Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent
A collection of recent papers on building autonomous agent. Two topics included: RL-based / LLM-based agents.
Stars: 521
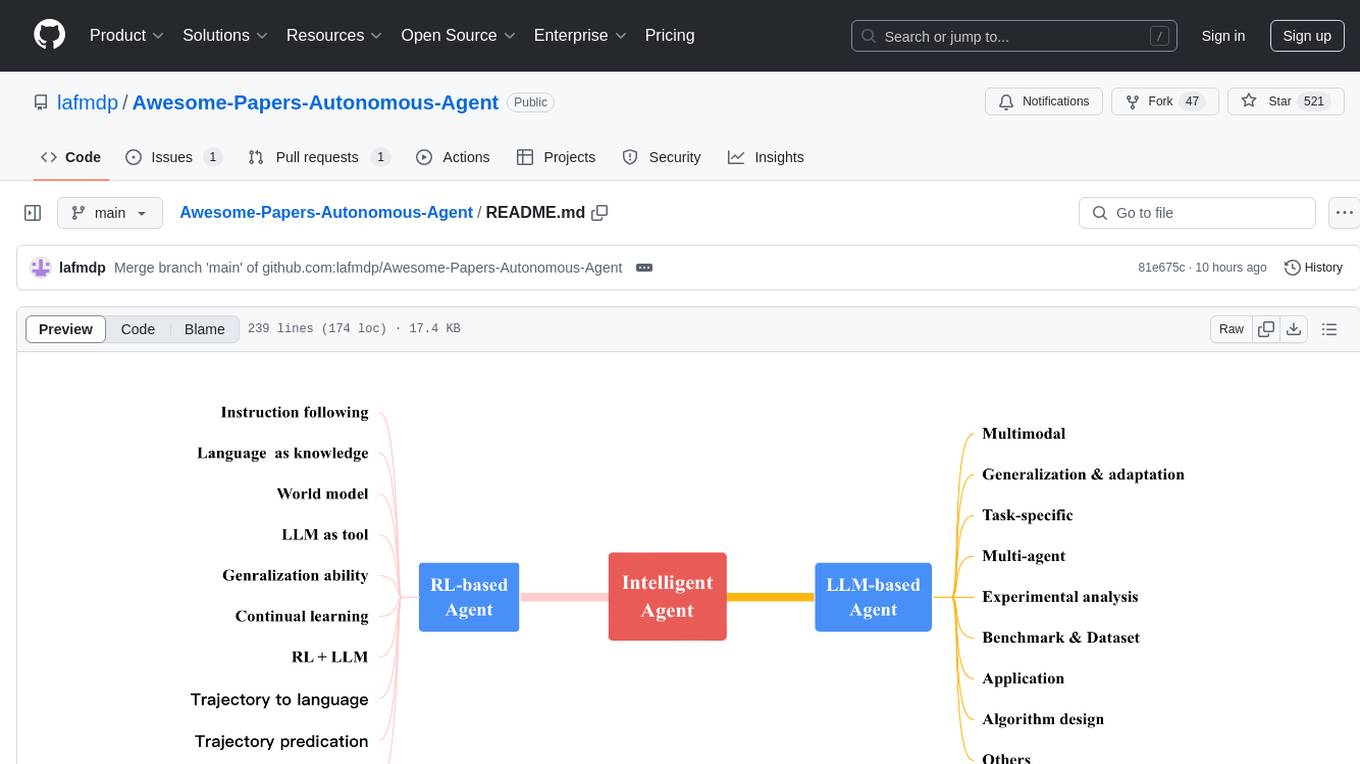
Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent is a curated collection of recent papers focusing on autonomous agents, specifically interested in RL-based agents and LLM-based agents. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in intelligent agents that can achieve goals, acquire knowledge, and continually improve. The collection includes papers on various topics such as instruction following, building agents based on world models, using language as knowledge, leveraging LLMs as a tool, generalization across tasks, continual learning, combining RL and LLM, transformer-based policies, trajectory to language, trajectory prediction, multimodal agents, training LLMs for generalization and adaptation, task-specific designing, multi-agent systems, experimental analysis, benchmarking, applications, algorithm design, and combining with RL.
README:
This is a collection of recent papers focusing on autonomous agent. Here is how Wikipedia defines Agent:
In artificial intelligence, an intelligent agent is an agent acting in an intelligent manner; It perceives its environment, takes actions autonomously in order to achieve goals, and may improve its performance with learning or acquiring knowledge. An intelligent agent may be simple or complex: A thermostator other control systemis considered an example of an intelligent agent, as is a human being, as is any system that meets the definition, such as a firm, a state, or a biome.
Thus, the key of an agent is that it can achieve goals, acquire knowledge and continually improve. The traditional agents in RL research will not be considered in this collection. Though LLM-based agents have caught people's eyes in recent research, RL-based agents also take their special position. Specifically, this repo is interested in two types of agent: RL-based agent and LLM-based agent.
Note that this paper list is under active maintaince. Free free to open an issue if you found any missed papers that fit the topic.
- 2024/01/31: Add a special list for surveys on autonomous agent.
- 2023/12/08: Add papers accepted by ICML'23 and ICLR'23 🚀
- 2023/11/08: Add papers accepted by NeurIPS'23. Add related links (project page or github) to these accepted papers 🎉
- 2023/10/25: Classify all papers based on their research topics. Check ToC for the standard of classification 👏
- 2023/10/18: Release first version of collection, including papers submitted to ICLR 2024 🚀
Table of Contents
- A Survey on Large Language Model based Autonomous Agents
- The Rise and Potential of Large Language Model Based Agents: A Survey
- [NeurIPS'23] Natural Language-conditioned Reinforcement Learning with Inside-out Task Language Development and Translation
- [NeurIPS'23] Guide Your Agent with Adaptive Multimodal Rewards [project]
- Compositional Instruction Following with Language Models and Reinforcement Learning
- RT-1: Robotics Transformer for Real-World Control at Scale [blog]
- RT-2: Vision-Language-Action Models Transfer Web Knowledge to Robotic Control [blog]
- Open X-Embodiment: Robotic Learning Datasets and RT-X Models [blog]
- [NeurIPS'23] Guide Your Agent with Adaptive Multimodal Rewards [project]
- LEO: An Embodied Generalist Agent in 3D World [project]
- [ICLR'23 Oral] Transformers are Sample-Efficient World Models [code]
- Learning to Model the World with Language
- MAMBA: an Effective World Model Approach for Meta-Reinforcement Learning
- Learning with Language Inference and Tips for Continual Reinforcement Learning
- Informing Reinforcement Learning Agents by Grounding Natural Language to Markov Decision Processes
- Language Reward Modulation for Pretraining Reinforcement Learning
- [NeurIPS'23] Efficient Policy Adaptation with Contrastive Prompt Ensemble for Embodied Agents
- [ICLR'23] Reward Design with Language Models [code]
- [ICML'23] RLang: A Declarative Language for Describing Partial World Knowledge to Reinforcement Learning Agents [Poster]
- [ICML'23] Do Embodied Agents Dream of Pixelated Sheep: Embodied Decision Making using Language Guided World Modelling [Project][Code]
- [ICML'23] Grounding Large Language Models in Interactive Environments with Online Reinforcement Learning
- Leveraging Large Language Models for Optimised Coordination in Textual Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
- Text2Reward: Dense Reward Generation with Language Models for Reinforcement Learning
- Language to Rewards for Robotic Skill Synthesis
- Eureka: Human-Level Reward Design via Coding Large Language Models
- STARLING: Self-supervised Training of Text-based Reinforcement Learning Agent with Large Language Models
- ADAPTER-RL: Adaptation of Any Agent using Reinforcement Learning
- Online Continual Learning for Interactive Instruction Following Agents
- [NeurIPS'23] A Definition of Continual Reinforcement Learning
- [NeurIPS'23] Large Language Models Are Semi-Parametric Reinforcement Learning Agents
- RoboGPT : An intelligent agent of making embodied long-term decisions for daily instruction tasks
- Can Language Agents Approach the Performance of RL? An Empirical Study On OpenAI Gym
- RLAdapter: Bridging Large Language Models to Reinforcement Learning in Open Worlds
- [NeurIPS'23] Cross-Episodic Curriculum for Transformer Agents. [project]
- [NeurIPS'23] State2Explanation: Concept-Based Explanations to Benefit Agent Learning and User Understanding
- [NeurIPS'23] Semantic HELM: A Human-Readable Memory for Reinforcement Learning
- [ICML'23] Distilling Internet-Scale Vision-Language Models into Embodied Agents
- Understanding Your Agent: Leveraging Large Language Models for Behavior Explanation
- Enhancing Human Experience in Human-Agent Collaboration: A Human-Centered Modeling Approach Based on Positive Human Gain
- A Competition Winning Deep Reinforcement Learning Agent in microRTS
- Aligning Agents like Large Language Models
- [ICML'23] PaLM-E: An Embodied Multimodal Language Model
- Steve-Eye: Equipping LLM-based Embodied Agents with Visual Perception in Open Worlds
- Multimodal Web Navigation with Instruction-Finetuned Foundation Models
- You Only Look at Screens: Multimodal Chain-of-Action Agents
- Learning Embodied Vision-Language Programming From Instruction, Exploration, and Environmental Feedback
- An Embodied Generalist Agent in 3D World
- JARVIS-1: Open-world Multi-task Agents with Memory-Augmented Multimodal Language Models
- FireAct: Toward Language Agent Finetuning
- Adapting LLM Agents Through Communication
- AgentTuning: Enabling Generalized Agent Abilities for LLMs
- Retroformer: Retrospective Large Language Agents with Policy Gradient Optimization
- [NeurIPS'23] Describe, Explain, Plan and Select: Interactive Planning with LLMs Enables Open-World Multi-Task Agents
- [NeurIPS'23] SwiftSage: A Generative Agent with Fast and Slow Thinking for Complex Interactive Tasks [Github]
- Rethinking the Buyer’s Inspection Paradox in Information Markets with Language Agents
- A Language-Agent Approach to Formal Theorem-Proving
- Agent Instructs Large Language Models to be General Zero-Shot Reasoners
- Ghost in the Minecraft: Hierarchical Agents for Minecraft via Large Language Models with Text-based Knowledge and Memory
- PaperQA: Retrieval-Augmented Generative Agent for Scientific Research
- Language Agents for Detecting Implicit Stereotypes in Text-to-image Models at Scale
- Suspicion-Agent: Playing Imperfect Information Games with Theory of Mind Aware GPT-4
- CoMM: Collaborative Multi-Agent, Multi-Reasoning-Path Prompting for Complex Problem Solving
- Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models
- OKR-Agent: An Object and Key Results Driven Agent System with Hierarchical Self-Collaboration and Self-Evaluation
- MetaGPT: Meta Programming for Multi-Agent Collaborative Framework
- AutoAgents: A Framework for Automatic Agent Generation
- Dynamic LLM-Agent Network: An LLM-agent Collaboration Framework with Agent Team Optimization
- AgentVerse: Facilitating Multi-Agent Collaboration and Exploring Emergent Behaviors
- Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View
- REX: Rapid Exploration and eXploitation for AI agents
- Emergence of Social Norms in Large Language Model-based Agent Societies
- Identifying the Risks of LM Agents with an LM-Emulated Sandbox
- Evaluating Multi-Agent Coordination Abilities in Large Language Models
- Large Language Models as Gaming Agents
- Benchmarking Large Language Models as AI Research Agents
- Adaptive Environmental Modeling for Task-Oriented Language Agents
- CLIN: A Continually Learning Language Agent for Rapid Task Adaptation and Generalization
- [ACL'24] A Controllable World of Apps and People for Benchmarking Interactive Coding Agents [website][blog]
- [ICLR'23] Task Ambiguity in Humans and Language Models [code]
- SmartPlay : A Benchmark for LLMs as Intelligent Agents
- AgentBench: Evaluating LLMs as Agents
- Put Your Money Where Your Mouth Is: Evaluating Strategic Planning and Execution of LLM Agents in an Auction Arena
- SOTOPIA: Interactive Evaluation for Social Intelligence in Language Agents
- SocioDojo: Building Lifelong Analytical Agents with Real-world Text and Time Series
- WebArena: A Realistic Web Environment for Building Autonomous Agents
- LLM-Deliberation: Evaluating LLMs with Interactive Multi-Agent Negotiation Game
- Evaluating Large Language Models at Evaluating Instruction Following
- CivRealm: A Learning and Reasoning Odyssey for Decision-Making Agents
- Lyfe Agents: generative agents for low-cost real-time social interactions
- AutoGen: Enabling Next-Gen LLM Applications via Multi-Agent Conversation
- [ICLR'23 Oral] ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models [code]
- [NeurIPS'23] AdaPlanner: Adaptive Planning from Feedback with Language Models [github]
- Prospector: Improving LLM Agents with Self-Asking and Trajectory Ranking
- Formally Specifying the High-Level Behavior of LLM-Based Agents
- Cumulative Reasoning With Large Language Models
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent
Similar Open Source Tools

Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent
Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent is a curated collection of recent papers focusing on autonomous agents, specifically interested in RL-based agents and LLM-based agents. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in intelligent agents that can achieve goals, acquire knowledge, and continually improve. The collection includes papers on various topics such as instruction following, building agents based on world models, using language as knowledge, leveraging LLMs as a tool, generalization across tasks, continual learning, combining RL and LLM, transformer-based policies, trajectory to language, trajectory prediction, multimodal agents, training LLMs for generalization and adaptation, task-specific designing, multi-agent systems, experimental analysis, benchmarking, applications, algorithm design, and combining with RL.
Awesome-Embodied-AI
Awesome-Embodied-AI is a curated list of papers on Embodied AI and related resources, tracking and summarizing research and industrial progress in the field. It includes surveys, workshops, tutorials, talks, blogs, and papers covering various aspects of Embodied AI, such as vision-language navigation, large language model-based agents, robotics, and more. The repository welcomes contributions and aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the advancements in Embodied AI.
awesome-lifelong-llm-agent
This repository is a collection of papers and resources related to Lifelong Learning of Large Language Model (LLM) based Agents. It focuses on continual learning and incremental learning of LLM agents, identifying key modules such as Perception, Memory, and Action. The repository serves as a roadmap for understanding lifelong learning in LLM agents and provides a comprehensive overview of related research and surveys.
rlhf_thinking_model
This repository is a collection of research notes and resources focusing on training large language models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It includes methodologies, techniques, and state-of-the-art approaches for optimizing preferences and model alignment in LLM training. The purpose is to serve as a reference for researchers and engineers interested in reinforcement learning, large language models, model alignment, and alternative RL-based methods.
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
This repository compiles a list of academic papers that evaluate, align, simulate, and provide surveys or perspectives on the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of Social Science. The papers cover various aspects of LLM research, including assessing their alignment with human values, evaluating their capabilities in tasks such as opinion formation and moral reasoning, and exploring their potential for simulating social interactions and addressing issues in diverse fields of Social Science. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in the intersection of LLMs and Social Science.
agentsociety
AgentSociety is an advanced framework designed for building agents in urban simulation environments. It integrates LLMs' planning, memory, and reasoning capabilities to generate realistic behaviors. The framework supports dataset-based, text-based, and rule-based environments with interactive visualization. It includes tools for interviews, surveys, interventions, and metric recording tailored for social experimentation.

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
AI6127
AI6127 is a course focusing on deep neural networks for natural language processing (NLP). It covers core NLP tasks and machine learning models, emphasizing deep learning methods using libraries like Pytorch. The course aims to teach students state-of-the-art techniques for practical NLP problems, including writing, debugging, and training deep neural models. It also explores advancements in NLP such as Transformers and ChatGPT.
GenAI_Agents
GenAI Agents is a comprehensive repository for developing and implementing Generative AI (GenAI) agents, ranging from simple conversational bots to complex multi-agent systems. It serves as a valuable resource for learning, building, and sharing GenAI agents, offering tutorials, implementations, and a platform for showcasing innovative agent creations. The repository covers a wide range of agent architectures and applications, providing step-by-step tutorials, ready-to-use implementations, and regular updates on advancements in GenAI technology.
agent
Stately Agent is a library for building stateful, interactive agents using OpenAI's GPT-3 API. With Stately Agent, you can create agents that can remember past conversations, track state, and generate text that is both informative and engaging.
llm-course
The LLM course is divided into three parts: 1. 🧩 **LLM Fundamentals** covers essential knowledge about mathematics, Python, and neural networks. 2. 🧑🔬 **The LLM Scientist** focuses on building the best possible LLMs using the latest techniques. 3. 👷 **The LLM Engineer** focuses on creating LLM-based applications and deploying them. For an interactive version of this course, I created two **LLM assistants** that will answer questions and test your knowledge in a personalized way: * 🤗 **HuggingChat Assistant**: Free version using Mixtral-8x7B. * 🤖 **ChatGPT Assistant**: Requires a premium account. ## 📝 Notebooks A list of notebooks and articles related to large language models. ### Tools | Notebook | Description | Notebook | |----------|-------------|----------| | 🧐 LLM AutoEval | Automatically evaluate your LLMs using RunPod |  | | 🥱 LazyMergekit | Easily merge models using MergeKit in one click. |  | | 🦎 LazyAxolotl | Fine-tune models in the cloud using Axolotl in one click. |  | | ⚡ AutoQuant | Quantize LLMs in GGUF, GPTQ, EXL2, AWQ, and HQQ formats in one click. |  | | 🌳 Model Family Tree | Visualize the family tree of merged models. |  | | 🚀 ZeroSpace | Automatically create a Gradio chat interface using a free ZeroGPU. |  |
LAMBDA
LAMBDA is a code-free multi-agent data analysis system that utilizes large models to address data analysis challenges in complex data-driven applications. It allows users to perform complex data analysis tasks through human language instruction, seamlessly generate and debug code using two key agent roles, integrate external models and algorithms, and automatically generate reports. The system has demonstrated strong performance on various machine learning datasets, enhancing data science practice by integrating human and artificial intelligence.
llm_benchmarks
llm_benchmarks is a collection of benchmarks and datasets for evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs). It includes various tasks and datasets to assess LLMs' knowledge, reasoning, language understanding, and conversational abilities. The repository aims to provide comprehensive evaluation resources for LLMs across different domains and applications, such as education, healthcare, content moderation, coding, and conversational AI. Researchers and developers can leverage these benchmarks to test and improve the performance of LLMs in various real-world scenarios.
Coding-Tutor
This repository explores the potential of LLMs as coding tutors through the proposed Traver agent workflow. It focuses on incorporating knowledge tracing and turn-by-turn verification to tackle challenges in coding tutoring. The method extends beyond coding to other task-tutoring scenarios, adapting content to users' varying levels of background knowledge. The repository introduces the DICT evaluation protocol for assessing tutor performance through student simulation and coding tests. It also discusses the inference-time scaling with verifiers and provides resources for training and evaluation.
LLMs-in-science
The 'LLMs-in-science' repository is a collaborative environment for organizing papers related to large language models (LLMs) and autonomous agents in the field of chemistry. The goal is to discuss trend topics, challenges, and the potential for supporting scientific discovery in the context of artificial intelligence. The repository aims to maintain a systematic structure of the field and welcomes contributions from the community to keep the content up-to-date and relevant.
For similar tasks
Awesome-LLM-RAG
This repository, Awesome-LLM-RAG, aims to record advanced papers on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in Large Language Models (LLMs). It serves as a resource hub for researchers interested in promoting their work related to LLM RAG by updating paper information through pull requests. The repository covers various topics such as workshops, tutorials, papers, surveys, benchmarks, retrieval-enhanced LLMs, RAG instruction tuning, RAG in-context learning, RAG embeddings, RAG simulators, RAG search, RAG long-text and memory, RAG evaluation, RAG optimization, and RAG applications.
Awesome_LLM_System-PaperList
Since the emergence of chatGPT in 2022, the acceleration of Large Language Model has become increasingly important. Here is a list of papers on LLMs inference and serving.
LLM-Tool-Survey
This repository contains a collection of papers related to tool learning with large language models (LLMs). The papers are organized according to the survey paper 'Tool Learning with Large Language Models: A Survey'. The survey focuses on the benefits and implementation of tool learning with LLMs, covering aspects such as task planning, tool selection, tool calling, response generation, benchmarks, evaluation, challenges, and future directions in the field. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of tool learning with LLMs and inspire further exploration in this emerging area.
Awesome-CVPR2024-ECCV2024-AIGC
A Collection of Papers and Codes for CVPR 2024 AIGC. This repository compiles and organizes research papers and code related to CVPR 2024 and ECCV 2024 AIGC (Artificial Intelligence and Graphics Computing). It serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in the latest advancements in the field of computer vision and artificial intelligence. Users can find a curated list of papers and accompanying code repositories for further exploration and research. The repository encourages collaboration and contributions from the community through stars, forks, and pull requests.

LLMs-in-science
The 'LLMs-in-science' repository is a collaborative environment for organizing papers related to large language models (LLMs) and autonomous agents in the field of chemistry. The goal is to discuss trend topics, challenges, and the potential for supporting scientific discovery in the context of artificial intelligence. The repository aims to maintain a systematic structure of the field and welcomes contributions from the community to keep the content up-to-date and relevant.

Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent
Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent is a curated collection of recent papers focusing on autonomous agents, specifically interested in RL-based agents and LLM-based agents. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in intelligent agents that can achieve goals, acquire knowledge, and continually improve. The collection includes papers on various topics such as instruction following, building agents based on world models, using language as knowledge, leveraging LLMs as a tool, generalization across tasks, continual learning, combining RL and LLM, transformer-based policies, trajectory to language, trajectory prediction, multimodal agents, training LLMs for generalization and adaptation, task-specific designing, multi-agent systems, experimental analysis, benchmarking, applications, algorithm design, and combining with RL.

awesome-lifelong-llm-agent
This repository is a collection of papers and resources related to Lifelong Learning of Large Language Model (LLM) based Agents. It focuses on continual learning and incremental learning of LLM agents, identifying key modules such as Perception, Memory, and Action. The repository serves as a roadmap for understanding lifelong learning in LLM agents and provides a comprehensive overview of related research and surveys.
LLM-Agent-Survey
LLM-Agent-Survey is a comprehensive repository that provides a curated list of papers related to Large Language Model (LLM) agents. The repository categorizes papers based on LLM-Profiled Roles and includes high-quality publications from prestigious conferences and journals. It aims to offer a systematic understanding of LLM-based agents, covering topics such as tool use, planning, and feedback learning. The repository also includes unpublished papers with insightful analysis and novelty, marked for future updates. Users can explore a wide range of surveys, tool use cases, planning workflows, and benchmarks related to LLM agents.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.