter.ts file and the -c envName option.
- Define your environments in
parameter.tsas shown above - Each environment will have its own set of resources with environment-specific prefixes
To deploy a specific environment:
# Deploy the dev environment
npx cdk deploy --all -c envName=dev
# Deploy the prod environment
npx cdk deploy --all -c envName=prodIf no environment is specified, the "default" environment is used:
# Deploy the default environment
npx cdk deploy --all-
Stack Naming:
- The main stacks for each environment will be prefixed with the environment name (e.g.,
dev-BedrockChatStack,prod-BedrockChatStack) - However, custom bot stacks (
BrChatKbStack*) and API publishing stacks (ApiPublishmentStack*) do not receive environment prefixes as they are created dynamically at runtime
- The main stacks for each environment will be prefixed with the environment name (e.g.,
-
Resource Naming:
- Only some resources receive environment prefixes in their names (e.g.,
dev_ddb_exporttable,dev-FrontendWebAcl) - Most resources maintain their original names but are isolated by being in different stacks
- Only some resources receive environment prefixes in their names (e.g.,
-
Environment Identification:
- All resources are tagged with a
CDKEnvironmenttag containing the environment name - You can use this tag to identify which environment a resource belongs to
- Example:
CDKEnvironment: devorCDKEnvironment: prod
- All resources are tagged with a
-
Default Environment Override: If you define a "default" environment in
parameter.ts, it will override the settings incdk.json. To continue usingcdk.json, don't define a "default" environment inparameter.ts. -
Environment Requirements: To create environments other than "default", you must use
parameter.ts. The-c envNameoption alone is not sufficient without corresponding environment definitions. -
Resource Isolation: Each environment creates its own set of resources, allowing you to have development, testing, and production environments in the same AWS account without conflicts.
Update enableMistral to true in cdk.json, and run npx cdk deploy.
...
"enableMistral": true,[!Important] This project focus on Anthropic Claude models, the Mistral models are limited supported. For example, prompt examples are based on Claude models. This is a Mistral-only option, once you toggled to enable Mistral models, you can only use Mistral models for all the chat features, NOT both Claude and Mistral models.
Users can adjust the text generation parameters from the custom bot creation screen. If the bot is not used, the default parameters set in config.py will be used.
DEFAULT_GENERATION_CONFIG = {
"max_tokens": 2000,
"top_k": 250,
"top_p": 0.999,
"temperature": 0.6,
"stop_sequences": ["Human: ", "Assistant: "],
}If using cli and CDK, please npx cdk destroy. If not, access CloudFormation and then delete BedrockChatStack and FrontendWafStack manually. Please note that FrontendWafStack is in us-east-1 region.
This asset automatically detects the language using i18next-browser-languageDetector. You can switch languages from the application menu. Alternatively, you can use Query String to set the language as shown below.
https://example.com?lng=ja
This sample has self sign up enabled by default. To disable self sign up, open cdk.json and switch selfSignUpEnabled as false. If you configure external identity provider, the value will be ignored and automatically disabled.
By default, this sample does not restrict the domains for sign-up email addresses. To allow sign-ups only from specific domains, open cdk.json and specify the domains as a list in allowedSignUpEmailDomains.
"allowedSignUpEmailDomains": ["example.com"],This sample supports external identity provider. Currently we support Google and custom OIDC provider.
This sample has the following groups to give permissions to users:
If you want newly created users to automatically join groups, you can specify them in cdk.json.
"autoJoinUserGroups": ["CreatingBotAllowed"],By default, newly created users will be joined to the CreatingBotAllowed group.
enableRagReplicas is an option in cdk.json that controls the replica settings for the RAG database, specifically the Knowledge Bases using Amazon OpenSearch Serverless.
- Default: true
- true: Enhances availability by enabling additional replicas, making it suitable for production environments but increasing costs.
- false: Reduces costs by using fewer replicas, making it suitable for development and testing.
This is an account/region-level setting, affecting the entire application rather than individual bots.
[!Note] As of June 2024, Amazon OpenSearch Serverless supports 0.5 OCU, lowering entry costs for small-scale workloads. Production deployments can start with 2 OCUs, while dev/test workloads can use 1 OCU. OpenSearch Serverless automatically scales based on workload demands. For more detail, visit announcement.
Cross-region inference allows Amazon Bedrock to dynamically route model inference requests across multiple AWS regions, enhancing throughput and resilience during peak demand periods. To configure, edit cdk.json.
"enableBedrockCrossRegionInference": trueLambda SnapStart improves cold start times for Lambda functions, providing faster response times for better user experience. On the other hand, for Python functions, there is a charge depending on cache size and not available in some regions currently. To disable SnapStart, edit cdk.json.
"enableLambdaSnapStart": falseYou can configure a custom domain for the CloudFront distribution by setting the following parameters in cdk.json:
{
"alternateDomainName": "chat.example.com",
"hostedZoneId": "Z0123456789ABCDEF"
}-
alternateDomainName: The custom domain name for your chat application (e.g., chat.example.com) -
hostedZoneId: The ID of your Route 53 hosted zone where the domain records will be created
When these parameters are provided, the deployment will automatically:
- Create an ACM certificate with DNS validation in us-east-1 region
- Create the necessary DNS records in your Route 53 hosted zone
- Configure CloudFront to use your custom domain
[!Note] The domain must be managed by Route 53 in your AWS account. The hosted zone ID can be found in the Route 53 console.
See LOCAL DEVELOPMENT.
Thank you for considering contributing to this repository! We welcome bug fixes, language translations (i18n), feature enhancements, agent tools, and other improvements.
For feature enhancements and other improvements, before creating a Pull Request, we would greatly appreciate it if you could create a Feature Request Issue to discuss the implementation approach and details. For bug fixes and language translations (i18n), proceed with creating a Pull Request directly.
Please also take a look at the following guidelines before contributing:
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for bedrock-claude-chat
Similar Open Source Tools

bedrock-claude-chat
This repository is a sample chatbot using the Anthropic company's LLM Claude, one of the foundational models provided by Amazon Bedrock for generative AI. It allows users to have basic conversations with the chatbot, personalize it with their own instructions and external knowledge, and analyze usage for each user/bot on the administrator dashboard. The chatbot supports various languages, including English, Japanese, Korean, Chinese, French, German, and Spanish. Deployment is straightforward and can be done via the command line or by using AWS CDK. The architecture is built on AWS managed services, eliminating the need for infrastructure management and ensuring scalability, reliability, and security.
kwaak
Kwaak is a tool that allows users to run a team of autonomous AI agents locally from their own machine. It enables users to write code, improve test coverage, update documentation, and enhance code quality while focusing on building innovative projects. Kwaak is designed to run multiple agents in parallel, interact with codebases, answer questions about code, find examples, write and execute code, create pull requests, and more. It is free and open-source, allowing users to bring their own API keys or models via Ollama. Kwaak is part of the bosun.ai project, aiming to be a platform for autonomous code improvement.
OpenAI-sublime-text
The OpenAI Completion plugin for Sublime Text provides first-class code assistant support within the editor. It utilizes LLM models to manipulate code, engage in chat mode, and perform various tasks. The plugin supports OpenAI, llama.cpp, and ollama models, allowing users to customize their AI assistant experience. It offers separated chat histories and assistant settings for different projects, enabling context-specific interactions. Additionally, the plugin supports Markdown syntax with code language syntax highlighting, server-side streaming for faster response times, and proxy support for secure connections. Users can configure the plugin's settings to set their OpenAI API key, adjust assistant modes, and manage chat history. Overall, the OpenAI Completion plugin enhances the Sublime Text editor with powerful AI capabilities, streamlining coding workflows and fostering collaboration with AI assistants.
Memori
Memori is a memory fabric designed for enterprise AI that seamlessly integrates into existing software and infrastructure. It is agnostic to LLM, datastore, and framework, providing support for major foundational models and databases. With features like vectorized memories, in-memory semantic search, and a knowledge graph, Memori simplifies the process of attributing LLM interactions and managing sessions. It offers Advanced Augmentation for enhancing memories at different levels and supports various platforms, frameworks, database integrations, and datastores. Memori is designed to reduce development overhead and provide efficient memory management for AI applications.
oasis
OASIS is a scalable, open-source social media simulator that integrates large language models with rule-based agents to realistically mimic the behavior of up to one million users on platforms like Twitter and Reddit. It facilitates the study of complex social phenomena such as information spread, group polarization, and herd behavior, offering a versatile tool for exploring diverse social dynamics and user interactions in digital environments. With features like scalability, dynamic environments, diverse action spaces, and integrated recommendation systems, OASIS provides a comprehensive platform for simulating social media interactions at a large scale.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using a local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration for tasks, command line interface for running tasks, push to Hugging Face Hub for dataset upload, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration or Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM to interface with LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub.
promptwright
Promptwright is a Python library designed for generating large synthetic datasets using local LLM and various LLM service providers. It offers flexible interfaces for generating prompt-led synthetic datasets. The library supports multiple providers, configurable instructions and prompts, YAML configuration, command line interface, push to Hugging Face Hub, and system message control. Users can define generation tasks using YAML configuration files or programmatically using Python code. Promptwright integrates with LiteLLM for LLM providers and supports automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub. The library is not responsible for the content generated by models and advises users to review the data before using it in production environments.
magic-cli
Magic CLI is a command line utility that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance command line efficiency. It is inspired by projects like Amazon Q and GitHub Copilot for CLI. The tool allows users to suggest commands, search across command history, and generate commands for specific tasks using local or remote LLM providers. Magic CLI also provides configuration options for LLM selection and response generation. The project is still in early development, so users should expect breaking changes and bugs.
uni-api
uni-api is a project that unifies the management of large language model APIs, allowing you to call multiple backend services through a single unified API interface, converting them all to OpenAI format, and supporting load balancing. It supports various backend services such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Vertex, Azure, xai, Cohere, Groq, Cloudflare, OpenRouter, and more. The project offers features like no front-end, pure configuration file setup, unified management of multiple backend services, support for multiple standard OpenAI format interfaces, rate limiting, automatic retry, channel cooling, fine-grained model timeout settings, and fine-grained permission control.

ash_ai
Ash AI is a tool that provides a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for exposing tool definitions to an MCP client. It allows for the installation of dev and production MCP servers, and supports features like OAuth2 flow with AshAuthentication, tool data access, tool execution callbacks, prompt-backed actions, and vectorization strategies. Users can also generate a chat feature for their Ash & Phoenix application using `ash_oban` and `ash_postgres`, and specify LLM API keys for OpenAI. The tool is designed to help developers experiment with tools and actions, monitor tool execution, and expose actions as tool calls.
web-llm
WebLLM is a modular and customizable javascript package that directly brings language model chats directly onto web browsers with hardware acceleration. Everything runs inside the browser with no server support and is accelerated with WebGPU. WebLLM is fully compatible with OpenAI API. That is, you can use the same OpenAI API on any open source models locally, with functionalities including json-mode, function-calling, streaming, etc. We can bring a lot of fun opportunities to build AI assistants for everyone and enable privacy while enjoying GPU acceleration.
hash
HASH is a self-building, open-source database which grows, structures and checks itself. With it, we're creating a platform for decision-making, which helps you integrate, understand and use data in a variety of different ways.
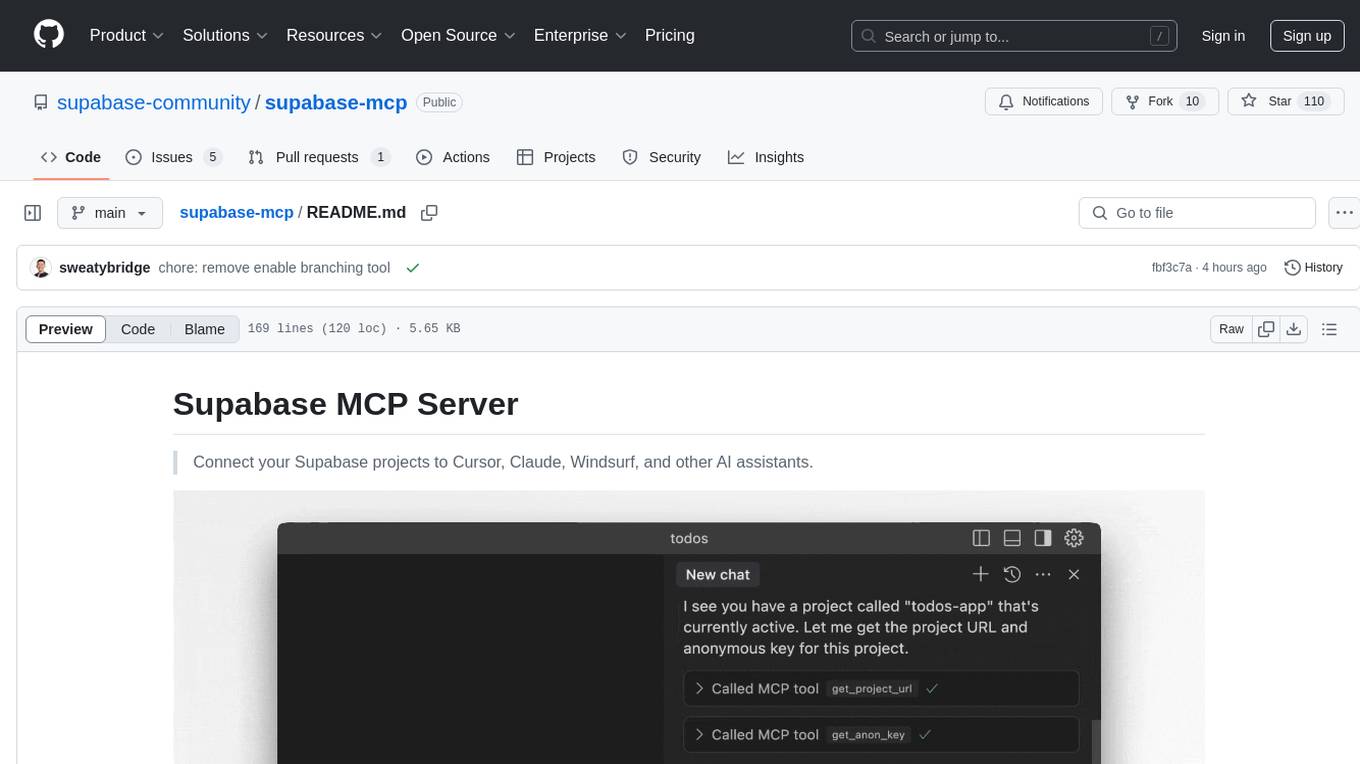
supabase-mcp
Supabase MCP Server standardizes how Large Language Models (LLMs) interact with Supabase, enabling AI assistants to manage tables, fetch config, and query data. It provides tools for project management, database operations, project configuration, branching (experimental), and development tools. The server is pre-1.0, so expect some breaking changes between versions.
basic-memory
Basic Memory is a tool that enables users to build persistent knowledge through natural conversations with Large Language Models (LLMs) like Claude. It uses the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to allow compatible LLMs to read and write to a local knowledge base stored in simple Markdown files on the user's computer. The tool facilitates creating structured notes during conversations, maintaining a semantic knowledge graph, and keeping all data local and under user control. Basic Memory aims to address the limitations of ephemeral LLM interactions by providing a structured, bi-directional, and locally stored knowledge management solution.
agenticSeek
AgenticSeek is a voice-enabled AI assistant powered by DeepSeek R1 agents, offering a fully local alternative to cloud-based AI services. It allows users to interact with their filesystem, code in multiple languages, and perform various tasks autonomously. The tool is equipped with memory to remember user preferences and past conversations, and it can divide tasks among multiple agents for efficient execution. AgenticSeek prioritizes privacy by running entirely on the user's hardware without sending data to the cloud.
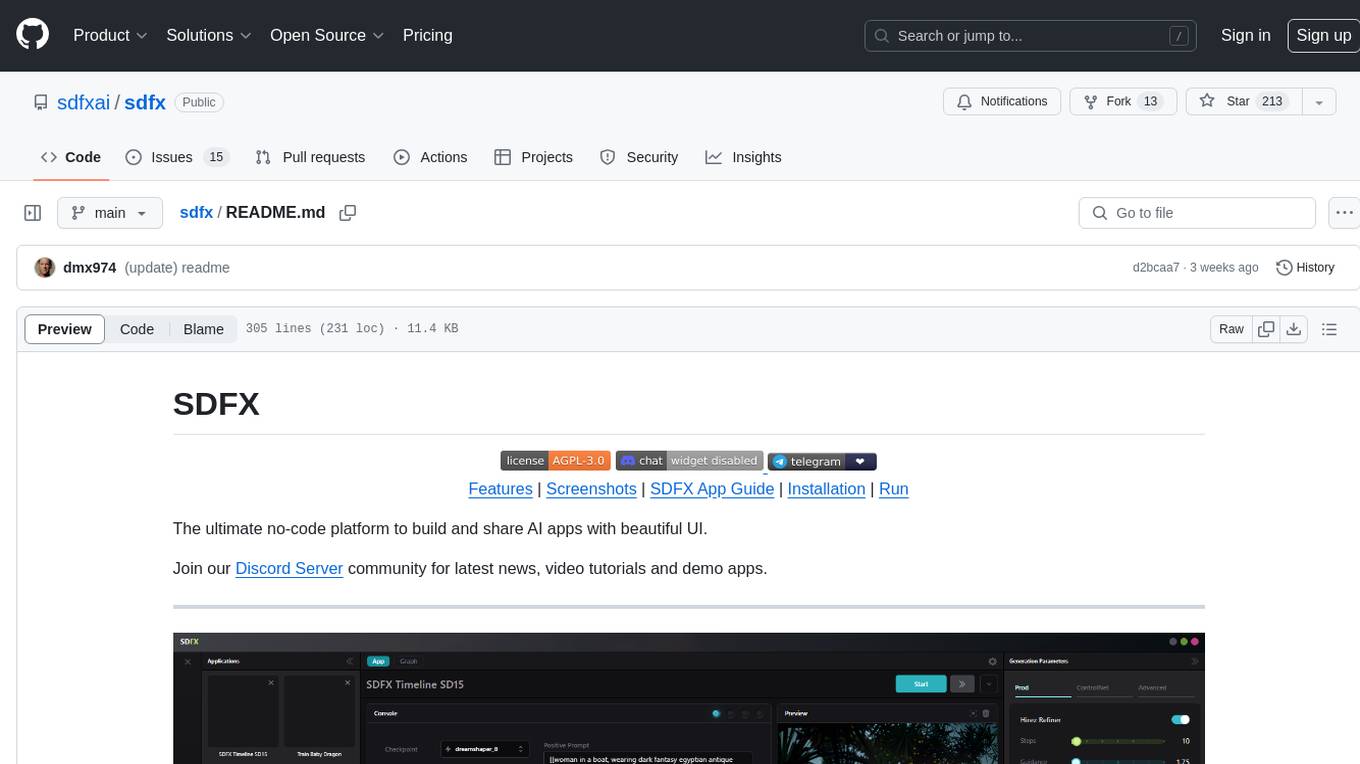
sdfx
SDFX is the ultimate no-code platform for building and sharing AI apps with beautiful UI. It enables the creation of user-friendly interfaces for complex workflows by combining Comfy workflow with a UI. The tool is designed to merge the benefits of form-based UI and graph-node based UI, allowing users to create intricate graphs with a high-level UI overlay. SDFX is fully compatible with ComfyUI, abstracting the need for installing ComfyUI. It offers features like animated graph navigation, node bookmarks, UI debugger, custom nodes manager, app and template export, image and mask editor, and more. The tool compiles as a native app or web app, making it easy to maintain and add new features.
For similar tasks

bedrock-claude-chat
This repository is a sample chatbot using the Anthropic company's LLM Claude, one of the foundational models provided by Amazon Bedrock for generative AI. It allows users to have basic conversations with the chatbot, personalize it with their own instructions and external knowledge, and analyze usage for each user/bot on the administrator dashboard. The chatbot supports various languages, including English, Japanese, Korean, Chinese, French, German, and Spanish. Deployment is straightforward and can be done via the command line or by using AWS CDK. The architecture is built on AWS managed services, eliminating the need for infrastructure management and ensuring scalability, reliability, and security.
MITSUHA
OneReality is a virtual waifu/assistant that you can speak to through your mic and it'll speak back to you! It has many features such as: * You can speak to her with a mic * It can speak back to you * Has short-term memory and long-term memory * Can open apps * Smarter than you * Fluent in English, Japanese, Korean, and Chinese * Can control your smart home like Alexa if you set up Tuya (more info in Prerequisites) It is built with Python, Llama-cpp-python, Whisper, SpeechRecognition, PocketSphinx, VITS-fast-fine-tuning, VITS-simple-api, HyperDB, Sentence Transformers, and Tuya Cloud IoT.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.