
quick-start-guide-to-llms
The Official Repo for "Quick Start Guide to Large Language Models"
Stars: 254
This GitHub repository serves as the companion to the 'Quick Start Guide to Large Language Models - Second Edition' book. It contains code snippets and notebooks demonstrating various applications and advanced techniques in working with Transformer models and large language models (LLMs). The repository is structured into directories for notebooks, data, and images, with each notebook corresponding to a chapter in the book. Users can explore topics such as semantic search, prompt engineering, model fine-tuning, custom embeddings, advanced LLM usage, moving LLMs into production, and evaluating LLMs. The repository aims to provide practical examples and insights for working with LLMs in different contexts.
README:
Get your copy today and please leave a rating/review to tell me what you thought! ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Welcome to the GitHub repository for the "Quick Start Guide to Large Language Models - Second Edition". This repository contains the code snippets and notebooks used in the book, demonstrating various applications and advanced techniques in working with Transformer models and large language models (LLMs). View the code for the First Edition here
-
notebooks: Contains Jupyter notebooks for each chapter in the book. -
data: Contains the datasets used in the notebooks. -
images: Contains images and graphs used in the notebooks.
Below is a list of the notebooks included in the notebooks directory, organized by the chapters in the book.
-
Chapter 2: Semantic Search with LLMs
-
02_semantic_search.ipynb: An introduction to semantic search using OpenAI and open-source models.
-
-
Chapter 3: First Steps with Prompt Engineering
-
03_prompt_engineering.ipynb: A guide to effective prompt engineering for instruction-aligned LLMs.
-
-
Chapter 4: The AI Ecosystem: Putting the Pieces Together
-
04_rag_retrieval.ipynb: Building a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline. -
04_agent.ipynb: Constructing an AI agent using LLMs and other tools.
-
-
Chapter 5: Optimizing LLMs with Customized Fine-Tuning
-
05_bert_app_review.ipynb: Fine-tuning a BERT model for app review classification. -
05_openai_app_review_fine_tuning.ipynb: Fine-tuning OpenAI models for app review classification.
-
-
Chapter 6: Advanced Prompt Engineering
-
06_adv_prompt_engineering.ipynb: Advanced techniques in prompt engineering, including output validation and semantic few-shot learning. -
06_adv_prompt_engineering - DEEPSEEK.ipynb: Extending the MathQA case study to Deepseek V3 and R1. Prompting stil seems to matter :)
-
-
Chapter 7: Customizing Embeddings and Model Architectures
-
07_recommendation_engine.ipynb: Building a recommendation engine using custom fine-tuned LLMs and embeddings.
-
-
Chapter 9: Moving Beyond Foundation Models
-
09_constructing_a_vqa_system.ipynb: Step-by-step guide to constructing a Visual Question Answering (VQA) system using GPT-2 and Vision Transformer. -
09_using_our_vqa.ipynb: Using the VQA system built in the previous notebook. -
09_flan_t5_rl.ipynb: Using Reinforcement Learning (RL) to improve FLAN-T5 model outputs.
-
-
Chapter 10: Advanced Open-Source LLM Fine-Tuning
-
10_SAWYER_LLAMA_SFT.ipynb: Fine-tuning the Llama-3 model to create the SAWYER bot. -
10_SAWYER_Reward_Model.ipynb: Training a reward model from human preferences for the SAWYER bot. -
10_SAWYER_RLF.ipynb: Applying Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) to align the SAWYER bot. -
10_SAWYER_USE_SAWYER.ipynb: Using the SAWYER bot. -
10_anime_category_classification_model_freezing.ipynb: Fine-tuning a BERT model for anime category classification, comparing layer freezing techniques. -
10_latex_gpt2.ipynb: Fine-tuning GPT-2 to generate LaTeX formulas. -
10_optimizing_fine_tuning.ipynb: Best practices for optimizing fine-tuning of transformer models.
-
-
Chapter 11: Moving LLMs into Production
-
11_distillation_example_1.ipynb: Exploring knowledge distillation techniques for transformer models. -
11_distillation_example_2.ipynb: Advanced distillation methods and applications. -
11_llama_quantization.ipynb: Quantizing Llama models for efficient deployment.
-
-
Chapter 12: Evaluating LLMs
-
12_llm_calibration.ipynb: Techniques for calibrating LLM outputs. -
12_llm_gen_eval.ipynb: Methods for evaluating the generative capabilities of LLMs. -
12_cluster.ipynb: Clustering techniques for analyzing LLM outputs. - Probing - There are over a dozen notebooks for Probing so I will only share a few key ones here:
-
To use this repository:
- Clone the repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/quick-start-llms.git- Navigate to the notebooks directory and open the Jupyter notebook of your choice:
cd quick-start-llms- Install the necessary libraries:
pip install -r requirements.txtNote: Some notebooks may require specific datasets, which can be found in the data directory.
Contributions are welcome! If you have any additions, corrections, or enhancements, feel free to submit a pull request.
This repository is for educational purposes and is meant to accompany the "Quick Start Guide to Large Language Models - Second Edition" book. Please refer to the book for in-depth explanations and discussions of the topics covered in the notebooks.
- Check out Sinan's Newsletter AI Office Hours for more AI/LLM content!
- Sinan has a podcast called Practically Intelligent where he chats about the latest and greatest in AI!
- Follow the Getting Started with Data, LLMs and ChatGPT Playlist on O'Reilly for a curated list of Sinan's work!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for quick-start-guide-to-llms
Similar Open Source Tools

quick-start-guide-to-llms
This GitHub repository serves as the companion to the 'Quick Start Guide to Large Language Models - Second Edition' book. It contains code snippets and notebooks demonstrating various applications and advanced techniques in working with Transformer models and large language models (LLMs). The repository is structured into directories for notebooks, data, and images, with each notebook corresponding to a chapter in the book. Users can explore topics such as semantic search, prompt engineering, model fine-tuning, custom embeddings, advanced LLM usage, moving LLMs into production, and evaluating LLMs. The repository aims to provide practical examples and insights for working with LLMs in different contexts.
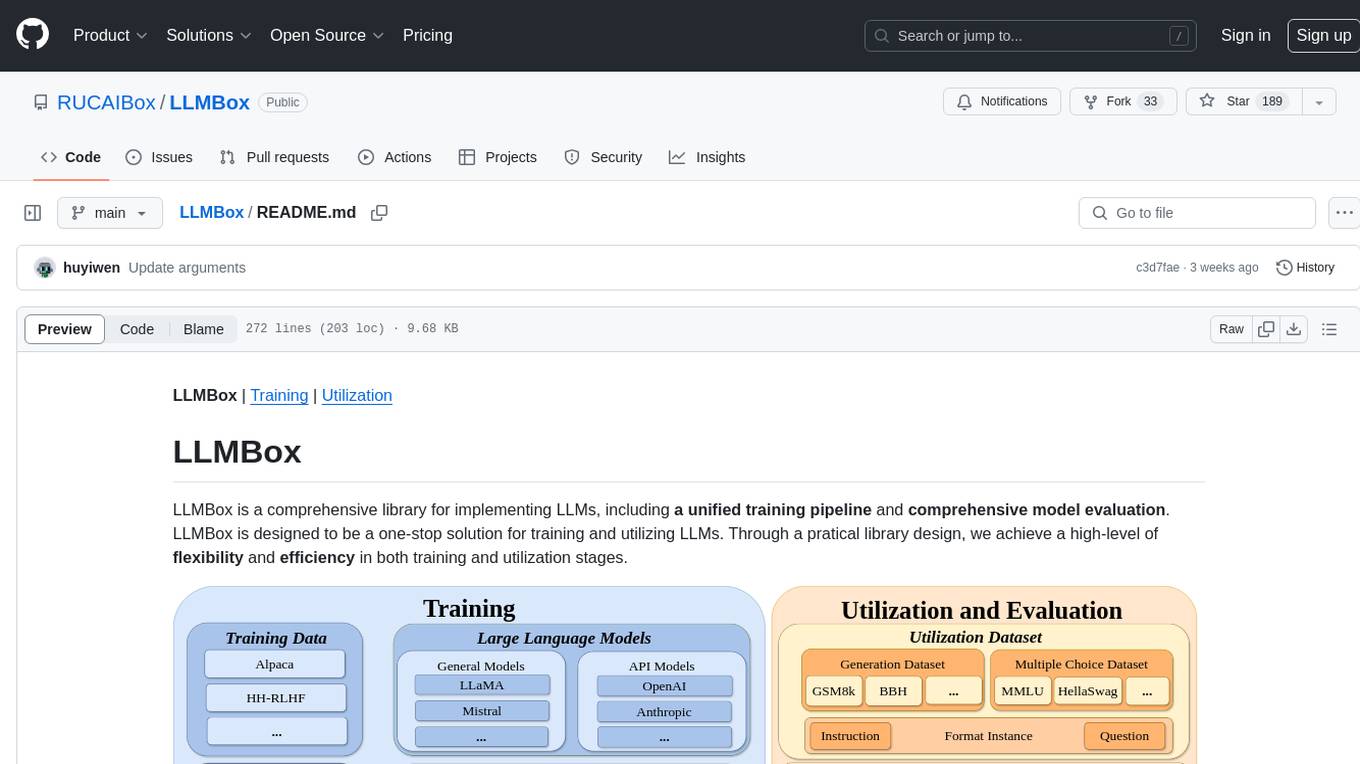
LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
ell
ell is a lightweight, functional prompt engineering framework that treats prompts as programs rather than strings. It provides tools for prompt versioning, monitoring, and visualization, as well as support for multimodal inputs and outputs. The framework aims to simplify the process of prompt engineering for language models.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
llm-memorization
The 'llm-memorization' project is a tool designed to index, archive, and search conversations with a local LLM using a SQLite database enriched with automatically extracted keywords. It aims to provide personalized context at the start of a conversation by adding memory information to the initial prompt. The tool automates queries from local LLM conversational management libraries, offers a hybrid search function, enhances prompts based on posed questions, and provides an all-in-one graphical user interface for data visualization. It supports both French and English conversations and prompts for bilingual use.
codellm-devkit
Codellm-devkit (CLDK) is a Python library that serves as a multilingual program analysis framework bridging traditional static analysis tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for code (CodeLLMs). It simplifies the process of analyzing codebases across multiple programming languages, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights and facilitating LLM-based code analysis. The library provides a unified interface for integrating outputs from various analysis tools and preparing them for effective use by CodeLLMs. Codellm-devkit aims to enable the development and experimentation of robust analysis pipelines that combine traditional program analysis tools and CodeLLMs, reducing friction in multi-language code analysis and ensuring compatibility across different tools and LLM platforms. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with popular analysis tools like WALA, Tree-sitter, LLVM, and CodeQL, acting as a crucial intermediary layer for efficient communication between these tools and CodeLLMs. The project is continuously evolving to include new tools and frameworks, maintaining its versatility for code analysis and LLM integration.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
generative-models
Generative Models by Stability AI is a repository that provides various generative models for research purposes. It includes models like Stable Video 4D (SV4D) for video synthesis, Stable Video 3D (SV3D) for multi-view synthesis, SDXL-Turbo for text-to-image generation, and more. The repository focuses on modularity and implements a config-driven approach for building and combining submodules. It supports training with PyTorch Lightning and offers inference demos for different models. Users can access pre-trained models like SDXL-base-1.0 and SDXL-refiner-1.0 under a CreativeML Open RAIL++-M license. The codebase also includes tools for invisible watermark detection in generated images.
humanoid-gym
Humanoid-Gym is a reinforcement learning framework designed for training locomotion skills for humanoid robots, focusing on zero-shot transfer from simulation to real-world environments. It integrates a sim-to-sim framework from Isaac Gym to Mujoco for verifying trained policies in different physical simulations. The codebase is verified with RobotEra's XBot-S and XBot-L humanoid robots. It offers comprehensive training guidelines, step-by-step configuration instructions, and execution scripts for easy deployment. The sim2sim support allows transferring trained policies to accurate simulated environments. The upcoming features include Denoising World Model Learning and Dexterous Hand Manipulation. Installation and usage guides are provided along with examples for training PPO policies and sim-to-sim transformations. The code structure includes environment and configuration files, with instructions on adding new environments. Troubleshooting tips are provided for common issues, along with a citation and acknowledgment section.
py-llm-core
PyLLMCore is a light-weighted interface with Large Language Models with native support for llama.cpp, OpenAI API, and Azure deployments. It offers a Pythonic API that is simple to use, with structures provided by the standard library dataclasses module. The high-level API includes the assistants module for easy swapping between models. PyLLMCore supports various models including those compatible with llama.cpp, OpenAI, and Azure APIs. It covers use cases such as parsing, summarizing, question answering, hallucinations reduction, context size management, and tokenizing. The tool allows users to interact with language models for tasks like parsing text, summarizing content, answering questions, reducing hallucinations, managing context size, and tokenizing text.
atropos
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.
Curie
Curie is an AI-agent framework designed for automated and rigorous scientific experimentation. It automates end-to-end workflow management, ensures methodical procedure, reliability, and interpretability, and supports ML research, system analysis, and scientific discovery. It provides a benchmark with questions from 4 Computer Science domains. Users can customize experiment agents and adapt to their own tasks by configuring base_config.json. Curie is suitable for hyperparameter tuning, algorithm behavior analysis, system performance benchmarking, and automating computational simulations.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
artkit
ARTKIT is a Python framework developed by BCG X for automating prompt-based testing and evaluation of Gen AI applications. It allows users to develop automated end-to-end testing and evaluation pipelines for Gen AI systems, supporting multi-turn conversations and various testing scenarios like Q&A accuracy, brand values, equitability, safety, and security. The framework provides a simple API, asynchronous processing, caching, model agnostic support, end-to-end pipelines, multi-turn conversations, robust data flows, and visualizations. ARTKIT is designed for customization by data scientists and engineers to enhance human-in-the-loop testing and evaluation, emphasizing the importance of tailored testing for each Gen AI use case.
Easy-Translate
Easy-Translate is a script designed for translating large text files with a single command. It supports various models like M2M100, NLLB200, SeamlessM4T, LLaMA, and Bloom. The tool is beginner-friendly and offers seamless and customizable features for advanced users. It allows acceleration on CPU, multi-CPU, GPU, multi-GPU, and TPU, with support for different precisions and decoding strategies. Easy-Translate also provides an evaluation script for translations. Built on HuggingFace's Transformers and Accelerate library, it supports prompt usage and loading huge models efficiently.
ai-shifu
AI-Shifu is an AI-led chat flow tool powered by LLM that provides an interactive and immersive experience for users. It allows users to follow a preset chat flow while being able to ask questions and affect the conversation. The tool can make personalized outputs based on user identity, interests, and preferences, making users feel like they are receiving one-on-one service. It is suitable for education, storytelling, product guides, surveys, and game NPC scenarios.
For similar tasks

quick-start-guide-to-llms
This GitHub repository serves as the companion to the 'Quick Start Guide to Large Language Models - Second Edition' book. It contains code snippets and notebooks demonstrating various applications and advanced techniques in working with Transformer models and large language models (LLMs). The repository is structured into directories for notebooks, data, and images, with each notebook corresponding to a chapter in the book. Users can explore topics such as semantic search, prompt engineering, model fine-tuning, custom embeddings, advanced LLM usage, moving LLMs into production, and evaluating LLMs. The repository aims to provide practical examples and insights for working with LLMs in different contexts.
foundations-of-gen-ai
This repository contains code for the O'Reilly Live Online Training for 'Transformer Architectures for Generative AI'. The course provides a deep understanding of transformer architectures and their impact on natural language processing (NLP) and vision tasks. Participants learn to harness transformers to tackle problems in text, image, and multimodal AI through theory and practical exercises.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.
tonic_validate
Tonic Validate is a framework for the evaluation of LLM outputs, such as Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines. Validate makes it easy to evaluate, track, and monitor your LLM and RAG applications. Validate allows you to evaluate your LLM outputs through the use of our provided metrics which measure everything from answer correctness to LLM hallucination. Additionally, Validate has an optional UI to visualize your evaluation results for easy tracking and monitoring.
llm
LLM is a Rust library that allows users to utilize multiple LLM backends (OpenAI, Anthropic, Ollama, DeepSeek, xAI, Phind, Groq, Google) in a single project. It provides a unified API and builder style for creating chat or text completion requests without the need for multiple structures and crates. Key features include multi-backend management, multi-step chains, templates for complex prompts, builder pattern for easy configuration, extensibility, validation, evaluation, parallel evaluation, function calling, REST API support, vision integration, and reasoning capabilities.

dstack
Dstack is an open-source orchestration engine for running AI workloads in any cloud. It supports a wide range of cloud providers (such as AWS, GCP, Azure, Lambda, TensorDock, Vast.ai, CUDO, RunPod, etc.) as well as on-premises infrastructure. With Dstack, you can easily set up and manage dev environments, tasks, services, and pools for your AI workloads.
one-click-llms
The one-click-llms repository provides templates for quickly setting up an API for language models. It includes advanced inferencing scripts for function calling and offers various models for text generation and fine-tuning tasks. Users can choose between Runpod and Vast.AI for different GPU configurations, with recommendations for optimal performance. The repository also supports Trelis Research and offers templates for different model sizes and types, including multi-modal APIs and chat models.

starcoder2-self-align
StarCoder2-Instruct is an open-source pipeline that introduces StarCoder2-15B-Instruct-v0.1, a self-aligned code Large Language Model (LLM) trained with a fully permissive and transparent pipeline. It generates instruction-response pairs to fine-tune StarCoder-15B without human annotations or data from proprietary LLMs. The tool is primarily finetuned for Python code generation tasks that can be verified through execution, with potential biases and limitations. Users can provide response prefixes or one-shot examples to guide the model's output. The model may have limitations with other programming languages and out-of-domain coding tasks.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
