
m3p2i-aip
Code for the IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters paper titled "Multi-Modal MPPI and Active Inference for Reactive Task and Motion Planning"
Stars: 58
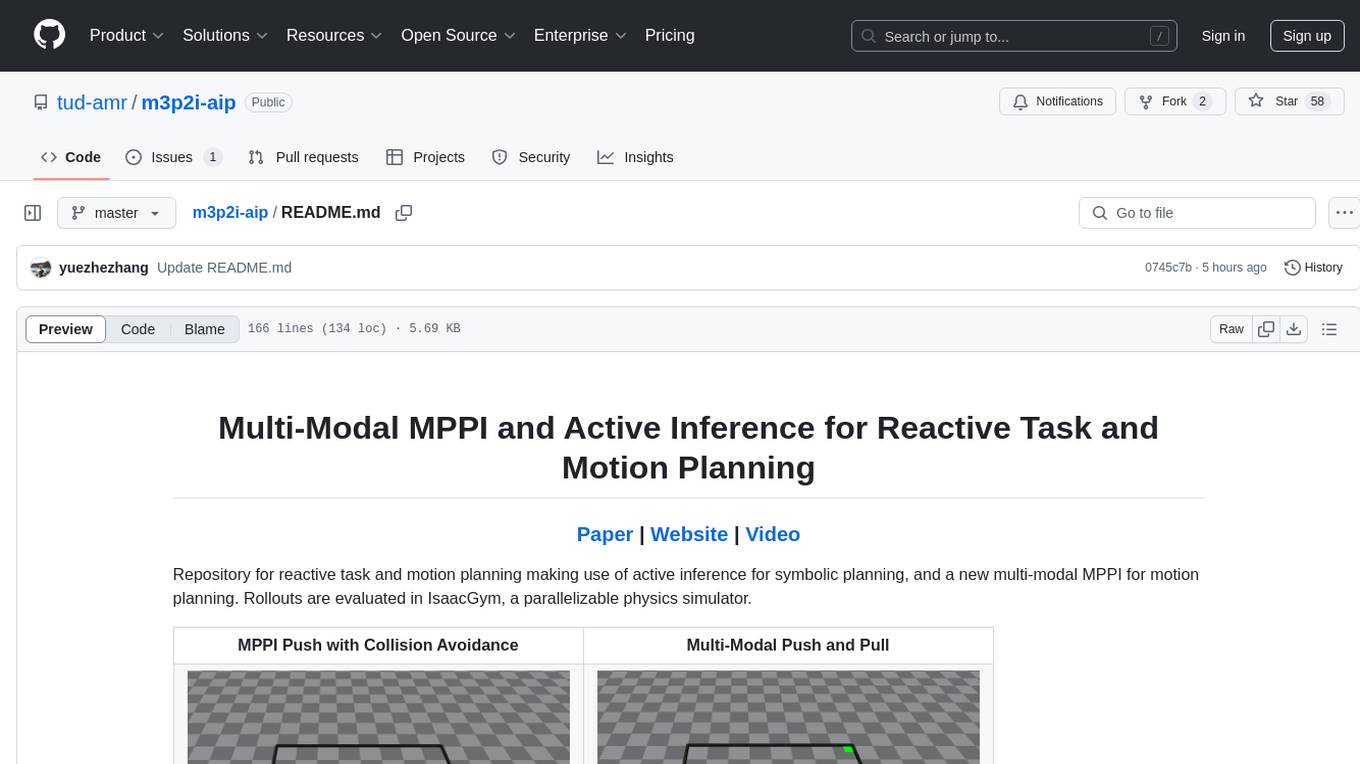
Repository for reactive task and motion planning using active inference for symbolic planning and multi-modal MPPI for motion planning. Rollouts are evaluated in IsaacGym, a parallelizable physics simulator. The tool provides functionalities for push, pull, pick, and multi-modal push-pull tasks with collision avoidance.
README:
Repository for reactive task and motion planning making use of active inference for symbolic planning, and a new multi-modal MPPI for motion planning. Rollouts are evaluated in IsaacGym, a parallelizable physics simulator.
| MPPI Push with Collision Avoidance | Multi-Modal Push and Pull |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| MPPI Reactive Pick | Multi-Modal Pick with Collision Avoidance |
 |
 |
First, clone the repo in your folder and create the conda environment.
cd <project_folder>
git clone https://github.com/tud-amr/m3p2i-aip.git
conda create -n m3p2i-aip python=3.8
conda activate m3p2i-aipThis project requires the source code of IsaacGym. Check for the prerequisites and troubleshooting. Download it from https://developer.nvidia.com/isaac-gym, unzip and paste it in the thirdparty folder. Move to IsaacGym and install the package.
cd <project_folder>/m3p2i-aip/thirdparty/IsaacGym_Preview_4_Package/isaacgym/python
pip install -e. Then install the current package by:
cd <project_folder>/m3p2i-aip
pip install -e. Now you are ready to test an example file, where you can drive the robot around with ASDW keys.
cd <project_folder>/m3p2i-aip/examples
python3 example_key.pyIf you want to test the TAMP framework, you will need two instances of Isaac Gym, one for throwing the rollouts and deriving the optimal solution, and one for updating the "real system". Please run the commands below in two terminals from the scripts folder with activated python environment.
Run this terminal first:
cd <project_folder>/m3p2i-aip/scripts
conda activate m3p2i-aip
python3 reactive_tamp.pyThen run the second terminal:
cd <project_folder>/m3p2i-aip/scripts
conda activate m3p2i-aip
python3 sim.pySpecifically, you can test the following:
python3 reactive_tamp.py task=navigation goal="[-3, 3]"python3 sim.py[!NOTE] Feel free to change the goal position.
python3 reactive_tamp.py task=push goal="[-1, -1]"python3 sim.py[!NOTE] Feel free to change the goal position. Pushing will always fail if the initial position is in the corner.
python3 reactive_tamp.py task=pull goal="[0, 0]"python3 sim.py task=pull[!NOTE] Feel free to change the goal position. Pulling will always fail if the goal is in the corner.
python3 reactive_tamp.py task=push_pull multi_modal=True goal="[-3.75, -3.75]"python3 sim.py task=push_pull[!NOTE] Feel free to change the goal position. The corner positions are [-3.75, -3.75], [3.75, 3.75], [3.75, -3.75], [-3.75, 3.75].
Pick the cube from the table:
python3 reactive_tamp.py -cn config_pandapython3 sim.py -cn config_panda[!NOTE] You can play with the cubes using ASDW keys and keyup, keydown, keyleft and keyright.
Pick the cube from the shelf:
python3 reactive_tamp.py -cn config_panda multi_modal=True cube_on_shelf=Truepython3 sim.py -cn config_panda multi_modal=True cube_on_shelf=True[!NOTE] You can play with the cubes using ASDW keys and keyup, keydown, keyleft and keyright.
If you find the code useful, please cite:
@article{zhang2024multi,
title={Multi-Modal MPPI and Active Inference for Reactive Task and Motion Planning},
author={Zhang, Yuezhe and Pezzato, Corrado and Trevisan, Elia and Salmi, Chadi and Corbato, Carlos Hern{\'a}ndez and Alonso-Mora, Javier},
journal={IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters},
year={2024},
publisher={IEEE}
}- Isaac-mppi: an MPPI implementation that uses IsaacGym as a dynamic model (paper, website, code).
- Biased-mppi: an MPPI implementation whose sampling distribution is informed with ancillary controllers (paper, website, code).
- AIP: an Active Inference planner for decision making (paper, video, code).
We thank the pioneers (Grady Williams, pytorch_mppi, storm) who have paved the way and the future newcomers who will propel MPPI forward!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for m3p2i-aip
Similar Open Source Tools

m3p2i-aip
Repository for reactive task and motion planning using active inference for symbolic planning and multi-modal MPPI for motion planning. Rollouts are evaluated in IsaacGym, a parallelizable physics simulator. The tool provides functionalities for push, pull, pick, and multi-modal push-pull tasks with collision avoidance.

AutoAgent
AutoAgent is a fully-automated and zero-code framework that enables users to create and deploy LLM agents through natural language alone. It is a top performer on the GAIA Benchmark, equipped with a native self-managing vector database, and allows for easy creation of tools, agents, and workflows without any coding. AutoAgent seamlessly integrates with a wide range of LLMs and supports both function-calling and ReAct interaction modes. It is designed to be dynamic, extensible, customized, and lightweight, serving as a personal AI assistant.
aira-dojo
aira-dojo is a scalable and customizable framework for AI research agents, designed to accelerate hill-climbing on research capabilities toward a fully automated AI research scientist. The framework provides a general abstraction for tasks and agents, implements the MLE-bench task, and includes state-of-the-art agents. It features an isolated code execution environment that integrates smoothly with job schedulers like Slurm, enabling large-scale experiments and rapid iteration across a portfolio of tasks and solvers.
trieve
Trieve is an advanced relevance API for hybrid search, recommendations, and RAG. It offers a range of features including self-hosting, semantic dense vector search, typo tolerant full-text/neural search, sub-sentence highlighting, recommendations, convenient RAG API routes, the ability to bring your own models, hybrid search with cross-encoder re-ranking, recency biasing, tunable popularity-based ranking, filtering, duplicate detection, and grouping. Trieve is designed to be flexible and customizable, allowing users to tailor it to their specific needs. It is also easy to use, with a simple API and well-documented features.

shellChatGPT
ShellChatGPT is a shell wrapper for OpenAI's ChatGPT, DALL-E, Whisper, and TTS, featuring integration with LocalAI, Ollama, Gemini, Mistral, Groq, and GitHub Models. It provides text and chat completions, vision, reasoning, and audio models, voice-in and voice-out chatting mode, text editor interface, markdown rendering support, session management, instruction prompt manager, integration with various service providers, command line completion, file picker dialogs, color scheme personalization, stdin and text file input support, and compatibility with Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and Termux for a responsive experience.

joinly
joinly.ai is a connector middleware designed to enable AI agents to actively participate in video calls, providing essential meeting tools for AI agents to perform tasks and interact in real time. It supports live interaction, conversational flow, cross-platform compatibility, bring-your-own-LLM, and choose-your-preferred-TTS/STT services. The tool is 100% open-source, self-hosted, and privacy-first, aiming to make meetings accessible to AI agents by joining and participating in video calls.
aiconfig
AIConfig is a framework that makes it easy to build generative AI applications for production. It manages generative AI prompts, models and model parameters as JSON-serializable configs that can be version controlled, evaluated, monitored and opened in a local editor for rapid prototyping. It allows you to store and iterate on generative AI behavior separately from your application code, offering a streamlined AI development workflow.
react-grab
React Grab is a tool that allows users to select context for coding agents directly from a website by pointing at any element and copying the file name, React component, and HTML source code. It enhances the performance of tools like Cursor, Claude Code, and Copilot by making them run up to 3 times faster and more accurately. Users can install React Grab, connect it to coding agents, and easily copy element contexts for pasting into their coding environment. The tool can be manually installed in various React frameworks and build tools, and it also provides an API for extending functionality with plugins, hooks, actions, themes, and custom agents.

Fabric
Fabric is an open-source framework designed to augment humans using AI by organizing prompts by real-world tasks. It addresses the integration problem of AI by creating and organizing prompts for various tasks. Users can create, collect, and organize AI solutions in a single place for use in their favorite tools. Fabric also serves as a command-line interface for those focused on the terminal. It offers a wide range of features and capabilities, including support for multiple AI providers, internationalization, speech-to-text, AI reasoning, model management, web search, text-to-speech, desktop notifications, and more. The project aims to help humans flourish by leveraging AI technology to solve human problems and enhance creativity.
RoboMatrix
RoboMatrix is a skill-centric hierarchical framework for scalable robot task planning and execution in an open-world environment. It provides a structured approach to robot task execution using a combination of hardware components, environment configuration, installation procedures, and data collection methods. The framework is developed using the ROS2 framework on Ubuntu and supports robots from DJI's RoboMaster series. Users can follow the provided installation guidance to set up RoboMatrix and utilize it for various tasks such as data collection, task execution, and dataset construction. The framework also includes a supervised fine-tuning dataset and aims to optimize communication and release additional components in the future.
metis
Metis is an open-source, AI-driven tool for deep security code review, created by Arm's Product Security Team. It helps engineers detect subtle vulnerabilities, improve secure coding practices, and reduce review fatigue. Metis uses LLMs for semantic understanding and reasoning, RAG for context-aware reviews, and supports multiple languages and vector store backends. It provides a plugin-friendly and extensible architecture, named after the Greek goddess of wisdom, Metis. The tool is designed for large, complex, or legacy codebases where traditional tooling falls short.
consult-llm-mcp
Consult LLM MCP is an MCP server that enables users to consult powerful AI models like GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and DeepSeek Reasoner for complex problem-solving. It supports multi-turn conversations, direct queries with optional file context, git changes inclusion for code review, comprehensive logging with cost estimation, and various CLI modes for Gemini and Codex. The tool is designed to simplify the process of querying AI models for assistance in resolving coding issues and improving code quality.
torchchat
torchchat is a codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. It allows running LLMs using Python in various environments such as desktop, server, iOS, and Android. The tool supports running models via PyTorch, chatting, generating text, running chat in the browser, and running models on desktop/server without Python. It also provides features like AOT Inductor for faster execution, running in C++ using the runner, and deploying and running on iOS and Android. The tool supports popular hardware and OS including Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS, with various data types and execution modes available.
ChatIDE
ChatIDE is an AI assistant that integrates with your IDE, allowing you to converse with OpenAI's ChatGPT or Anthropic's Claude within your development environment. It provides a seamless way to access AI-powered assistance while coding, enabling you to get real-time help, generate code snippets, debug errors, and brainstorm ideas without leaving your IDE.
wcgw
wcgw is a shell and coding agent designed for Claude and Chatgpt. It provides full shell access with no restrictions, desktop control on Claude for screen capture and control, interactive command handling, large file editing, and REPL support. Users can use wcgw to create, execute, and iterate on tasks, such as solving problems with Python, finding code instances, setting up projects, creating web apps, editing large files, and running server commands. Additionally, wcgw supports computer use on Docker containers for desktop control. The tool can be extended with a VS Code extension for pasting context on Claude app and integrates with Chatgpt for custom GPT interactions.
pear-landing-page
PearAI Landing Page is an open-source AI-powered code editor managed by Nang and Pan. It is built with Next.js, Vercel, Tailwind CSS, and TypeScript. The project requires setting up environment variables for proper configuration. Users can run the project locally by starting the development server and visiting the specified URL in the browser. Recommended extensions include Prettier, ESLint, and JavaScript and TypeScript Nightly. Contributions to the project are welcomed and appreciated.
For similar tasks

m3p2i-aip
Repository for reactive task and motion planning using active inference for symbolic planning and multi-modal MPPI for motion planning. Rollouts are evaluated in IsaacGym, a parallelizable physics simulator. The tool provides functionalities for push, pull, pick, and multi-modal push-pull tasks with collision avoidance.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.