
DALM
Domain Adapted Language Modeling Toolkit - E2E RAG
Stars: 276
The DALM (Domain Adapted Language Modeling) toolkit is designed to unify general LLMs with vector stores to ground AI systems in efficient, factual domains. It provides developers with tools to build on top of Arcee's open source Domain Pretrained LLMs, enabling organizations to deeply tailor AI according to their unique intellectual property and worldview. The toolkit contains code for fine-tuning a fully differential Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG-end2end) architecture, incorporating in-batch negative concept alongside RAG's marginalization for efficiency. It includes training scripts for both retriever and generator models, evaluation scripts, data processing codes, and synthetic data generation code.
README:
A great rift has emerged between general LLMs and the vector stores that are providing them with contextual information. The unification of these systems is an important step in grounding AI systems in efficient, factual domains, where they are utilized not only for their generality, but for their specificity and uniqueness. To this end, we are excited to open source the Arcee Domain Adapted Language Model (DALM) toolkit for developers to build on top of our Arcee open source Domain Pretrained (DPT) LLMs. We believe that our efforts will help as we begin next phase of language modeling, where organizations deeply tailor AI to operate according to their unique intellectual property and worldview.
Query example DALMs created by the Arcee Team.
| DALM-Patent | DALM-PubMed | DALM-SEC | DALM-Yours |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
This repository primarily contains code for fine-tuning a fully differential Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG-end2end) architecture.
For the first time in the literature, we modified the initial RAG-end2end model (TACL paper, HuggingFace implementation) to work with decoder-only language models like Llama, Falcon, or GPT. We also incorporated the in-batch negative concept alongside the RAG's marginalization to make the entire process efficient.
-
Inside the training folder, you'll find two codes to train the RAG-end2end and Retriever with contrastive learning.
-
All evaluations related to the Retriever and the Generator are located in the eval folder.
-
Additionally, we have data processing codes and synthetic data generation code inside the datasets folder.
To perform training and evaluation for both the retriever model and the new rag-e2e model, please adhere to the following steps.
The system reqs depend on the retriever model, generator model, and batch size. But for reference (e2e rag), we used the following for our experiments (eval results below):
- retriever:
BAAI/bge-large-en - generator:
meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf - batch size: 18
- dataset size: 200k
This took 7 hours on a single A100 GPU (80GB).
You can install this repo directly via pip install indomain
Alternatively, for development or research, you can clone and install the repo locally:
git clone https://github.com/arcee-ai/DALM.git && cd DALM
pip install --upgrade -e .This will install the DALM repo and all necessary dependencies.
Make sure things are installed correctly by running dalm version. On an non-intel Mac you may need to downgrade transformers library: pip install transformers==4.30.
You can run dalm qa-gen <path-to-dataset> to preprocess your dataset for training. See dalm qa-gen --help for more options
If you do not have a dataset, you can start with ours
# Note - our dataset already has queries and answers, so you don't actually need to run this.
# replace `toy_dataset_train.csv` with your dataset of titles and passages
dalm qa-gen dalm/datasets/toy_data_train.csv- The setup for training and evaluation can be effortlessly executed provided you possess a CSV file containing two/three columns:
Passage,Query(andAnswerif running e2e). You can utilize the script question_answer_generation.py to generate this CSV. - It's important to highlight that the retriever-only training method employs solely the passages and queries, whereas the rag-e2e training code utilizes all three columns.
- In our experiments, we utilize
BAAI/bge-large-enas the default retriever and employmeta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hfas the default generator. The code is designed to be compatible with any embedding model or autoregressive model available in the Hugging Face model repository at https://huggingface.co/models.
You can leverage our scripts directly if you'd like, or you can use the dalm cli. The arguments for both are identical
Train BAAI/bge-large-en retriever with contrastive learning.
python dalm/training/retriever_only/train_retriever_only.py \
--dataset_path "./dalm/datasets/toy_data_train.csv" \
--retriever_name_or_path "BAAI/bge-large-en" \
--output_dir "retriever_only_checkpoints" \
--use_peft \
--with_tracking \
--report_to all \
--per_device_train_batch_size 150or
dalm train-retriever-only "BAAI/bge-large-en" "./dalm/datasets/toy_data_train.csv" \
--output-dir "retriever_only_checkpoints" \
--use-peft \
--with-tracking \
--report-to all \
--per-device-train-batch-size 150For all available arguments and options, see dalm train-retriever-only --help
Train Llama-2-7b generator jointly with the retriever model BAAI/bge-large-en.
python dalm/training/rag_e2e/train_rage2e.py \
--dataset_path "./dalm/datasets/toy_data_train.csv" \
--retriever_name_or_path "BAAI/bge-large-en" \
--generator_name_or_path "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf" \
--output_dir "rag_e2e_checkpoints" \
--with_tracking \
--report_to all \
--per_device_train_batch_size 20or
dalm train-rag-e2e \
"./dalm/datasets/toy_data_train.csv" \
"BAAI/bge-large-en" \
"meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf" \
--output-dir "rag_e2e_checkpoints" \
--with-tracking \
--report-to all \
--per-device-train-batch-size 20For all available arguments and options, see dalm train-rag-e2e --help
The Retriever in general is trained to be good at finding the most relevant passages in a corpus given a query.
Given a ground-truth test dataset that is a 200,000-line CSV containing patent abstracts and more importantly this evaluation dataset was not present in the training dataset, the below listed steps were followed:
- Use the trained retriever to encode all passages into an ad-hoc indexed vector store using the HNSW library.
- Take each query and use the trained retriever to encode it into an embedding vector (QE)
- For each encoded passage (PE) in the vector store, find the nearest neighbor similarity search score between QE and PE (Note: with HNSW, exhaustiveness is avoided)
- Find the top-K (eg, top 5) best matches based on nearest neighbor similarity search scores
- Compare the matches against the ground truth top-K best matches to calculate
recallandhit rate.
| Type of Retriever | Recall | Hit rate |
|---|---|---|
| Plain Retriever | 0.45984 | 0.45984 |
| Retriever with contrastive learning | 0.46037 | 0.46038 |
| Retriever End2End | 0.73634 | 0.73634 |
To run retriever only eval (make sure you have the checkpoints in the project root)
python dalm/eval/eval_retriever_only.py \
--dataset_path qa_pairs_test.csv \
--retriever_name_or_path "BAAI/bge-large-en" \
--passage_column_name Abstract \
--query_column_name Question \
--retriever_peft_model_path retriever_only_checkpointsor
dalm eval-retriever qa_pairs_test.csv \
--retriever-name-or-path "BAAI/bge-large-en" \
--passage-column-name Abstract \
--query-column-name Question \
--retriever-peft-model-path retriever_only_checkpointsSee dalm eval-retriever --help for all available arguments
For the e2e eval
python dalm/eval/eval_rag.py \
--dataset_path qa_pairs_test_2.csv \
--retriever_name_or_path "BAAI/bge-large-en" \
--generator_name_or_path "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf" \
--passage_column_name Abstract \
--query_column_name Question \
--answer_column_name Answer \
--evaluate_generator \
--query_batch_size 5 \
--retriever_peft_model_path rag_e2e_checkpoints/retriever \
--generator_peft_model_path rag_e2e_checkpoints/generatoror
dalm eval-rag qa_pairs_test.csv \
--retriever-name-or-path "BAAI/bge-large-en" \
--generator-name-or-path "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf" \
--retriever-peft-model-path rag_e2e_checkpoints/retriever \
--generator-peft-model-path rag_e2e_checkpoints/generator \
--passage-column-name Abstract \
--query-column-name Question \
--answer-column-name Answer \
--query-batch-size 5See dalm eval-rag --help for all available arguments
See CONTRIBUTING
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for DALM
Similar Open Source Tools

DALM
The DALM (Domain Adapted Language Modeling) toolkit is designed to unify general LLMs with vector stores to ground AI systems in efficient, factual domains. It provides developers with tools to build on top of Arcee's open source Domain Pretrained LLMs, enabling organizations to deeply tailor AI according to their unique intellectual property and worldview. The toolkit contains code for fine-tuning a fully differential Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG-end2end) architecture, incorporating in-batch negative concept alongside RAG's marginalization for efficiency. It includes training scripts for both retriever and generator models, evaluation scripts, data processing codes, and synthetic data generation code.
open-chatgpt
Open-ChatGPT is an open-source library that enables users to train a hyper-personalized ChatGPT-like AI model using their own data with minimal computational resources. It provides an end-to-end training framework for ChatGPT-like models, supporting distributed training and offloading for extremely large models. The project implements RLHF (Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback) powered by transformer library and DeepSpeed, allowing users to create high-quality ChatGPT-style models. Open-ChatGPT is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, aiming to empower users to develop their own conversational AI models easily.

marqo
Marqo is more than a vector database, it's an end-to-end vector search engine for both text and images. Vector generation, storage and retrieval are handled out of the box through a single API. No need to bring your own embeddings.
SWE-bench-Live
SWE-bench-Live is a live benchmark dataset for evaluating AI systems' ability to complete real-world software engineering tasks. It is continuously updated through an automated curation pipeline, providing the community with up-to-date task instances for rigorous and contamination-free evaluation. The dataset is designed to test the performance of various AI models on software engineering tasks and supports multiple programming languages and operating systems.
co-llm
Co-LLM (Collaborative Language Models) is a tool for learning to decode collaboratively with multiple language models. It provides a method for data processing, training, and inference using a collaborative approach. The tool involves steps such as formatting/tokenization, scoring logits, initializing Z vector, deferral training, and generating results using multiple models. Co-LLM supports training with different collaboration pairs and provides baseline training scripts for various models. In inference, it uses 'vllm' services to orchestrate models and generate results through API-like services. The tool is inspired by allenai/open-instruct and aims to improve decoding performance through collaborative learning.
friendly-stable-audio-tools
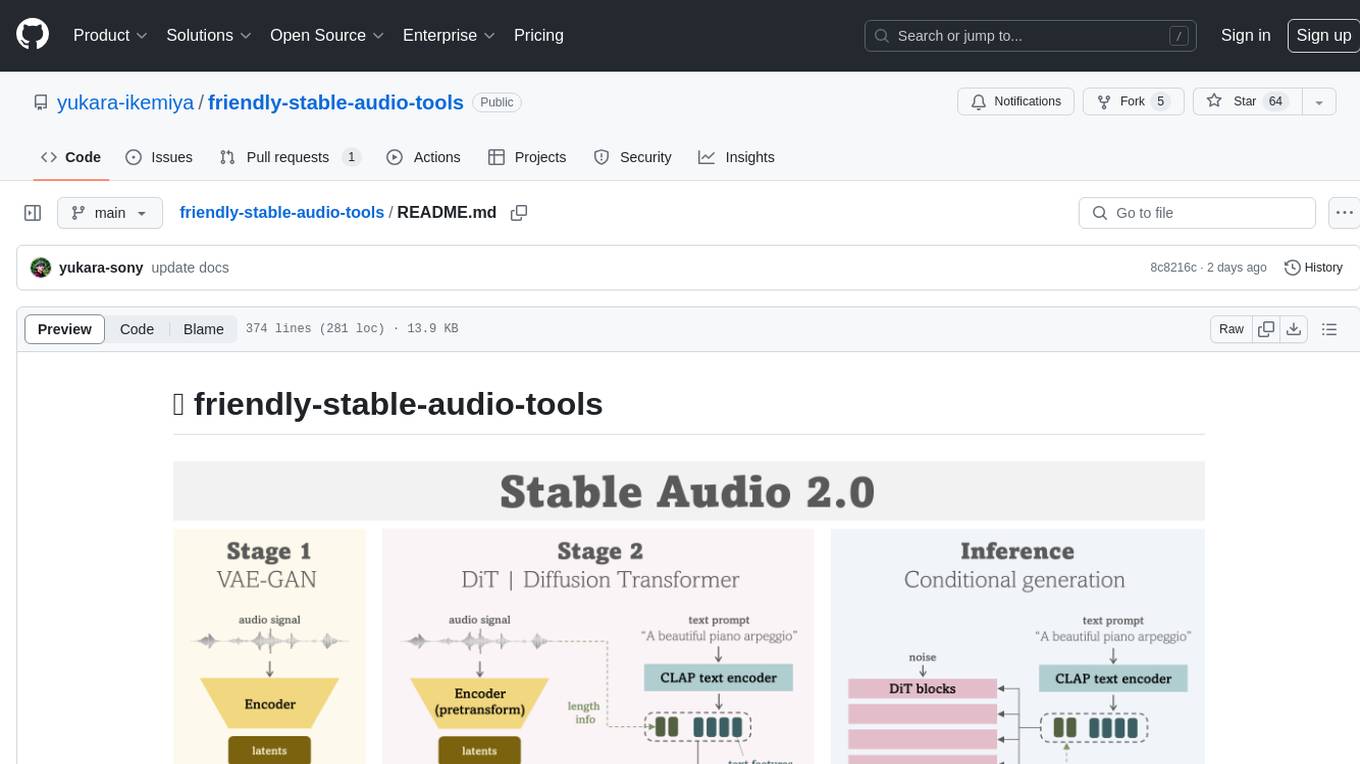
This repository is a refactored and updated version of `stable-audio-tools`, an open-source code for audio/music generative models originally by Stability AI. It contains refactored codes for improved readability and usability, useful scripts for evaluating and playing with trained models, and instructions on how to train models such as `Stable Audio 2.0`. The repository does not contain any pretrained checkpoints. Requirements include PyTorch 2.0 or later for Flash Attention support and Python 3.8.10 or later for development. The repository provides guidance on installing, building a training environment using Docker or Singularity, logging with Weights & Biases, training configurations, and stages for VAE-GAN and Diffusion Transformer (DiT) training.
ALMA
ALMA (Advanced Language Model-based Translator) is a many-to-many LLM-based translation model that utilizes a two-step fine-tuning process on monolingual and parallel data to achieve strong translation performance. ALMA-R builds upon ALMA models with LoRA fine-tuning and Contrastive Preference Optimization (CPO) for even better performance, surpassing GPT-4 and WMT winners. The repository provides ALMA and ALMA-R models, datasets, environment setup, evaluation scripts, training guides, and data information for users to leverage these models for translation tasks.
transformers
Transformers is a state-of-the-art pretrained models library that acts as the model-definition framework for machine learning models in text, computer vision, audio, video, and multimodal tasks. It centralizes model definition for compatibility across various training frameworks, inference engines, and modeling libraries. The library simplifies the usage of new models by providing simple, customizable, and efficient model definitions. With over 1M+ Transformers model checkpoints available, users can easily find and utilize models for their tasks.
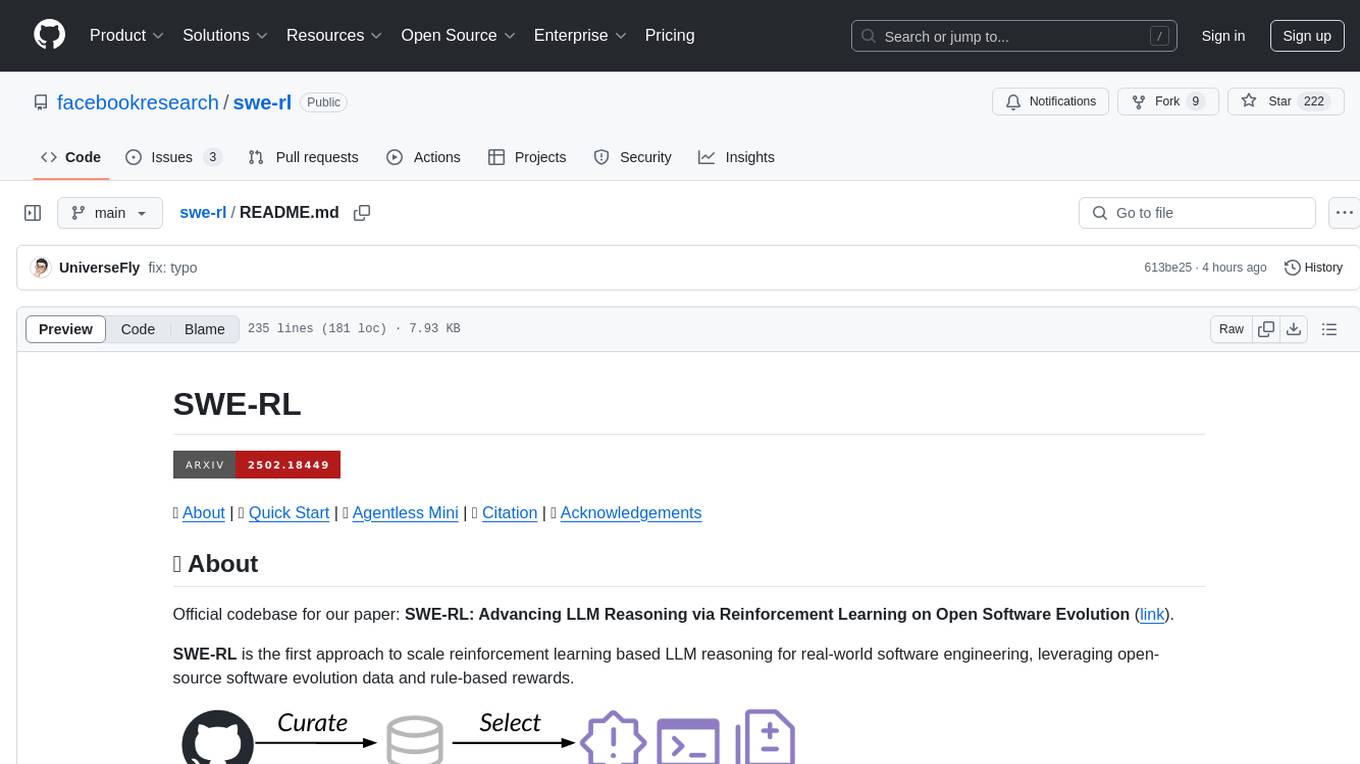
swe-rl
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.
LLM-Pruner
LLM-Pruner is a tool for structural pruning of large language models, allowing task-agnostic compression while retaining multi-task solving ability. It supports automatic structural pruning of various LLMs with minimal human effort. The tool is efficient, requiring only 3 minutes for pruning and 3 hours for post-training. Supported LLMs include Llama-3.1, Llama-3, Llama-2, LLaMA, BLOOM, Vicuna, and Baichuan. Updates include support for new LLMs like GQA and BLOOM, as well as fine-tuning results achieving high accuracy. The tool provides step-by-step instructions for pruning, post-training, and evaluation, along with a Gradio interface for text generation. Limitations include issues with generating repetitive or nonsensical tokens in compressed models and manual operations for certain models.
EmbodiedScan
EmbodiedScan is a holistic multi-modal 3D perception suite designed for embodied AI. It introduces a multi-modal, ego-centric 3D perception dataset and benchmark for holistic 3D scene understanding. The dataset includes over 5k scans with 1M ego-centric RGB-D views, 1M language prompts, 160k 3D-oriented boxes spanning 760 categories, and dense semantic occupancy with 80 common categories. The suite includes a baseline framework named Embodied Perceptron, capable of processing multi-modal inputs for 3D perception tasks and language-grounded tasks.
WildBench
WildBench is a tool designed for benchmarking Large Language Models (LLMs) with challenging tasks sourced from real users in the wild. It provides a platform for evaluating the performance of various models on a range of tasks. Users can easily add new models to the benchmark by following the provided guidelines. The tool supports models from Hugging Face and other APIs, allowing for comprehensive evaluation and comparison. WildBench facilitates running inference and evaluation scripts, enabling users to contribute to the benchmark and collaborate on improving model performance.
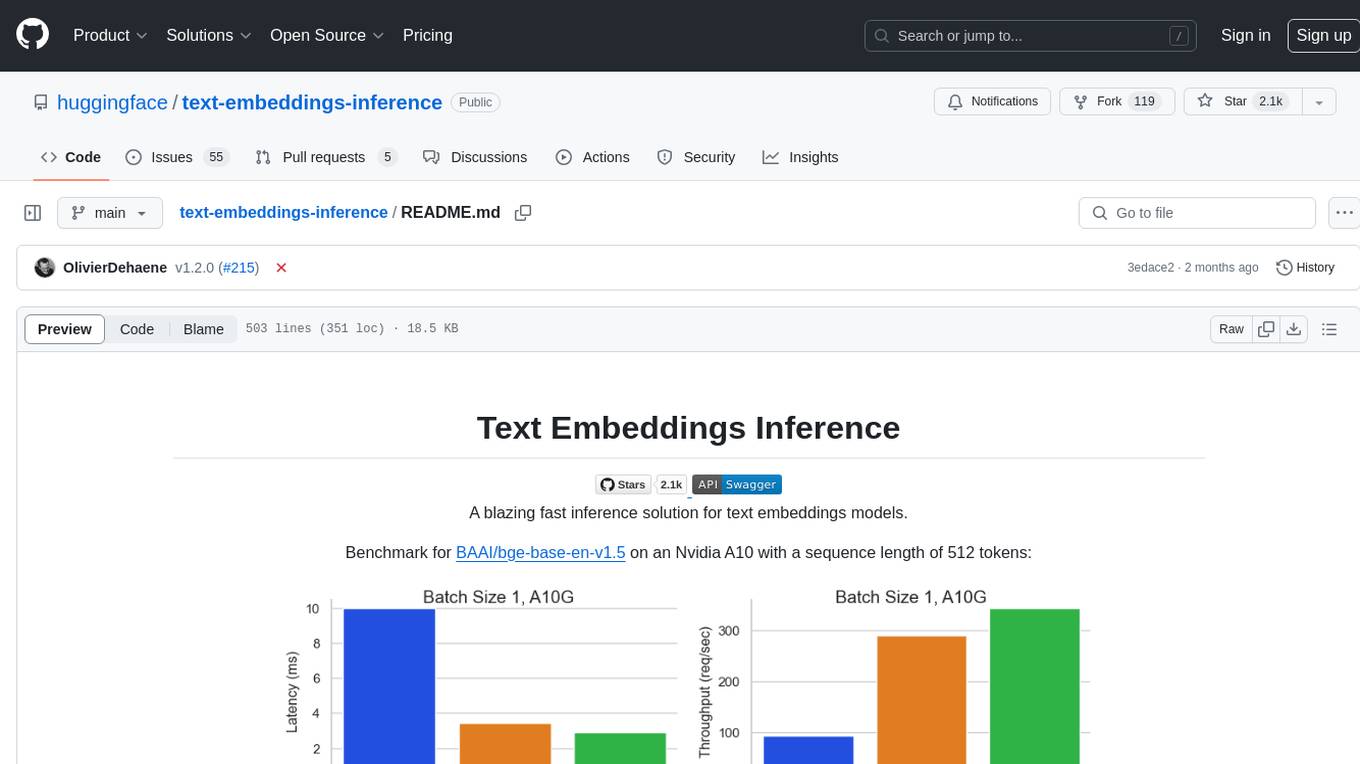
text-embeddings-inference
Text Embeddings Inference (TEI) is a toolkit for deploying and serving open source text embeddings and sequence classification models. TEI enables high-performance extraction for popular models like FlagEmbedding, Ember, GTE, and E5. It implements features such as no model graph compilation step, Metal support for local execution on Macs, small docker images with fast boot times, token-based dynamic batching, optimized transformers code for inference using Flash Attention, Candle, and cuBLASLt, Safetensors weight loading, and production-ready features like distributed tracing with Open Telemetry and Prometheus metrics.
evalverse
Evalverse is an open-source project designed to support Large Language Model (LLM) evaluation needs. It provides a standardized and user-friendly solution for processing and managing LLM evaluations, catering to AI research engineers and scientists. Evalverse supports various evaluation methods, insightful reports, and no-code evaluation processes. Users can access unified evaluation with submodules, request evaluations without code via Slack bot, and obtain comprehensive reports with scores, rankings, and visuals. The tool allows for easy comparison of scores across different models and swift addition of new evaluation tools.
MemoryLLM
MemoryLLM is a large language model designed for self-updating capabilities. It offers pretrained models with different memory capacities and features, such as chat models. The repository provides training code, evaluation scripts, and datasets for custom experiments. MemoryLLM aims to enhance knowledge retention and performance on various natural language processing tasks.
bigcodebench
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for code generation with practical and challenging programming tasks. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls. BigCodeBench focuses on the evaluation of LLM4Code with diverse function calls and complex instructions, providing precise evaluation & ranking and pre-generated samples to accelerate code intelligence research. It inherits the design of the EvalPlus framework but differs in terms of execution environment and test evaluation.
For similar tasks

DALM
The DALM (Domain Adapted Language Modeling) toolkit is designed to unify general LLMs with vector stores to ground AI systems in efficient, factual domains. It provides developers with tools to build on top of Arcee's open source Domain Pretrained LLMs, enabling organizations to deeply tailor AI according to their unique intellectual property and worldview. The toolkit contains code for fine-tuning a fully differential Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG-end2end) architecture, incorporating in-batch negative concept alongside RAG's marginalization for efficiency. It includes training scripts for both retriever and generator models, evaluation scripts, data processing codes, and synthetic data generation code.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
