AnyGPT
Code for "AnyGPT: Unified Multimodal LLM with Discrete Sequence Modeling"
Stars: 730
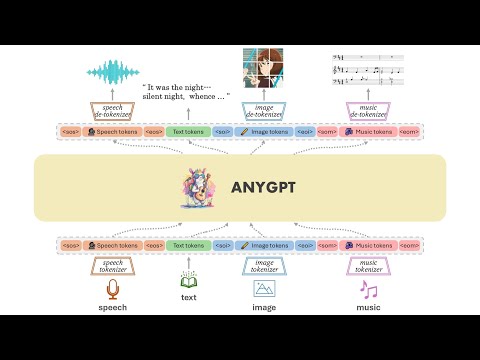
AnyGPT is a unified multimodal language model that utilizes discrete representations for processing various modalities like speech, text, images, and music. It aligns the modalities for intermodal conversions and text processing. AnyInstruct dataset is constructed for generative models. The model proposes a generative training scheme using Next Token Prediction task for training on a Large Language Model (LLM). It aims to compress vast multimodal data on the internet into a single model for emerging capabilities. The tool supports tasks like text-to-image, image captioning, ASR, TTS, text-to-music, and music captioning.
README:



We introduce AnyGPT, an any-to-any multimodal language model that utilizes discrete representations for the unified processing of various modalities, including speech, text, images, and music. The base model aligns the four modalities, allowing for intermodal conversions between different modalities and text. Furthermore, we constructed the AnyInstruct dataset based on various generative models, which contains instructions for arbitrary modal interconversion. Trained on this dataset, our chat model can engage in free multimodal conversations, where multimodal data can be inserted at will.
AnyGPT proposes a generative training scheme that converts all modal data into a unified discrete representation, using the Next Token Prediction task for unified training on a Large Language Model (LLM). From the perspective of 'compression is intelligence': when the quality of the Tokenizer is high enough, and the perplexity (PPL) of the LLM is low enough, it is possible to compress the vast amount of multimodal data on the internet into the same model, thereby emerging capabilities not present in a pure text-based LLM. Demos are shown in project page.
- [X] Base Model
- [X] Chat Model
- [X] Inference Code
- [X] Instruction Dataset
git clone https://github.com/OpenMOSS/AnyGPT.git
cd AnyGPT
conda create --name AnyGPT python=3.9
conda activate AnyGPT
pip install -r requirements.txt- Check the AnyGPT-base weights in fnlp/AnyGPT-base
- Check the AnyGPT-chat weights in fnlp/AnyGPT-chat
- Check the SpeechTokenizer and Soundstorm weights in fnlp/AnyGPT-speech-modules
- Check the SEED tokenizer weights in AILab-CVC/seed-tokenizer-2
The SpeechTokenizer is used for tokenizing and reconstructing speech, Soundstorm is responsible for completing paralinguistic information, and SEED-tokenizer is used for tokenizing images.
The model weights of unCLIP SD-UNet which are used to reconstruct the image, and Encodec-32k which are used to tokenize and reconstruct music will be downloaded automatically.
python anygpt/src/infer/cli_infer_base_model.py \
--model-name-or-path "path/to/AnyGPT-7B-base" \
--image-tokenizer-path 'path/to/model' \
--speech-tokenizer-path "path/to/model" \
--speech-tokenizer-config "path/to/config" \
--soundstorm-path "path/to/model" \
--output-dir "infer_output/base" for example
python anygpt/src/infer/cli_infer_base_model.py \
--model-name-or-path models/anygpt/base \
--image-tokenizer-path models/seed-tokenizer-2/seed_quantizer.pt \
--speech-tokenizer-path models/speechtokenizer/ckpt.dev \
--speech-tokenizer-config models/speechtokenizer/config.json \
--soundstorm-path models/soundstorm/speechtokenizer_soundstorm_mls.pt \
--output-dir "infer_output/base" The Base Model can perform various tasks, including text-to-image, image caption, Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Zero-shot Text-to-Speech (TTS), Text-to-Music, and Music Captioning.
We can perform inference following a specific instruction format.
- Text-to-Image
text|image|{caption}- example:
text|image|A bustling medieval market scene with vendors selling exotic goods under colorful tents
- Image Caption
image|text|{caption}- example:
image|text|static/infer/image/cat.jpg
- TTS(random voice)
text|speech|{speech content}- example:
text|speech|I could be bounded in a nutshell and count myself a king of infinite space.
- Zero-shot TTS
text|speech|{speech content}|{voice prompt}- example:
text|speech|I could be bounded in a nutshell and count myself a king of infinite space.|static/infer/speech/voice_prompt3.wav
- ASR
speech|text|{speech file path}- example:
speech|text|AnyGPT/static/infer/speech/voice_prompt2.wav
- Text-to-Music
text|music|{caption}- example:
text|music|features an indie rock sound with distinct elements that evoke a dreamy, soothing atmosphere
- Music Caption
music|text|{music file path}- example:
music|text|static/infer/music/features an indie rock sound with distinct element.wav
Notes
For different tasks, we used different language model decoding strategies. The decoding configuration files for image, speech, and music generation are located in config/image_generate_config.json, config/speech_generate_config.json, and config/music_generate_config.json, respectively. The decoding configuration files for other modalities to text are in config/text_generate_config.json. You can directly modify or add parameters to change the decoding strategy.
Due to limitations in data and training resources, the model's generation may still be unstable. You can generate multiple times or try different decoding strategies.
The speech and music response will be saved to .wav files, and the image response will be saved to a jpg. The filename will be a concatenation of the prompt and the time. The paths to these files will be indicated in the response.
python anygpt/src/infer/cli_infer_chat_model.py
\ --model-name-or-path 'path/to/model'
\ --image-tokenizer-path 'path/to/model'
\ --speech-tokenizer-path 'path/to/model'
\ --speech-tokenizer-config 'path/to/config'
\ --soundstorm-path 'path/to/model'
\ --output-dir "infer_output/chat"for example
python anygpt/src/infer/cli_infer_chat_model.py
\ --model-name-or-path models/anygpt/chat
\ --image-tokenizer-path models/seed-tokenizer-2/seed_quantizer.pt
\ --speech-tokenizer-path models/speechtokenizer/ckpt.dev
\ --speech-tokenizer-config models/speechtokenizer/config.json
\ --soundstorm-path models/soundstorm/speechtokenizer_soundstorm_mls.pt
\ --output-dir "infer_output/chat"Instruct format
interleaved|{text_instruction}|{modality}|{image_path}|{voice_prompt}|{speech_instruction}|{music_path}Where text_instruction is the input text command, speech_instruction is the input voice command; only one needs to be specified.
image_path and music_path are the paths for the input image and music, respectively. voice_prompt is the specified tone of the model's response; if not specified, a random tone is used.
modality refers to the type of output modality, which can be chosen as speech, image, or music; otherwise, it is considered as text. This will only affect which decoding configuration file under the config directory is used by the model (this is because the model's training is limited, leading to different decoding strategies for different modalities). It can also decode token by token, modifying the decoding strategy to the corresponding modality when generating the start token of the modality.
example
- interleaved||image|||static/infer/speech/instruction/Can you draw me a picture of a sunny beach.wav
- interleaved||music|||static/infer/speech/instruction/Give me a similar style of music.wav
To clear the conversation history, please input |clear
Please refer to scripts/stage1_pretrain.sh and scripts/stage2_sft.sh
We provide training data samples for reference. The organization of training formats includes pre-training data in data/pretrain and instruction data in data/instruction. For prompts of different tasks, refer to task_prompts, such as plain text dialogue, voice command text reply, text command voice reply, and special prompts for various tasks. You need to process multi-modal data into multi-round dialogue format according to the task template in advance. We use a voice conversation as an example in the command data, corresponding to the use of task_prompts in the "Speech-Instruction" and "Speech-Response":
[
{
"role": "user",
"message": "<sosp><🗣️1><🗣️1><🗣️1><eosp> Please acknowledge the user's vocal input, create a textual response"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"message": "<-Ins-> hello, how are you\n <-Res-> I am fine, thank you <sosp><🗣️2><🗣️2><🗣️2><eosp>"
}
]- SpeechGPT, Vicuna: The codebase we built upon.
- We thank the great work from SpeechTokenizer,soundstorm-speechtokenizer, SEED-tokenizer,
AnyGPT is released under the original License of LLaMA2.
If you find AnyGPT and AnyInstruct useful in your research or applications, please kindly cite:
@article{zhan2024anygpt,
title={AnyGPT: Unified Multimodal LLM with Discrete Sequence Modeling},
author={Zhan, Jun and Dai, Junqi and Ye, Jiasheng and Zhou, Yunhua and Zhang, Dong and Liu, Zhigeng and Zhang, Xin and Yuan, Ruibin and Zhang, Ge and Li, Linyang and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.12226},
year={2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AnyGPT
Similar Open Source Tools

AnyGPT
AnyGPT is a unified multimodal language model that utilizes discrete representations for processing various modalities like speech, text, images, and music. It aligns the modalities for intermodal conversions and text processing. AnyInstruct dataset is constructed for generative models. The model proposes a generative training scheme using Next Token Prediction task for training on a Large Language Model (LLM). It aims to compress vast multimodal data on the internet into a single model for emerging capabilities. The tool supports tasks like text-to-image, image captioning, ASR, TTS, text-to-music, and music captioning.
VMind
VMind is an open-source solution for intelligent visualization, providing an intelligent chart component based on LLM by VisActor. It allows users to create chart narrative works with natural language interaction, edit charts through dialogue, and export narratives as videos or GIFs. The tool is easy to use, scalable, supports various chart types, and offers one-click export functionality. Users can customize chart styles, specify themes, and aggregate data using LLM models. VMind aims to enhance efficiency in creating data visualization works through dialogue-based editing and natural language interaction.
llmgraph
llmgraph is a tool that enables users to create knowledge graphs in GraphML, GEXF, and HTML formats by extracting world knowledge from large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. It supports various entity types and relationships, offers cache support for efficient graph growth, and provides insights into LLM costs. Users can customize the model used and interact with different LLM providers. The tool allows users to generate interactive graphs based on a specified entity type and Wikipedia link, making it a valuable resource for knowledge graph creation and exploration.
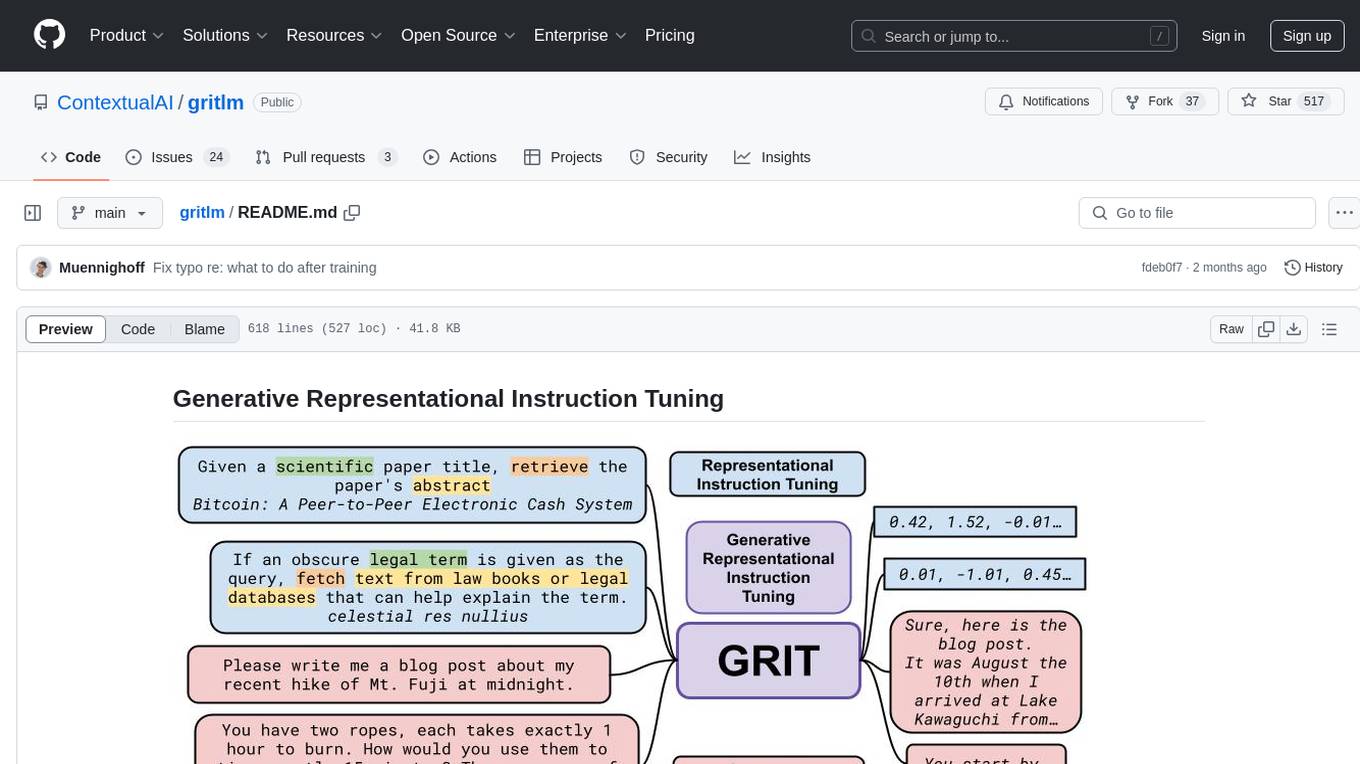
gritlm
The 'gritlm' repository provides all materials for the paper Generative Representational Instruction Tuning. It includes code for inference, training, evaluation, and known issues related to the GritLM model. The repository also offers models for embedding and generation tasks, along with instructions on how to train and evaluate the models. Additionally, it contains visualizations, acknowledgements, and a citation for referencing the work.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
mflux
MFLUX is a line-by-line port of the FLUX implementation in the Huggingface Diffusers library to Apple MLX. It aims to run powerful FLUX models from Black Forest Labs locally on Mac machines. The codebase is minimal and explicit, prioritizing readability over generality and performance. Models are implemented from scratch in MLX, with tokenizers from the Huggingface Transformers library. Dependencies include Numpy and Pillow for image post-processing. Installation can be done using `uv tool` or classic virtual environment setup. Command-line arguments allow for image generation with specified models, prompts, and optional parameters. Quantization options for speed and memory reduction are available. LoRA adapters can be loaded for fine-tuning image generation. Controlnet support provides more control over image generation with reference images. Current limitations include generating images one by one, lack of support for negative prompts, and some LoRA adapters not working.
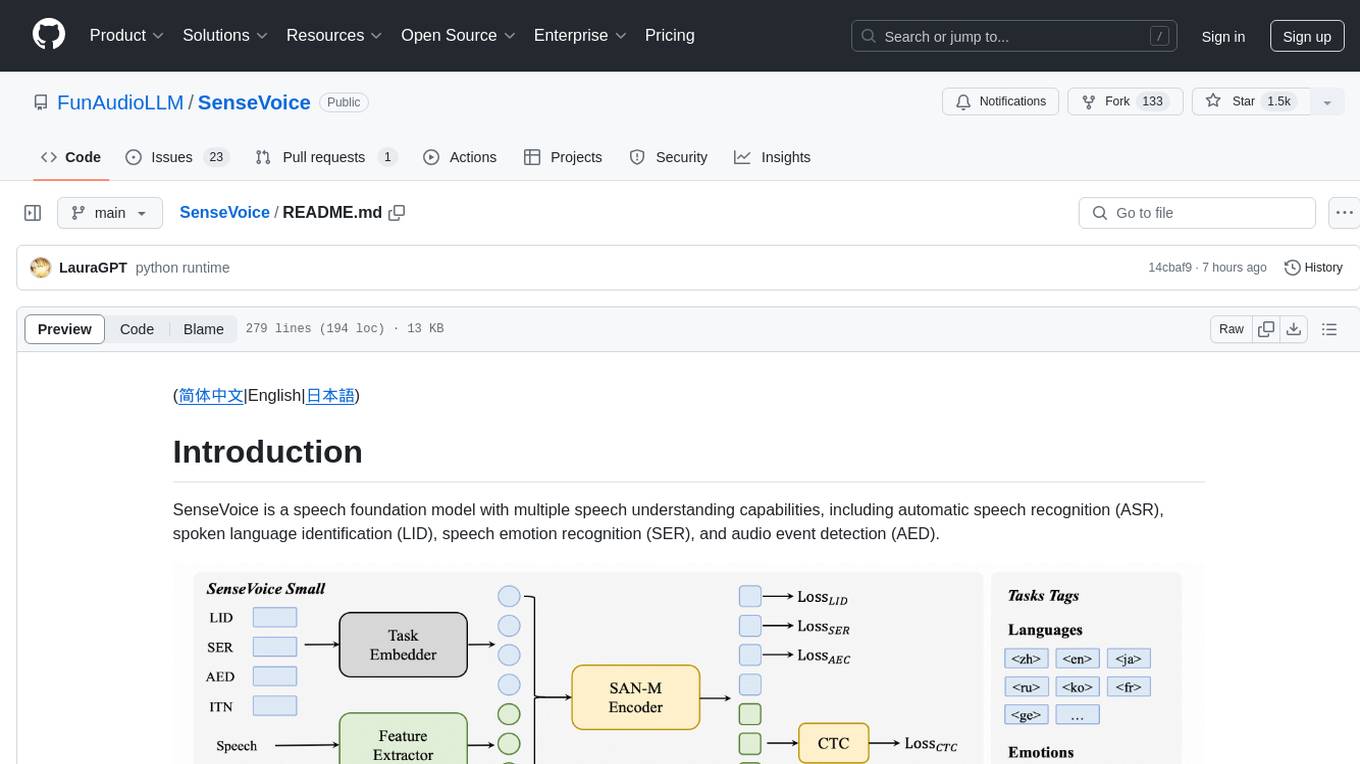
SenseVoice
SenseVoice is a speech foundation model focusing on high-accuracy multilingual speech recognition, speech emotion recognition, and audio event detection. Trained with over 400,000 hours of data, it supports more than 50 languages and excels in emotion recognition and sound event detection. The model offers efficient inference with low latency and convenient finetuning scripts. It can be deployed for service with support for multiple client-side languages. SenseVoice-Small model is open-sourced and provides capabilities for Mandarin, Cantonese, English, Japanese, and Korean. The tool also includes features for natural speech generation and fundamental speech recognition tasks.

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.

marqo
Marqo is more than a vector database, it's an end-to-end vector search engine for both text and images. Vector generation, storage and retrieval are handled out of the box through a single API. No need to bring your own embeddings.
RTL-Coder
RTL-Coder is a tool designed to outperform GPT-3.5 in RTL code generation by providing a fully open-source dataset and a lightweight solution. It targets Verilog code generation and offers an automated flow to generate a large labeled dataset with over 27,000 diverse Verilog design problems and answers. The tool addresses the data availability challenge in IC design-related tasks and can be used for various applications beyond LLMs. The tool includes four RTL code generation models available on the HuggingFace platform, each with specific features and performance characteristics. Additionally, RTL-Coder introduces a new LLM training scheme based on code quality feedback to further enhance model performance and reduce GPU memory consumption.
ai2-scholarqa-lib
Ai2 Scholar QA is a system for answering scientific queries and literature review by gathering evidence from multiple documents across a corpus and synthesizing an organized report with evidence for each claim. It consists of a retrieval component and a three-step generator pipeline. The retrieval component fetches relevant evidence passages using the Semantic Scholar public API and reranks them. The generator pipeline includes quote extraction, planning and clustering, and summary generation. The system is powered by the ScholarQA class, which includes components like PaperFinder and MultiStepQAPipeline. It requires environment variables for Semantic Scholar API and LLMs, and can be run as local docker containers or embedded into another application as a Python package.
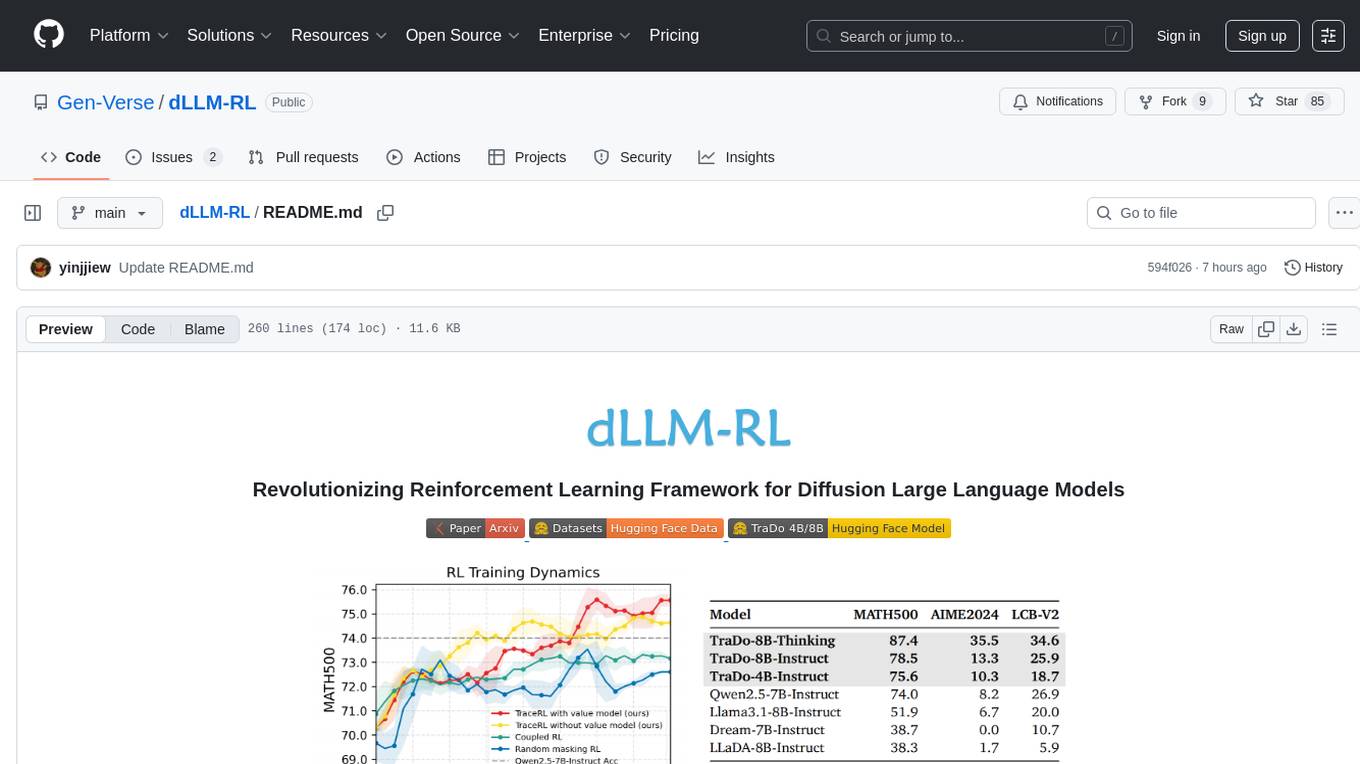
dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
co-llm
Co-LLM (Collaborative Language Models) is a tool for learning to decode collaboratively with multiple language models. It provides a method for data processing, training, and inference using a collaborative approach. The tool involves steps such as formatting/tokenization, scoring logits, initializing Z vector, deferral training, and generating results using multiple models. Co-LLM supports training with different collaboration pairs and provides baseline training scripts for various models. In inference, it uses 'vllm' services to orchestrate models and generate results through API-like services. The tool is inspired by allenai/open-instruct and aims to improve decoding performance through collaborative learning.
cortex
Cortex is a tool that simplifies and accelerates the process of creating applications utilizing modern AI models like chatGPT and GPT-4. It provides a structured interface (GraphQL or REST) to a prompt execution environment, enabling complex augmented prompting and abstracting away model connection complexities like input chunking, rate limiting, output formatting, caching, and error handling. Cortex offers a solution to challenges faced when using AI models, providing a simple package for interacting with NL AI models.
ChatRex
ChatRex is a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) designed to seamlessly integrate fine-grained object perception and robust language understanding. By adopting a decoupled architecture with a retrieval-based approach for object detection and leveraging high-resolution visual inputs, ChatRex addresses key challenges in perception tasks. It is powered by the Rexverse-2M dataset with diverse image-region-text annotations. ChatRex can be applied to various scenarios requiring fine-grained perception, such as object detection, grounded conversation, grounded image captioning, and region understanding.
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.
For similar tasks

AnyGPT
AnyGPT is a unified multimodal language model that utilizes discrete representations for processing various modalities like speech, text, images, and music. It aligns the modalities for intermodal conversions and text processing. AnyInstruct dataset is constructed for generative models. The model proposes a generative training scheme using Next Token Prediction task for training on a Large Language Model (LLM). It aims to compress vast multimodal data on the internet into a single model for emerging capabilities. The tool supports tasks like text-to-image, image captioning, ASR, TTS, text-to-music, and music captioning.
speech-trident
Speech Trident is a repository focusing on speech/audio large language models, covering representation learning, neural codec, and language models. It explores speech representation models, speech neural codec models, and speech large language models. The repository includes contributions from various researchers and provides a comprehensive list of speech/audio language models, representation models, and codec models.
AudioLLM
AudioLLMs is a curated collection of research papers focusing on developing, implementing, and evaluating language models for audio data. The repository aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a comprehensive resource to explore the latest advancements in AudioLLMs. It includes models for speech interaction, speech recognition, speech translation, audio generation, and more. Additionally, it covers methodologies like multitask audioLLMs and segment-level Q-Former, as well as evaluation benchmarks like AudioBench and AIR-Bench. Adversarial attacks such as VoiceJailbreak are also discussed.
wunjo.wladradchenko.ru
Wunjo AI is a comprehensive tool that empowers users to explore the realm of speech synthesis, deepfake animations, video-to-video transformations, and more. Its user-friendly interface and privacy-first approach make it accessible to both beginners and professionals alike. With Wunjo AI, you can effortlessly convert text into human-like speech, clone voices from audio files, create multi-dialogues with distinct voice profiles, and perform real-time speech recognition. Additionally, you can animate faces using just one photo combined with audio, swap faces in videos, GIFs, and photos, and even remove unwanted objects or enhance the quality of your deepfakes using the AI Retouch Tool. Wunjo AI is an all-in-one solution for your voice and visual AI needs, offering endless possibilities for creativity and expression.
airunner
AI Runner is a multi-modal AI interface that allows users to run open-source large language models and AI image generators on their own hardware. The tool provides features such as voice-based chatbot conversations, text-to-speech, speech-to-text, vision-to-text, text generation with large language models, image generation capabilities, image manipulation tools, utility functions, and more. It aims to provide a stable and user-friendly experience with security updates, a new UI, and a streamlined installation process. The application is designed to run offline on users' hardware without relying on a web server, offering a smooth and responsive user experience.
Wechat-AI-Assistant
Wechat AI Assistant is a project that enables multi-modal interaction with ChatGPT AI assistant within WeChat. It allows users to engage in conversations, role-playing, respond to voice messages, analyze images and videos, summarize articles and web links, and search the internet. The project utilizes the WeChatFerry library to control the Windows PC desktop WeChat client and leverages the OpenAI Assistant API for intelligent multi-modal message processing. Users can interact with ChatGPT AI in WeChat through text or voice, access various tools like bing_search, browse_link, image_to_text, text_to_image, text_to_speech, video_analysis, and more. The AI autonomously determines which code interpreter and external tools to use to complete tasks. Future developments include file uploads for AI to reference content, integration with other APIs, and login support for enterprise WeChat and WeChat official accounts.
Generative-AI-Pharmacist
Generative AI Pharmacist is a project showcasing the use of generative AI tools to create an animated avatar named Macy, who delivers medication counseling in a realistic and professional manner. The project utilizes tools like Midjourney for image generation, ChatGPT for text generation, ElevenLabs for text-to-speech conversion, and D-ID for creating a photorealistic talking avatar video. The demo video featuring Macy discussing commonly-prescribed medications demonstrates the potential of generative AI in healthcare communication.
Pallaidium
Pallaidium is a generative AI movie studio integrated into the Blender video editor. It allows users to AI-generate video, image, and audio from text prompts or existing media files. The tool provides various features such as text to video, text to audio, text to speech, text to image, image to image, image to video, video to video, image to text, and more. It requires a Windows system with a CUDA-supported Nvidia card and at least 6 GB VRAM. Pallaidium offers batch processing capabilities, text to audio conversion using Bark, and various performance optimization tips. Users can install the tool by downloading the add-on and following the installation instructions provided. The tool comes with a set of restrictions on usage, prohibiting the generation of harmful, pornographic, violent, or false content.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.