
LLMsKnow
None
Stars: 57
LLMs Know More Than They Show is a repository containing code to reproduce the results in the paper. It includes scripts to generate model answers, extract exact answers, probe all layers and tokens, probe specific layers and tokens, conduct generalization experiments, perform resampling for error type probing and answer selection experiments, and run other baselines like logprob detection and p_true detection. The repository supports various datasets such as TriviaQA, Movies, HotpotQA, Winobias, Winogrande, NLI, IMDB, Math, and Natural questions. It also provides supported models like Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2, Mistral-7B-v0.3, Meta-Llama-3-8B, and Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct.
README:
Hadas Orgad, Michael Toker, Zorik Gekhman, Roi Reichart, Idan Szpektor, Hadas Kotek, Yonatan Belinkov
The code in this repo can be used to reproduce the results in the paper, by following these guidelines:
- We used Python 3.11.6.
- Use your favorite package manager to install the requirements.txt file.
- Notice that all scripts use
wandbto log the experiments results. This platform is free. For more information: https://wandb.ai/site. - Below we describe the most straightforward way to reproduce the results in the paper. However, there are other flags in the script which can be seen by running
python script.py --help.
(*) If you find any bugs, please open a Github issue - we are monitoring it and will fix it.
Below we describe for each dataset what you need to do to run the scripts on it.
-
TriviaQA: Requires
data/triviaqa-unfiltered/unfiltered-web-train.jsonanddata/triviaqa-unfiltered/unfiltered-web-dev.json, which can be downloaded from here, download the unfiltered version. -
Movies: Requires
data/movie_qa_test.csvanddata/movie_qa_train.csv, provided in this git repo. -
HotpotQA: No files requires. Loaded using huggingface
datasetslibrary. -
Winobias: Requires
data/winobias_dev.csvanddata/winobias_test.csv, provided in this git repo. -
Winogrande: Requires
data/winogrande_dev.csvanddata/winogrande_test.csv, provided in this git repo. -
NLI: (called mnli in the code) Requires Requires
data/mnli_train.csvanddata/mnli_validation.csv, provided in this git repo. -
IMDB: No files requires. Loaded using huggingface
datasetslibrary. -
Math: Requires
data/AnswerableMath_test.csvanddata/AnswerableMath.csv, provided in this git repo. -
Natural questions: Reqiores
nq_wc_dataset.csv, provided in this git repo.
mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.3meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8Bmeta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct
The first thing you need to do is to generate the answers for each dataset and extract exact answers.
generate_model_answers.py --model [model name] --dataset [dataset name]
Notice that for each dataset, e.g., triviaqa, you need to generate the answers for both the train and the test set. For example:
generate_model_answers.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --dataset triviaqa
and
generate_model_answers.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --dataset triviaqa_test
Next, you need to extract exact answer, also for the train and test sets separately:
extract_exact_answer.py --model [model name] --dataset [dataset name]
Not all tasks need to extract exact answers, because we are able to extract it during generation. These are the datasets:
- Winobias
- Winogrande
- IMDB
- NLI
probe_all_layers_and_tokens.py --model [model name] --probe_at [location] --seed [seed] --n_samples [n_samples] --dataset [dataset]
Due to memory constraints, we perform this step on a subset of 1000 samples. For example:
probe_all_layers_and_tokens.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --probe_at mlp_last_layer_only_input --seed 0 --n_samples 1000 --dataset triviaqa
Use save_clf flag to save the classifier. If running again, this flag indicates to load the trained classifier and only evaluate on the test set.
Saving the classifier is necessary for later use in the answer choice experiment.
probe.py --model [model] --model [model name] --probe_at [location] --seeds [seeds] --n_samples ['all' for all, number for subset] [--save_clf] --dataset [dataset] --layer [layer] --token [token]
For example:
probe.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --extraction_model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --probe_at mlp --seeds 0 5 26 42 63 --n_samples all --save_clf --dataset triviaqa --layer 15 --token exact_answer_last_token
Generalization experiments are also run with the probe.py script, but with the --test_dataset flag indicating a different dataset.
Here, if you already ran save_clf in a previous step, it will shorten the generalization running because the classifier will simply be loaded.
probe.py --model [model] --probe_at [location] --seeds [seeds] --n_samples ['all' for all, number for subset] [--save_clf] --dataset [dataset] --layer [layer] --token [token]
For example:
probe.py --model [model] --probe_at [location] --seeds [seeds] --n_samples ['all' for all, number for subset] --save_clf --dataset [dataset] --layer [layer] --token [token]
This step is required for probing type of error and for the answer choice experiments (sections 5 and 6)
resampling.py --model [model] --seed [seed] --n_resamples [N] --dataset [dataset name]
-
You'll need to run this both for the train and the test set for section 5 results (e.g., both for
TriviaQAandTriviaQA_test), and only the test set for section 6 results (e.g., onlyTriviaQA_test). -
This run can take a long time, especially if you do 30 resamples like in the paper. For shortening the waiting time, you can run this in parallel on different GPUs with different seeds and then merge the files in the end. Use the
--tagflag to do this, which will make sure the files don't have overlapping names. Make sure you give a different "tag" and seed for each run. For instance, here we split to six runs of 5 resamples each:resampling.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --seed 0 --dataset triviaqa --n_resamples 5 --tag 0 resampling.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --seed 5 --dataset triviaqa --n_resamples 5 --tag 1 resampling.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --seed 26 --dataset triviaqa --n_resamples 5 --tag 2 resampling.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --seed 42 --dataset triviaqa --n_resamples 5 --tag 3 resampling.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --seed 63 --dataset triviaqa --n_resamples 5 --tag 4 resampling.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --seed 70 --dataset triviaqa --n_resamples 5 --tag 5
Then, you can use the script resampling_merge_runs.py to merge the files. The script is written for six runs of 5 resamples each, so you might need to adjust it if you have a different number of resamples.
merge_resampling_files.py --model [model] --dataset [dataset]
After resampling + merging is done, you need to extract exact answers. We use the extract_exact_answer.py script for this as well. The do_resampling flag is used to indicate that we are extracting exact answers for resampled files and for how many resamples.
extract_exact_answer.py --dataset [dataset] --do_resampling [N] --model [model] --extraction_model [model_used_for_extraction]
Again, you don't need to extract exact answers for some of the datasets (mentioned above).
-
--merge_typesflag is used for the results of the paper: we merge the different subtypes discussed in the paper, e.g, consistently incorrect A + B. You can also run it without the merging.probe_type_of_error.py --model [model] --probe_at [location] --seeds [seeds] --n_samples ['all' for all, number for subset] --n_resamples [N] --token [token] --dataset [dataset] --layer [layer] [--merge_types]
For example:
probe_type_of_error.py --model 'mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2' --probe_at mlp --seeds 0 5 26 42 63 --n_samples all --n_resamples 10 --token exact_answer_last_token --dataset triviaqa --layer 13 --token exact_answer_last_token --merge_types
You need to choose the layer and token to use for probing in this experiment. You need to have a saved classifier from the probe.py script with --save_clf flag.
Note that you need to run this for the test set only, e.g., triviaqa-test.
probe_choose_answer.py --model [model] --probe_at [location] --layer [layer] --token [token] --dataset [dataset (test)] --n_resamples [N] --seeds [seeds]
For example:
probe_choose_answer.py --model mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 --probe_at mlp --layer 13 --token exact_answer_last_token --dataset triviaqa_test --n_resamples 30 --seed 0 5 26 42 63
We also provide the scripts to run the other baselines in the paper, namely p_true and logprob.
In both cases, you can run the version that uses exact answer and the version that does not by using the flag use_exact_answer.
Using these scripts is pretty straightforward.
Running logprob detection:
logprob_detection.py --model [model] --dataset [dataset] --seeds [seeds] [--use_exact_answer]
Running detection with p_true:
p_true_detection.py --model [model] --dataset [dataset] --seeds [seeds] [--use_exact_answer]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLMsKnow
Similar Open Source Tools

LLMsKnow
LLMs Know More Than They Show is a repository containing code to reproduce the results in the paper. It includes scripts to generate model answers, extract exact answers, probe all layers and tokens, probe specific layers and tokens, conduct generalization experiments, perform resampling for error type probing and answer selection experiments, and run other baselines like logprob detection and p_true detection. The repository supports various datasets such as TriviaQA, Movies, HotpotQA, Winobias, Winogrande, NLI, IMDB, Math, and Natural questions. It also provides supported models like Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2, Mistral-7B-v0.3, Meta-Llama-3-8B, and Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct.
MiniCheck
MiniCheck is an efficient fact-checking tool designed to verify claims against grounding documents using large language models. It provides a sentence-level fact-checking model that can be used to evaluate the consistency of claims with the provided documents. MiniCheck offers different models, including Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, which is the state-of-the-art and commercially usable. The tool enables users to fact-check multi-sentence claims by breaking them down into individual sentences for optimal performance. It also supports automatic prefix caching for faster inference when repeatedly fact-checking the same document with different claims.
instructor_ex
Instructor is a tool designed to structure outputs from OpenAI and other OSS LLMs by coaxing them to return JSON that maps to a provided Ecto schema. It allows for defining validation logic to guide LLMs in making corrections, and supports automatic retries. Instructor is primarily used with the OpenAI API but can be extended to work with other platforms. The tool simplifies usage by creating an ecto schema, defining a validation function, and making calls to chat_completion with instructions for the LLM. It also offers features like max_retries to fix validation errors iteratively.
WildBench
WildBench is a tool designed for benchmarking Large Language Models (LLMs) with challenging tasks sourced from real users in the wild. It provides a platform for evaluating the performance of various models on a range of tasks. Users can easily add new models to the benchmark by following the provided guidelines. The tool supports models from Hugging Face and other APIs, allowing for comprehensive evaluation and comparison. WildBench facilitates running inference and evaluation scripts, enabling users to contribute to the benchmark and collaborate on improving model performance.
MemoryLLM
MemoryLLM is a large language model designed for self-updating capabilities. It offers pretrained models with different memory capacities and features, such as chat models. The repository provides training code, evaluation scripts, and datasets for custom experiments. MemoryLLM aims to enhance knowledge retention and performance on various natural language processing tasks.
chromem-go
chromem-go is an embeddable vector database for Go with a Chroma-like interface and zero third-party dependencies. It enables retrieval augmented generation (RAG) and similar embeddings-based features in Go apps without the need for a separate database. The focus is on simplicity and performance for common use cases, allowing querying of documents with minimal memory allocations. The project is in beta and may introduce breaking changes before v1.0.0.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
raid
RAID is the largest and most comprehensive dataset for evaluating AI-generated text detectors. It contains over 10 million documents spanning 11 LLMs, 11 genres, 4 decoding strategies, and 12 adversarial attacks. RAID is designed to be the go-to location for trustworthy third-party evaluation of popular detectors. The dataset covers diverse models, domains, sampling strategies, and attacks, making it a valuable resource for training detectors, evaluating generalization, protecting against adversaries, and comparing to state-of-the-art models from academia and industry.
giskard
Giskard is an open-source Python library that automatically detects performance, bias & security issues in AI applications. The library covers LLM-based applications such as RAG agents, all the way to traditional ML models for tabular data.
LLM-Pruner
LLM-Pruner is a tool for structural pruning of large language models, allowing task-agnostic compression while retaining multi-task solving ability. It supports automatic structural pruning of various LLMs with minimal human effort. The tool is efficient, requiring only 3 minutes for pruning and 3 hours for post-training. Supported LLMs include Llama-3.1, Llama-3, Llama-2, LLaMA, BLOOM, Vicuna, and Baichuan. Updates include support for new LLMs like GQA and BLOOM, as well as fine-tuning results achieving high accuracy. The tool provides step-by-step instructions for pruning, post-training, and evaluation, along with a Gradio interface for text generation. Limitations include issues with generating repetitive or nonsensical tokens in compressed models and manual operations for certain models.
CogAgent
CogAgent is an advanced intelligent agent model designed for automating operations on graphical interfaces across various computing devices. It supports platforms like Windows, macOS, and Android, enabling users to issue commands, capture device screenshots, and perform automated operations. The model requires a minimum of 29GB of GPU memory for inference at BF16 precision and offers capabilities for executing tasks like sending Christmas greetings and sending emails. Users can interact with the model by providing task descriptions, platform specifications, and desired output formats.
RLAIF-V
RLAIF-V is a novel framework that aligns MLLMs in a fully open-source paradigm for super GPT-4V trustworthiness. It maximally exploits open-source feedback from high-quality feedback data and online feedback learning algorithm. Notable features include achieving super GPT-4V trustworthiness in both generative and discriminative tasks, using high-quality generalizable feedback data to reduce hallucination of different MLLMs, and exhibiting better learning efficiency and higher performance through iterative alignment.
MathVerse
MathVerse is an all-around visual math benchmark designed to evaluate the capabilities of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in visual math problem-solving. It collects high-quality math problems with diagrams to assess how well MLLMs can understand visual diagrams for mathematical reasoning. The benchmark includes 2,612 problems transformed into six versions each, contributing to 15K test samples. It also introduces a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Evaluation strategy for fine-grained assessment of output answers.
SheetCopilot
SheetCopilot is an assistant agent that manipulates spreadsheets by following user commands. It leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with spreadsheets like a human expert, enabling non-expert users to complete tasks on complex software such as Google Sheets and Excel via a language interface. The tool observes spreadsheet states, polishes generated solutions based on external action documents and error feedback, and aims to improve success rate and efficiency. SheetCopilot offers a dataset with diverse task categories and operations, supporting operations like entry & manipulation, management, formatting, charts, and pivot tables. Users can interact with SheetCopilot in Excel or Google Sheets, executing tasks like calculating revenue, creating pivot tables, and plotting charts. The tool's evaluation includes performance comparisons with leading LLMs and VBA-based methods on specific datasets, showcasing its capabilities in controlling various aspects of a spreadsheet.
OpenMusic
OpenMusic is a repository providing an implementation of QA-MDT, a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for music generation. The code integrates state-of-the-art models and offers training strategies for music generation. The repository includes implementations of AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. Users can train or fine-tune the model using different strategies and datasets. The model is well-pretrained and can be used for music generation tasks. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets, training the model, and performing inference. Contact information is provided for any questions or suggestions regarding the project.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.
For similar tasks
Open-Prompt-Injection
OpenPromptInjection is an open-source toolkit for attacks and defenses in LLM-integrated applications, enabling easy implementation, evaluation, and extension of attacks, defenses, and LLMs. It supports various attack and defense strategies, including prompt injection, paraphrasing, retokenization, data prompt isolation, instructional prevention, sandwich prevention, perplexity-based detection, LLM-based detection, response-based detection, and know-answer detection. Users can create models, tasks, and apps to evaluate different scenarios. The toolkit currently supports PaLM2 and provides a demo for querying models with prompts. Users can also evaluate ASV for different scenarios by injecting tasks and querying models with attacked data prompts.
LLM-LieDetector
This repository contains code for reproducing experiments on lie detection in black-box LLMs by asking unrelated questions. It includes Q/A datasets, prompts, and fine-tuning datasets for generating lies with language models. The lie detectors rely on asking binary 'elicitation questions' to diagnose whether the model has lied. The code covers generating lies from language models, training and testing lie detectors, and generalization experiments. It requires access to GPUs and OpenAI API calls for running experiments with open-source models. Results are stored in the repository for reproducibility.
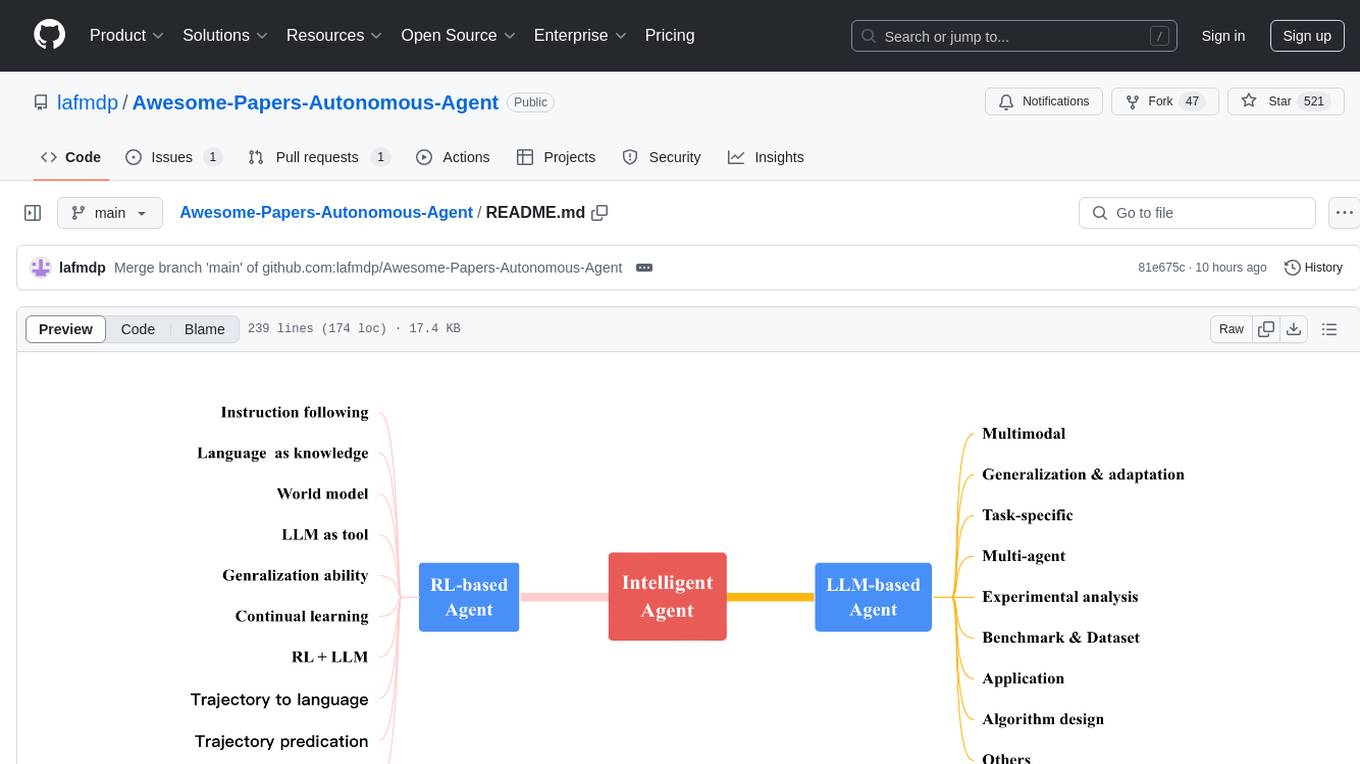
Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent
Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent is a curated collection of recent papers focusing on autonomous agents, specifically interested in RL-based agents and LLM-based agents. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in intelligent agents that can achieve goals, acquire knowledge, and continually improve. The collection includes papers on various topics such as instruction following, building agents based on world models, using language as knowledge, leveraging LLMs as a tool, generalization across tasks, continual learning, combining RL and LLM, transformer-based policies, trajectory to language, trajectory prediction, multimodal agents, training LLMs for generalization and adaptation, task-specific designing, multi-agent systems, experimental analysis, benchmarking, applications, algorithm design, and combining with RL.
SwiftSage
SwiftSage is a tool designed for conducting experiments in the field of machine learning and artificial intelligence. It provides a platform for researchers and developers to implement and test various algorithms and models. The tool is particularly useful for exploring new ideas and conducting experiments in a controlled environment. SwiftSage aims to streamline the process of developing and testing machine learning models, making it easier for users to iterate on their ideas and achieve better results. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, SwiftSage is a valuable tool for anyone working in the field of AI and ML.

MemoryLLM
MemoryLLM is a large language model designed for self-updating capabilities. It offers pretrained models with different memory capacities and features, such as chat models. The repository provides training code, evaluation scripts, and datasets for custom experiments. MemoryLLM aims to enhance knowledge retention and performance on various natural language processing tasks.
ppl.llm.kernel.cuda
Primitive cuda kernel library for ppl.nn.llm, part of PPL.LLM system, tested on Ampere and Hopper, requires Linux on x86_64 or arm64 CPUs, GCC >= 9.4.0, CMake >= 3.18, Git >= 2.7.0, CUDA Toolkit >= 11.4. 11.6 recommended. Provides cuda kernel functionalities for deep learning tasks.
craftium
Craftium is an open-source platform based on the Minetest voxel game engine and the Gymnasium and PettingZoo APIs, designed for creating fast, rich, and diverse single and multi-agent environments. It allows for connecting to Craftium's Python process, executing actions as keyboard and mouse controls, extending the Lua API for creating RL environments and tasks, and supporting client/server synchronization for slow agents. Craftium is fully extensible, extensively documented, modern RL API compatible, fully open source, and eliminates the need for Java. It offers a variety of environments for research and development in reinforcement learning.

LLMsKnow
LLMs Know More Than They Show is a repository containing code to reproduce the results in the paper. It includes scripts to generate model answers, extract exact answers, probe all layers and tokens, probe specific layers and tokens, conduct generalization experiments, perform resampling for error type probing and answer selection experiments, and run other baselines like logprob detection and p_true detection. The repository supports various datasets such as TriviaQA, Movies, HotpotQA, Winobias, Winogrande, NLI, IMDB, Math, and Natural questions. It also provides supported models like Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2, Mistral-7B-v0.3, Meta-Llama-3-8B, and Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.