
Grounded-Video-LLM
Grounded-VideoLLM: Sharpening Fine-grained Temporal Grounding in Video Large Language Models
Stars: 87
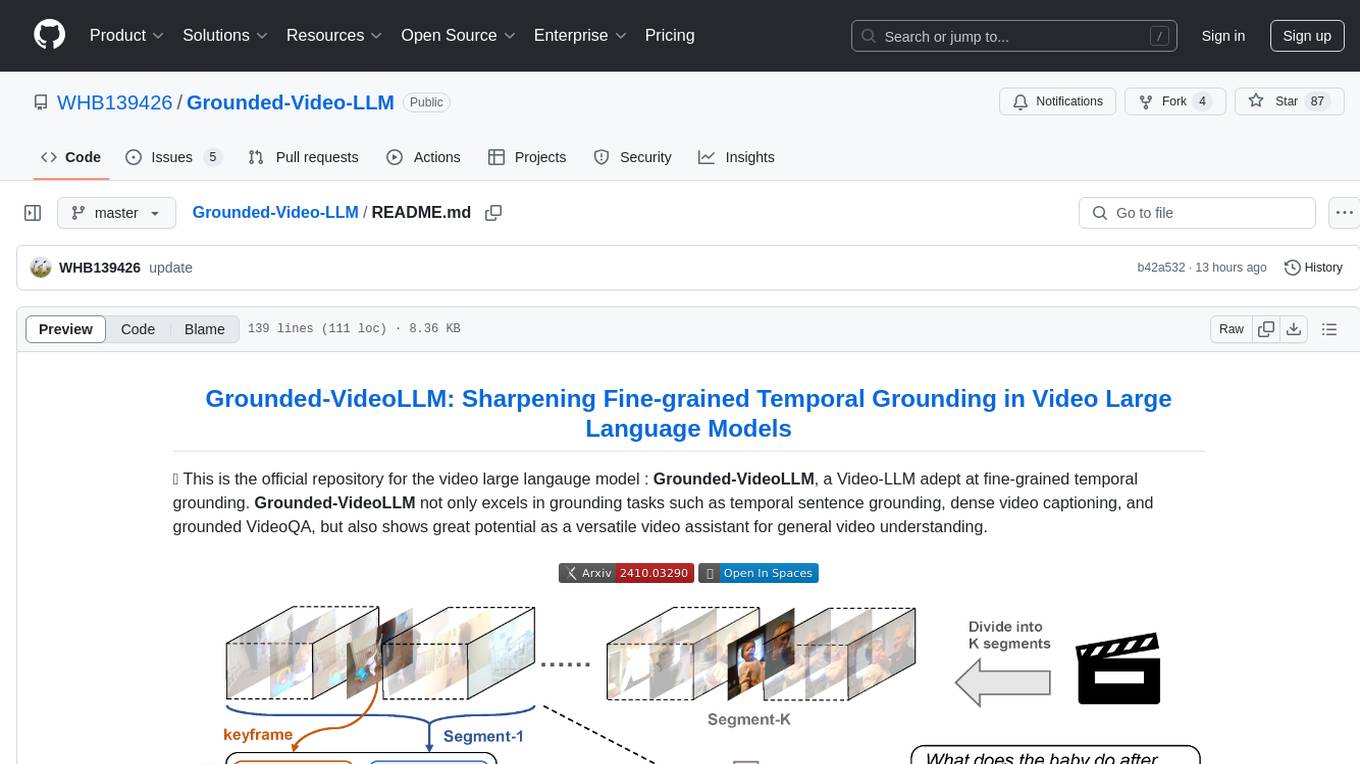
Grounded-VideoLLM is a Video Large Language Model specialized in fine-grained temporal grounding. It excels in tasks such as temporal sentence grounding, dense video captioning, and grounded VideoQA. The model incorporates an additional temporal stream, discrete temporal tokens with specific time knowledge, and a multi-stage training scheme. It shows potential as a versatile video assistant for general video understanding. The repository provides pretrained weights, inference scripts, and datasets for training. Users can run inference queries to get temporal information from videos and train the model from scratch.
README:
🌟 This is the official repository for the video large langauge model : Grounded-VideoLLM, a Video-LLM adept at fine-grained temporal grounding. Grounded-VideoLLM not only excels in grounding tasks such as temporal sentence grounding, dense video captioning, and grounded VideoQA, but also shows great potential as a versatile video assistant for general video understanding.
💡 We sharpen our model by incorporating:
- An additional temporal stream to encode the relationships between frames.
- Discrete temporal tokens enriched with specific time knowledge to represent timestamps.
- A multi-stage training scheme, beginning with simple video-captioning tasks and progressively introducing video temporal grounding tasks of increasing complexity. To further enhance the temporal reasoning capability, we also curate a grounded VideoQA dataset by an automatic annotation pipeline.
- [x] [2024.10.4] Release the inference scripts and pretrained checkpoints.
- [x] [2024.10.4] Release the annotated grounded-VideoQA dataset .
- [x] [2024.10.4] Release the Phi3.5-Vision-Instruct version.
- [x] [2024.10.29] Release the LLaVA-Next-LLAMA3-8B version, with stronger performance in both grounding tasks and general benchmarks.
- [x] Release the training scripts and training datasets. We will try to adapt more MLLMs as the base model for Grounded-VideoLLM in future.
| Model Name | LLM | Charades-STA ([email protected]/[email protected]/[email protected]/mIoU) | ActivityNet-Groudning ([email protected]/[email protected]/[email protected]/mIoU) | ActivityNet-Captions (SODA_c/METEOR) | NEXT-GQA (GQA/mIoP/mIoU) | MVbench | Video-MME (w/o subs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grounded-VideoLLM | Phi3.5-3.8B | 54.2/36.4/19.7/36.8 | 46.2/30.3/19.0/36.1 | 6.0/6.8 | 26.7/34.5/21.1 | 59.4 | 47.7 |
| Grounded-VideoLLM (*) | Phi3.5-3.8B | 70.2/55.9/33.2/49.4 | 64.9/47.8/30.4/47.2 | 6.6/6.5 | 29.4/37.4/27.0 | 60.0 | 48.1 |
- (*) means we incorporate a sub training set of Charades-STA and ActivityNet into the third training stage. Please refer to our paper for more results.
- Clone this repository and navigate to folder
git clone https://github.com/WHB139426/Grounded-Video-LLM.git
cd Grounded-Video-LLM- Install Package
conda create -n grounded-videollm python=3.10.14
conda activate grounded-videollm
pip install torch==2.1.2 torchaudio==2.1.2 torchvision==0.16.2 torchdata==0.8.0 # to make sure install torch before flash-attn
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install numpy==1.26.4 # to make sure numpy<2.0Some installation suggestions
- We recommend you to pip install
flash-attn==2.3.3and run the model withtorch.bfloat16. If your device doesn't support these, you can skip them and replace the argparse parameterattn_implementationanddtypeininference.py, which may result in subtle numerical difference.
Set your own weight_path to storage the pretrained weights. The folder should be organized as follows:
├── Grounded-Video-LLM
│ └── inference.py
│ └── models
│ └── mm_utils
│ └── training
│ └── scripts
│ └── ...
├── weight_path
│ └── Phi-3.5-mini-instruct
│ └── Phi-3.5-vision-instruct-seperated
│ └── Phi-3.5-vision-instruct
│ └── llama3-llava-next-8b
│ └── llama3-llava-next-8b-seperated
│ └── Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct
│ └── ckpt
│ └── internvideo
│ └──...
Download the pretrained weights [🤗HF] in your own weight_path.
We give a brief example to run the inference code. We recommend GPUs with 24GB memeroy for Phi3.5 version, while 32GB memeroy for LLaVA-Next-LLAMA3-8B version.
- replace the parameter
weight_pathinscripts/inference_phi3_5.shorscripts/inference_llama3.shwith your own weight_path that you set above. - run the command
bash scripts/inference_phi3_5.shorbash scripts/inference_llama3.shto reproduce the example below:
[USER] Give you a textual query: "The female host wearing purple clothes is reporting news in the studio". When does the described content occur in the video? Please return the start and end timestamps.
[Grounded-VideoLLM] From 14.20 seconds to 25.09 seconds.
[USER] Give you a textual query: "A sign written with 'NO TRESPASSING LOITERING DRUGS'". When does the described content occur in the video? Please return the start and end timestamps.
[Grounded-VideoLLM] From 107.95 seconds to 113.16 seconds.
[USER] What is happening from 70 seconds to 80 seconds?
[Grounded-VideoLLM] A woman with glasses and a red shirt is talking to a reporter.
[USER] Why was the man in green clothes interviewed?
[Grounded-VideoLLM] The man in green clothes was interviewed to provide his perspective on the incident and the history of violence in the apartment complex.
[USER] Question: What does this TV news report about?\nOptions:\n(A) thievery\n(B) community violence incidents\n(C) fashion show\n(D) aging population
[Grounded-VideoLLM] Answer: (B) community violence incidents
- You can change the parameter of
prompt_grounding,prompt_videoqa,prompt_referringandvideo_pathininference.py's argparse to run your own case.
We provide the Grounded-VideoQA dataset that we annotated with GPT-4o-mini in [🤗HF]. You can download the videos following [ActivityNet] and [QVHighlights].
- Prepare your training data:
Set your own
data_pathin th following .sh files to storage the data before running the commands (You can choose to only download the specific data you want by modifying the following scripts):
bash scripts/download_data_stage1.sh
bash scripts/download_data_stage2.sh
bash scripts/download_data_stage2.sh- Set up the
data_dirandweight_pathinscripts/phi3.5_xxx_8_a100.shwherexxxcan be [pretrain,grounded,sft], and then run the following commands:
bash scripts/phi3.5_pretrain_8_a100.sh
bash scripts/phi3.5_grounded_8_a100.sh
bash scripts/phi3.5_sft_8_a100.shThe checkpoints will be saved at ./experiments
If you find our paper and code useful in your research, please consider giving a star ⭐ and citation 📝.
@article{wang2024grounded,
title={Grounded-VideoLLM: Sharpening Fine-grained Temporal Grounding in Video Large Language Models},
author={Wang, Haibo and Xu, Zhiyang and Cheng, Yu and Diao, Shizhe and Zhou, Yufan and Cao, Yixin and Wang, Qifan and Ge, Weifeng and Huang, Lifu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.03290},
year={2024}
}We are grateful for the following awesome projects our Grounded-VideoLLM arising from: Prismatic-VLMs, Phi-3.5-vision-instruct, InternVideo2, LLaVA-Next, TimeChat, VTimeLLM, Momentor.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Grounded-Video-LLM
Similar Open Source Tools

Grounded-Video-LLM
Grounded-VideoLLM is a Video Large Language Model specialized in fine-grained temporal grounding. It excels in tasks such as temporal sentence grounding, dense video captioning, and grounded VideoQA. The model incorporates an additional temporal stream, discrete temporal tokens with specific time knowledge, and a multi-stage training scheme. It shows potential as a versatile video assistant for general video understanding. The repository provides pretrained weights, inference scripts, and datasets for training. Users can run inference queries to get temporal information from videos and train the model from scratch.
VideoTuna
VideoTuna is a codebase for text-to-video applications that integrates multiple AI video generation models for text-to-video, image-to-video, and text-to-image generation. It provides comprehensive pipelines in video generation, including pre-training, continuous training, post-training, and fine-tuning. The models in VideoTuna include U-Net and DiT architectures for visual generation tasks, with upcoming releases of a new 3D video VAE and a controllable facial video generation model.
EmbodiedScan
EmbodiedScan is a holistic multi-modal 3D perception suite designed for embodied AI. It introduces a multi-modal, ego-centric 3D perception dataset and benchmark for holistic 3D scene understanding. The dataset includes over 5k scans with 1M ego-centric RGB-D views, 1M language prompts, 160k 3D-oriented boxes spanning 760 categories, and dense semantic occupancy with 80 common categories. The suite includes a baseline framework named Embodied Perceptron, capable of processing multi-modal inputs for 3D perception tasks and language-grounded tasks.
LLM-Pruner
LLM-Pruner is a tool for structural pruning of large language models, allowing task-agnostic compression while retaining multi-task solving ability. It supports automatic structural pruning of various LLMs with minimal human effort. The tool is efficient, requiring only 3 minutes for pruning and 3 hours for post-training. Supported LLMs include Llama-3.1, Llama-3, Llama-2, LLaMA, BLOOM, Vicuna, and Baichuan. Updates include support for new LLMs like GQA and BLOOM, as well as fine-tuning results achieving high accuracy. The tool provides step-by-step instructions for pruning, post-training, and evaluation, along with a Gradio interface for text generation. Limitations include issues with generating repetitive or nonsensical tokens in compressed models and manual operations for certain models.
RLAIF-V
RLAIF-V is a novel framework that aligns MLLMs in a fully open-source paradigm for super GPT-4V trustworthiness. It maximally exploits open-source feedback from high-quality feedback data and online feedback learning algorithm. Notable features include achieving super GPT-4V trustworthiness in both generative and discriminative tasks, using high-quality generalizable feedback data to reduce hallucination of different MLLMs, and exhibiting better learning efficiency and higher performance through iterative alignment.
basiclingua-LLM-Based-NLP
BasicLingua is a Python library that provides functionalities for linguistic tasks such as tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, and many others. It is based on the Gemini Language Model, which has demonstrated promising results in dealing with text data. BasicLingua can be used as an API or through a web demo. It is available under the MIT license and can be used in various projects.
transformers
Transformers is a state-of-the-art pretrained models library that acts as the model-definition framework for machine learning models in text, computer vision, audio, video, and multimodal tasks. It centralizes model definition for compatibility across various training frameworks, inference engines, and modeling libraries. The library simplifies the usage of new models by providing simple, customizable, and efficient model definitions. With over 1M+ Transformers model checkpoints available, users can easily find and utilize models for their tasks.
MotionLLM
MotionLLM is a framework for human behavior understanding that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to jointly model videos and motion sequences. It provides a unified training strategy, dataset MoVid, and MoVid-Bench for evaluating human behavior comprehension. The framework excels in captioning, spatial-temporal comprehension, and reasoning abilities.
ALMA
ALMA (Advanced Language Model-based Translator) is a many-to-many LLM-based translation model that utilizes a two-step fine-tuning process on monolingual and parallel data to achieve strong translation performance. ALMA-R builds upon ALMA models with LoRA fine-tuning and Contrastive Preference Optimization (CPO) for even better performance, surpassing GPT-4 and WMT winners. The repository provides ALMA and ALMA-R models, datasets, environment setup, evaluation scripts, training guides, and data information for users to leverage these models for translation tasks.
CuMo
CuMo is a project focused on scaling multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with Co-Upcycled Mixture-of-Experts. It introduces CuMo, which incorporates Co-upcycled Top-K sparsely-gated Mixture-of-experts blocks into the vision encoder and the MLP connector, enhancing the capabilities of multimodal LLMs. The project adopts a three-stage training approach with auxiliary losses to stabilize the training process and maintain a balanced loading of experts. CuMo achieves comparable performance to other state-of-the-art multimodal LLMs on various Visual Question Answering (VQA) and visual-instruction-following benchmarks.
RD-Agent
RD-Agent is a tool designed to automate critical aspects of industrial R&D processes, focusing on data-driven scenarios to streamline model and data development. It aims to propose new ideas ('R') and implement them ('D') automatically, leading to solutions of significant industrial value. The tool supports scenarios like Automated Quantitative Trading, Data Mining Agent, Research Copilot, and more, with a framework to push the boundaries of research in data science. Users can create a Conda environment, install the RDAgent package from PyPI, configure GPT model, and run various applications for tasks like quantitative trading, model evolution, medical prediction, and more. The tool is intended to enhance R&D processes and boost productivity in industrial settings.
LL3DA
LL3DA is a Large Language 3D Assistant that responds to both visual and textual interactions within complex 3D environments. It aims to help Large Multimodal Models (LMM) comprehend, reason, and plan in diverse 3D scenes by directly taking point cloud input and responding to textual instructions and visual prompts. LL3DA achieves remarkable results in 3D Dense Captioning and 3D Question Answering, surpassing various 3D vision-language models. The code is fully released, allowing users to train customized models and work with pre-trained weights. The tool supports training with different LLM backends and provides scripts for tuning and evaluating models on various tasks.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.

YuE
YuE (乐) is an open-source foundation model designed for music generation, specifically transforming lyrics into full songs. It can generate complete songs in various genres and vocal styles, ensuring a polished and cohesive result. The model requires significant GPU memory for generating long sequences and recommends specific configurations for optimal performance. Users can customize the number of sessions for memory usage. The tool provides a quickstart guide for generating music using Transformers and includes tips for execution time and tag selection. The project is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial 4.0.
WildBench
WildBench is a tool designed for benchmarking Large Language Models (LLMs) with challenging tasks sourced from real users in the wild. It provides a platform for evaluating the performance of various models on a range of tasks. Users can easily add new models to the benchmark by following the provided guidelines. The tool supports models from Hugging Face and other APIs, allowing for comprehensive evaluation and comparison. WildBench facilitates running inference and evaluation scripts, enabling users to contribute to the benchmark and collaborate on improving model performance.
baml
BAML is a config file format for declaring LLM functions that you can then use in TypeScript or Python. With BAML you can Classify or Extract any structured data using Anthropic, OpenAI or local models (using Ollama) ## Resources  [Discord Community](https://discord.gg/boundaryml)  [Follow us on Twitter](https://twitter.com/boundaryml) * Discord Office Hours - Come ask us anything! We hold office hours most days (9am - 12pm PST). * Documentation - Learn BAML * Documentation - BAML Syntax Reference * Documentation - Prompt engineering tips * Boundary Studio - Observability and more #### Starter projects * BAML + NextJS 14 * BAML + FastAPI + Streaming ## Motivation Calling LLMs in your code is frustrating: * your code uses types everywhere: classes, enums, and arrays * but LLMs speak English, not types BAML makes calling LLMs easy by taking a type-first approach that lives fully in your codebase: 1. Define what your LLM output type is in a .baml file, with rich syntax to describe any field (even enum values) 2. Declare your prompt in the .baml config using those types 3. Add additional LLM config like retries or redundancy 4. Transpile the .baml files to a callable Python or TS function with a type-safe interface. (VSCode extension does this for you automatically). We were inspired by similar patterns for type safety: protobuf and OpenAPI for RPCs, Prisma and SQLAlchemy for databases. BAML guarantees type safety for LLMs and comes with tools to give you a great developer experience:  Jump to BAML code or how Flexible Parsing works without additional LLM calls. | BAML Tooling | Capabilities | | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | BAML Compiler install | Transpiles BAML code to a native Python / Typescript library (you only need it for development, never for releases) Works on Mac, Windows, Linux  | | VSCode Extension install | Syntax highlighting for BAML files Real-time prompt preview Testing UI | | Boundary Studio open (not open source) | Type-safe observability Labeling |
For similar tasks
VideoLLaMA2
VideoLLaMA 2 is a project focused on advancing spatial-temporal modeling and audio understanding in video-LLMs. It provides tools for multi-choice video QA, open-ended video QA, and video captioning. The project offers model zoo with different configurations for visual encoder and language decoder. It includes training and evaluation guides, as well as inference capabilities for video and image processing. The project also features a demo setup for running a video-based Large Language Model web demonstration.
vigenair
ViGenAiR is a tool that harnesses the power of Generative AI models on Google Cloud Platform to automatically transform long-form Video Ads into shorter variants, targeting different audiences. It generates video, image, and text assets for Demand Gen and YouTube video campaigns. Users can steer the model towards generating desired videos, conduct A/B testing, and benefit from various creative features. The tool offers benefits like diverse inventory, compelling video ads, creative excellence, user control, and performance insights. ViGenAiR works by analyzing video content, splitting it into coherent segments, and generating variants following Google's best practices for effective ads.

Grounded-Video-LLM
Grounded-VideoLLM is a Video Large Language Model specialized in fine-grained temporal grounding. It excels in tasks such as temporal sentence grounding, dense video captioning, and grounded VideoQA. The model incorporates an additional temporal stream, discrete temporal tokens with specific time knowledge, and a multi-stage training scheme. It shows potential as a versatile video assistant for general video understanding. The repository provides pretrained weights, inference scripts, and datasets for training. Users can run inference queries to get temporal information from videos and train the model from scratch.
Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding
Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding is a repository dedicated to exploring Video Understanding with Large Language Models. It provides a comprehensive survey of the field, covering models, pretraining, instruction tuning, and hybrid methods. The repository also includes information on tasks, datasets, and benchmarks related to video understanding. Contributors are encouraged to add new papers, projects, and materials to enhance the repository.
finetrainers
FineTrainers is a work-in-progress library designed to support the training of video models, with a focus on LoRA training for popular video models in Diffusers. It aims to eventually extend support to other methods like controlnets, control-loras, distillation, etc. The library provides tools for training custom models, handling big datasets, and supporting multi-backend distributed training. It also offers tooling for curating small and high-quality video datasets for fine-tuning.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.


